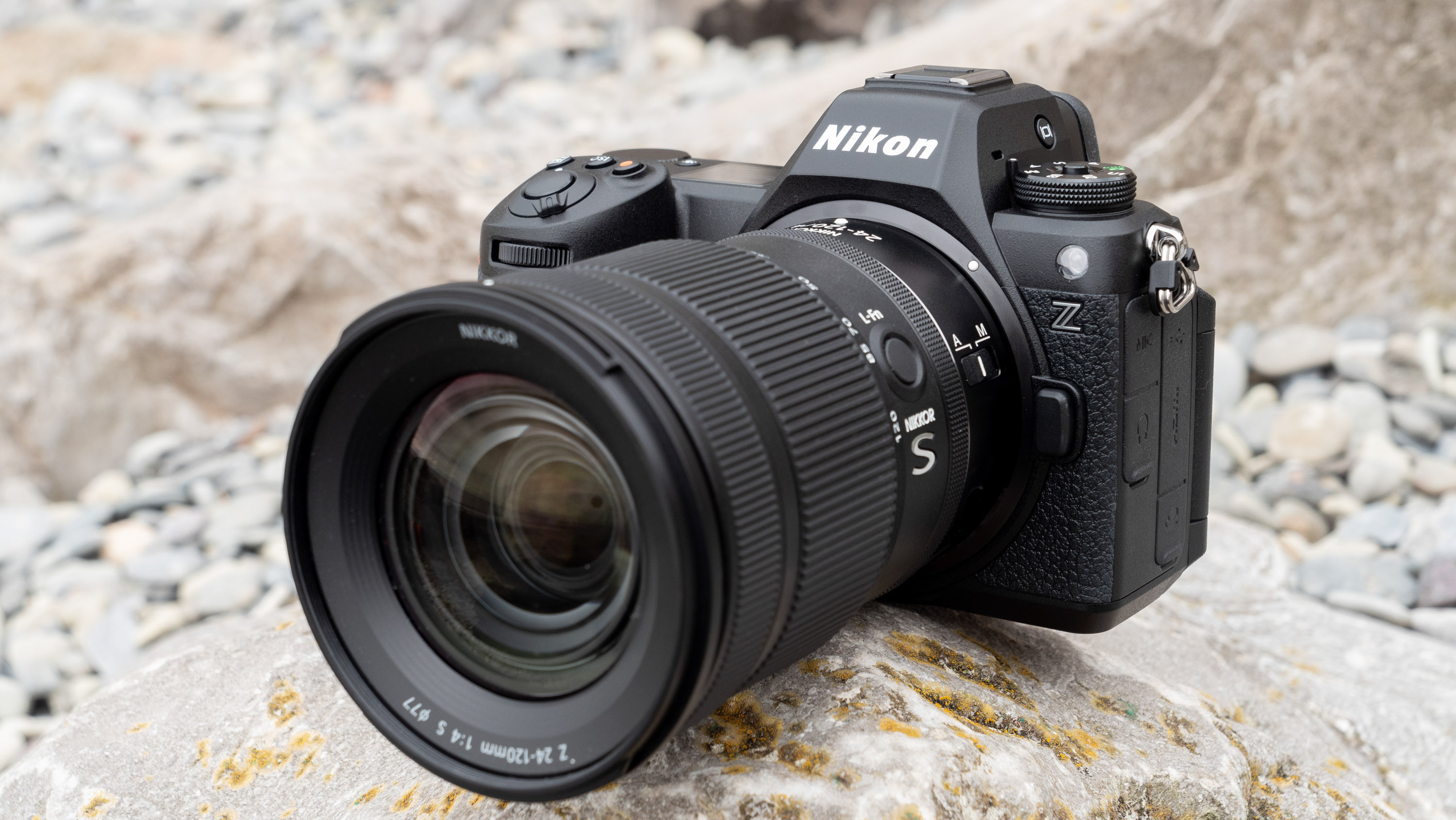
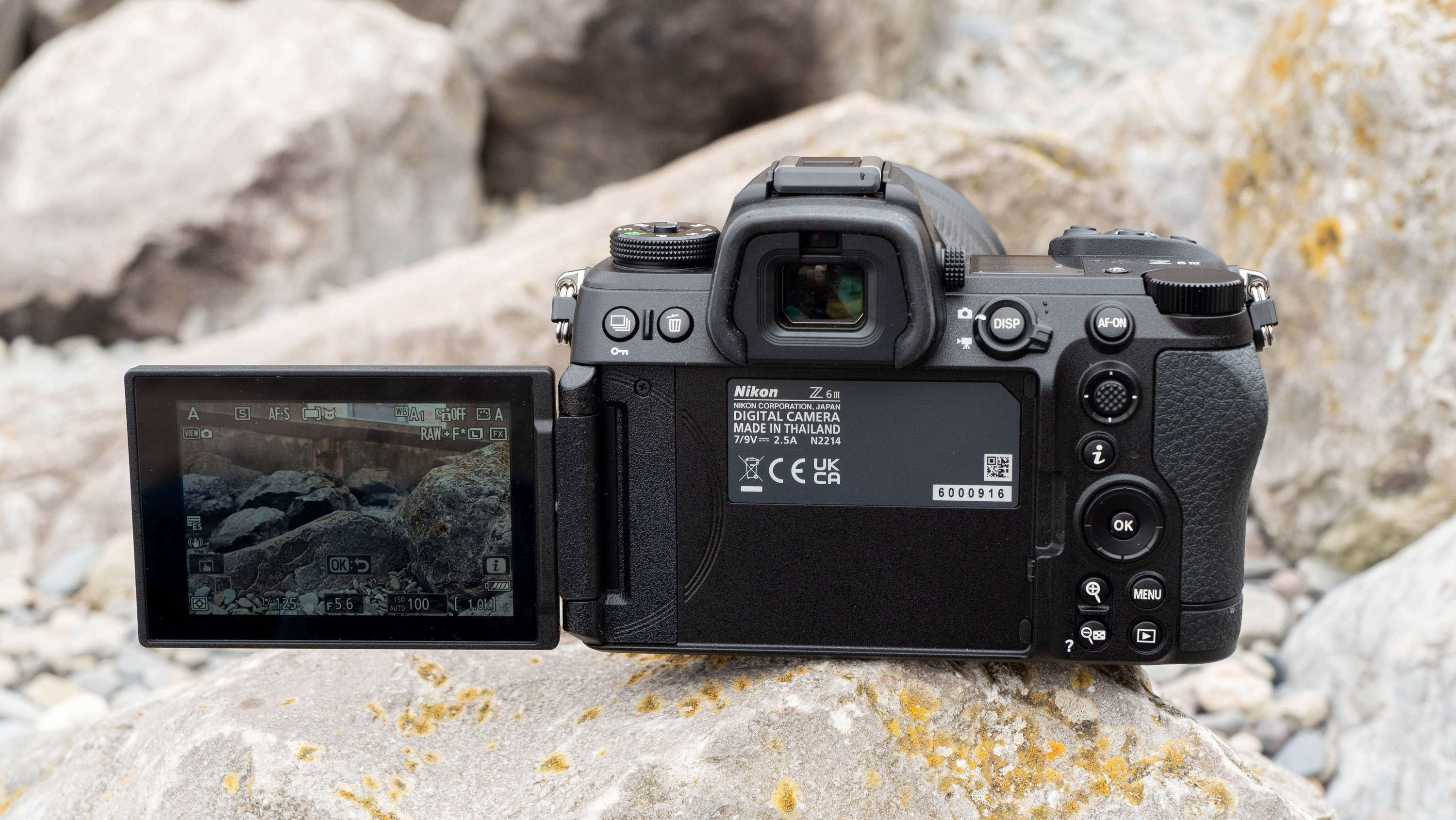
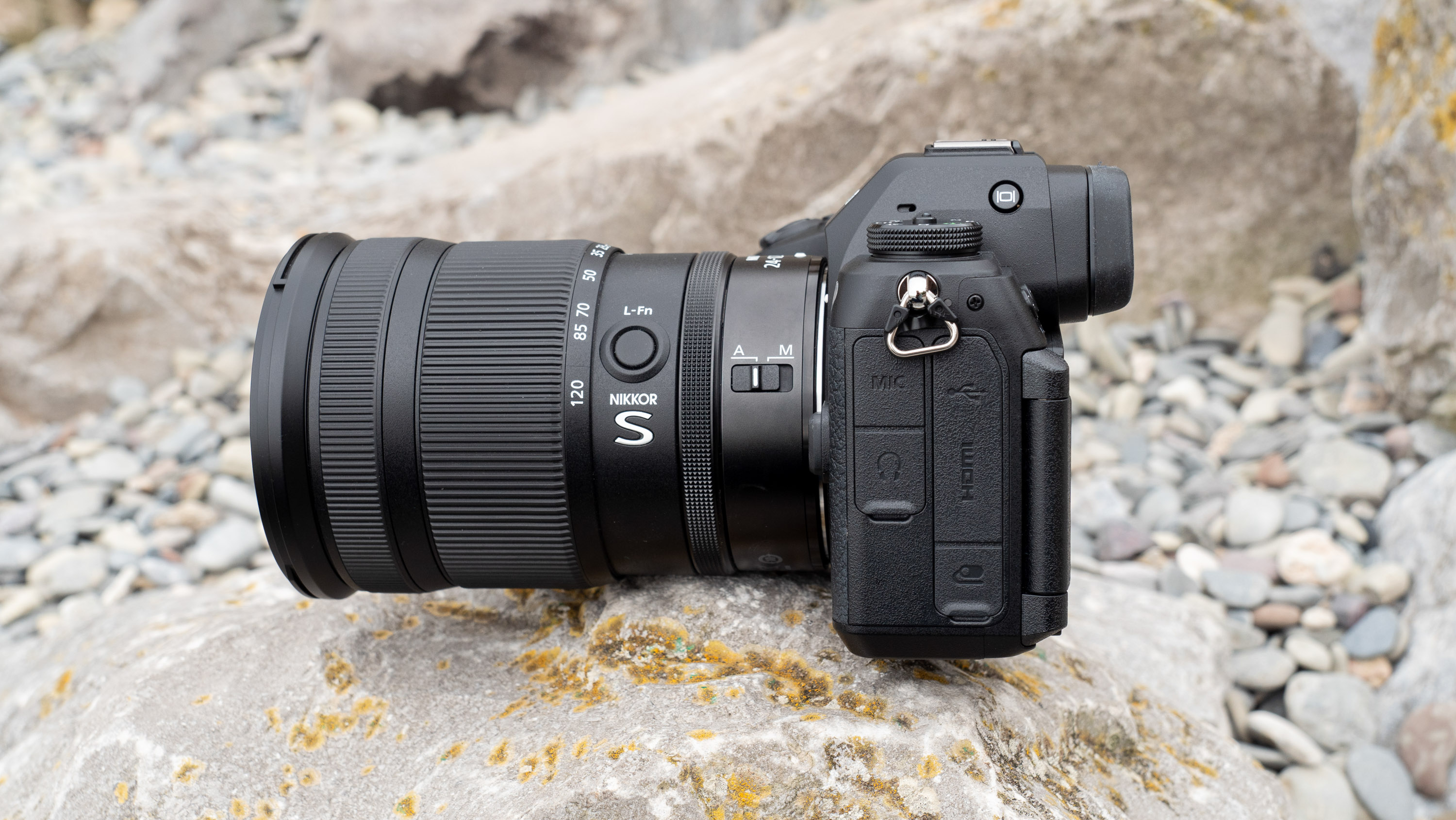
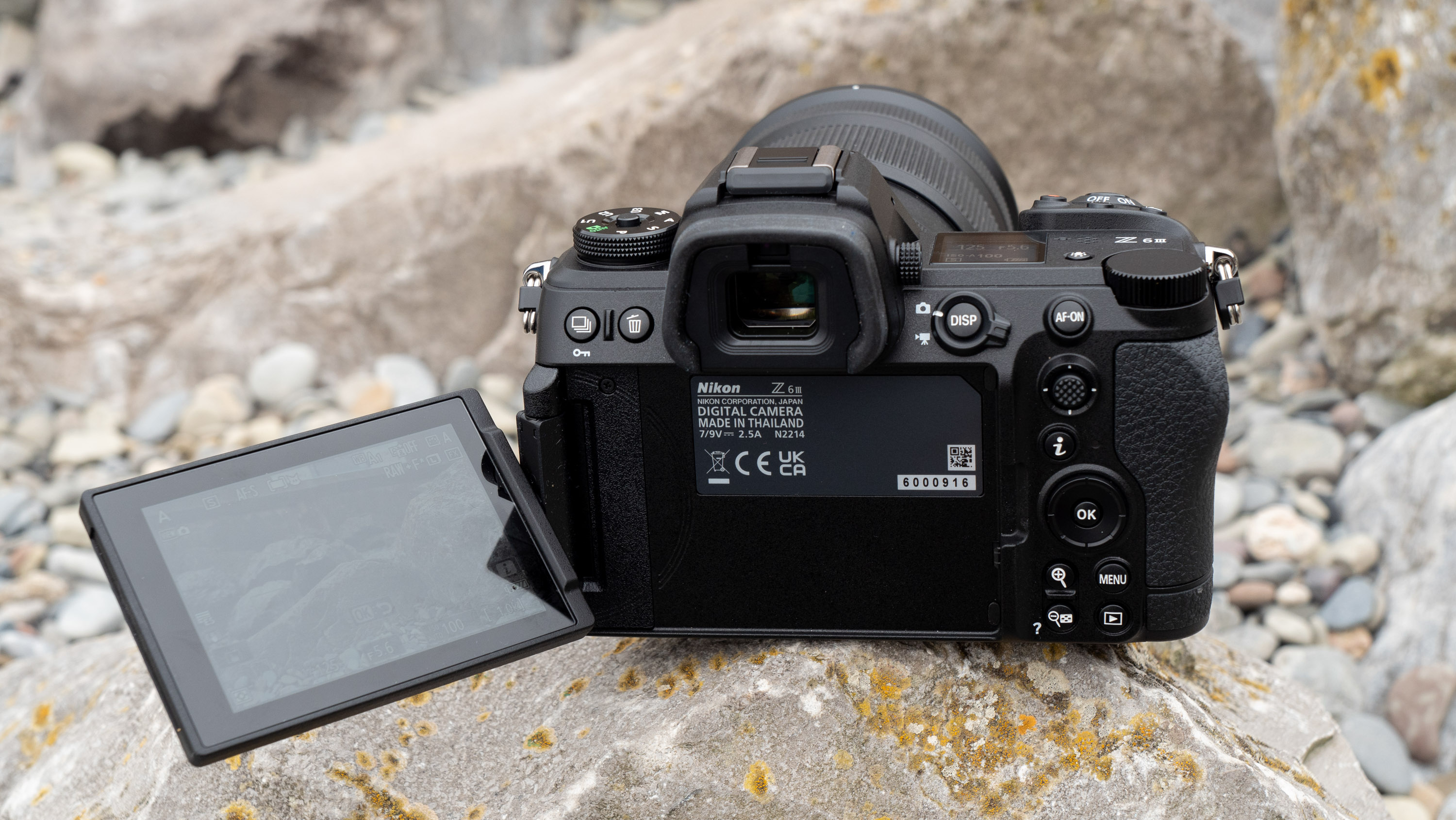
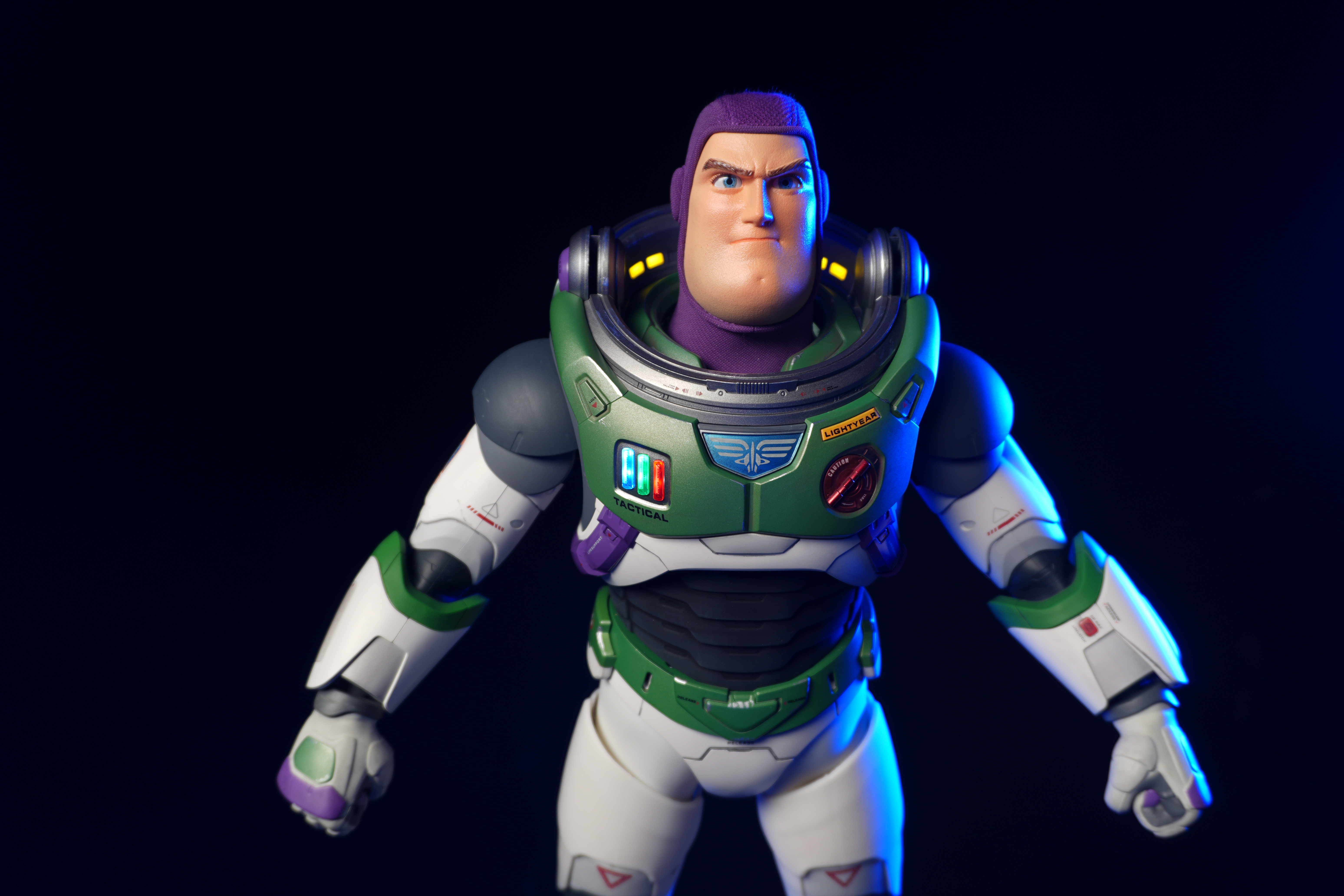
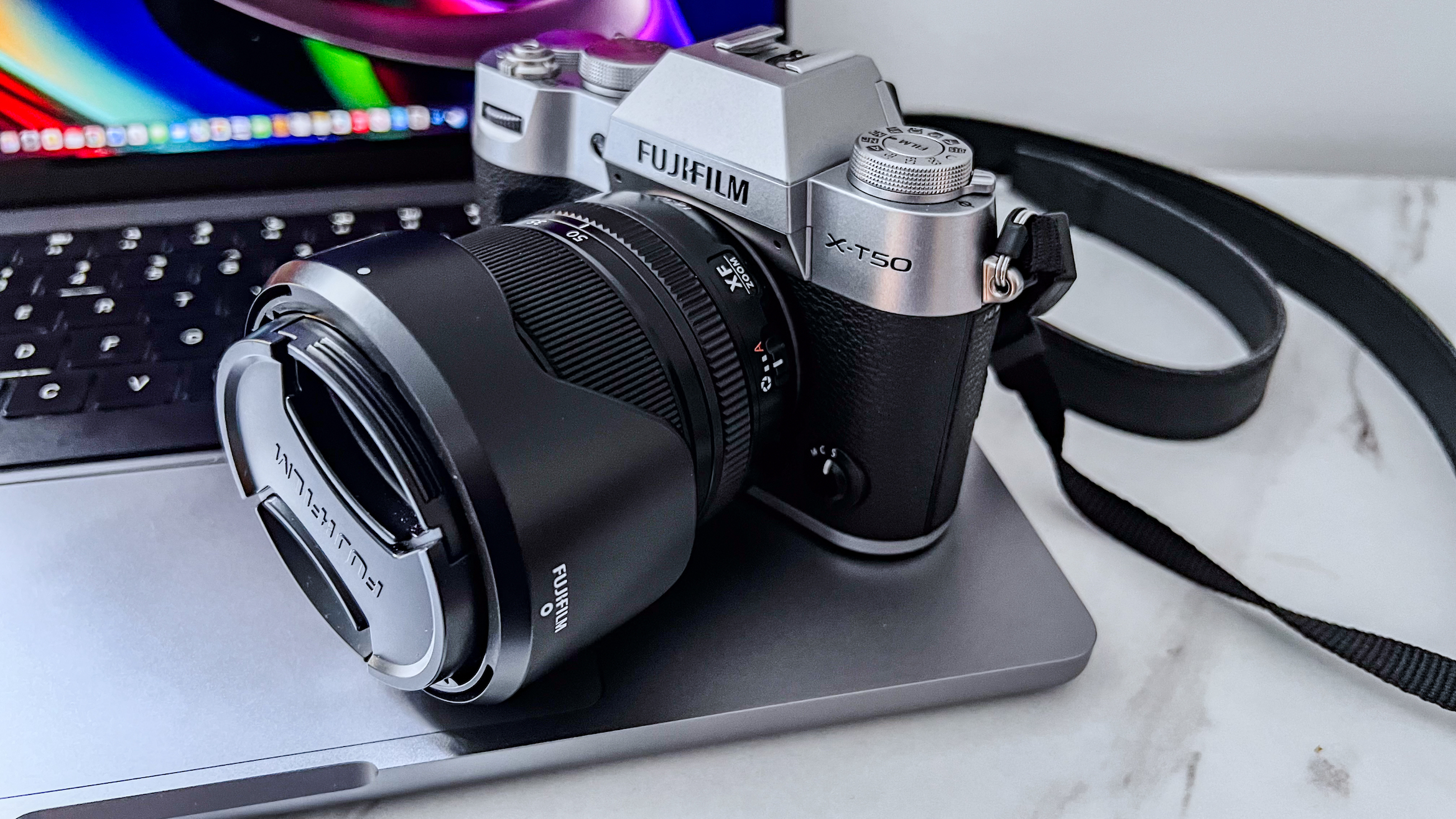
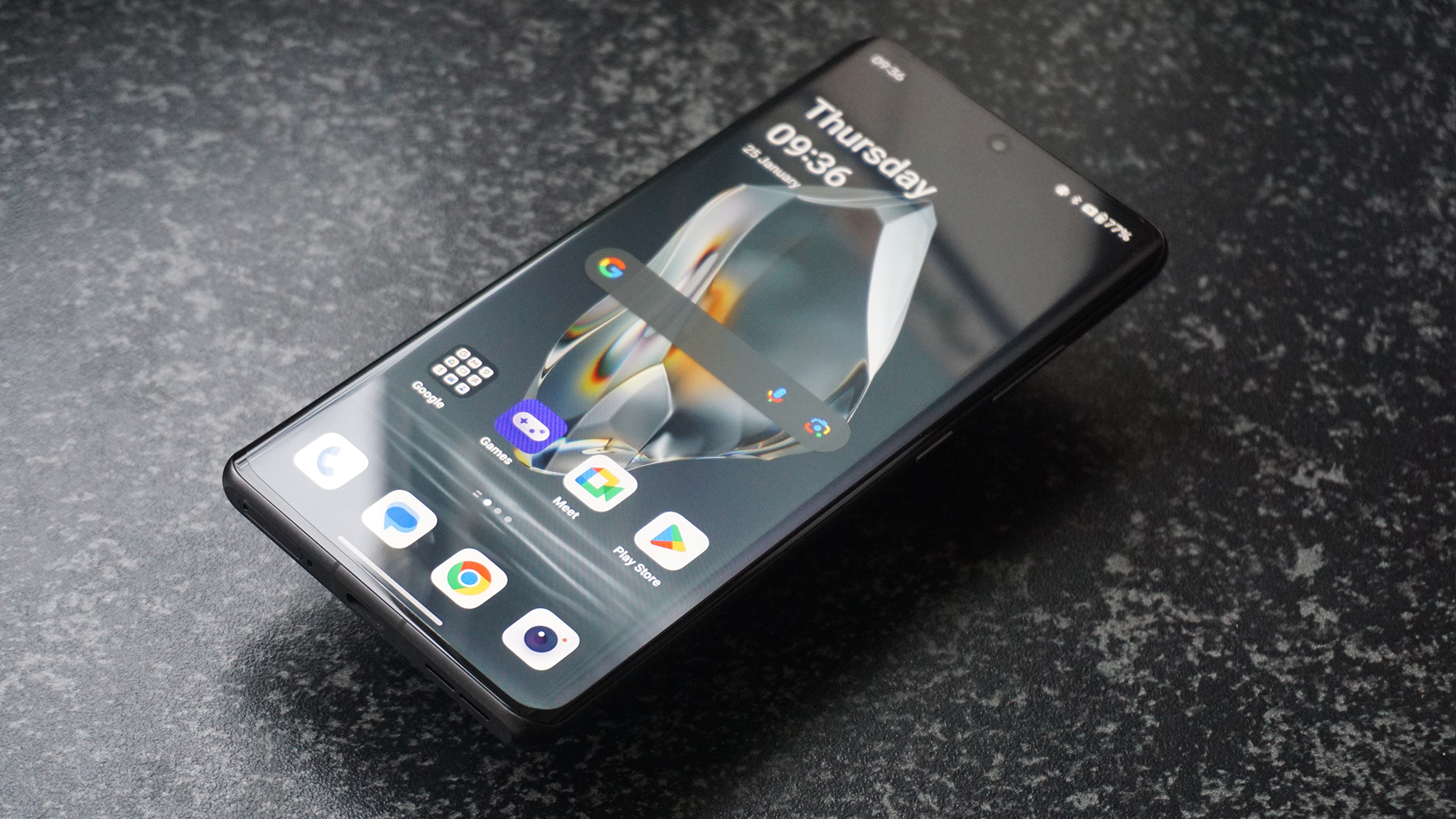
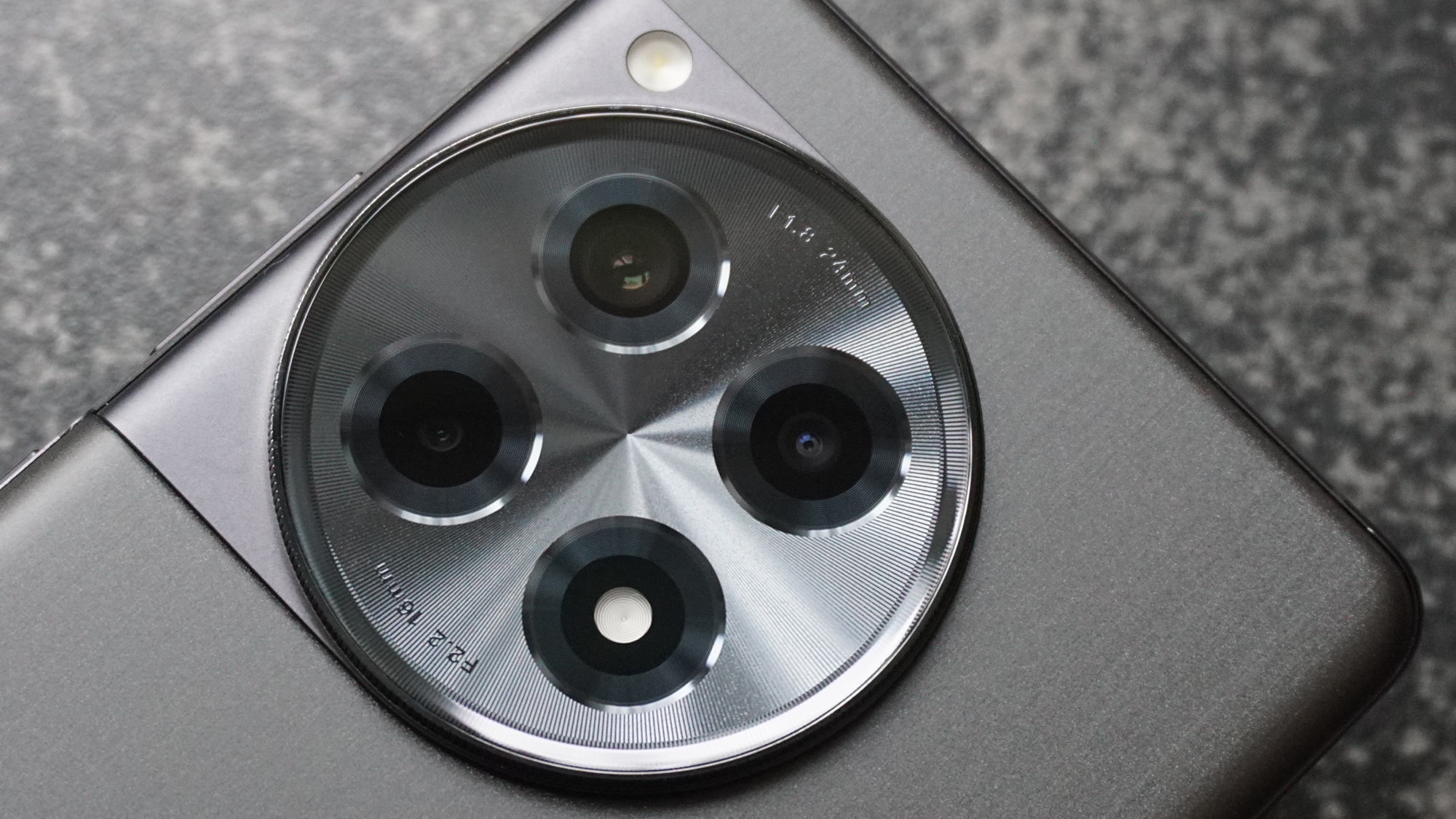
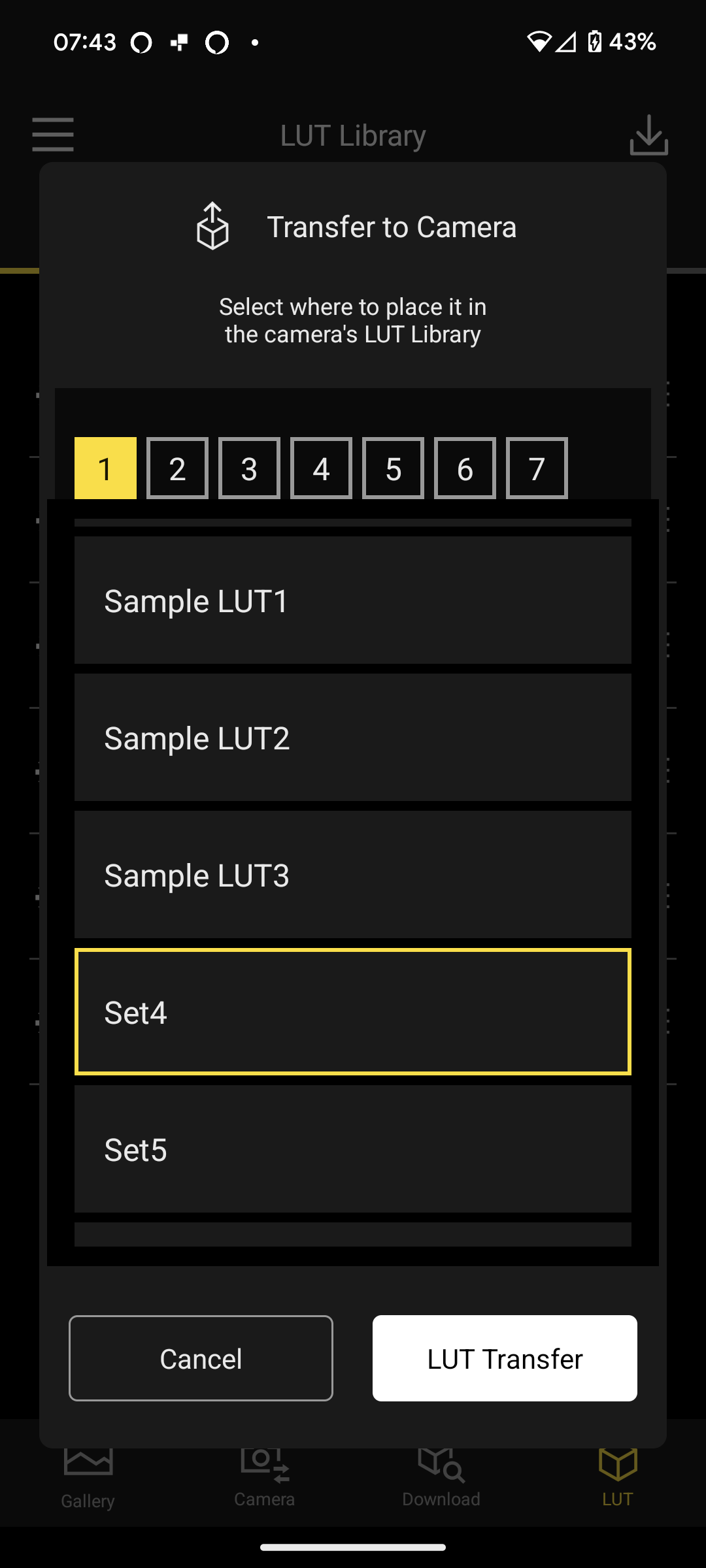
Canon EOS R5 Mark II: Two-minute review
When I originally wrote my Canon EOS R5 review, I called it the brand’s “best ever stills camera”. Four years later and I'm going to have to repeat myself – this time, however, I have to take it a step further and say that the EOS R5 Mark II is also Canon's most versatile camera yet.
There are quite a few significant differences between the two R5 generations that makes the Mark II feel more like an entirely new series rather than an upgrade. In fact, it has more in common with the Canon EOS R1 than the EOS R5, with the two new flagships sharing the headline features. So, essentially, what the Nikon Z8 is to the Nikon Z9, the R5 II is to the R1 – a smaller, albeit higher-resolution, version.
While the sensor resolution remains at 45MP, the R5 II now uses a stacked design that enables speedier readouts to minimize rolling shutter distortions, just like on the Nikon Z8. This, however, has resulted in a slight loss of dynamic range compared to the R5, but not so much that it will bother most photographers in real-world use.
The R5 II gains a second imaging processor – working in conjunction with the Digic X chip, the Digic Accelerator enables burst speeds of up to 30fps when shooting RAW, with an additional 15 frames available with pre-recording enabled. The Nikon Z8 tops out at 20fps in RAW.
Speed aside, the autofocus accuracy here is also better than what I experienced with the original R5 and, during my testing, the Mark II was more than ready to take on a challenge straight out of the box. In fact, I think the AF performance here is better than the Nikon Z8, which is my daily shooter. Not only has Canon improved its AF algorithm, it’s also added a couple of new features that make it really hard to miss a shot – you can select specific people to prioritize as your main subject in People Priority mode, while the new Action Priority feature uses deep-learning algorithms to tell the camera when a specific action is about to take place and automatically shift the focus point accordingly. The latter, however, is still a work in progress with only three team sports supported at launch.
Canon has been using Eye Control AF in its pro sports cameras – namely the EOS 1D X Mark III DSLR and the EOS R3 – but it’s now available on the R5 II. While it’s been improved in some ways, it’s still hard to calibrate it for all users.
Also new are a couple of AI-driven features that allow you to edit shots in-camera. The Image Upscaling feature can enhance resolution by 4x, after which you crop it in-camera to zoom in closer to a distant subject. It’s a handy feature to have, but only works for images shot as JPEG/HEIF and can be impractical for some photographers in the field. Photographers who find the need to push the limits of a camera’s ISO performance will be glad to know there’s a Neural Network Noise Reduction feature built in that can be employed, but you will need to shoot in RAW for this feature to work and the processed file is then saved as a JPEG.
Video specs have also been improved, with the R5 II capable of shooting 8K/60p clips (versus 30fps on the R5) for up to 120 minutes with a new Cooling Fan Grip. Importantly, Canon’s C-Log2 – the video encoding option previously only available in the brand’s cinema cameras – is now supported on the R5 II, offering better dynamic range and easier color grading compared to C-Log3.
Where it falls short compared to its predecessor is battery life. Despite a new high-powered LP-E6P pack, it’s only rated for 630 shots compared to the 950 that the LP-E6NH was rated for in the R5. To be fair, though, it is powering the new features and the higher speed.
Of course, new features come at a cost, but if they all do what they say on the tin, then it could be argued that the R5 II would be a worthy investment despite a higher price. What makes it even more so is that this camera truly does make pro photography easy and, given it can handle any scenario, it's a remarkably versatile shooter as well. Thankfully, though, Canon has priced its flagship well, with only a 10% increase over the launch price of the EOS R5.
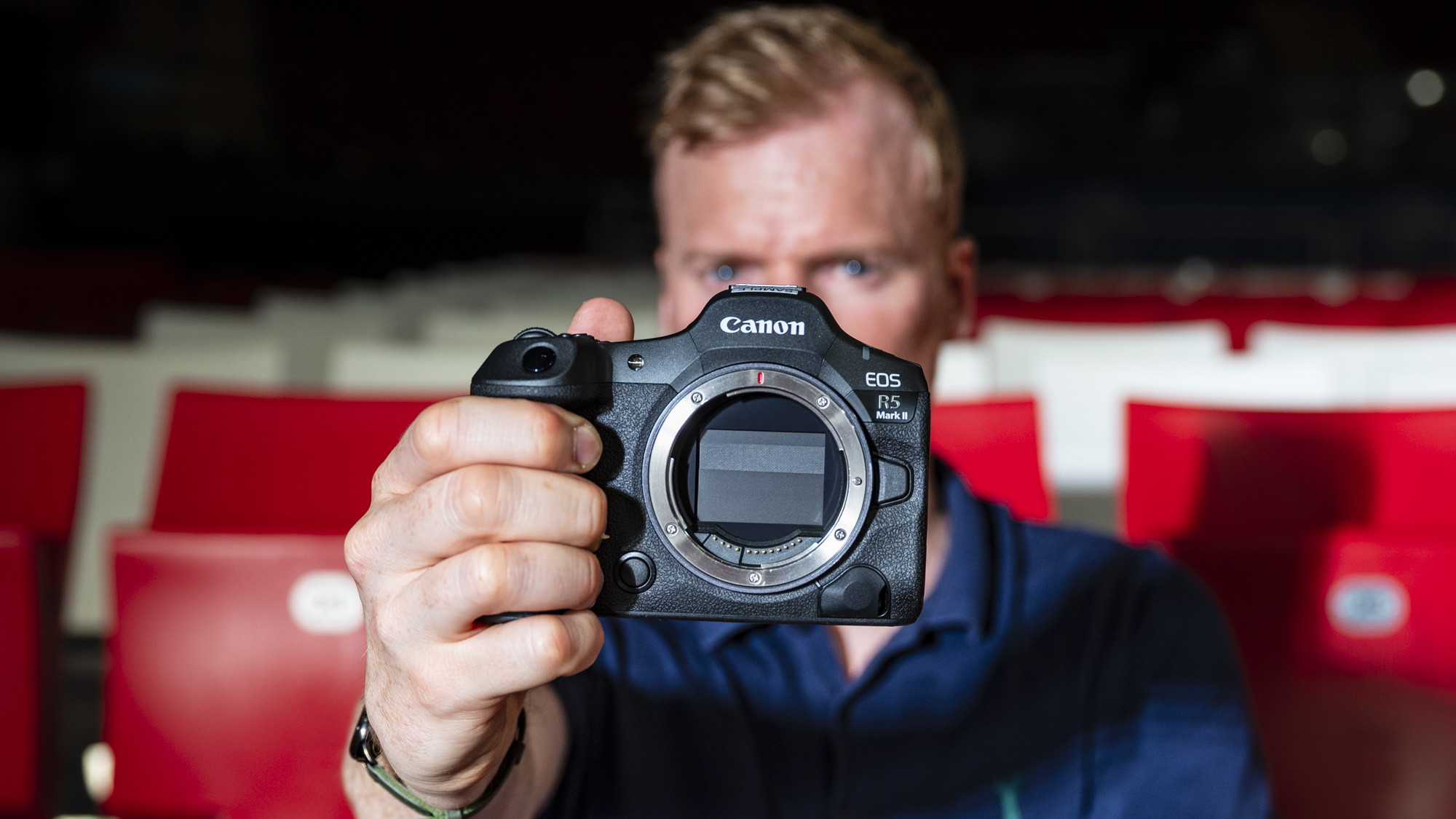

Canon EOS R5 Mark II review: Release date and price
- Body-only price is $4,299 / £4,499 / AU$6,499
- Available since August 2024
- Three optional grips: Standard BG-R20, battery BG-R20EP and cooling fan CF-R20EP
With a body-only suggested retail cost of $4,299 / £4,499 / AU$6,499, the EOS R5 II is quite competitively priced. It’s slightly more than the R5’s body-only launch price in some markets (which was $3,899 / £4,199 / AU$6,899 in July 2020), and that’s to be expected given the slew of updates it’s got over its predecessor.
Aussie photographers, though, should be overjoyed if they’ve been holding out for a worthy upgrade from an older camera, especially since it’s cheaper than the Nikon Z8’s launch price too ($3,999 / £3,999 / AU$6,999). That said, it’s now possible to find the Z8 at discounts of about $700 / £450 / AU$1,000 – making it a compelling alternative to its Canon competition.
The R5 II was slated for an August 2024 release and is now available to purchase from authorized retailers in the US and Australia, but is still listed as a pre-order in the UK at the time of publication.
It’s possible to also pick up a single-lens kit for $5,399 / £5,749 / $AU$7,999, which bundles the RF 24-105mm f/4 L IS lens with the R5 II.
For the first time for any camera maker, Canon has also released three optional grips that can be purchased separately, which includes a Cooling Fan Grip ($399 / £549 / AU$829) that improves video recording times but lacks the vertical control layout. For that, you’ll need to opt for the Battery Grip that will set you back $349 / £489.99 / AU$699.
• Price score: 4.5 / 5

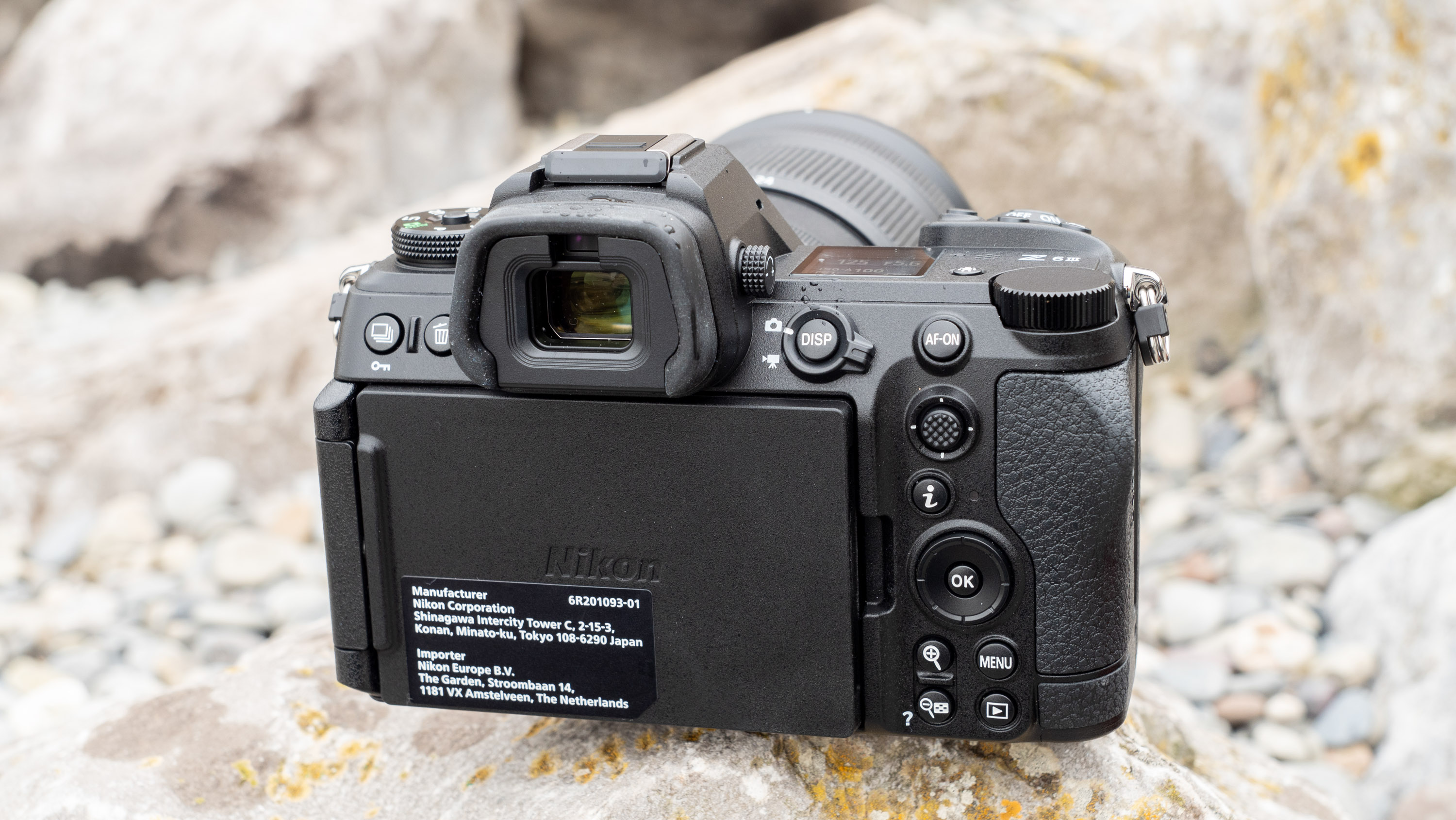
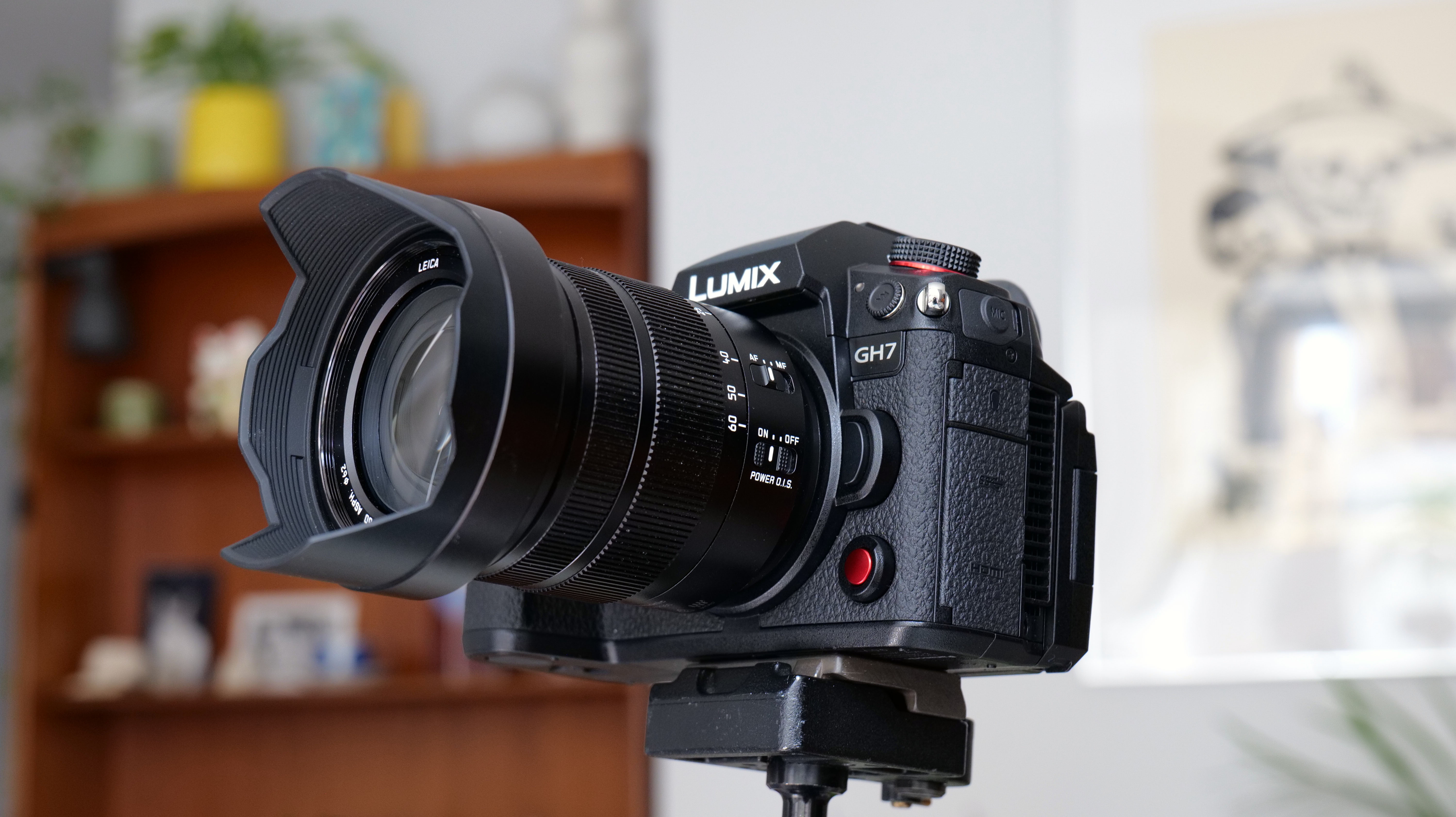
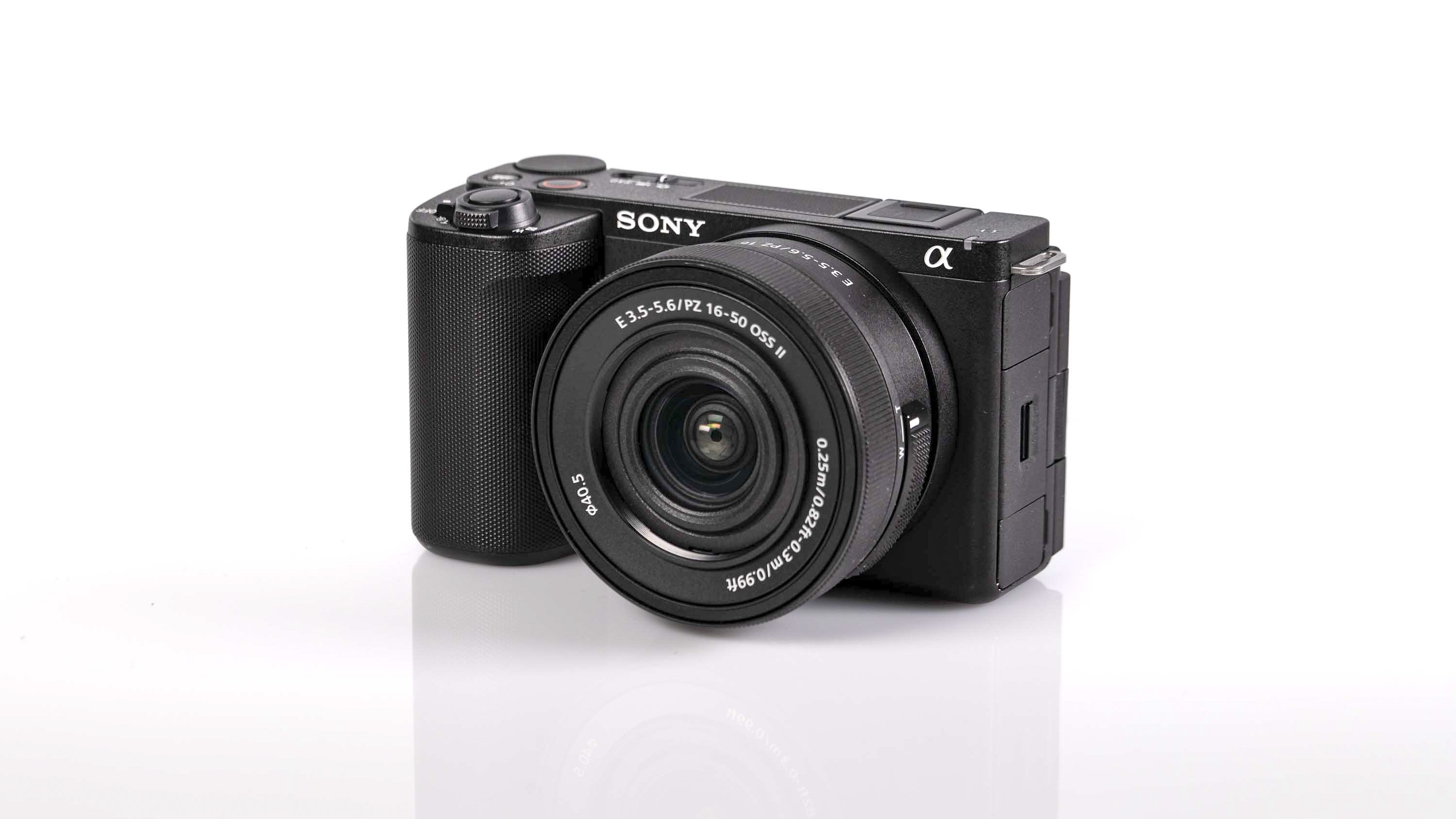
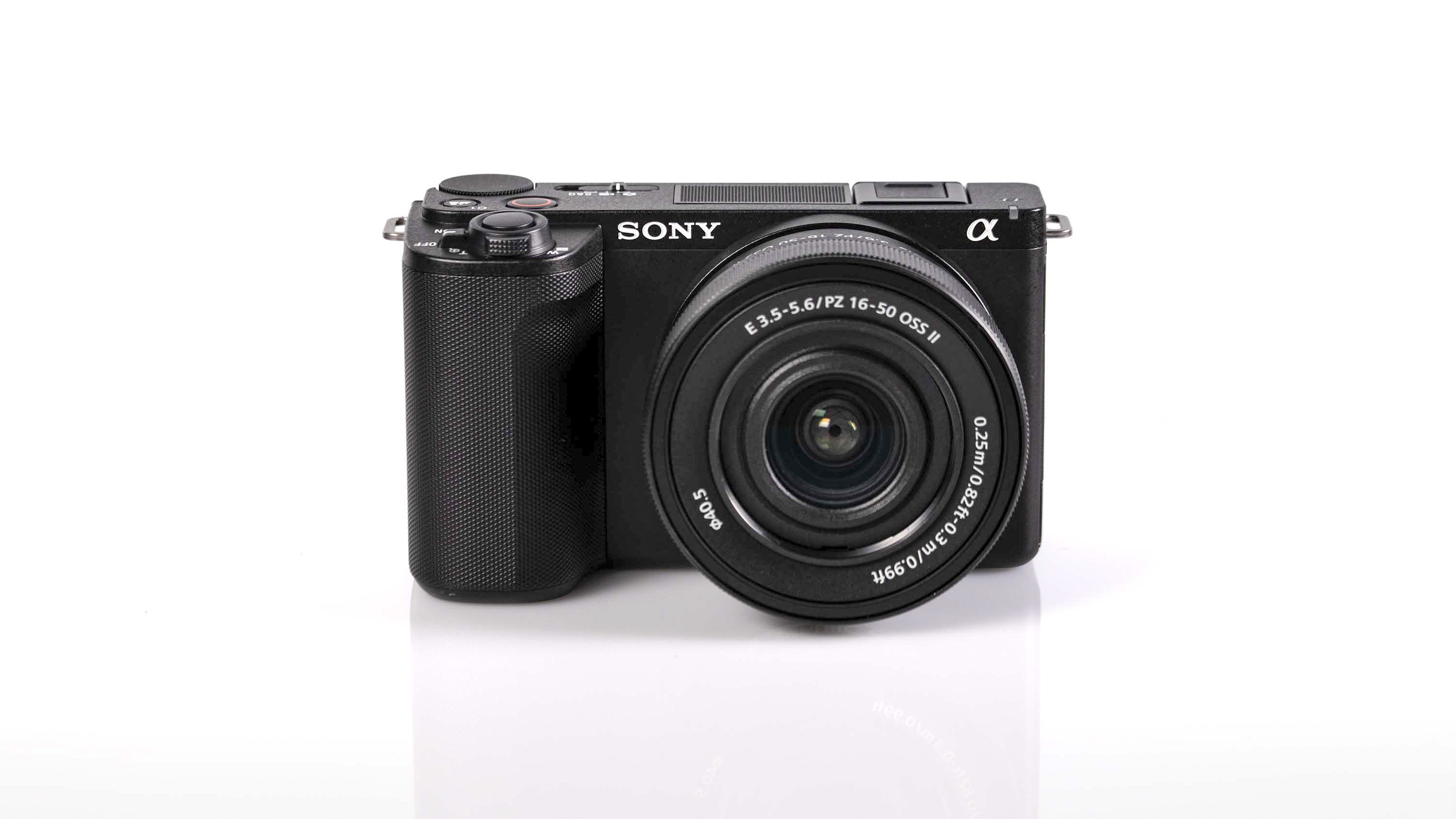
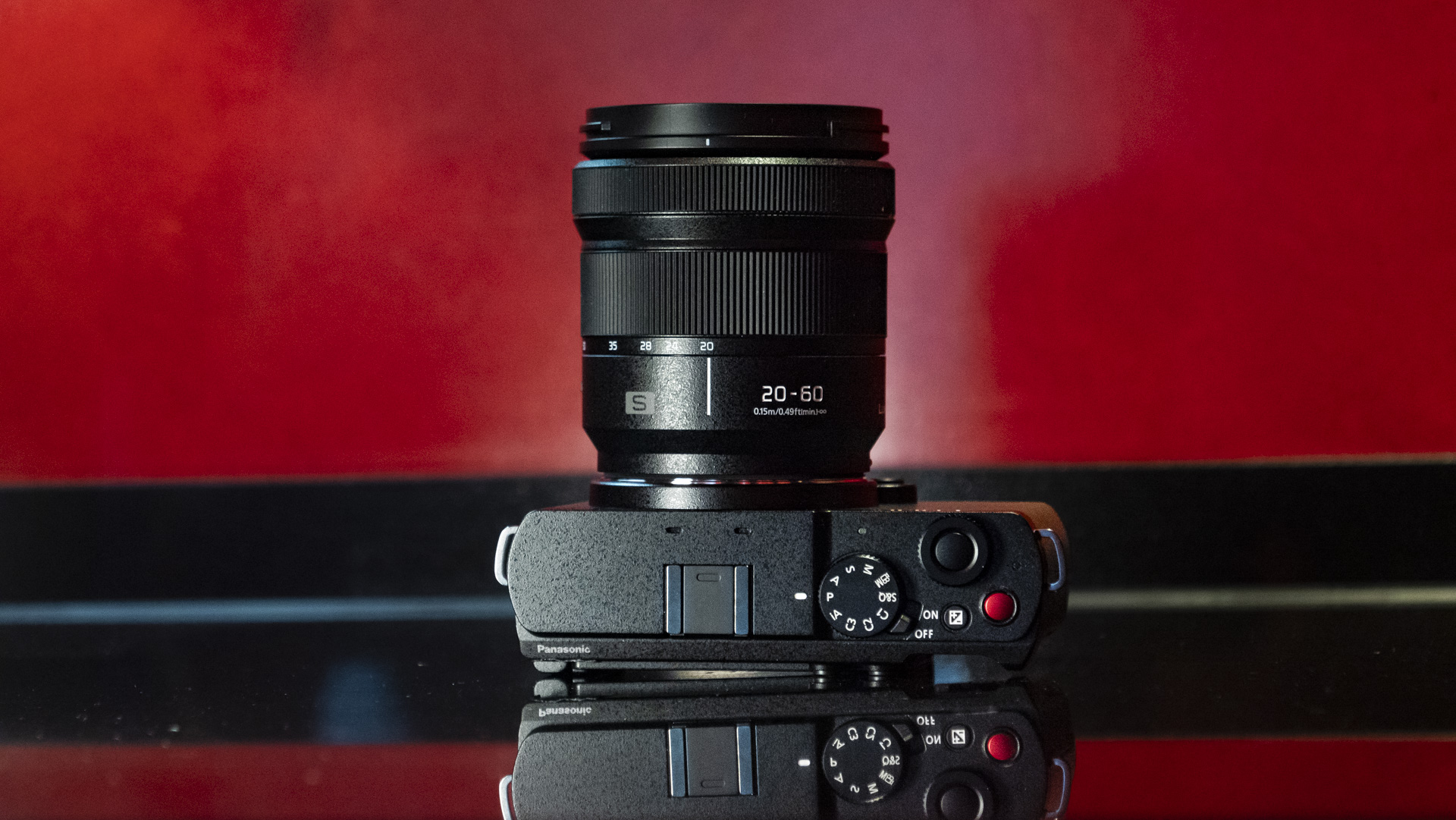
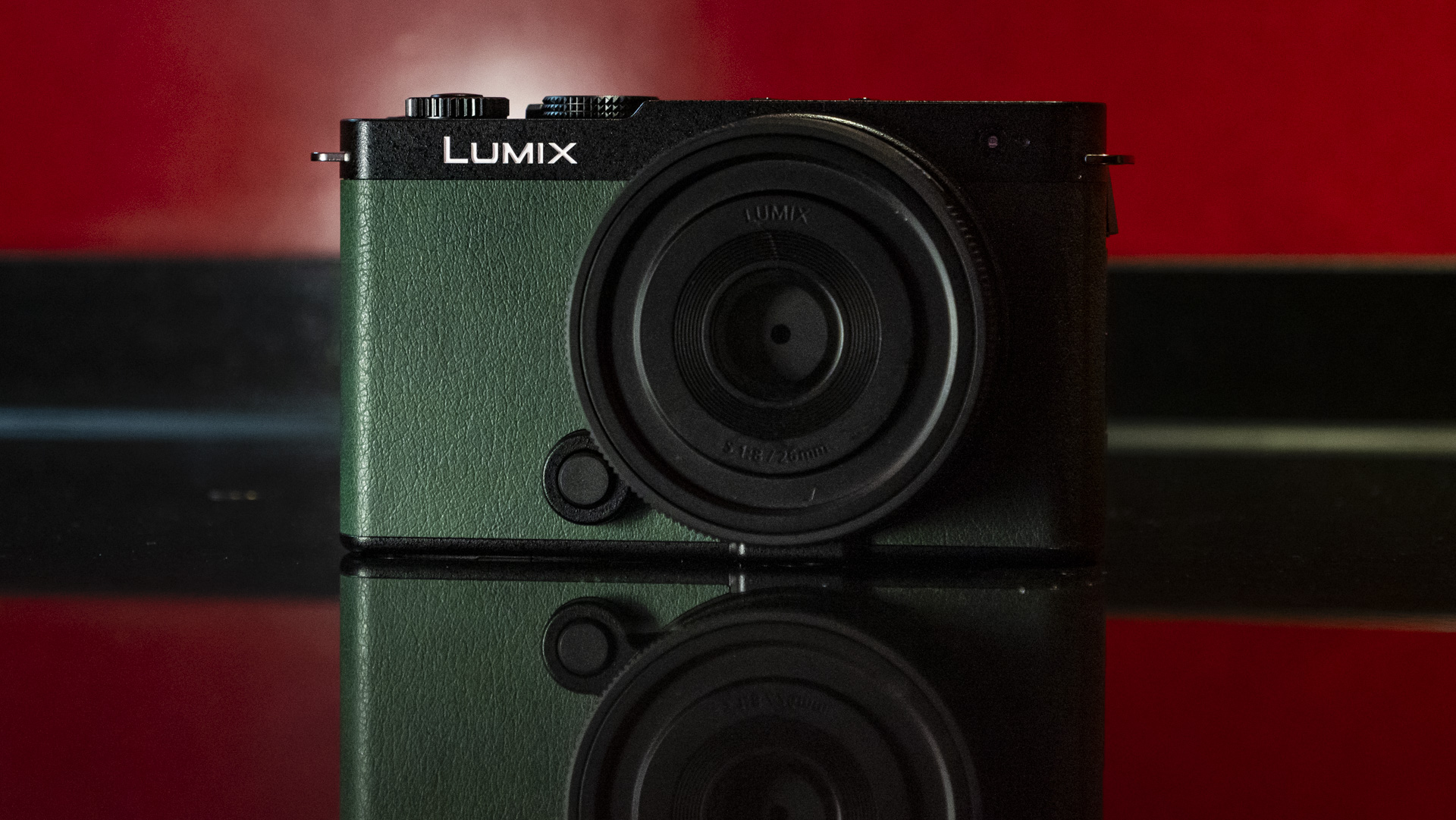
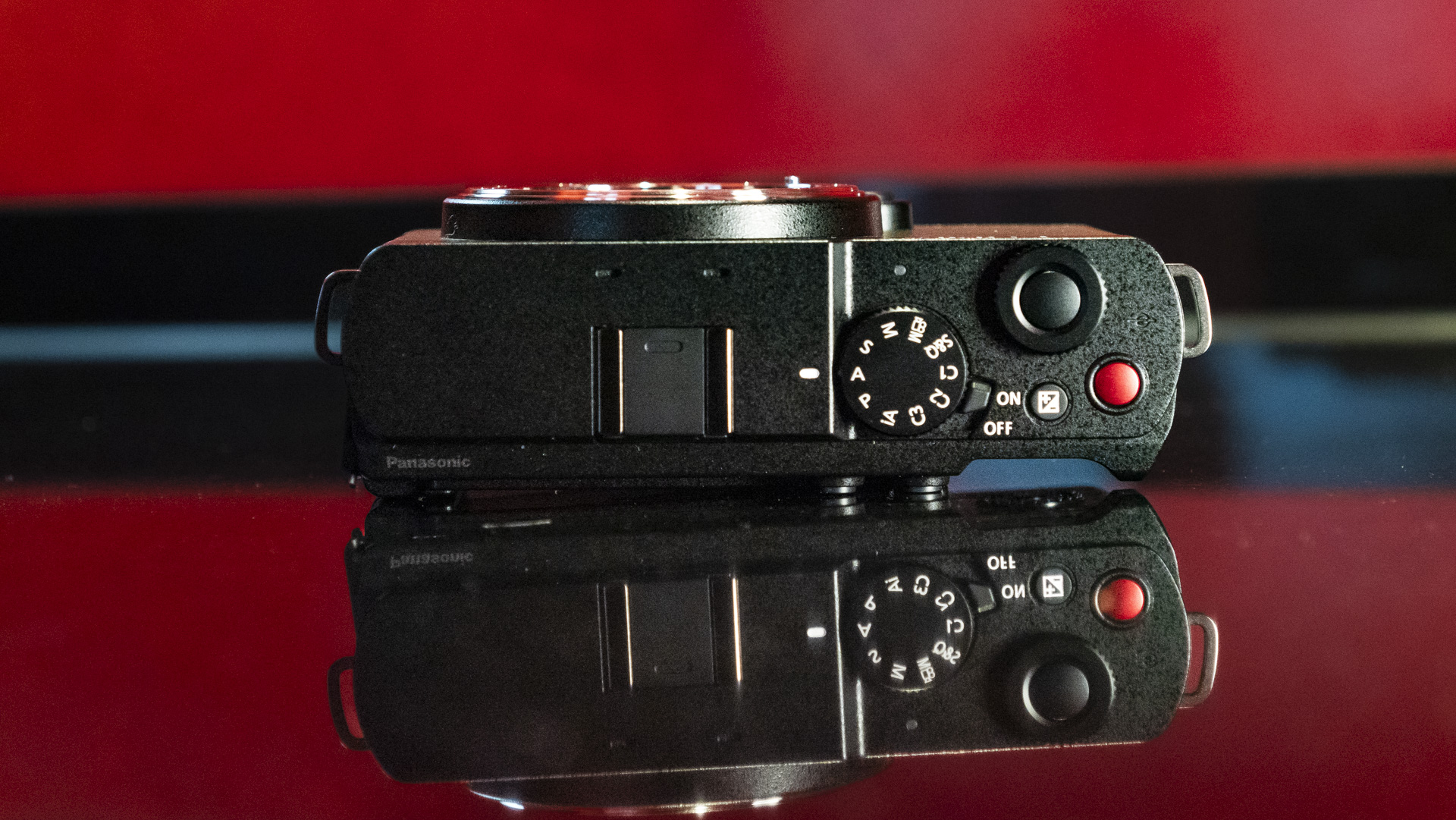
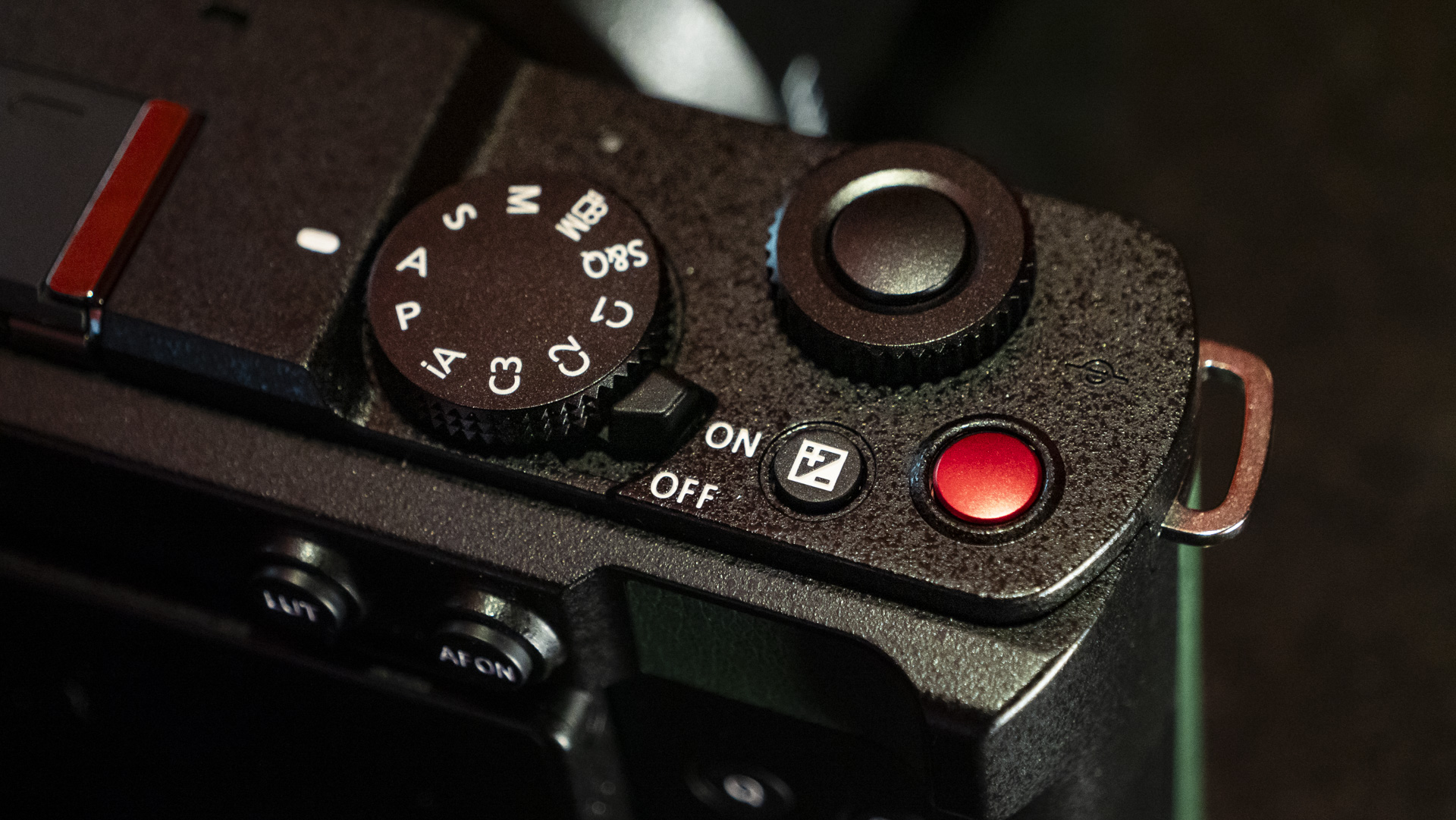
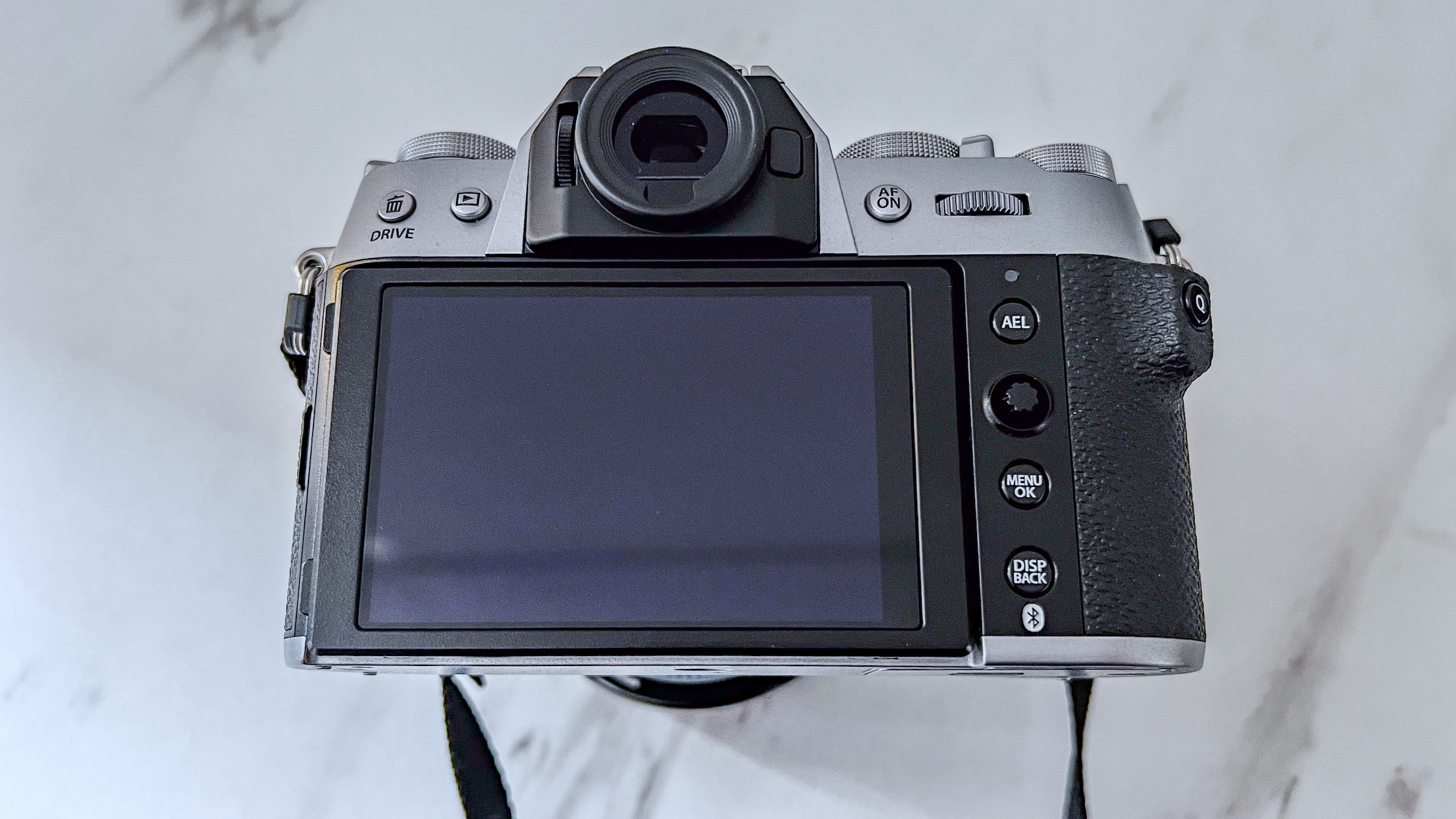
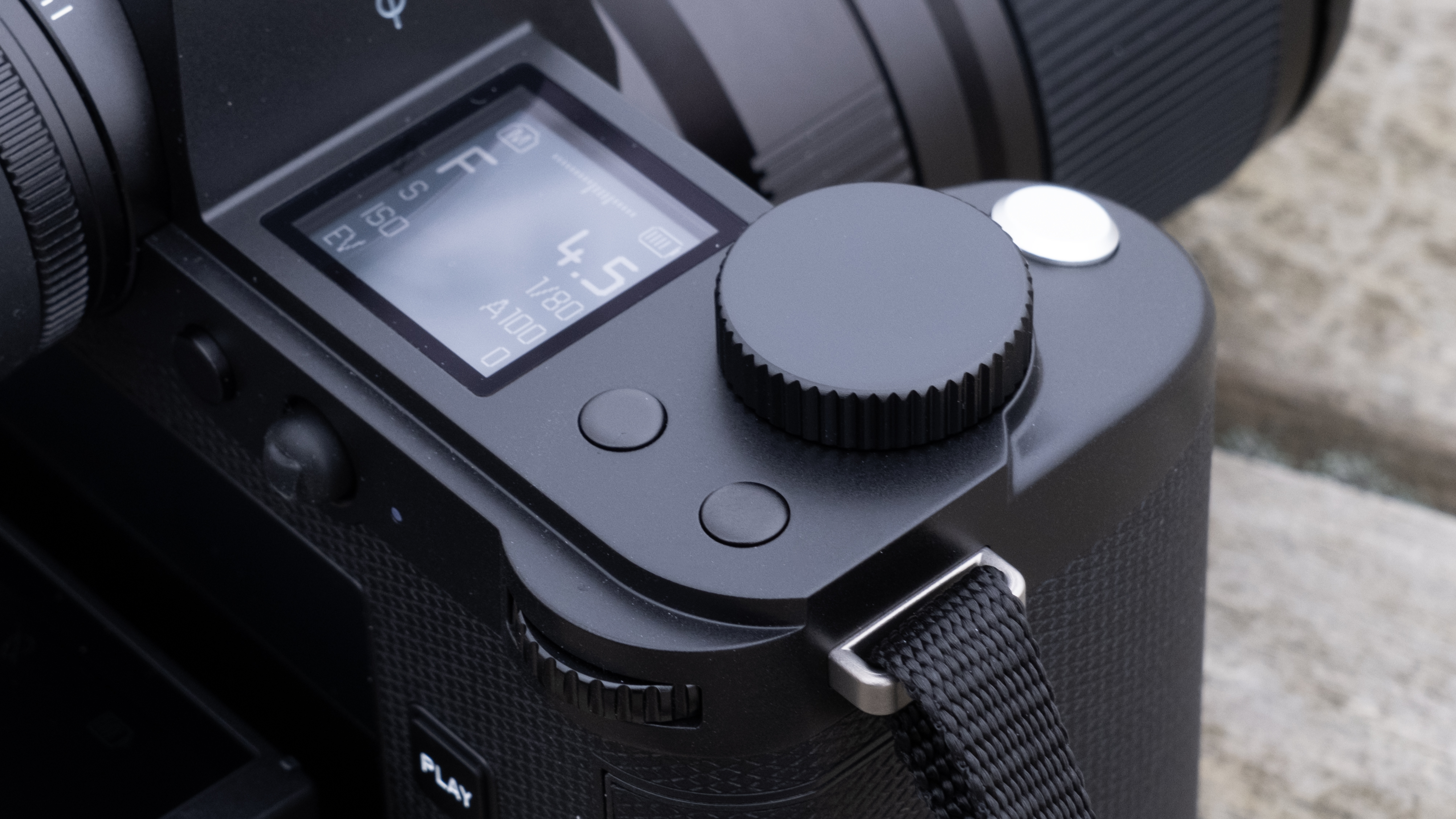
Canon EOS R5 Mark II review: Design and handling
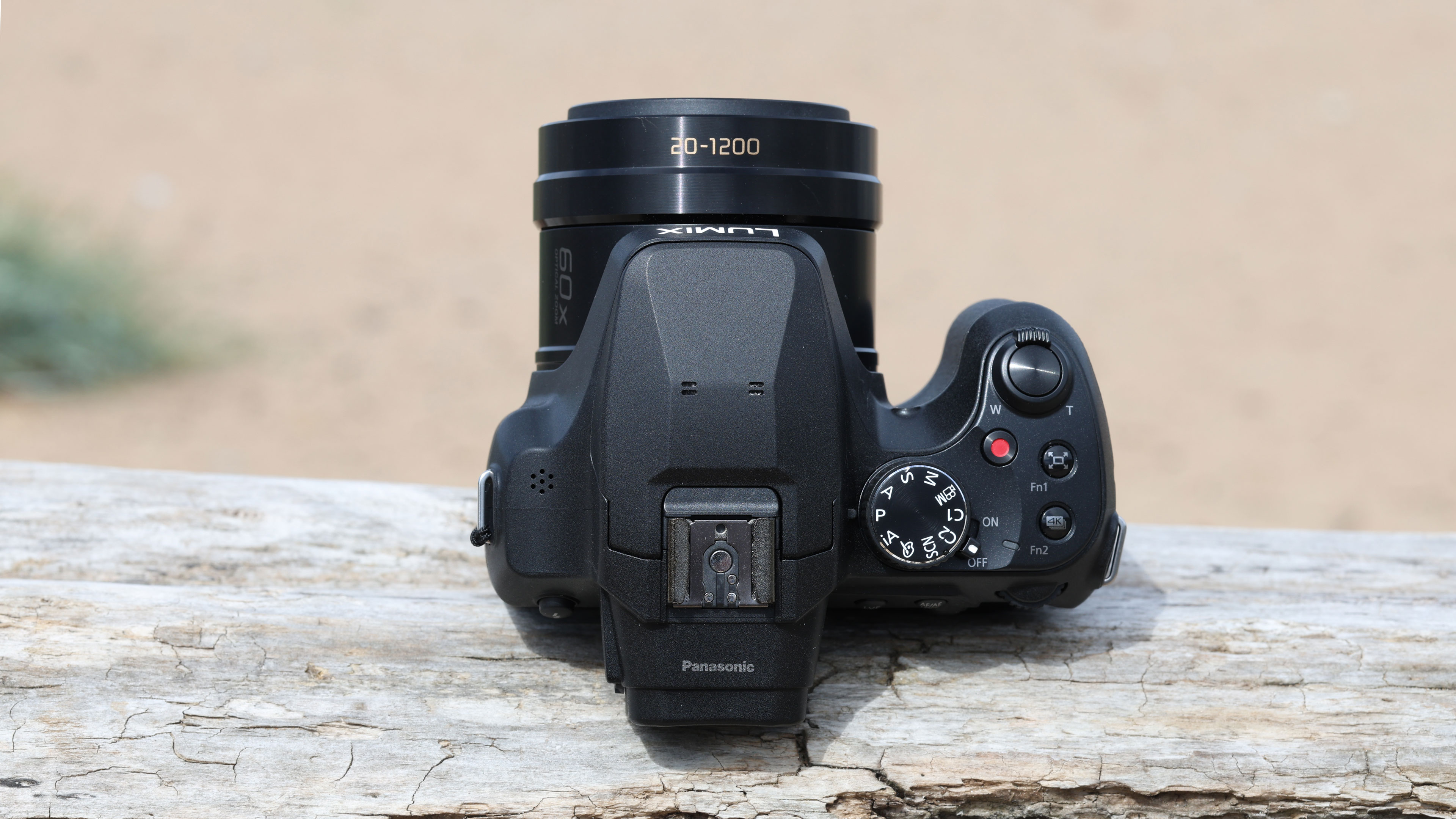
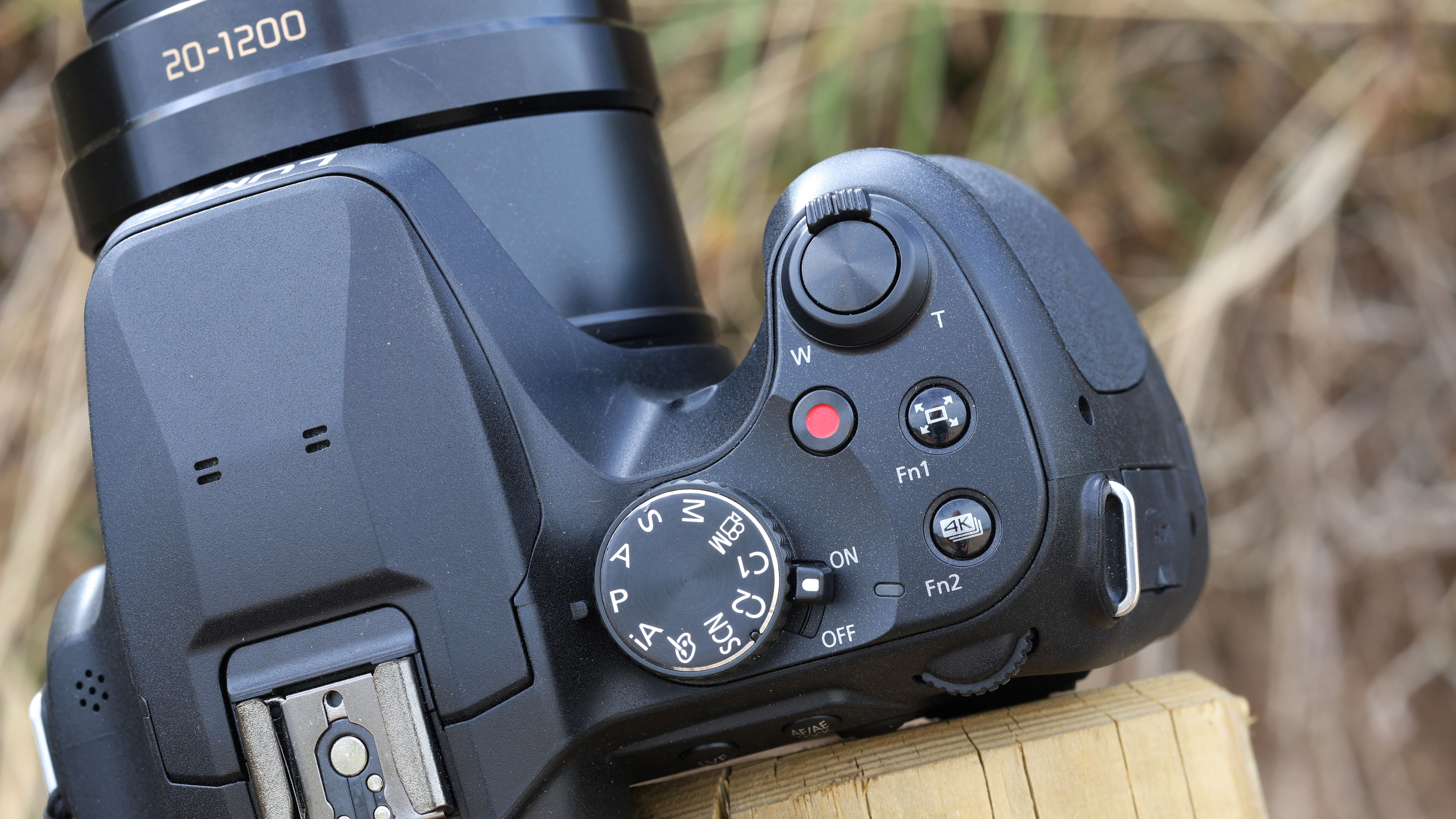
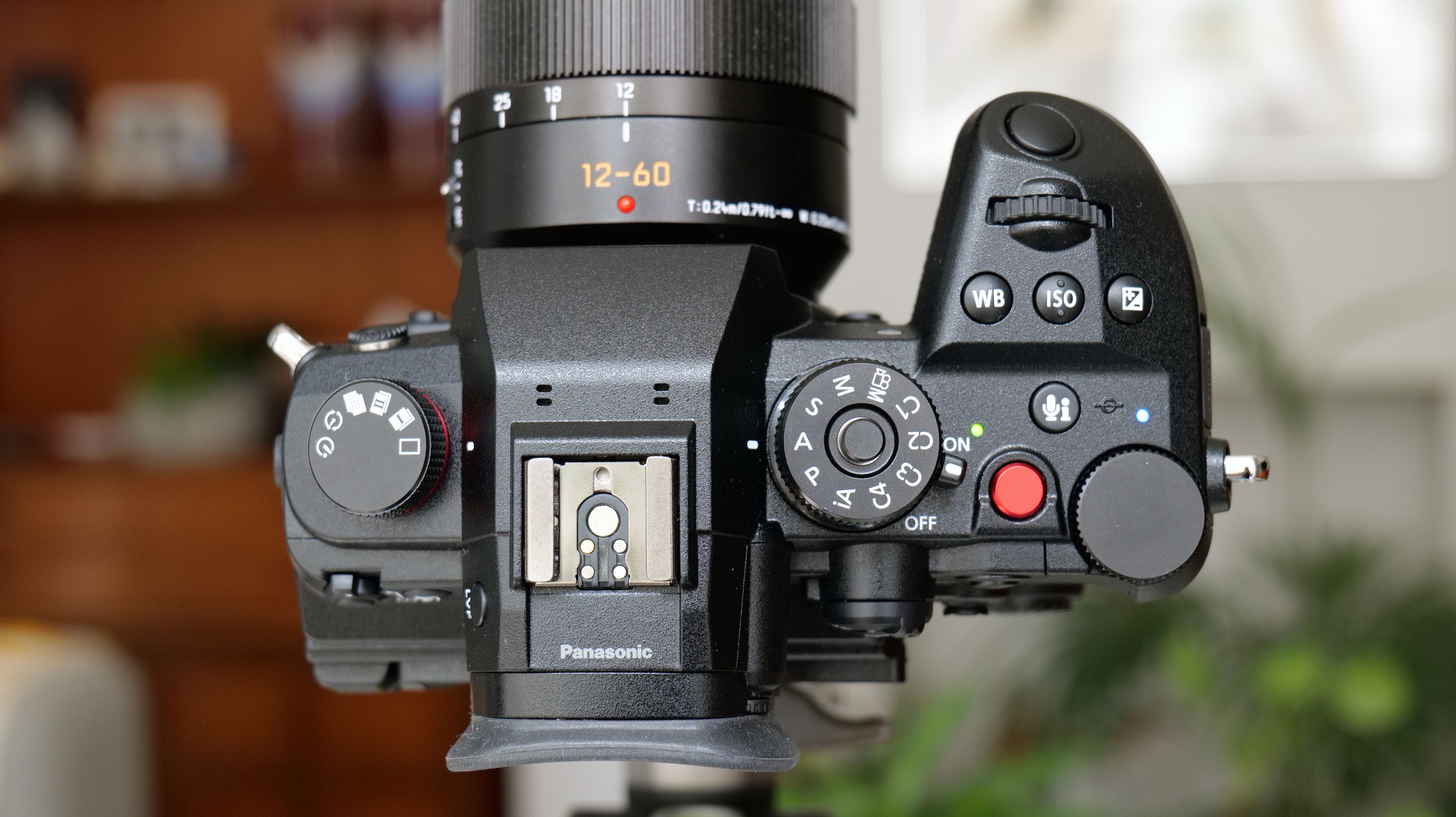
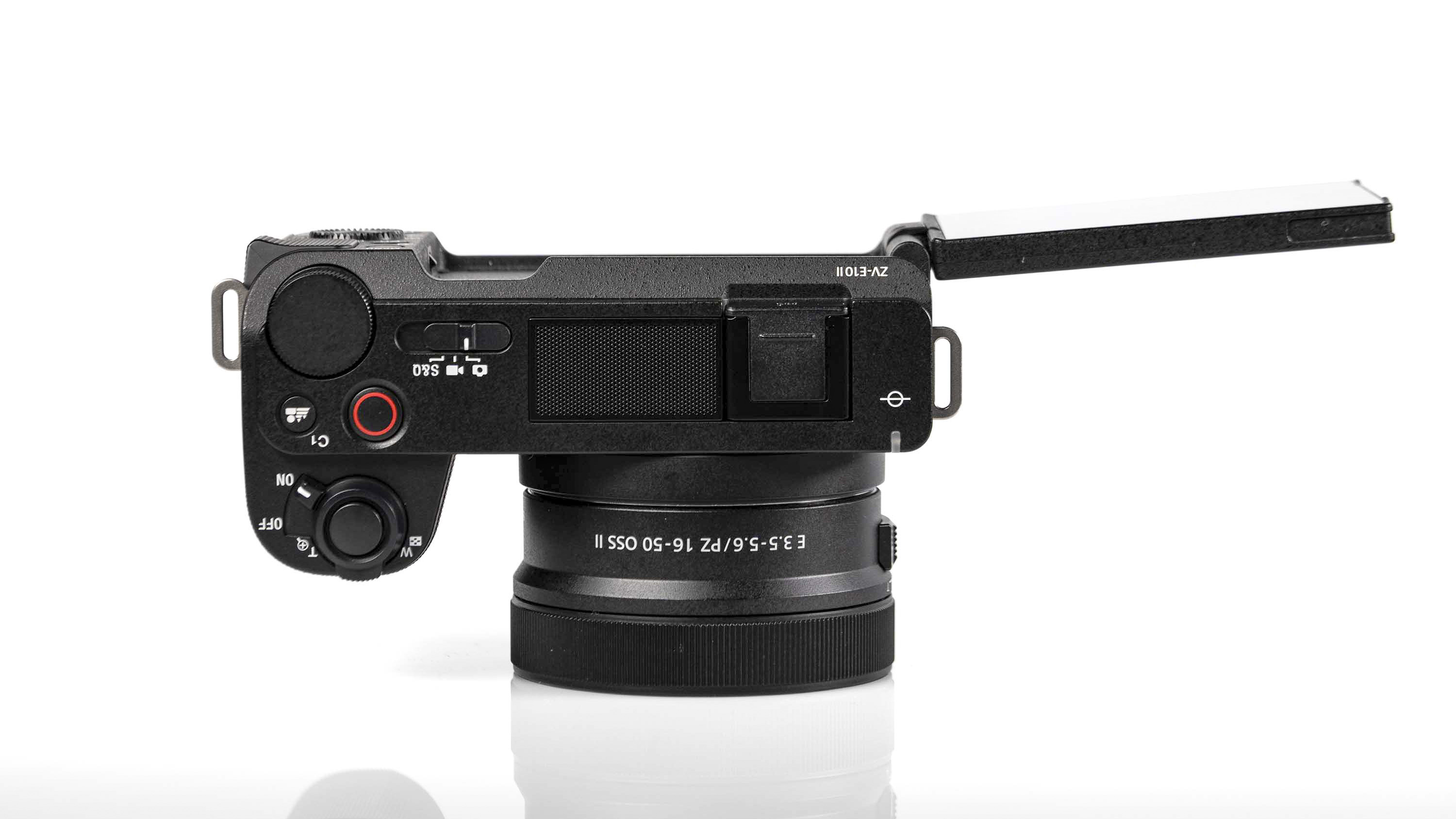
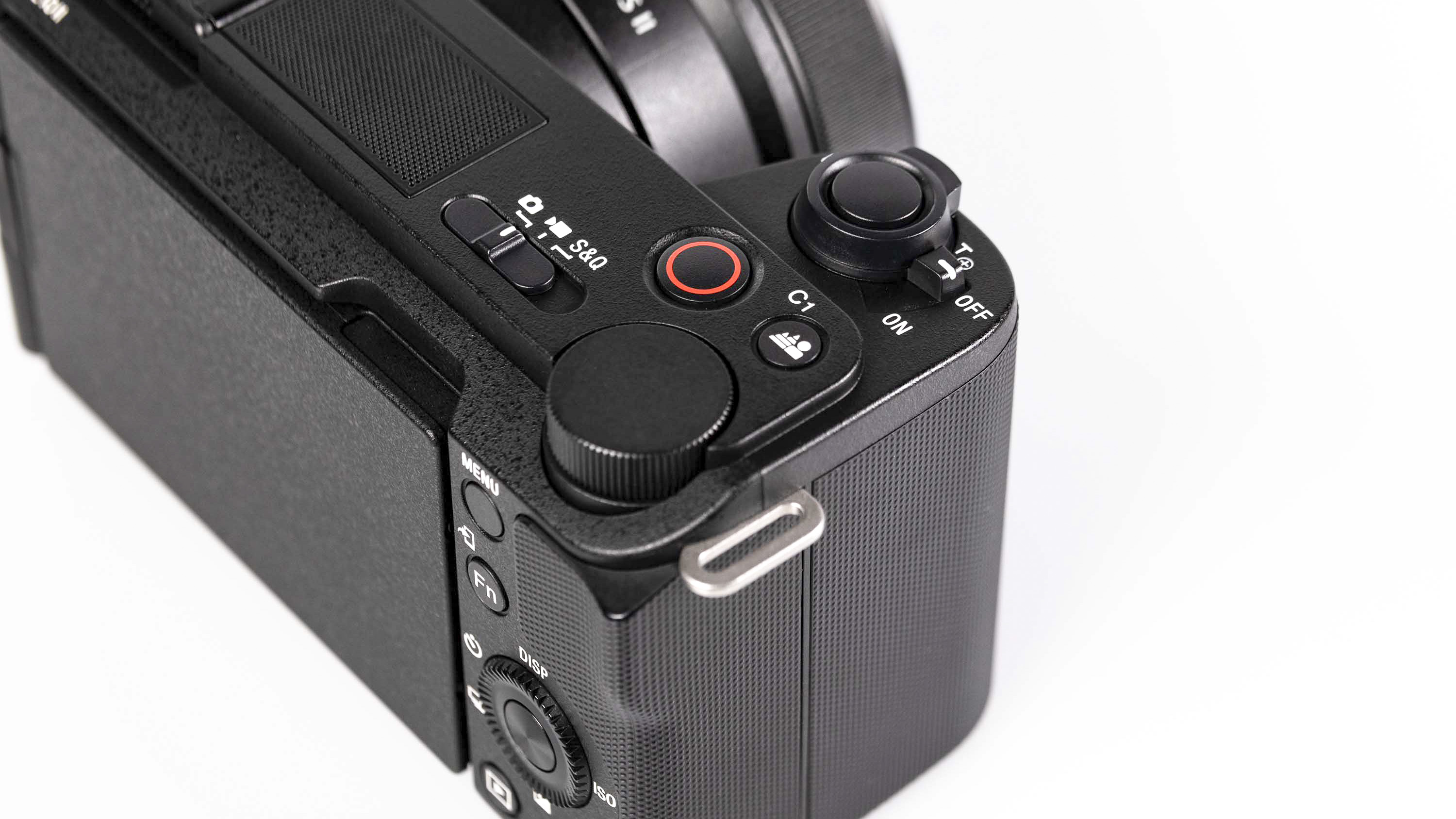
- Small changes to top plate control layout
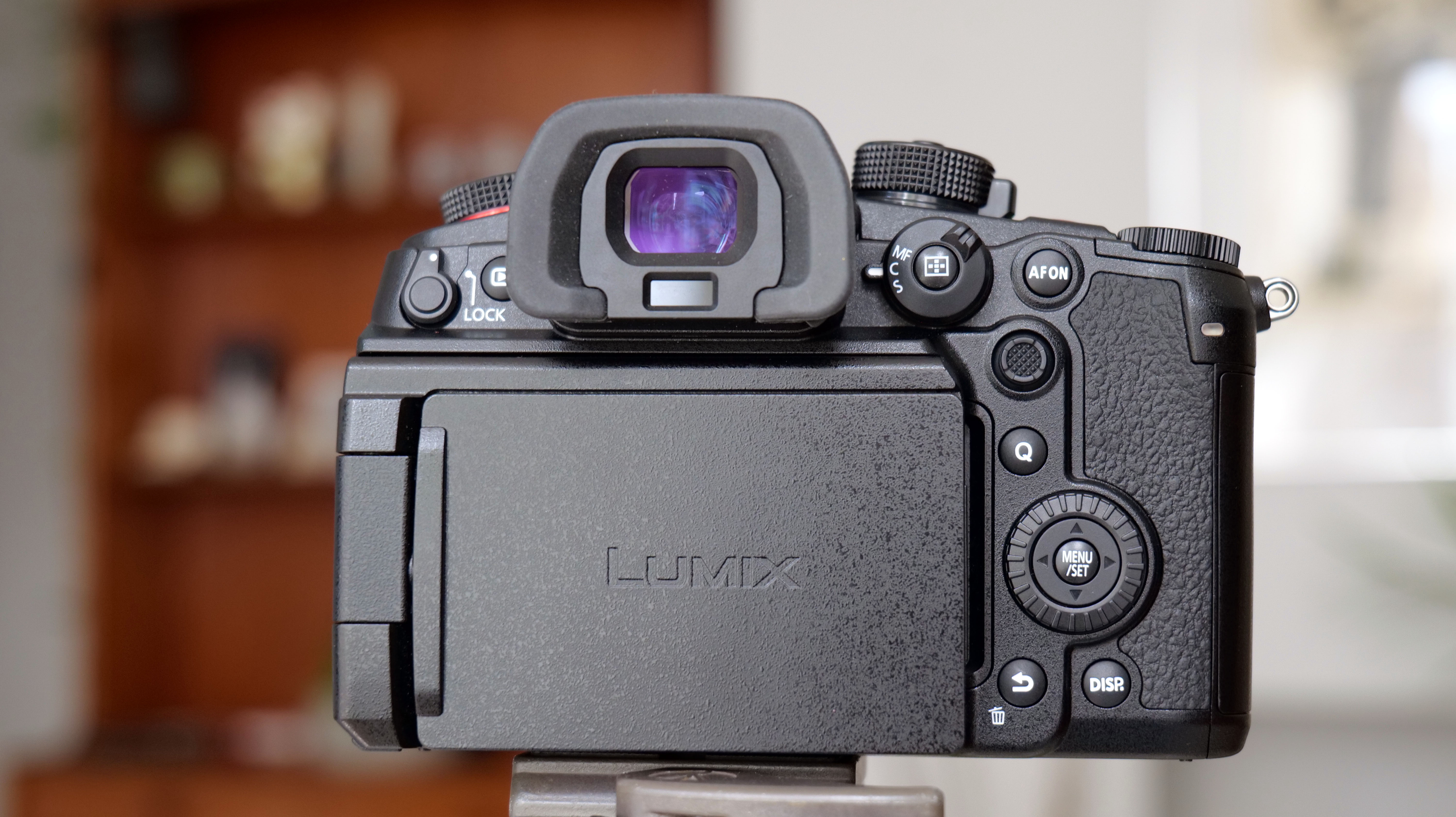
- Improved blackout-free 5.76m-dot OLED EVF with Eye Control AF
- Under-camera cooling vents keep the body slim
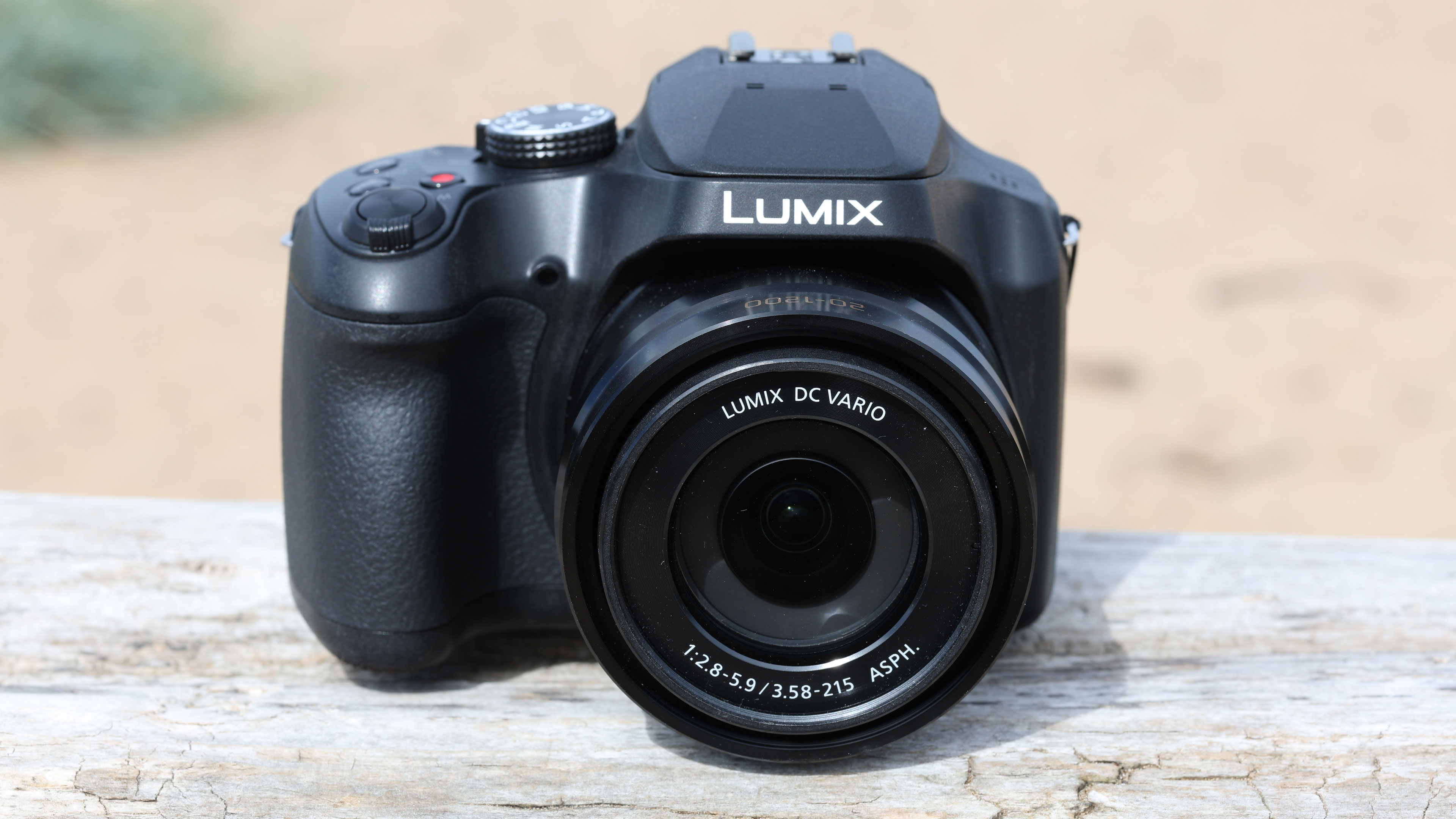
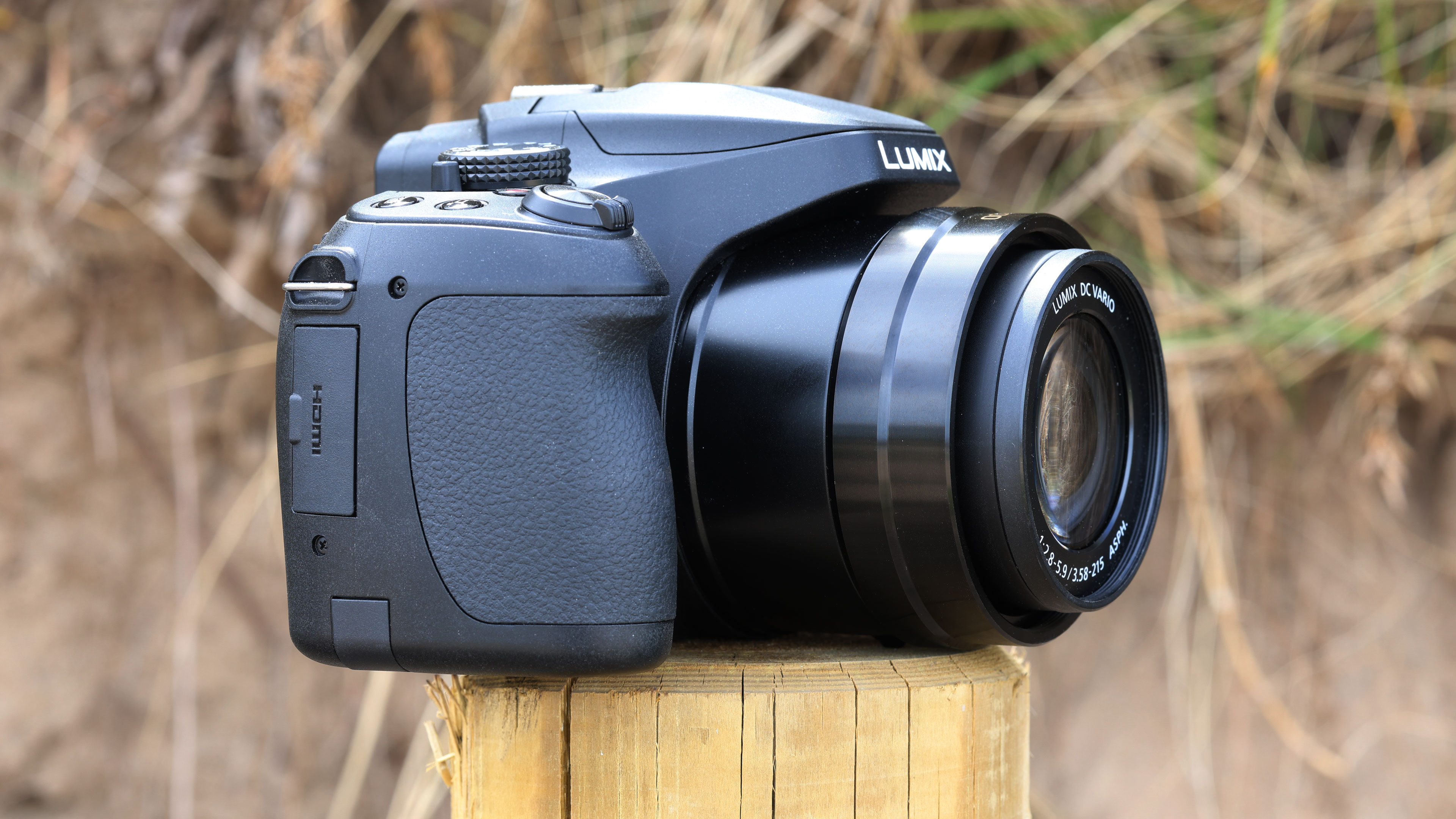
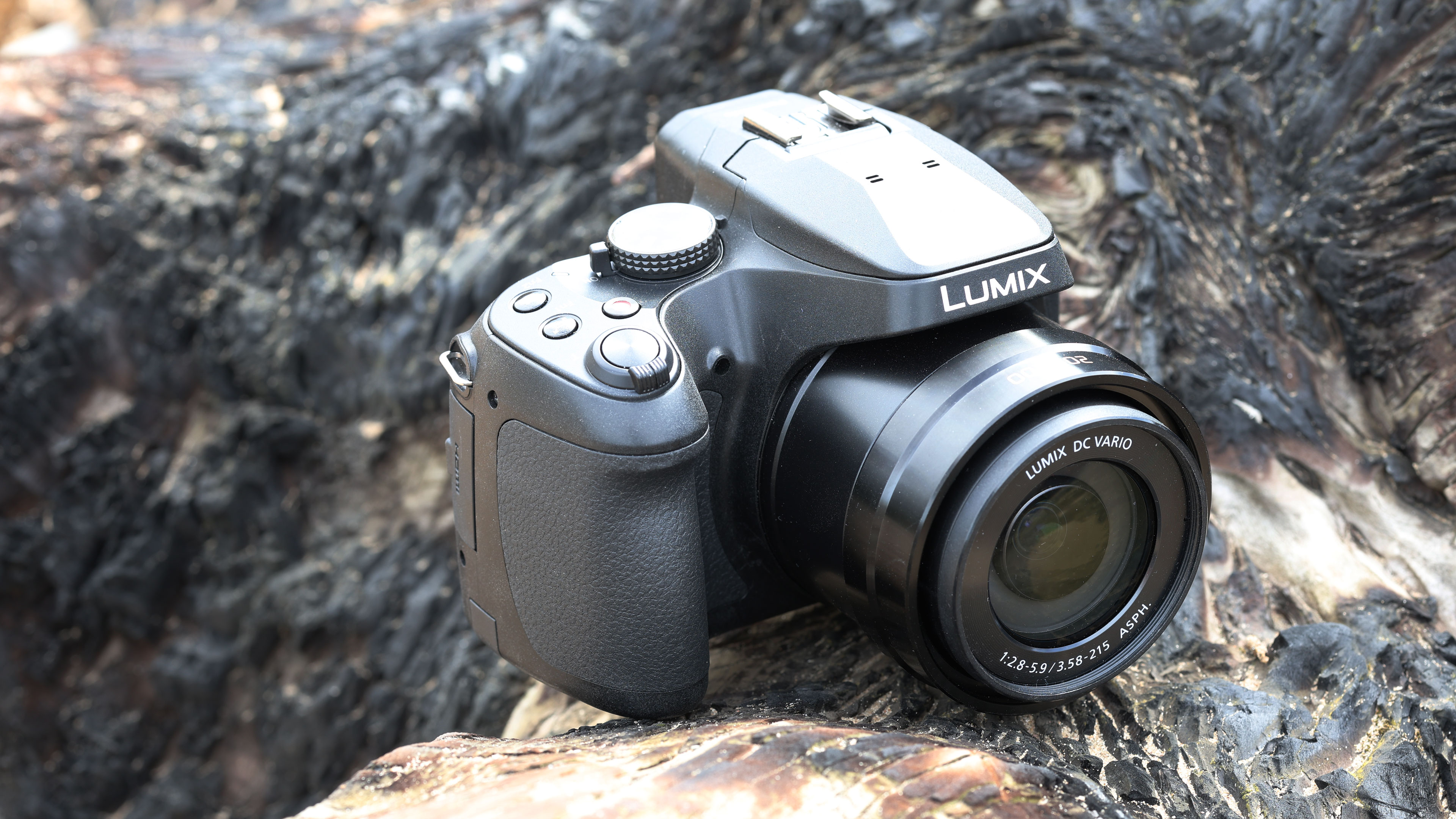
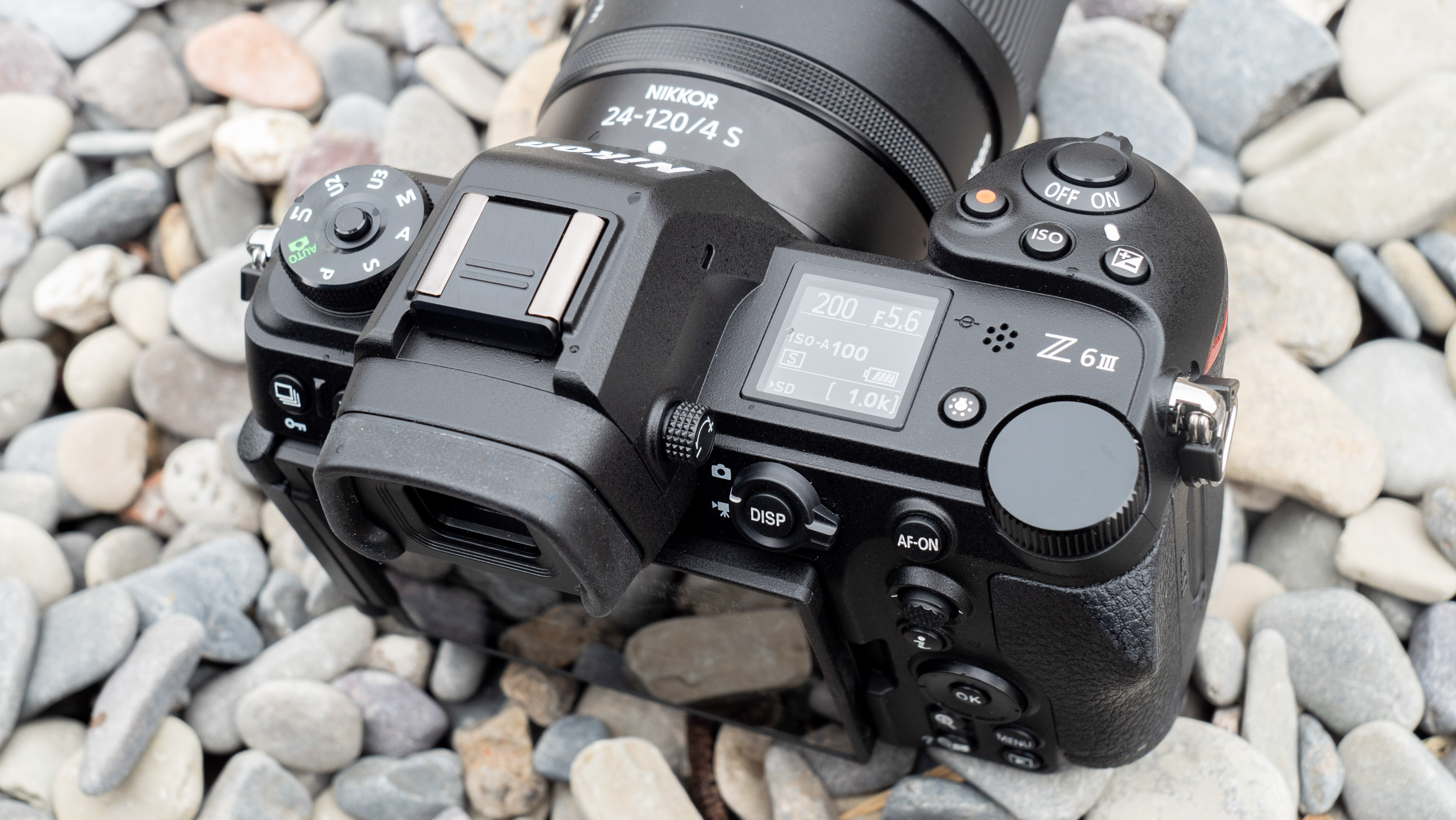
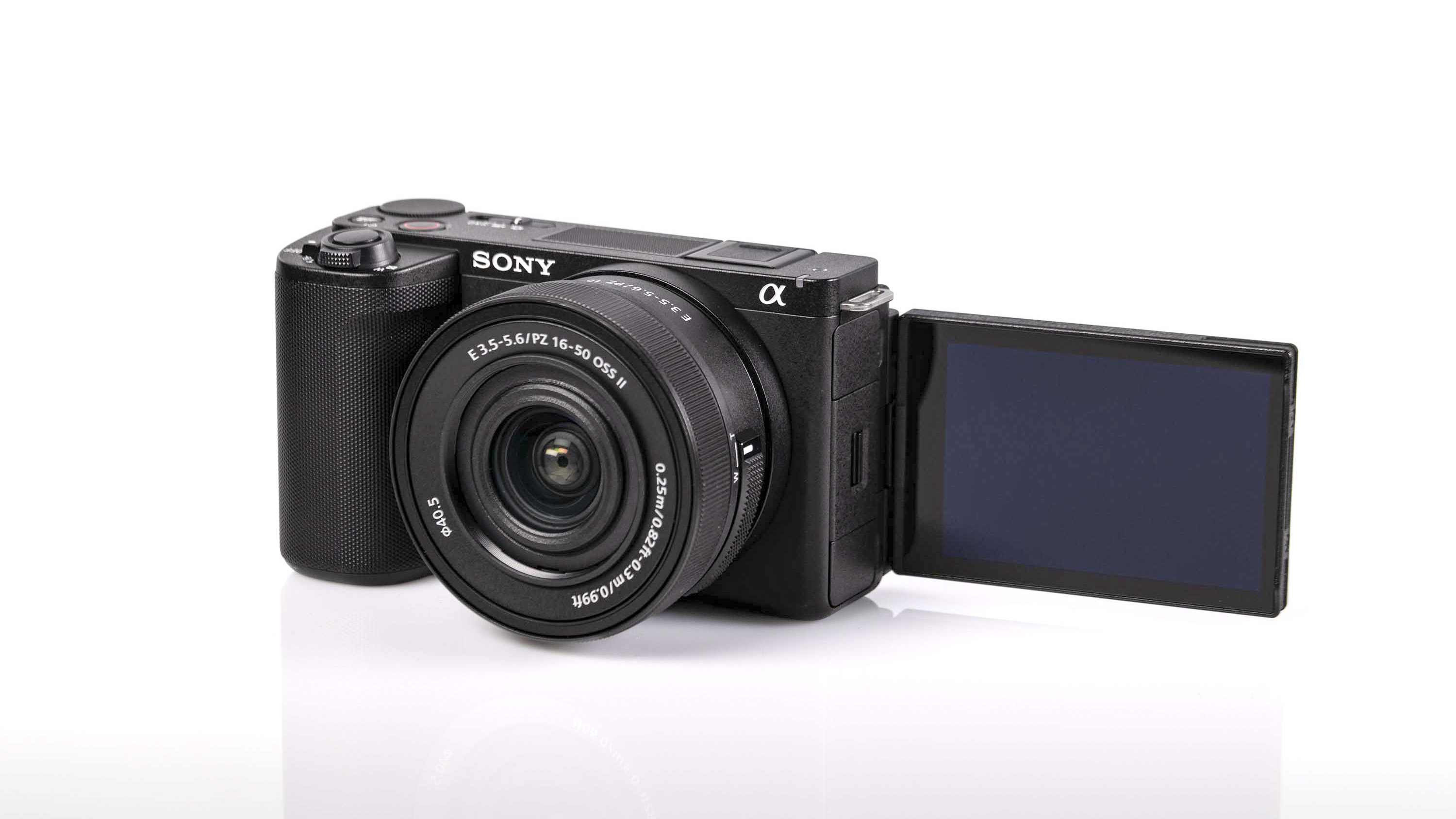
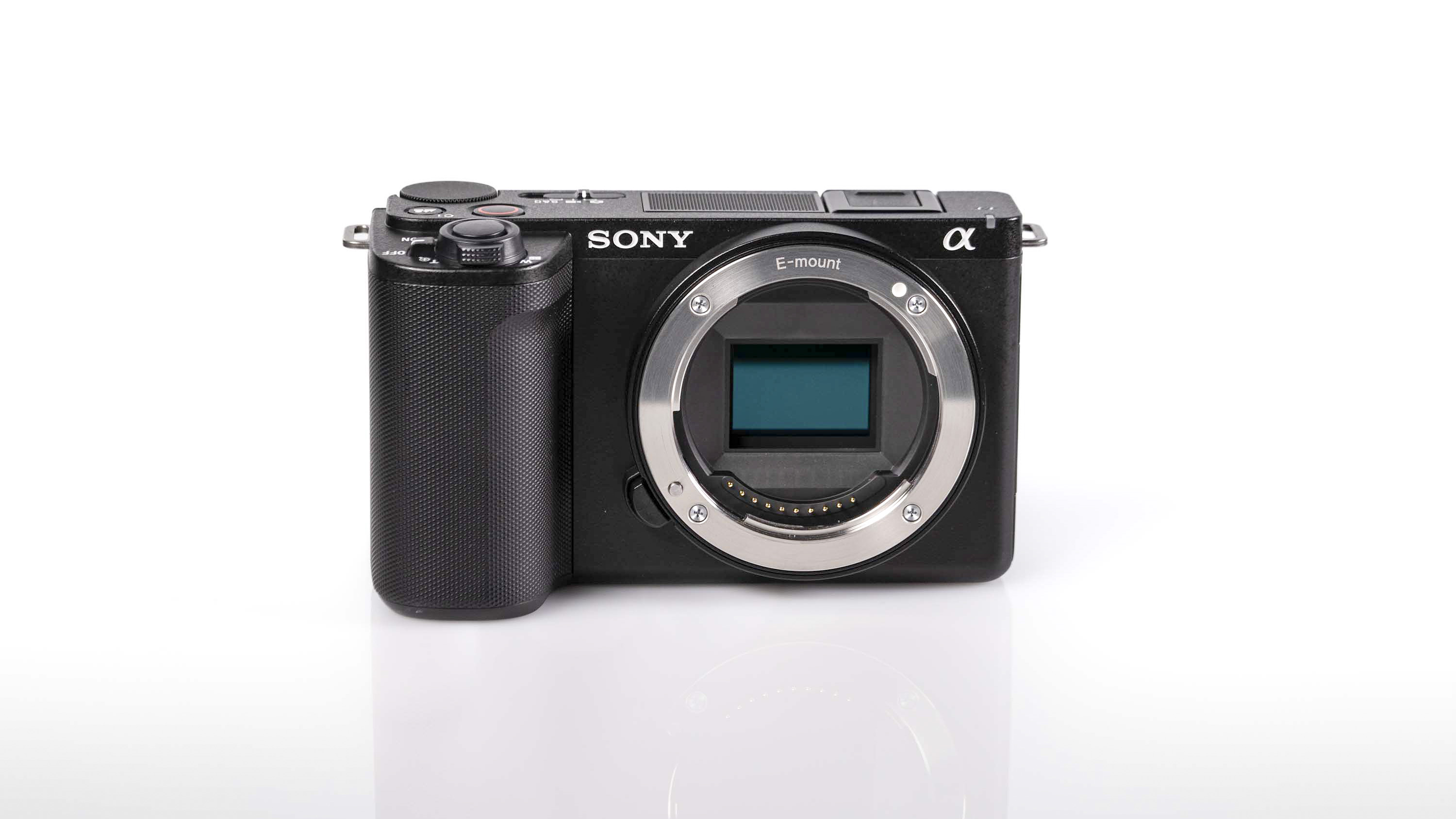
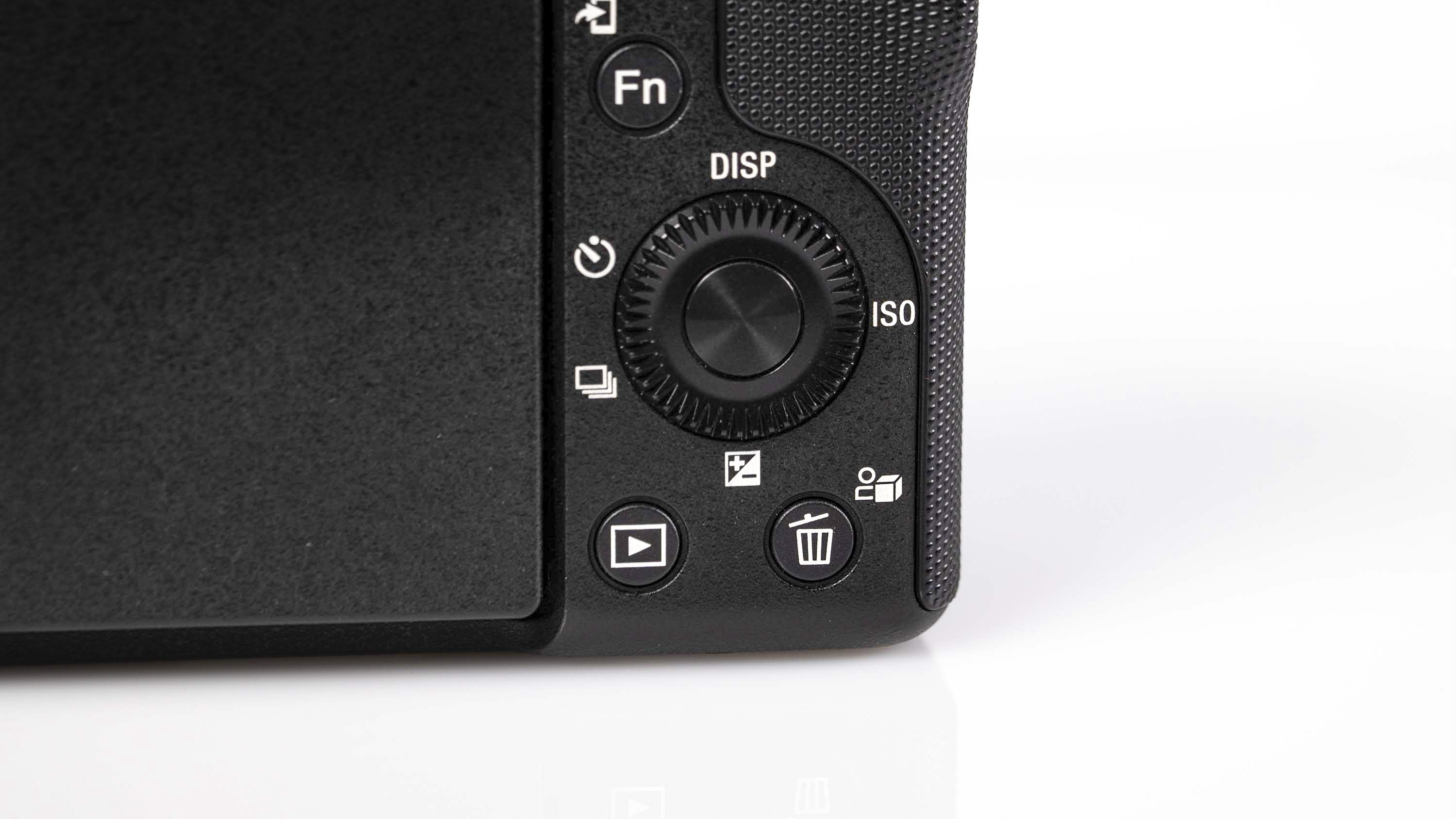
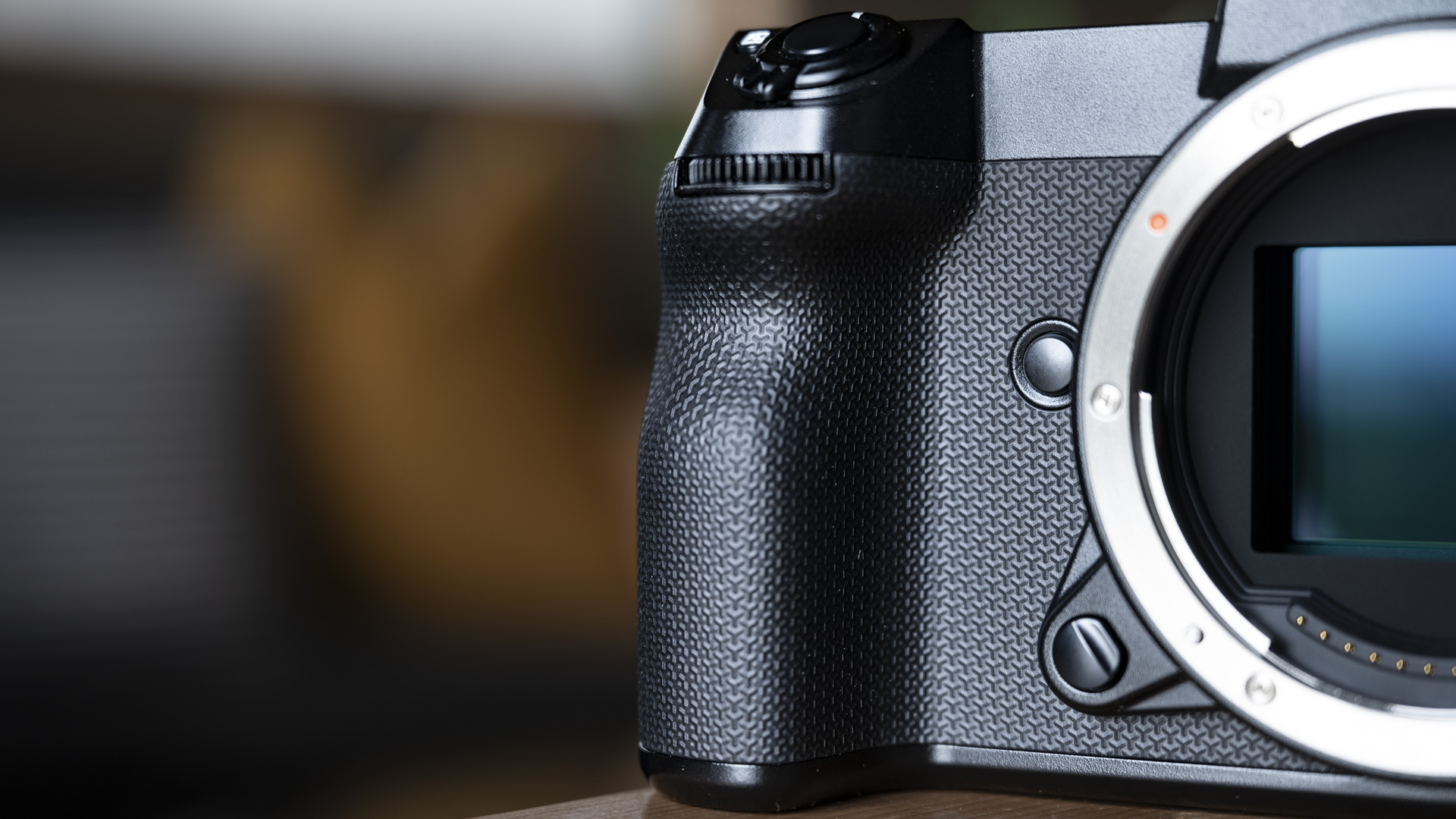
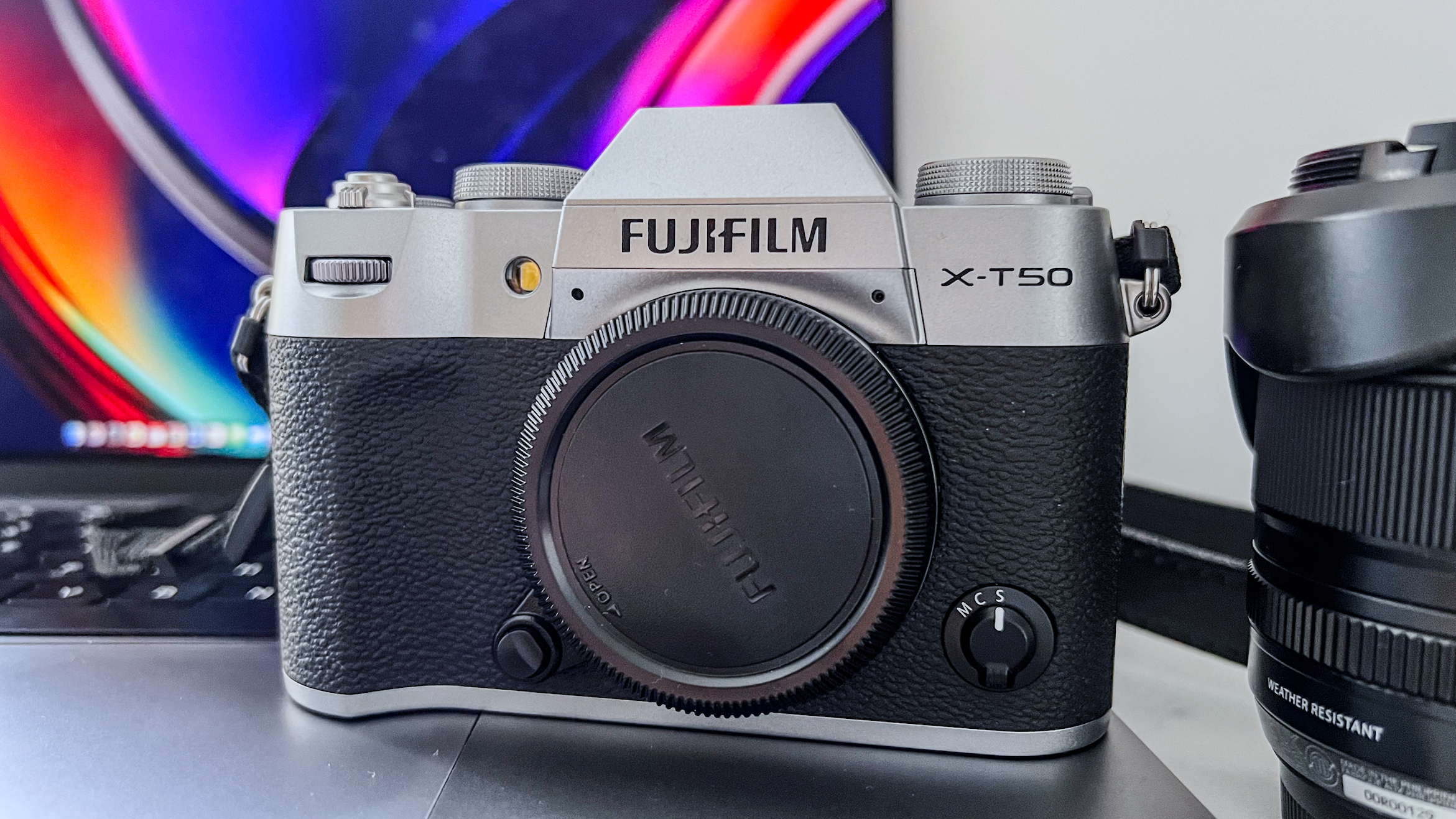
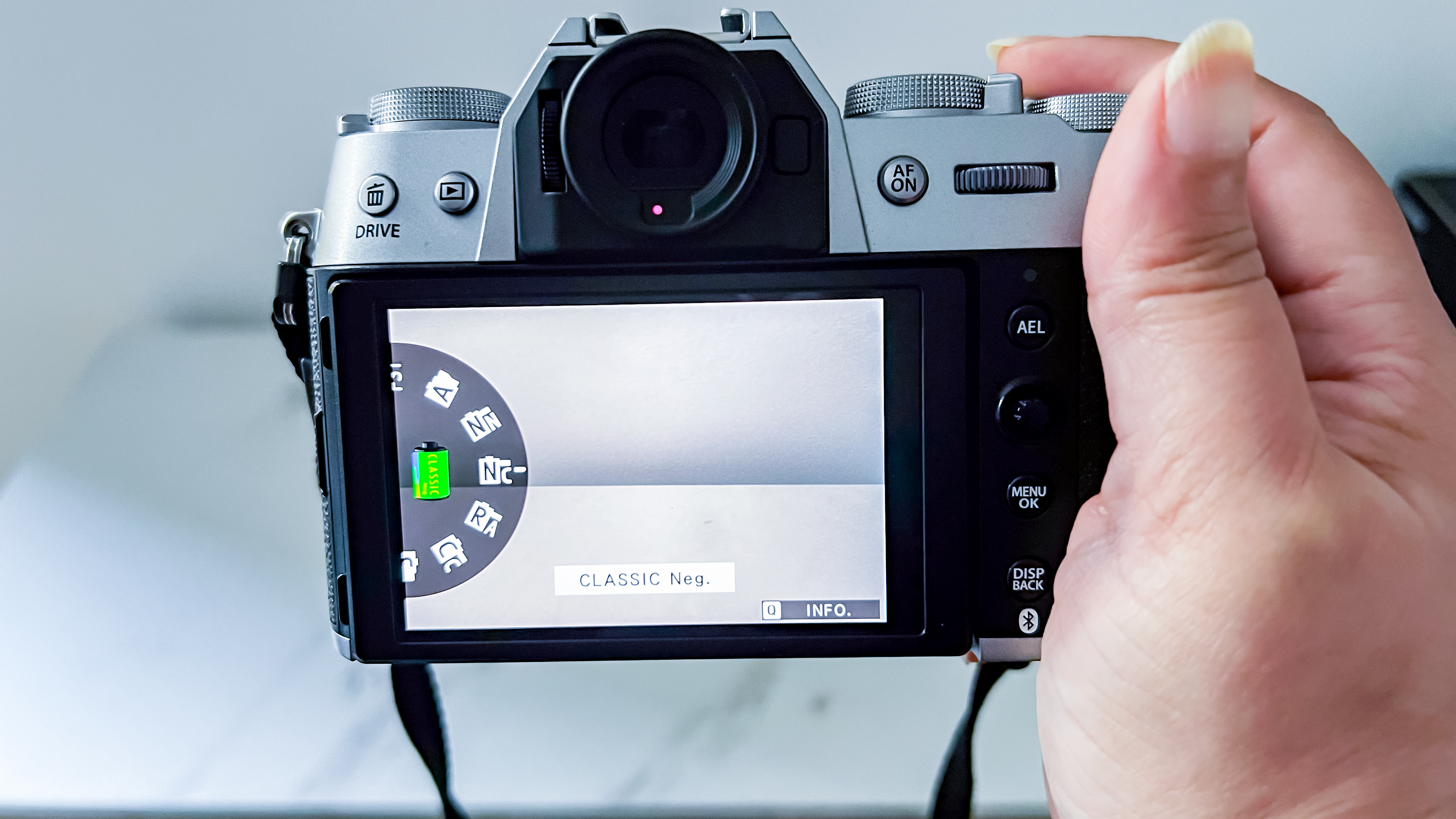
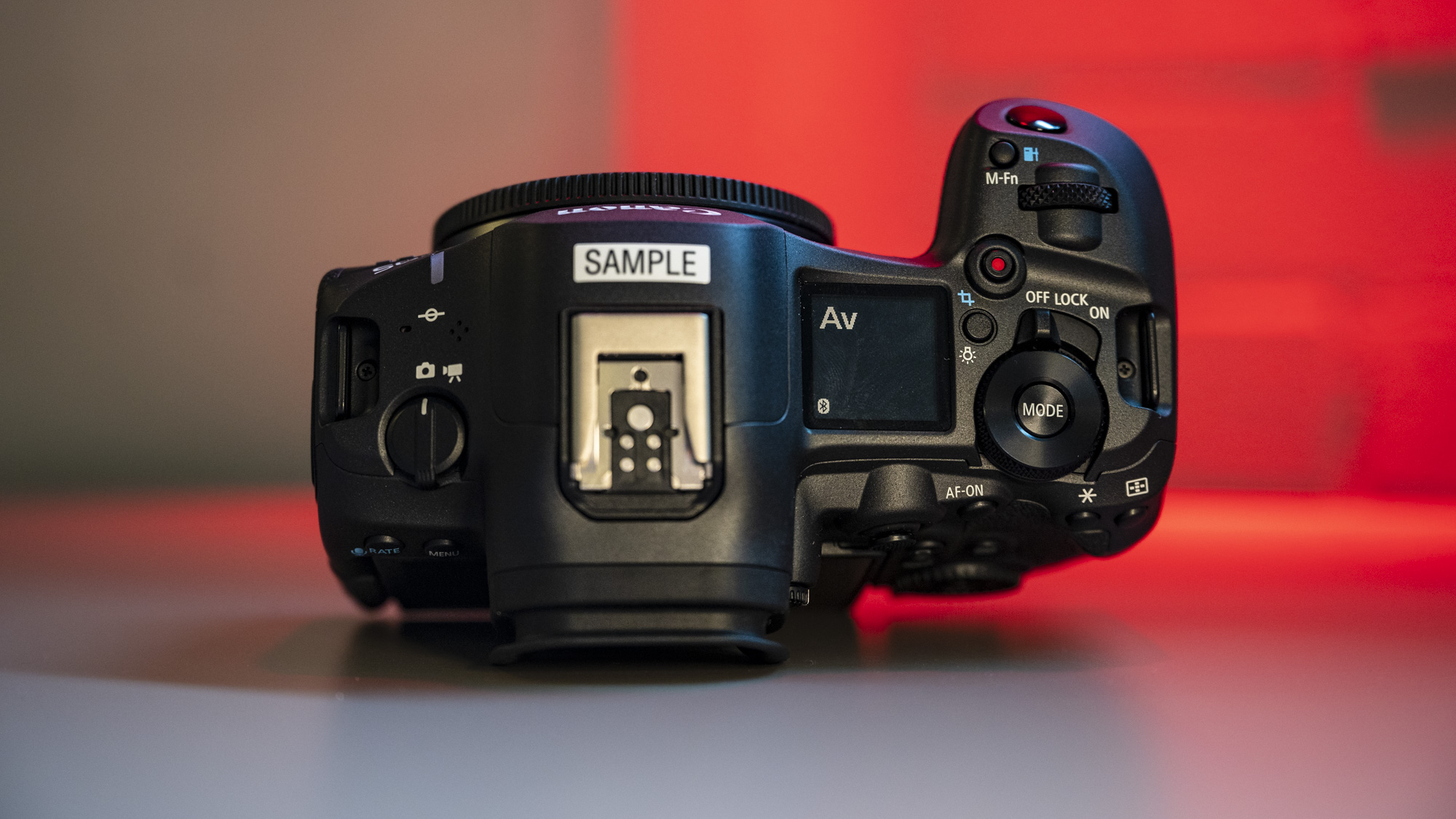
At first glance it’s easy to think the EOS R5 Mark II body is identical to its predecessor, but there’s one change Canon has made that makes me rather happy – the power controls that were on the left of the top plate on the R5 are now a ring around the Mode button on the top right of the Mark II. This means it’s a lot easier to switch the camera on and off in one hand. The old power wheel is now the toggle to switch between stills and video capture.
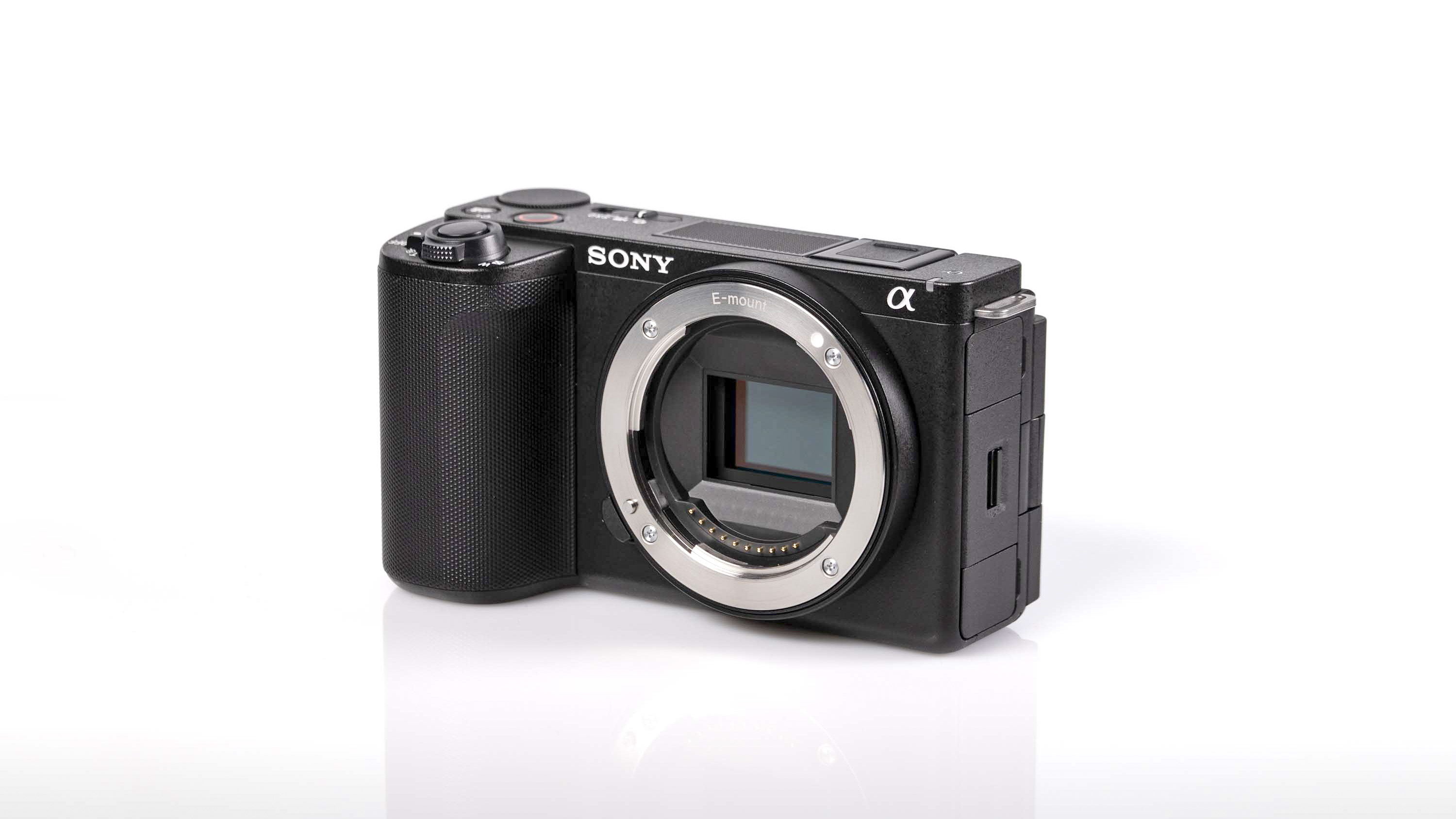
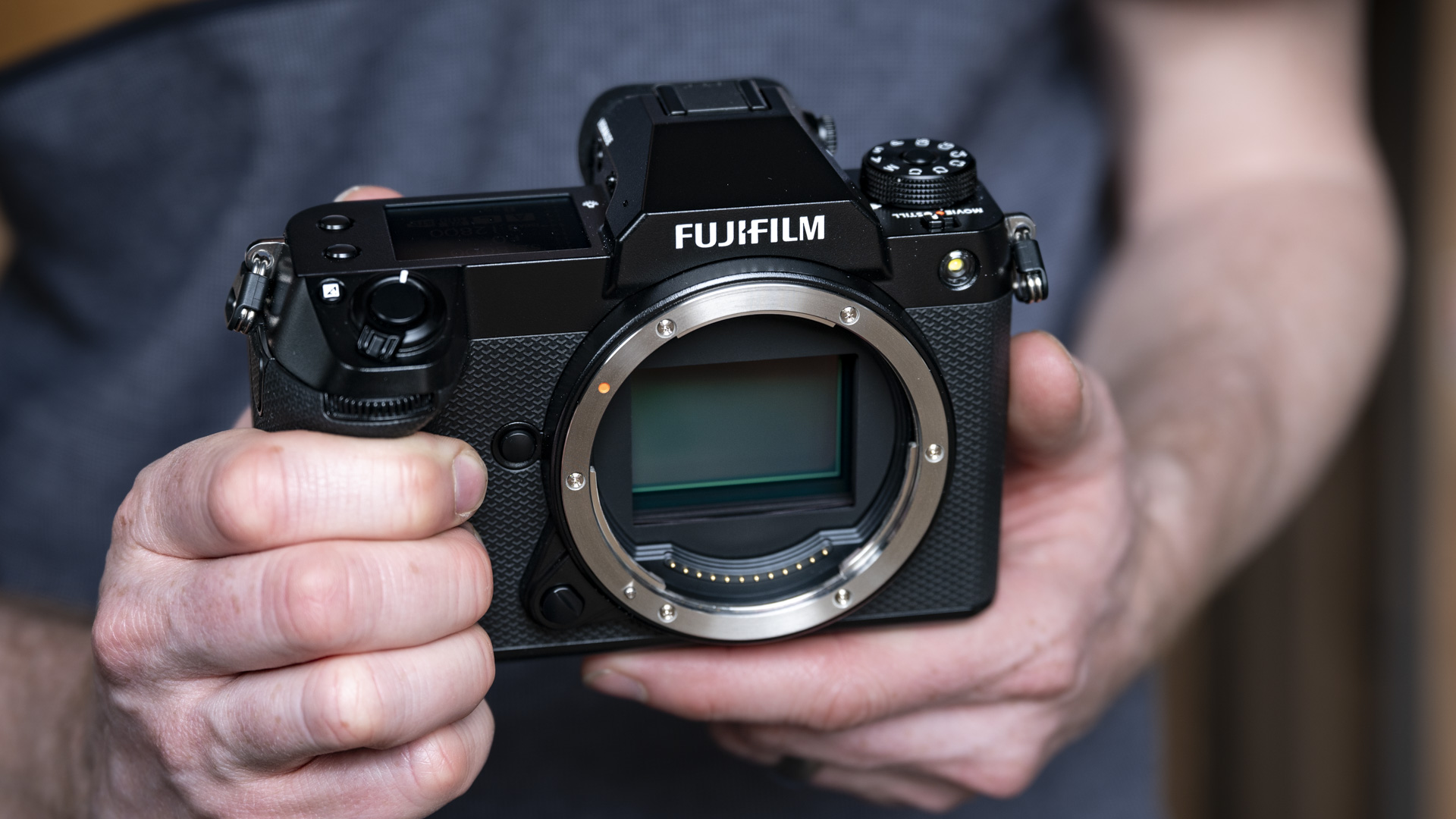
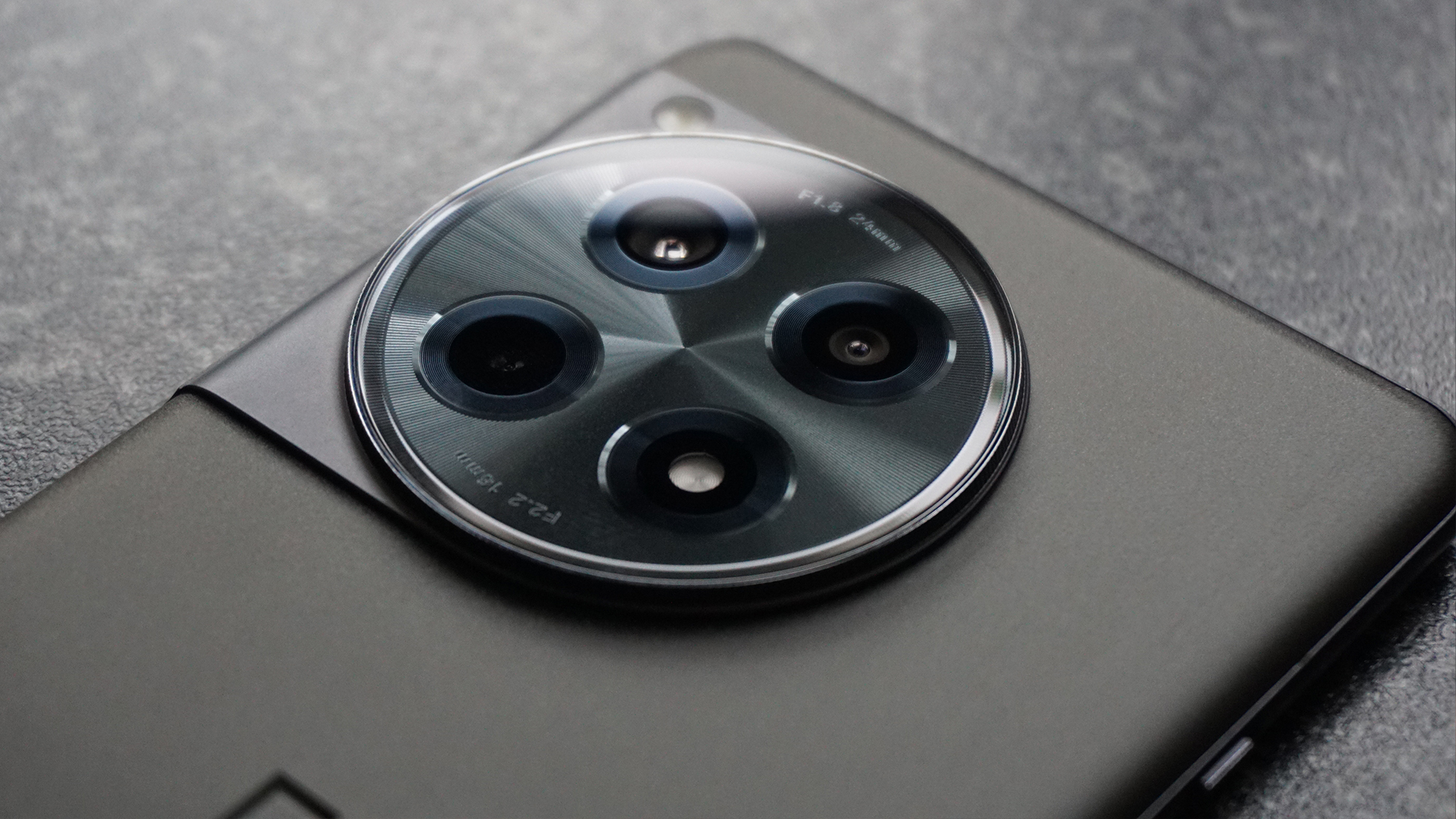
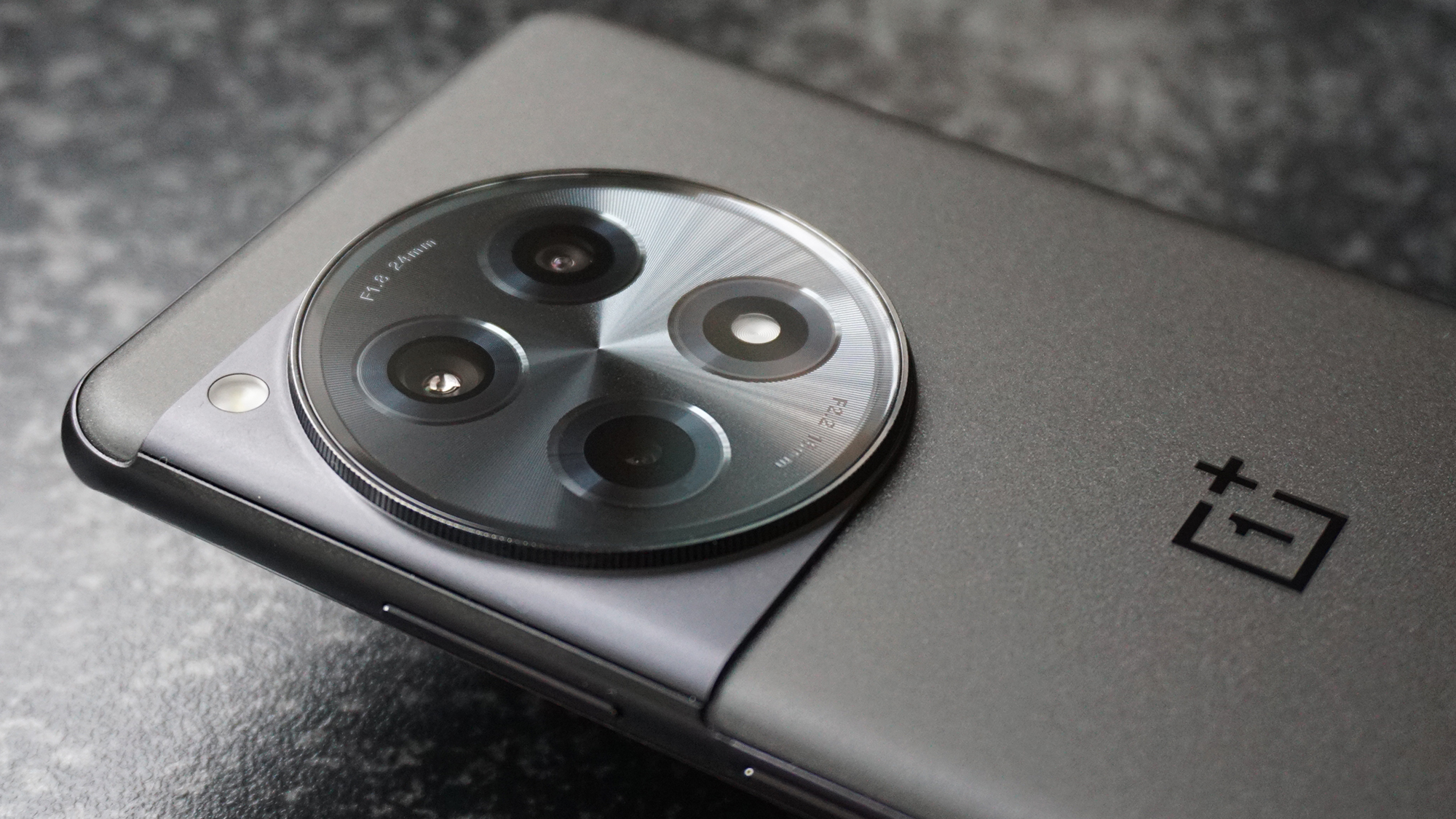
Sensor: 45MP full-frame BSI stacked CMOS sensor
AF system: Hybrid with phase-detect Dual Pixel AF
EVF: 5.76m-dot OLED
ISO range: 100 to 51,200 (ISO 50-102,400 extended range)
Video: 8K/60fps raw, 4K/120fps, 1080p/240fps
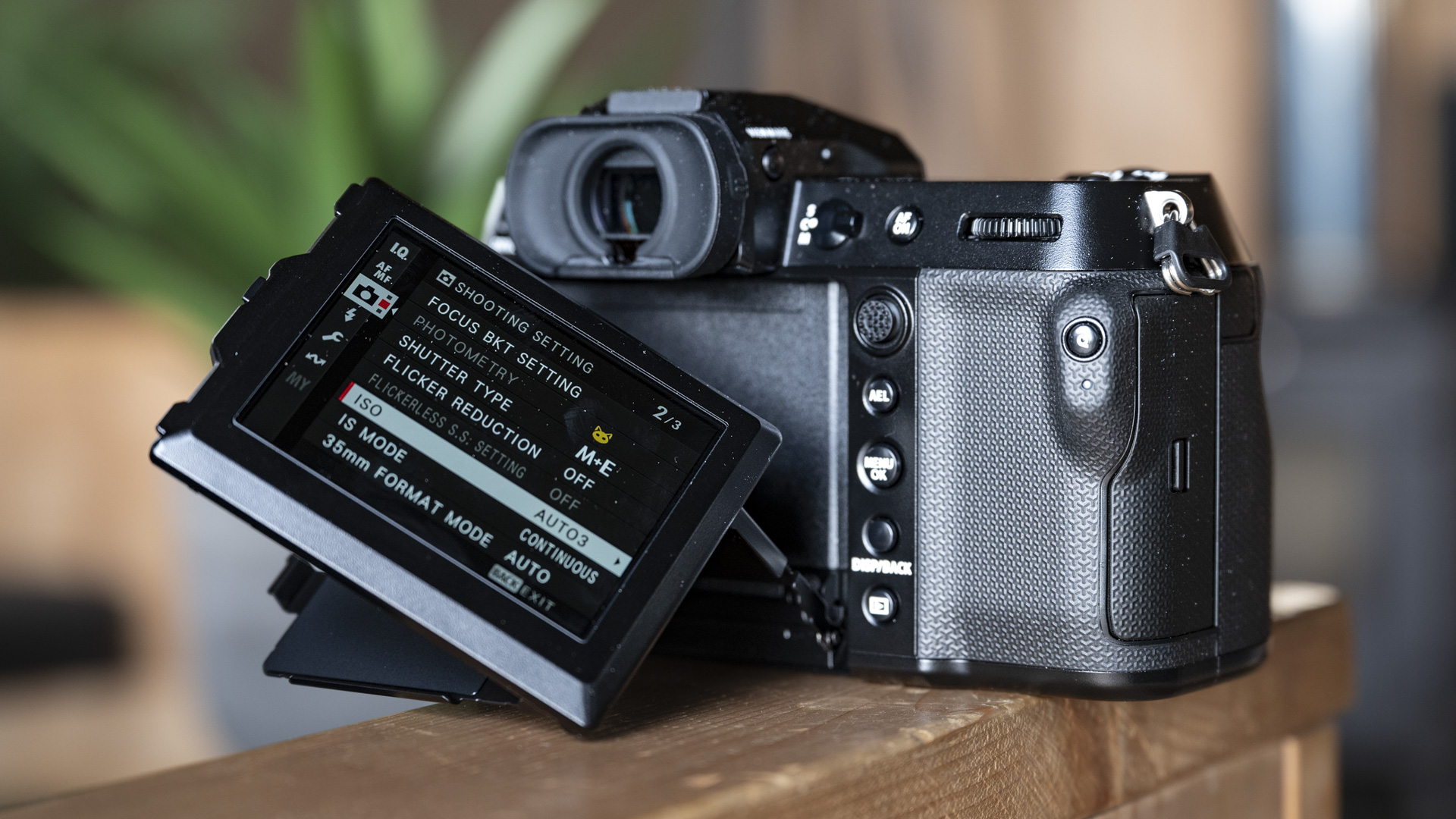
LCD: 3.2-inch vari-angle touchscreen, 2.1m-dots
Max burst: 30fps (electronic shutter, continuous autofocus)
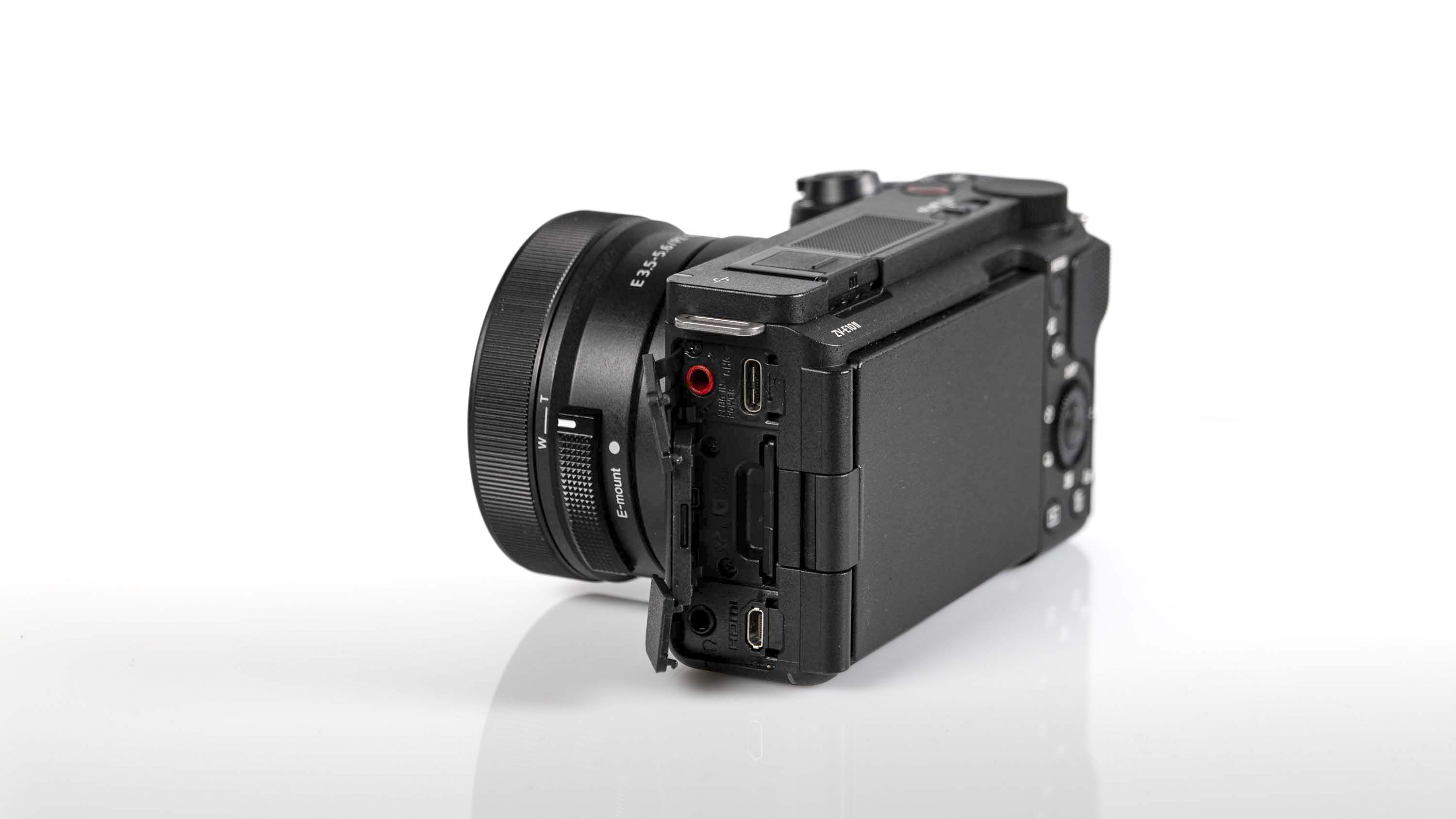
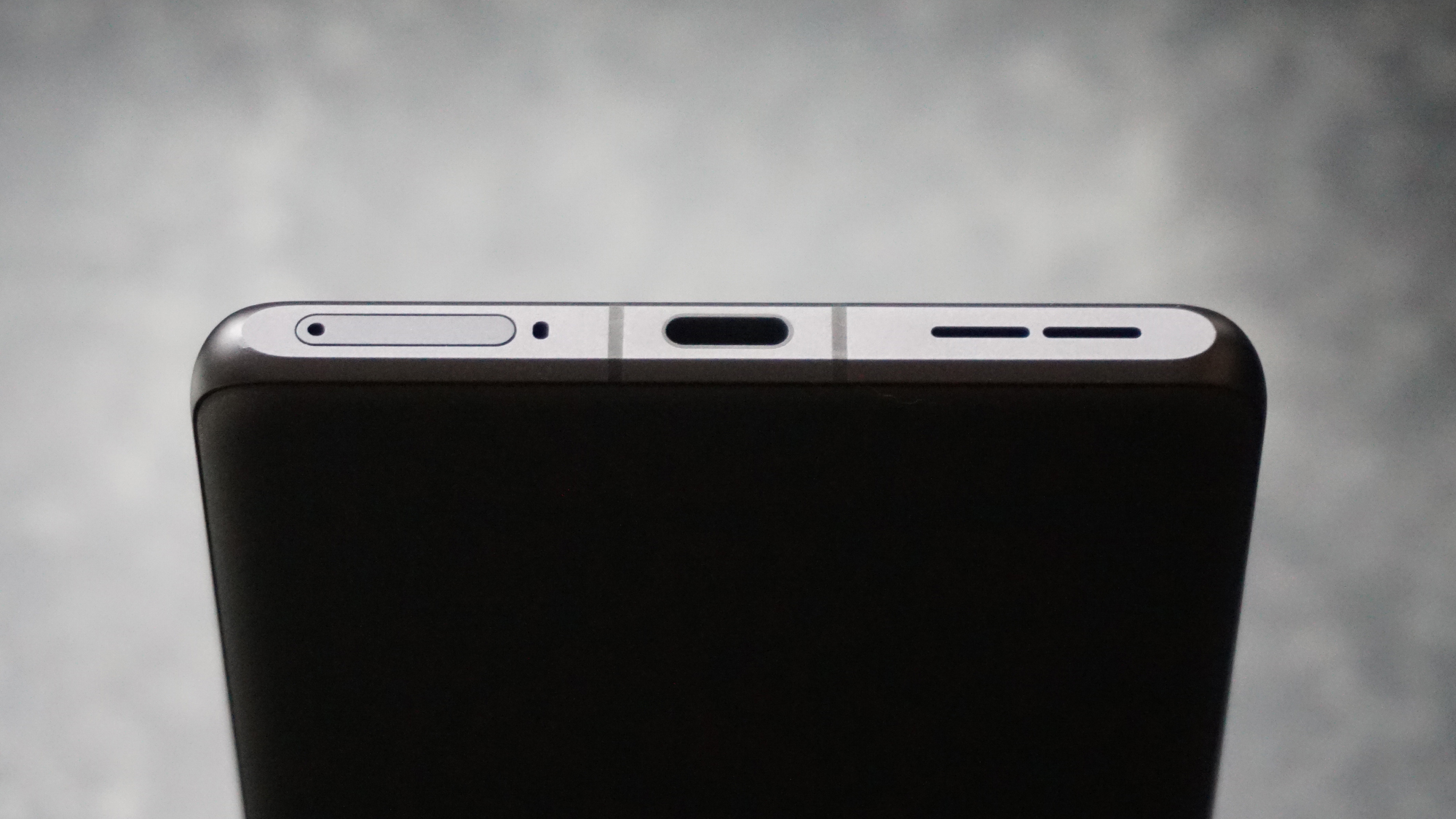
Connectivity: USB-C 3.2, Wi-Fi 6E, Bluetooth 5.3
Weight: 656g (body-only), 746g including battery and card
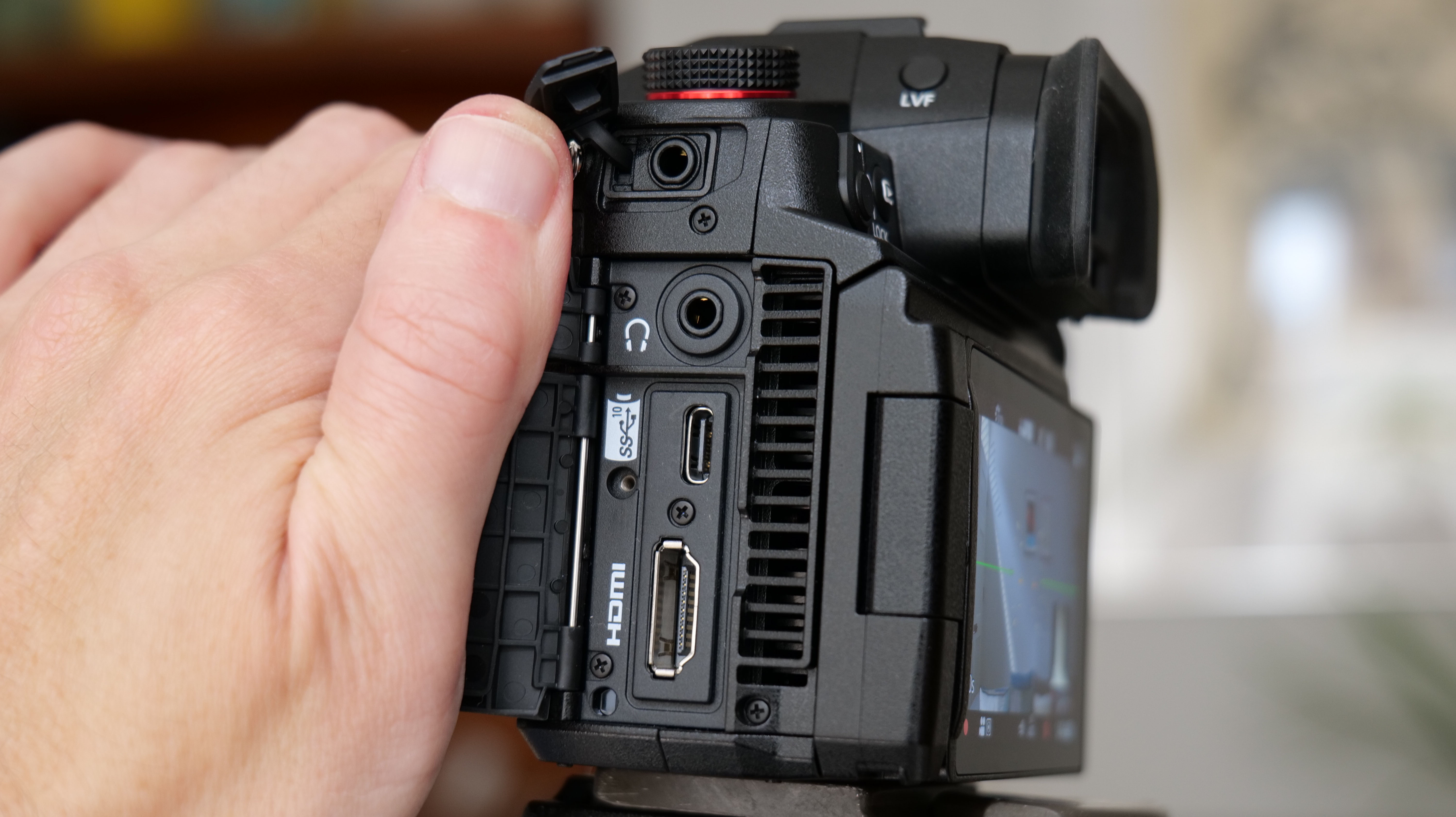
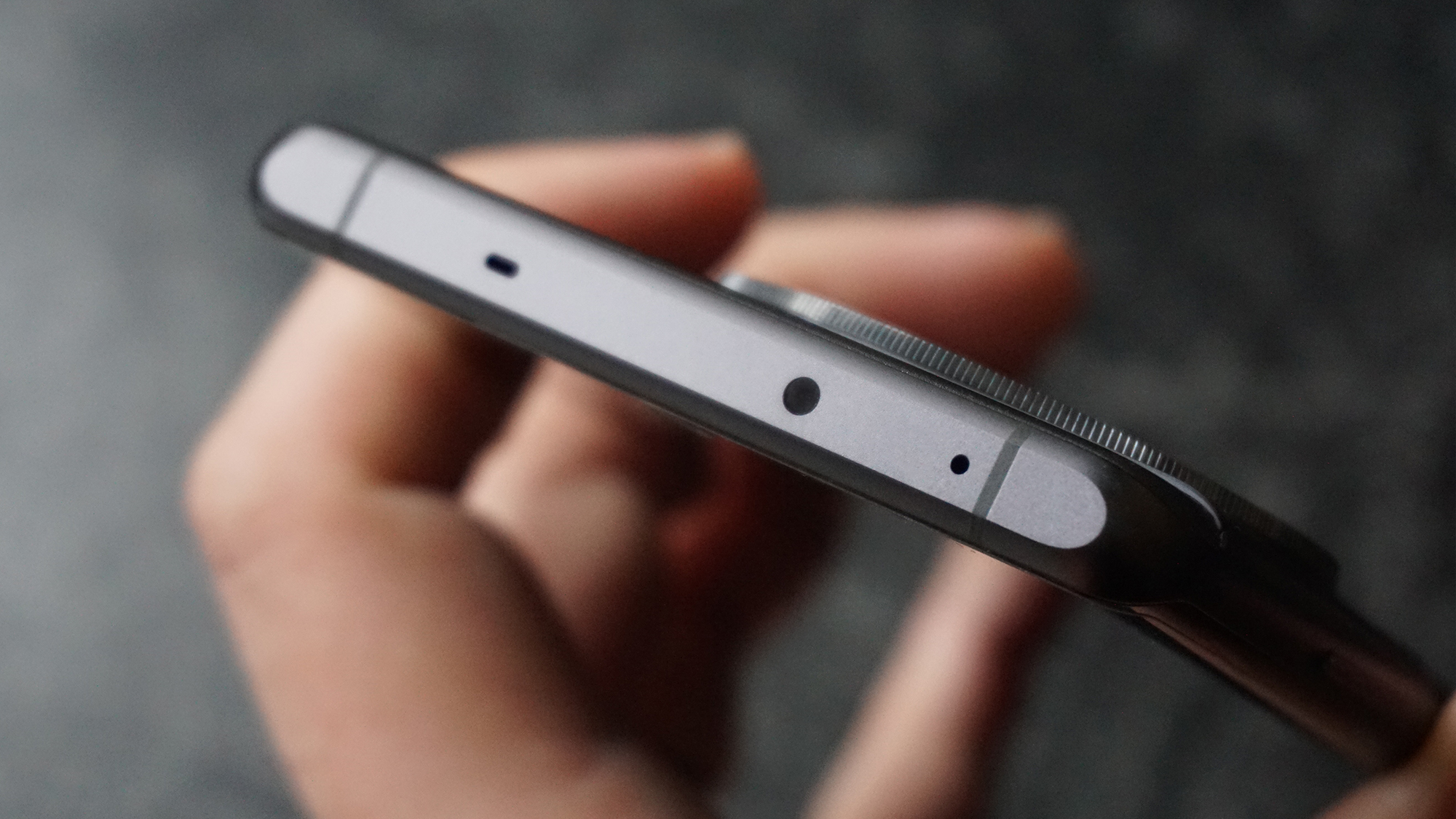
The one other minor change on the top plate is the new hot shoe cover. The R5 test unit that was sent to me for review in 2020 didn’t have such a cover, so this is new to me and I love the clean design – it makes the top of the R5 II look… well, ‘unblemished’ is the only word I can think of to describe it. As much as I like it, the cover is nigh impossible to release. I spent a lot of time trying to get it open and failed, meaning I wasn’t able to get a peek at the hot shoe during my few weeks with the camera.
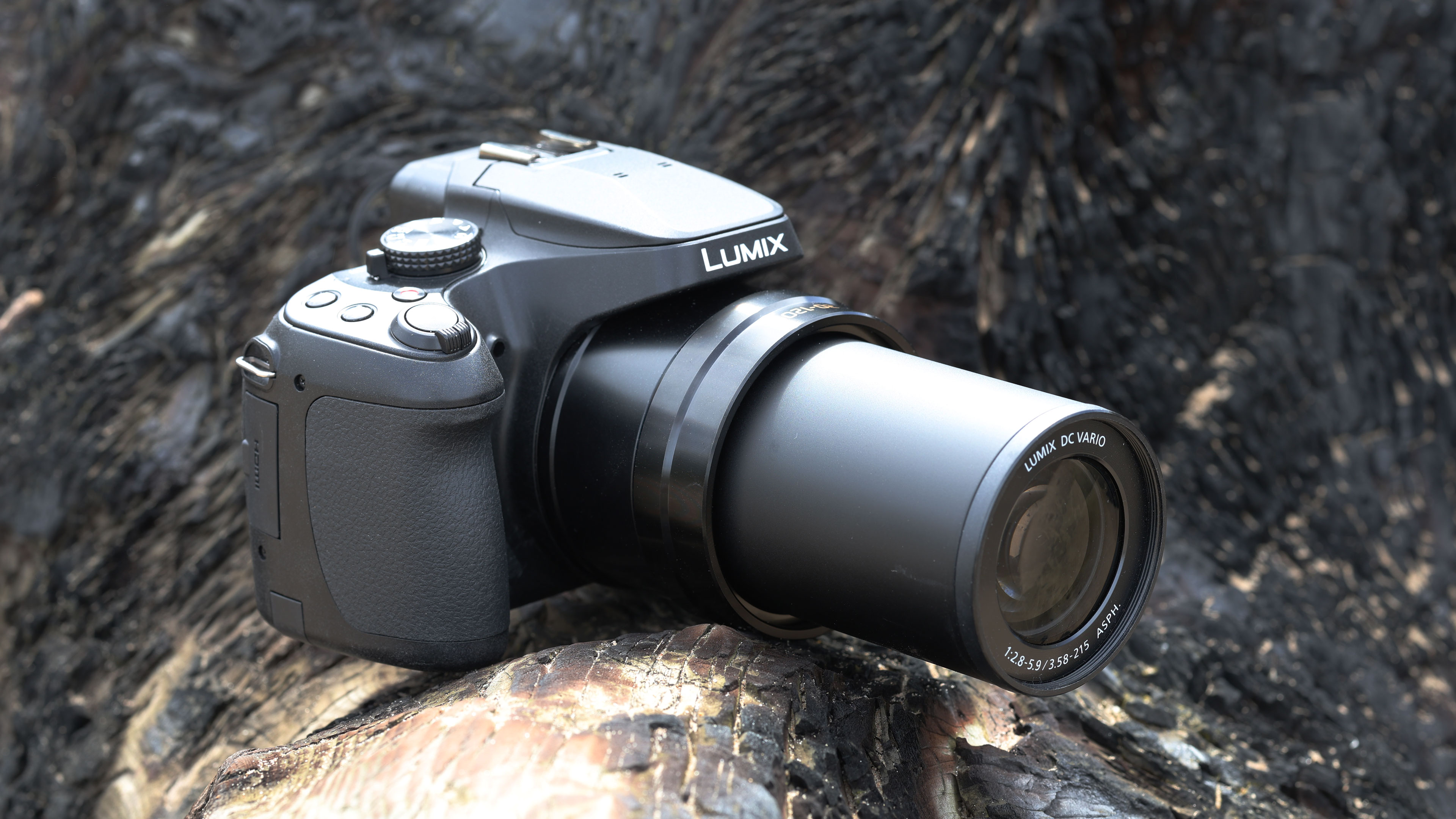
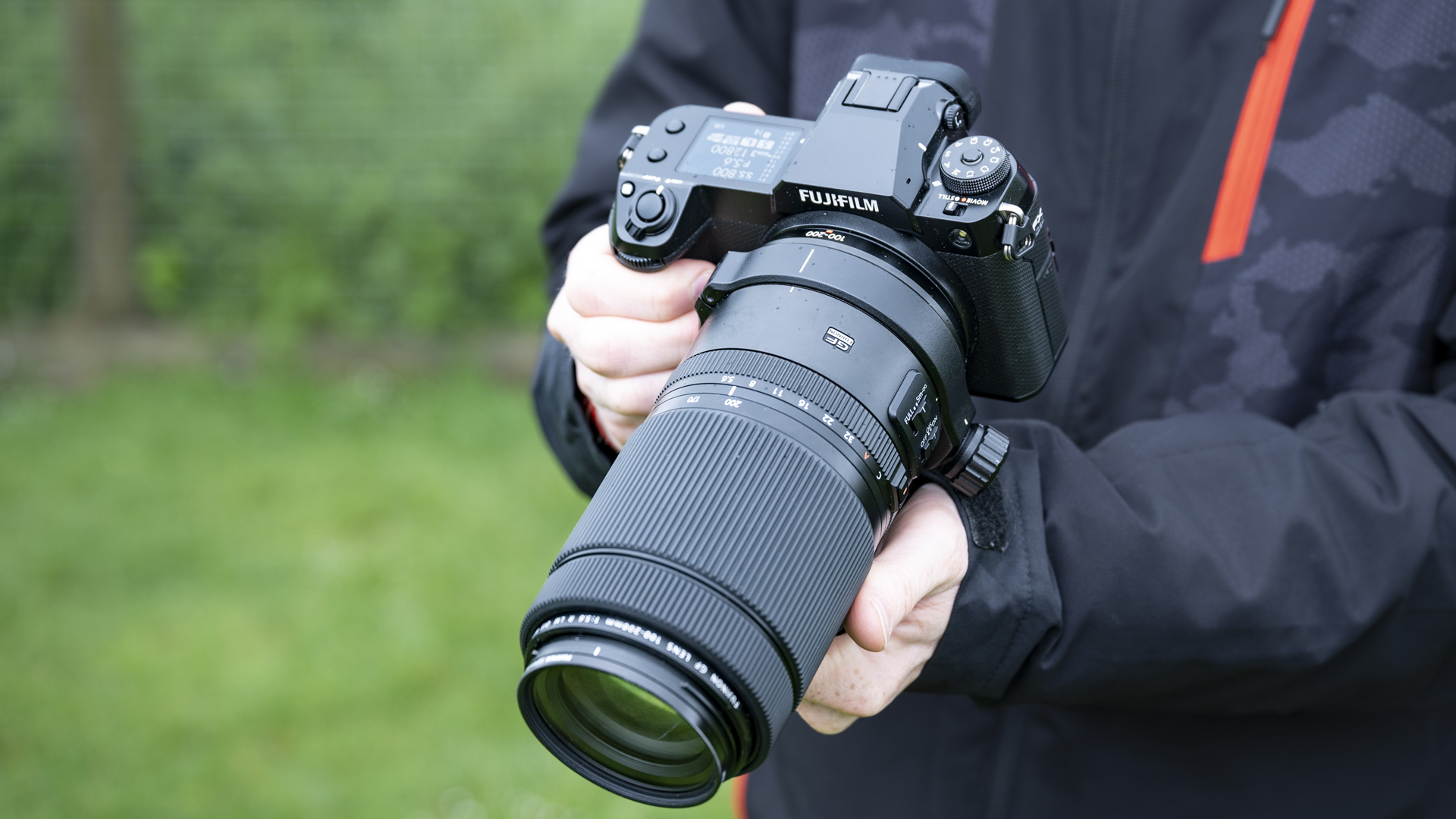
The rest of the control layout remains exactly the same as on the R5, which is a wise move as Canon’s designs have always been intuitive. It is, however, oh-so-slightly heavier than the older camera, tipping the scales at 26.3oz / 746g. That’s lighter than the Nikon Z8 (32oz / 910g) and more in line with the Sony A7R V. It feels comfortable in the hand during long periods of use, even with the beefy RF 24-70mm f/2.8L standard zoom and RF 100-500mm f/4.5-7.1L IS USM telephoto lenses that I used for this review.
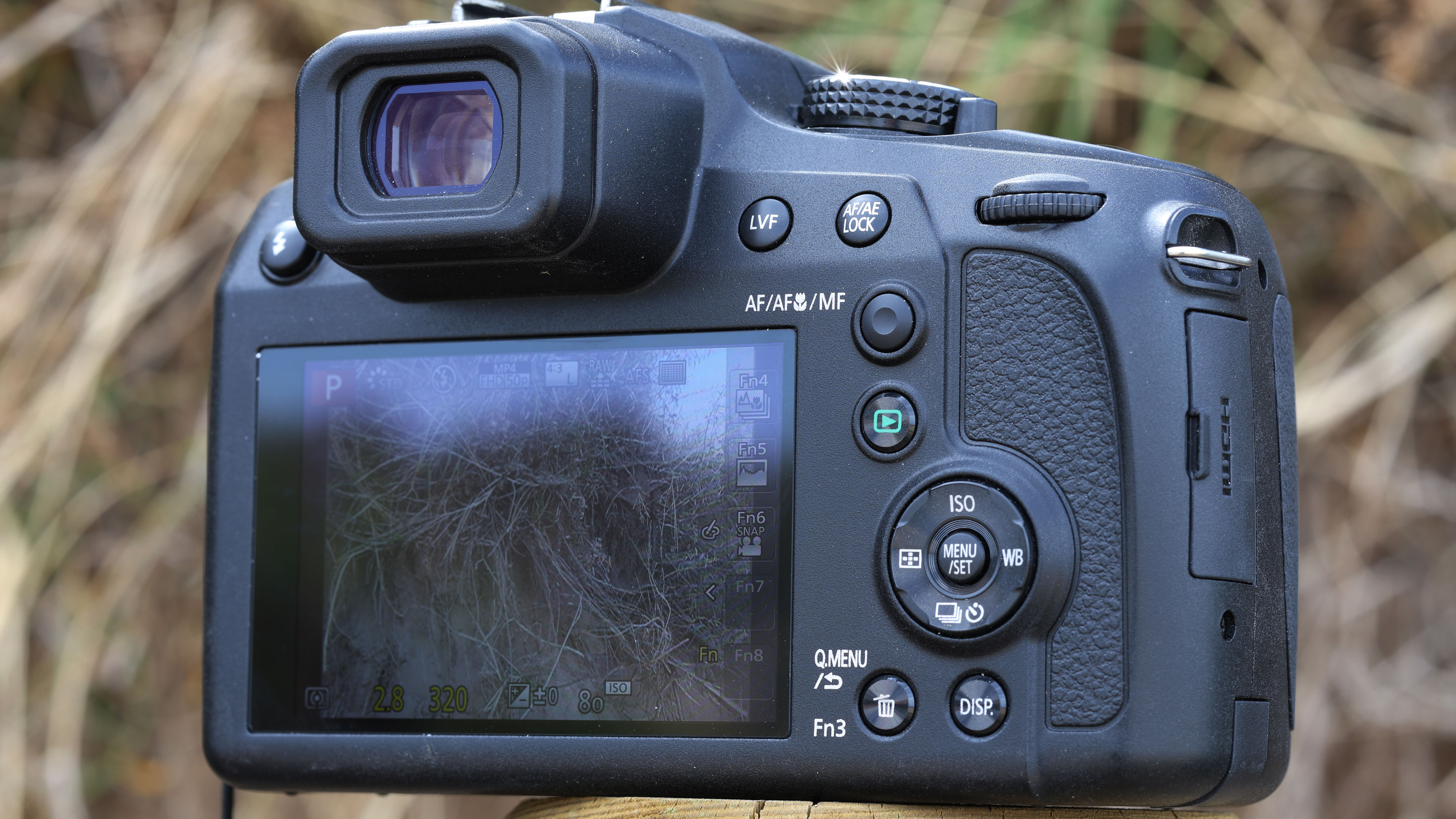
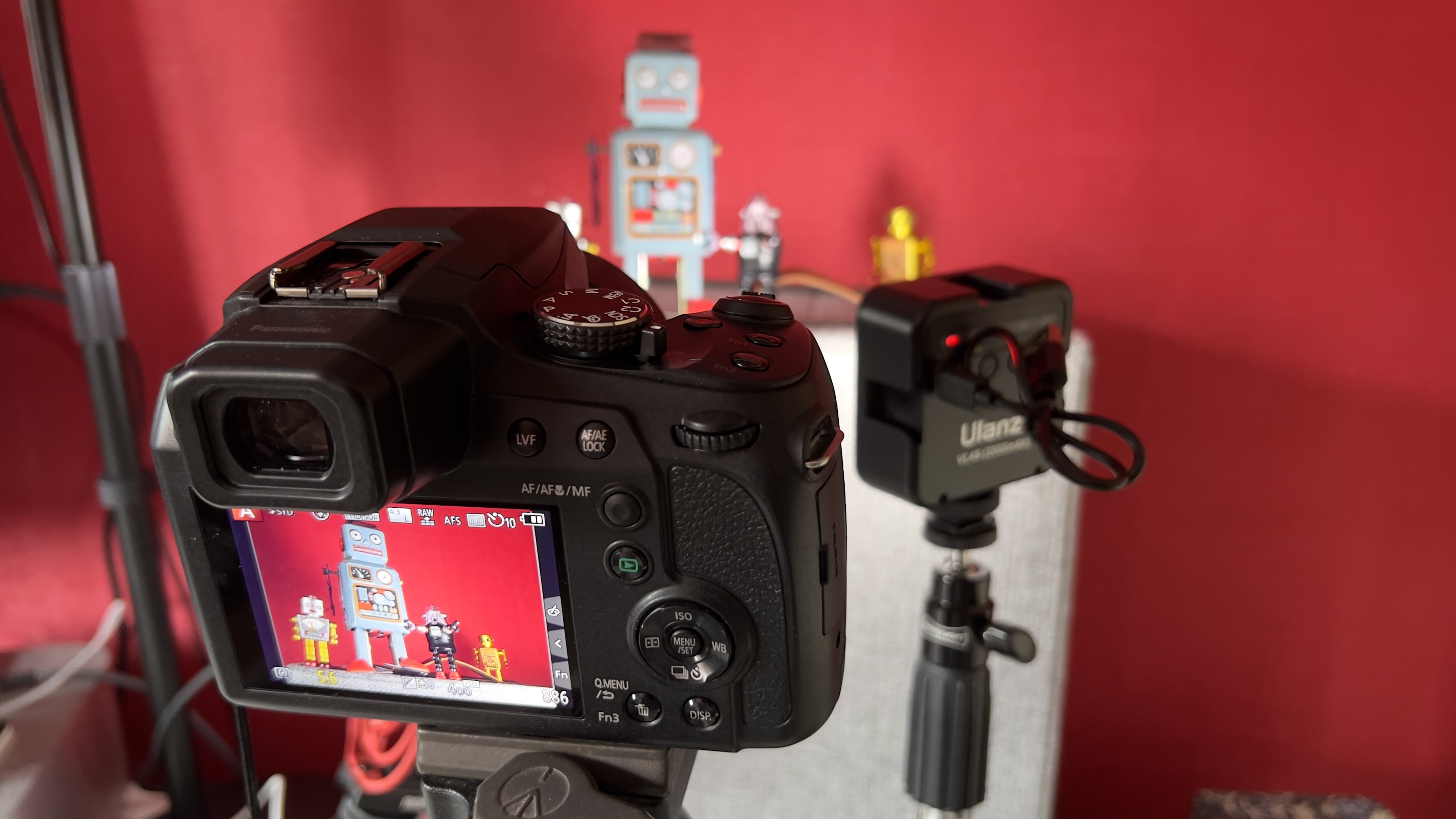
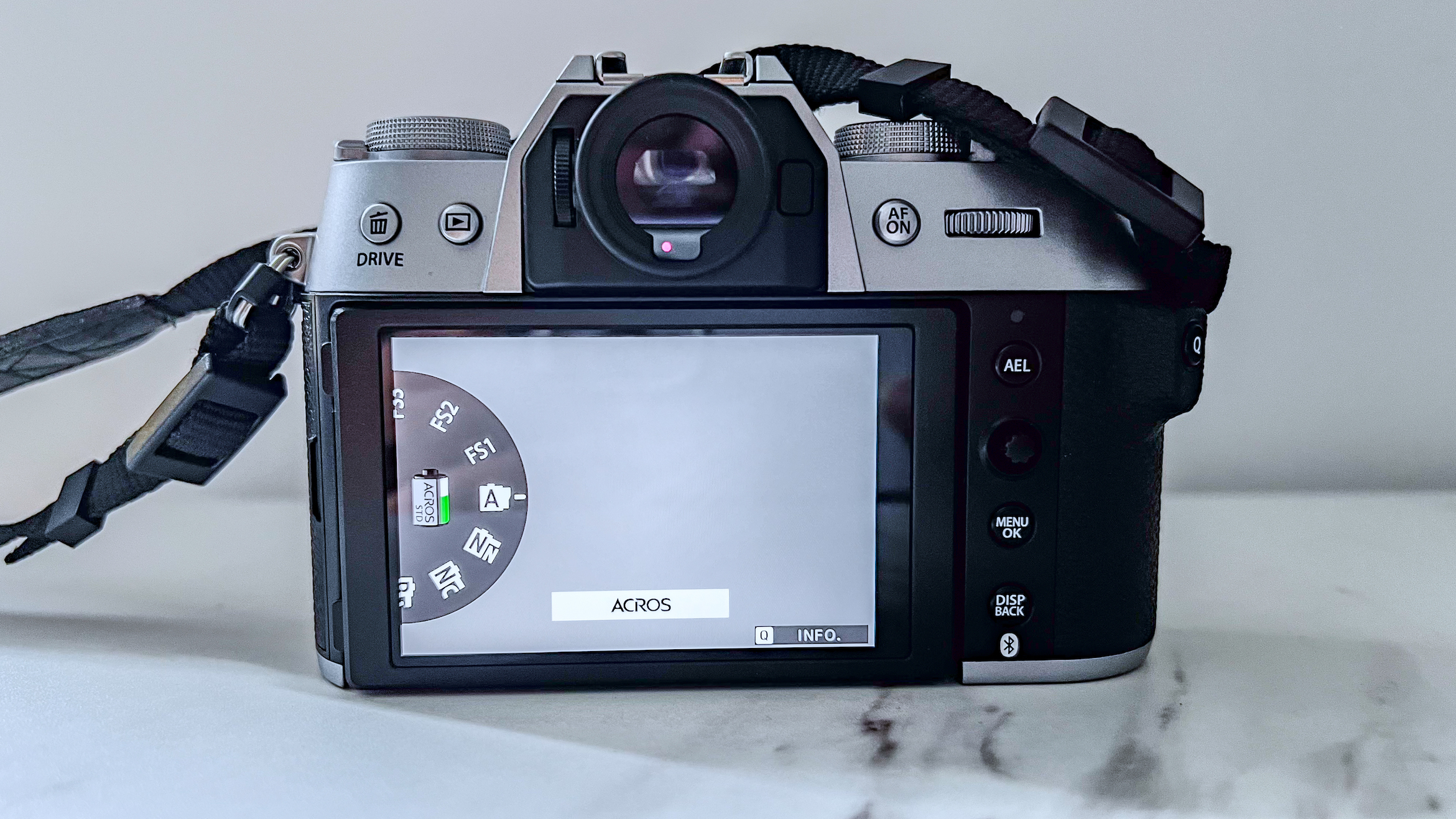
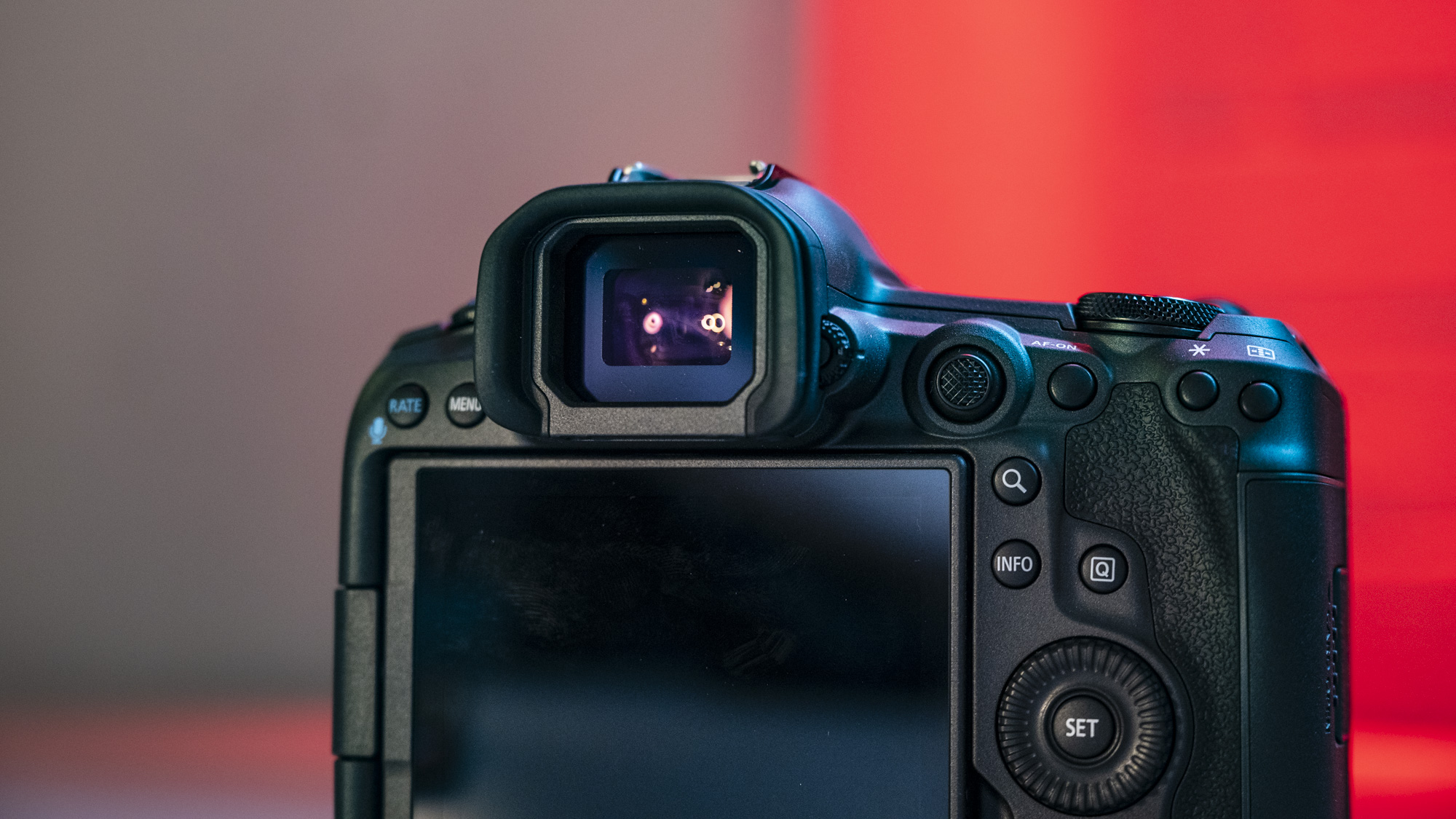
Another small but significant refinement is the 5.7 million dot OLED viewfinder – Canon says it’s twice as bright and blackout free. While I can’t vouch for the ‘twice’ part, it’s definitely a significant difference compared to the R5 and I prefer it over the 3.69m-dot EVF on the Nikon Z8. The new EVF also inherits Canon’s Eye Control AF that debuted on the EOS 1D X Mark III. This feature tracks your eye movements as you scan the scene through the viewfinder and shifts the focus point accordingly.
As with all Canon cameras, build quality is excellent. The R5 II features a magnesium-alloy chassis with a fully weather-sealed exterior, and the controls are robust. That said, I found the rear wheel movement on the R5 II a little clunky compared to what it feels like on the R1, where movement is nicely dampened and rotation is smooth.
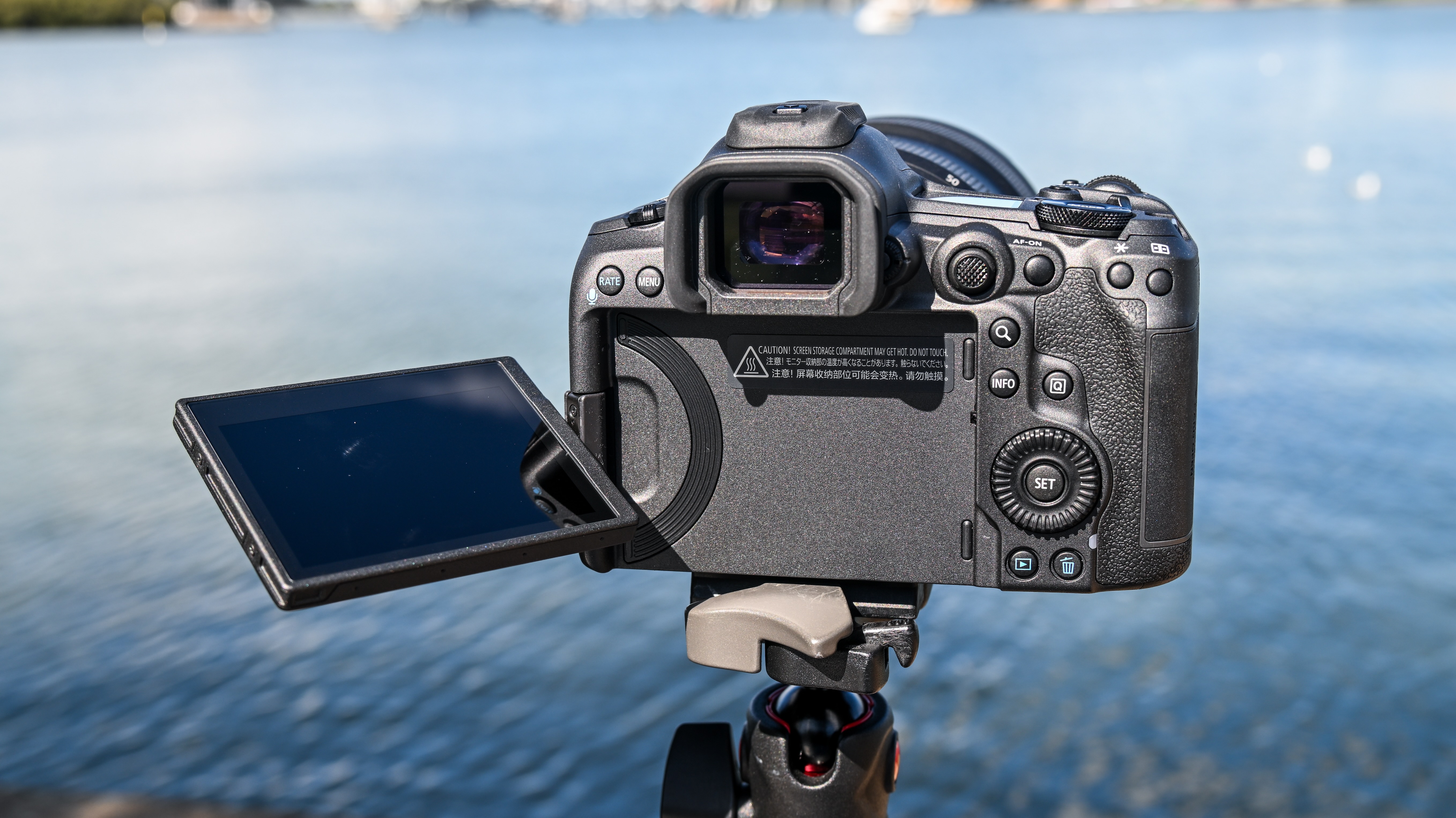
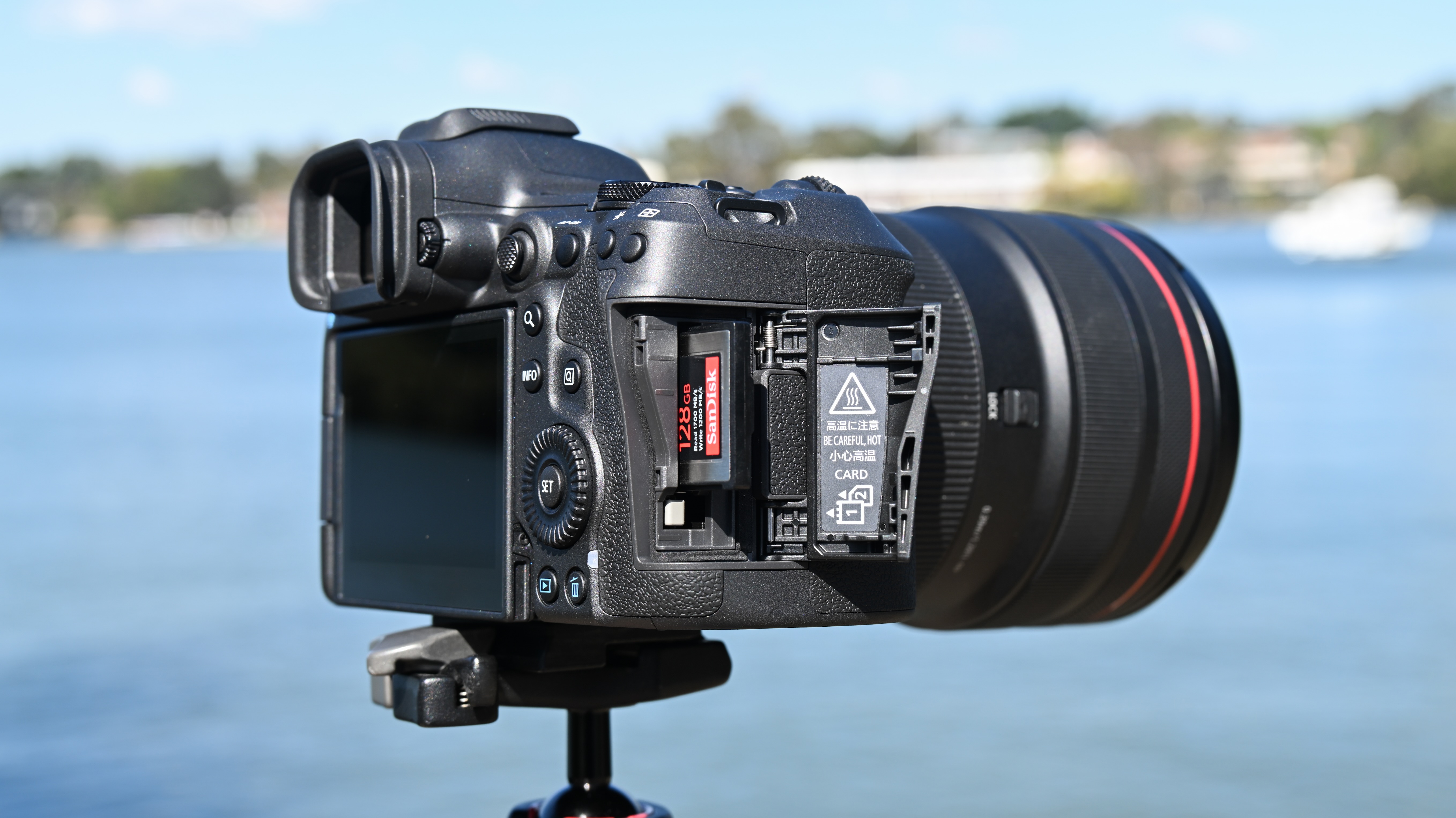






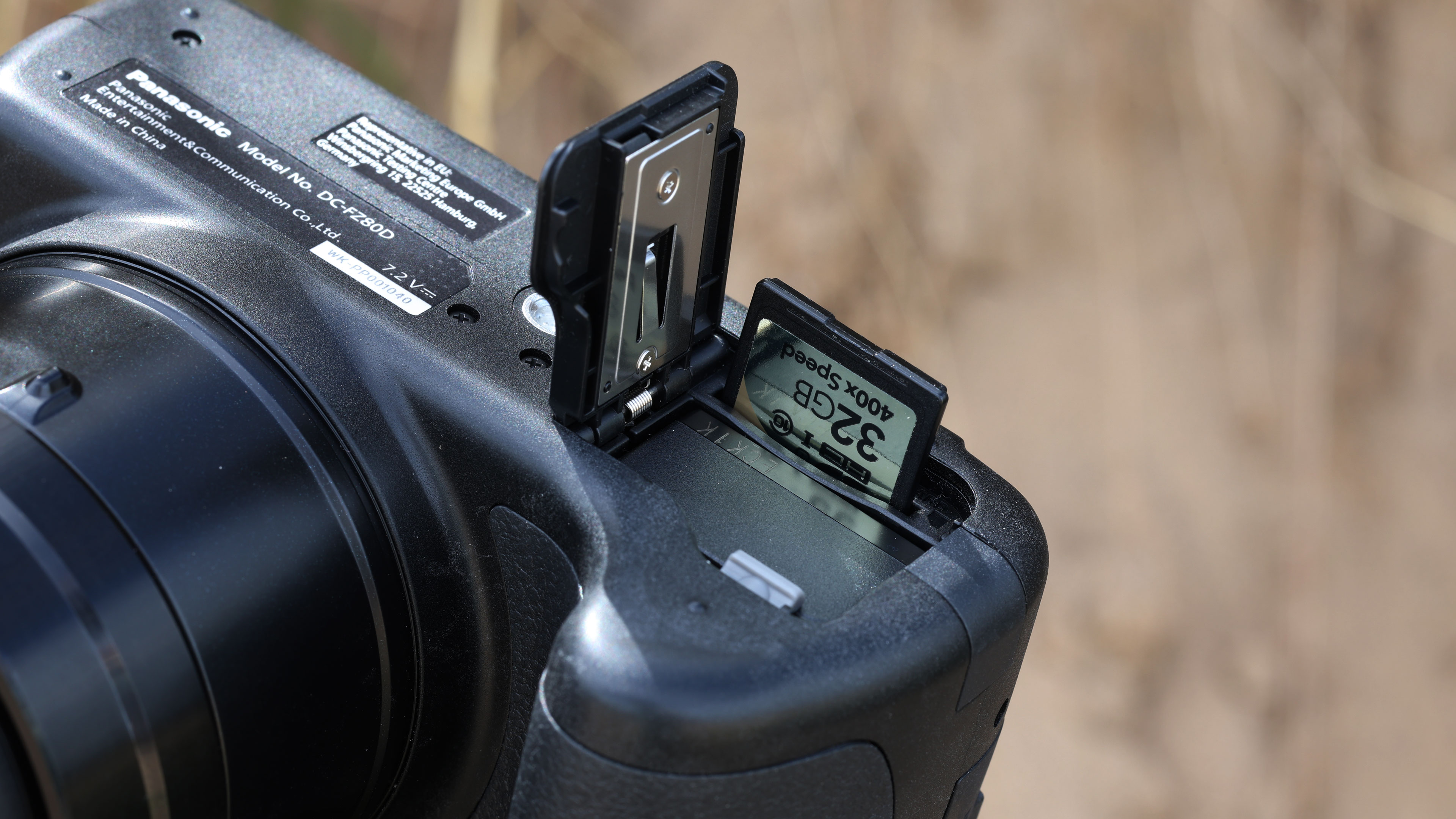
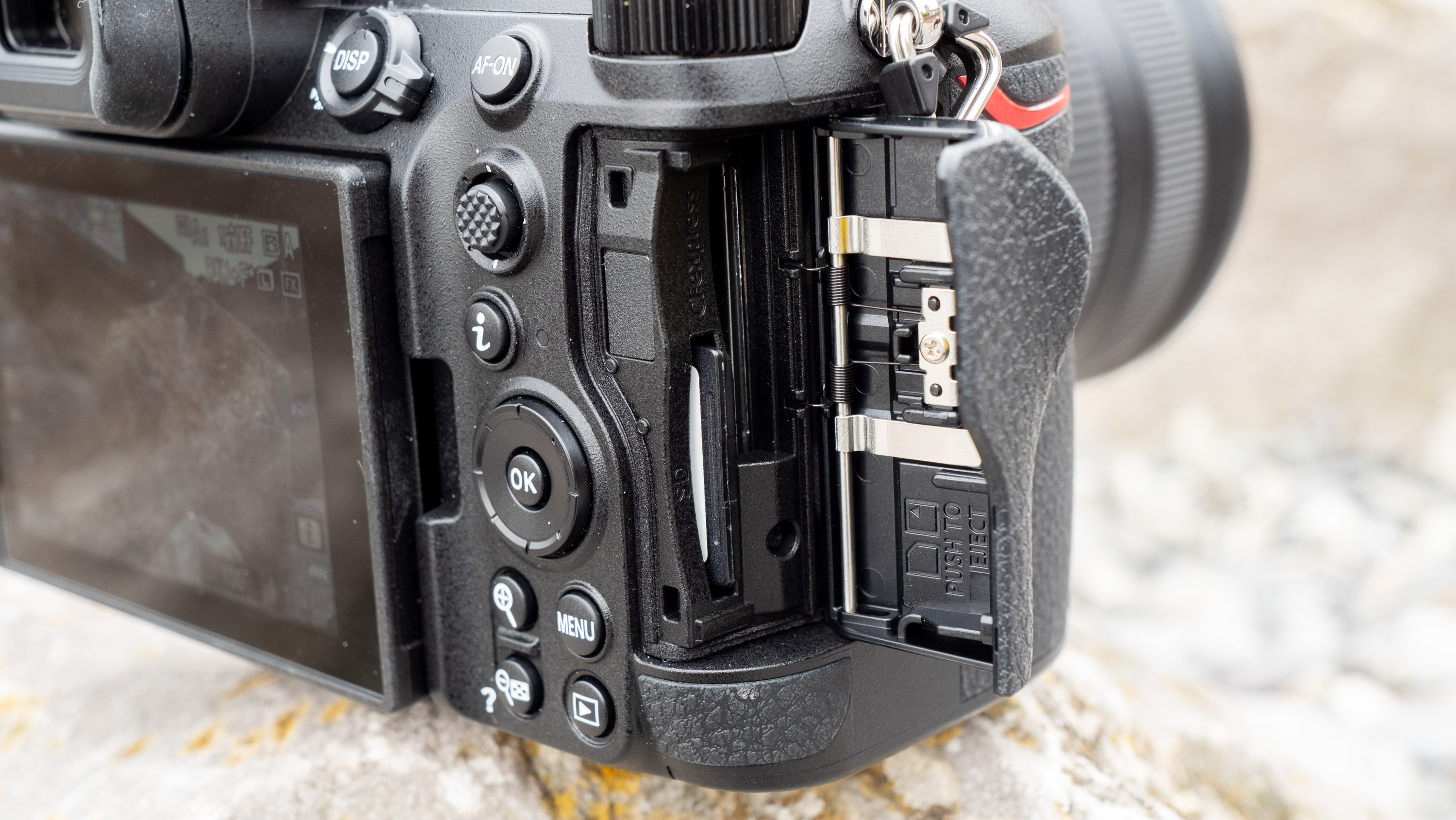
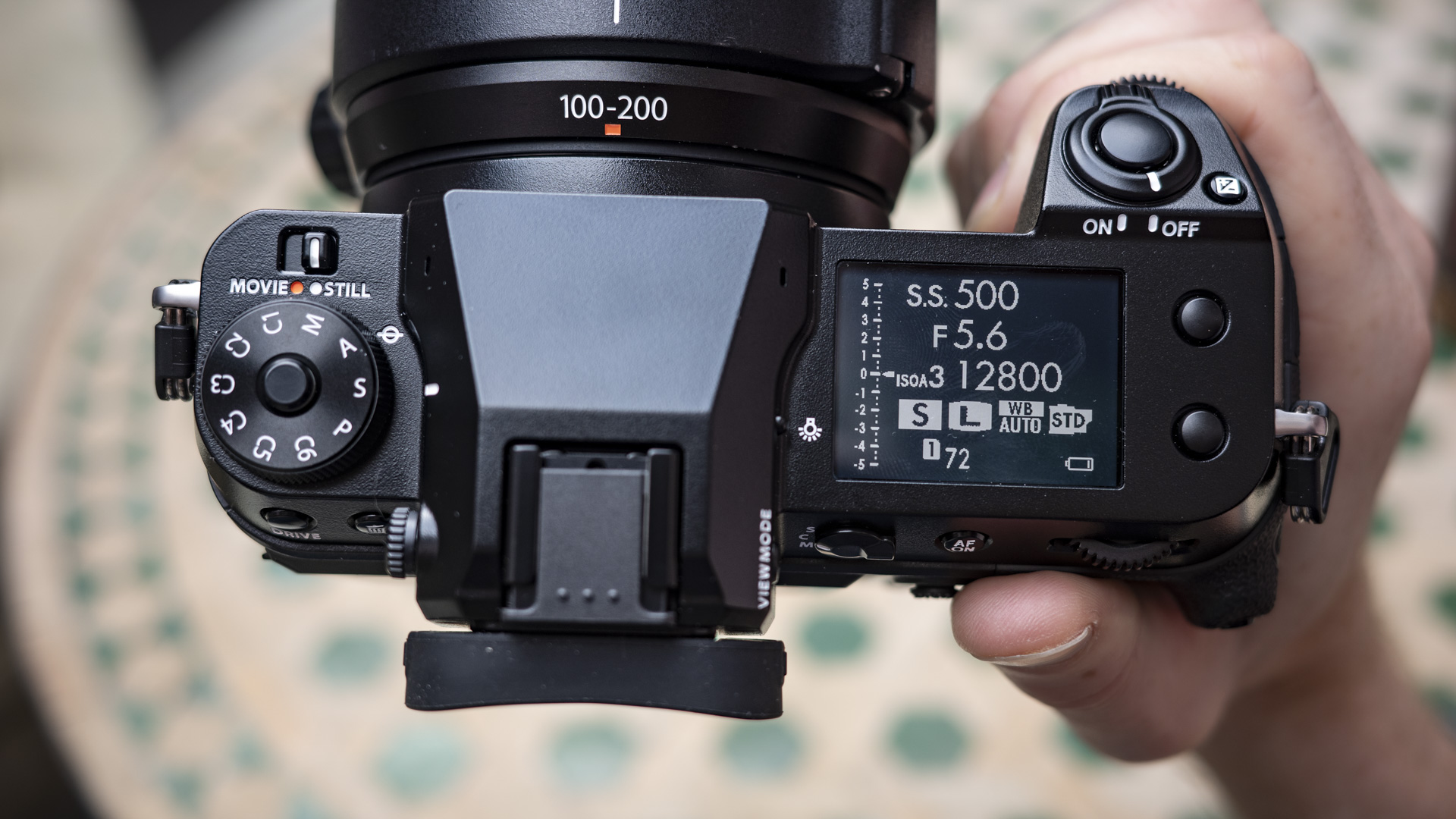
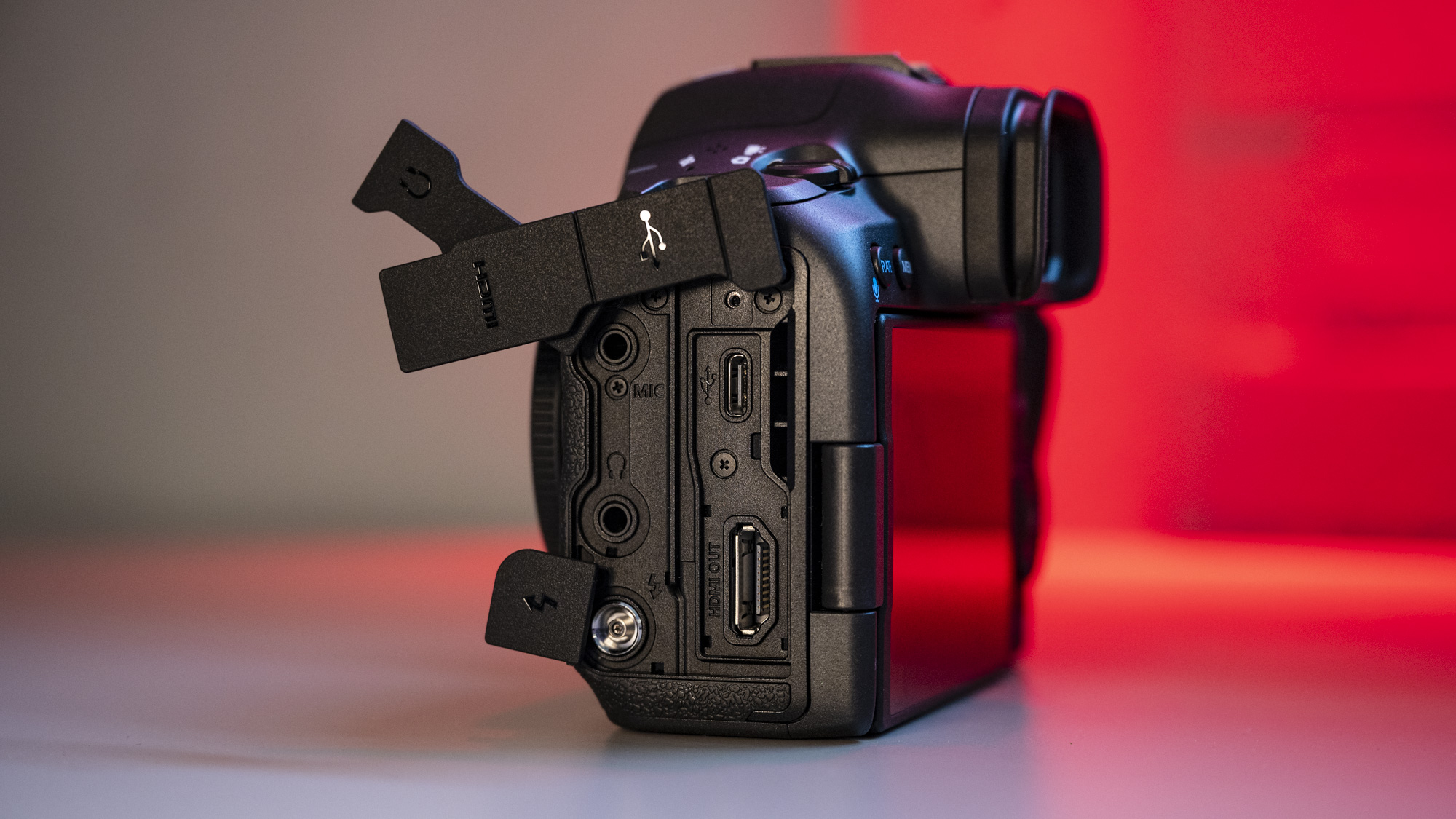
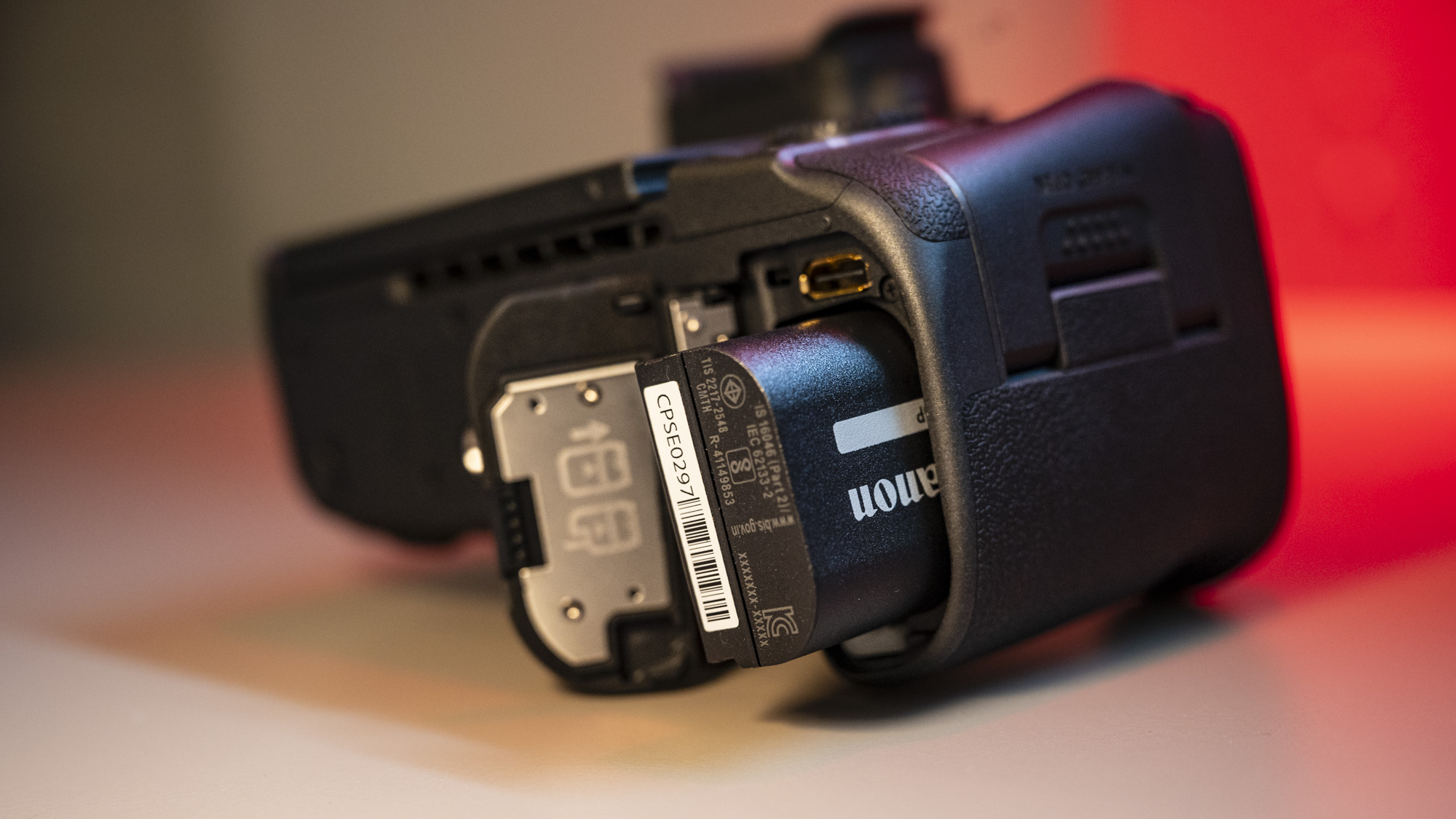
Everything else from a design standpoint is standard fare for a pro camera – an illuminated top LCD display, a textured AF joystick on the rear and dual card slots. One of these supports a CFexpress Type B device while the other supports a SD card with UHS-II speed, but you’ll need to invest in the former if you want to take full advantage of the R5 II’s speed.
Filmmakers will appreciate the fact that the EOS R5 II has a full-size HMDI port (the EOS R5 doesn't) and a tally lamp to indicate when you're recording. Moreover, key shooting information can be displayed on-screen.
There are also cooling vents on the camera's underside and they do an admirable job of keeping temperatures down when shooting high-resolution clips. In fact, temperature regulation is a lot better here than when I first tested the R5 (which was prior to the firmware updates that improved recording times). That said, I found that the R5 II can begin to get warm even when shooting constant bursts with Servo AF engaged, something sports photographers will likely need to do, but the temperature warning that appears on the display (or the EVF) never went beyond the first bar during my testing.
Naturally, there are both mic and headphone ports, plus USB-C for charging. The battery is an improved LP-E6P unit, which delivers up to 640 shots on a full charge, although that number will be a lot higher if you're capturing lots of high-speed bursts. Case in point, I ended up shooting over 8,000 frames during one testing session before the battery life dropped by three-quarters, but I couldn’t do much more as my 128GB CFexpress card was full.
• Design score: 5 / 5

Canon EOS R5 Mark II review: Features and performance
- New People and Action Priority modes
- In-camera editing features
- 15 frames of pre-recording
I’ve already listed the R5 II’s feature set at the start of this review, including the new stacked design for the sensor and the second processing unit that aids in maintaining the camera’s speed. Between the two, the R5 II is capable of rattling off at 30fps using the electronic shutter with autofocus engaged, and at a decent 1/160 second. While this helps with keeping rolling shutter distortions down to a minimum, a stacked sensor can reduce dynamic range, which is the case here, but it’s so insignificant that it would hardly be an issue in real-world use.
Buffer memory is better compared to the older R5, with the Mark II capable of saving up to 93 frames (or 3.1 seconds of capture) when shooting RAW to a memory card at 30fps (compared to 83 for the R5) or 230 RAW frames (or 8 seconds) when at 12fps (versus 180 with the R5). Buffer memory is over 1,000 frames when shooting JPG/HEIF, although I found that shooting constant bursts at 30fps in any format can bring up the temperature warning and slow the camera down a smidge.

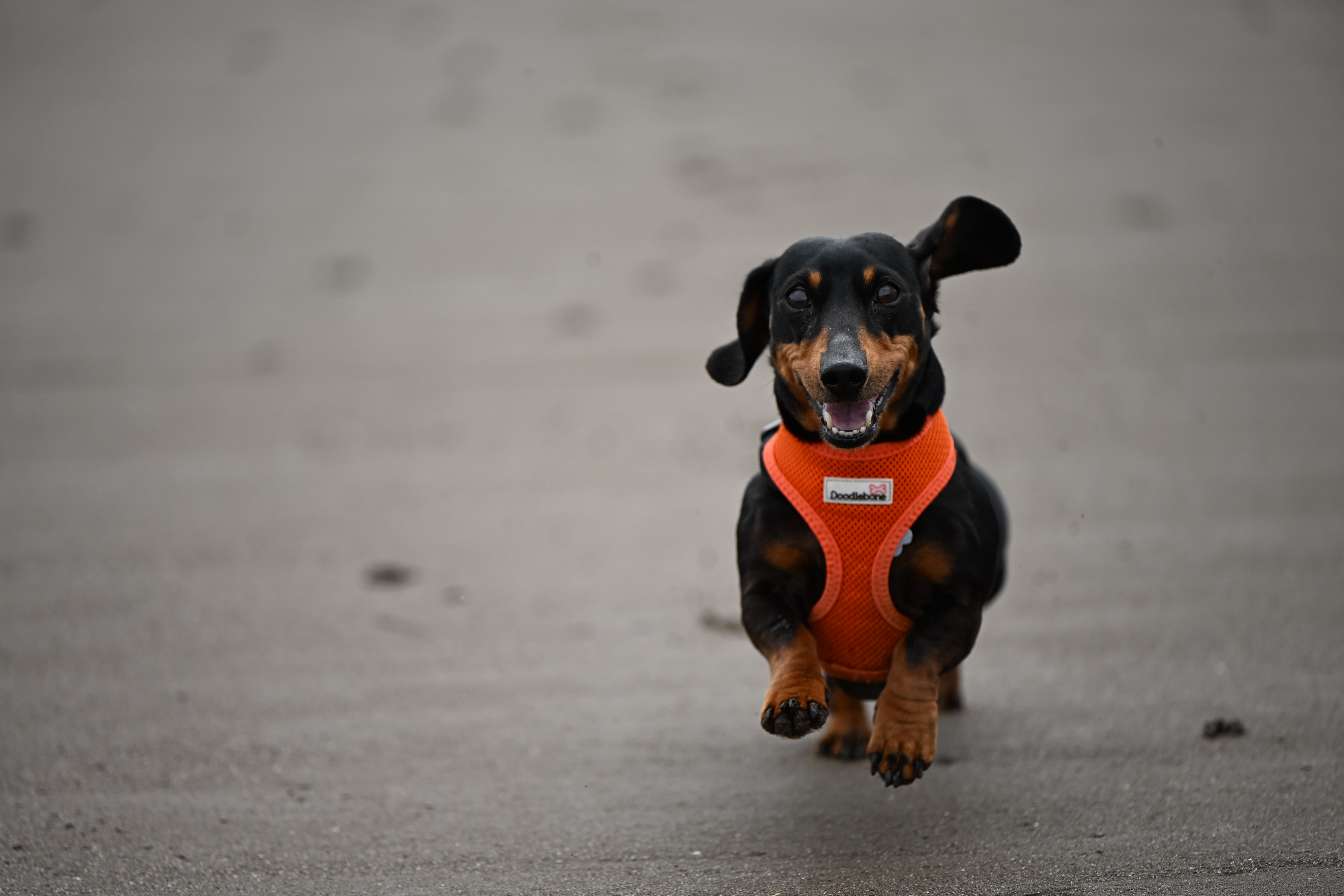
Despite that, the speed the R5 II offers is great for sports and wildlife photographers alike, and the additional 15 frames of pre-capture means it can be quite hard to miss a shot – that’s an extra half second of captures. Paired with what I think is arguably the best and easiest-to-use autofocus system in the camera world, the R5 II makes pro photography incredibly simple.
And I do mean ‘simple’. Straight out of the box, the camera is ready to shoot, but engage either the new People Priority or Action Priority modes and sports photography becomes incredibly easy – all you need to do as a photographer is get your framing right and the camera will do the rest.
People Priority takes face detection to the next level and is ideal for team sports or wedding photography. Within the camera’s menu system is the option to ‘register’ a face… or 10. You'll need to take a head shot – and it doesn’t even have to be perfect – or capture an image of the person(s) from the internet to Register People Priority. Depending on the order you capture the faces, the camera prioritizes them from 1 (most important) to 10 (least important) and will focus on the people within the frame with the highest priority.
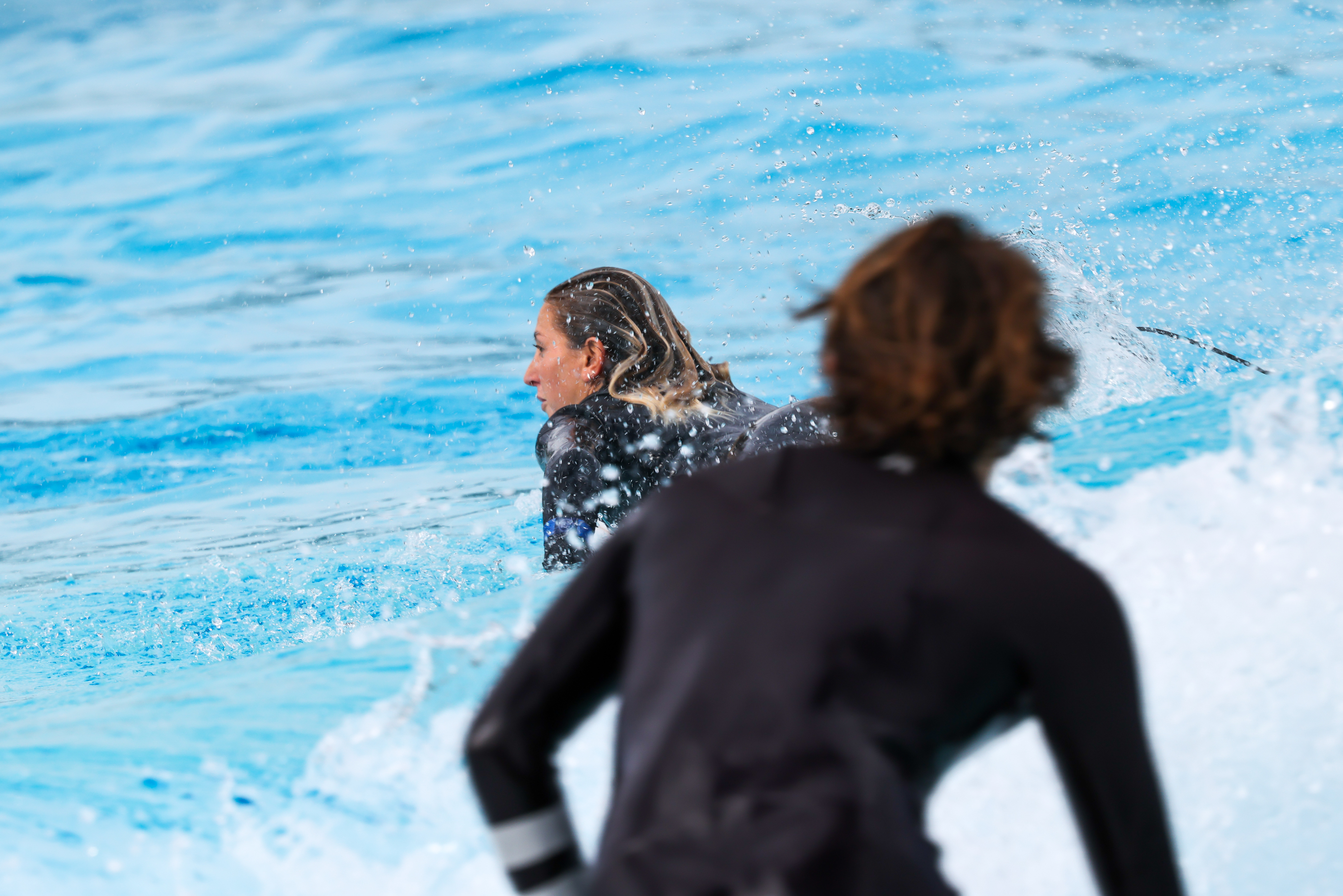
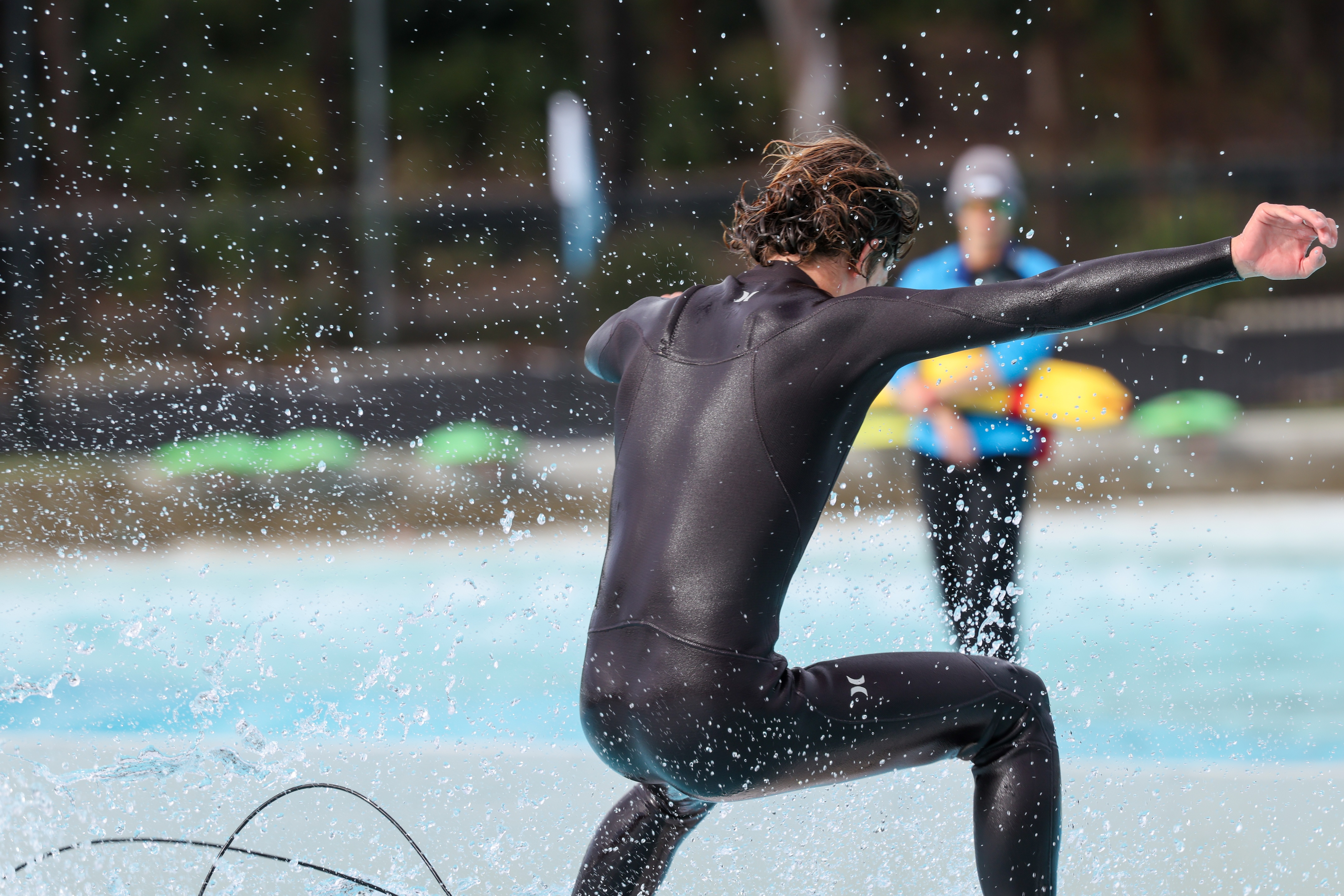


I didn’t get to try it with the maximum of 10 people during my testing, but it worked with pinpoint accuracy with three people in the frame. I also found that if a person with the highest priority within a scene only has a tiny fraction of their face turned to the camera (aka in partial profile), the R5 II will automatically shift the focus to the next highest priority face if it’s more visible. On the other hand, if a non-registered person appears in the frame, the camera can stick with the main subject even if only the back of the head is visible. That is intelligent autofocus indeed!
Action Priority is perfect for team sports that have a spherical ball in constant play but, at launch, Canon only has this feature set up for three sports – basketball, football (soccer) and volleyball. Using deep-learning algorithms, Canon has figured out how to ‘teach’ the camera to recognize body movements so the focus can shift to a player who either has the ball in possession or is about to get it. That means the R5 II can, in theory, predict where the ball is going next and focus on the right ‘moment’ rather than on a specific player.
I say ‘in theory’ because I didn’t get the opportunity to test this mode out on the three preset sports, but my colleague based in the UK got a chance to test Action Priority using a pre-production camera unit at a basketball game and it seemed to work then. That said, three sports is very limited and it would be great if Canon can start adding more (not just those with spherical balls) as quickly as possible. In fact, it’s the same case with the EOS R1 too, and it's as yet unclear whether the balls need to be a specific size to trigger the camera's response (aka, will it handle sports like tennis or cricket – that use smaller balls – just as well?).



There’s no easy way to switch between the two modes without delving back into the menu system, but nearly all the buttons on the camera can be customized. For example, I swapped the AE Lock button to trigger Action Priority and set the AF-On control on the rear panel for People Priority mode. I also set the M-Fn function to trigger Eye Control AF.
Speaking of which, this is the only autofocus feature on the R5 II that I had trouble with. While my colleague was suitably impressed, I just couldn’t get the calibration right – I even reset the camera to try again and failed. And this is despite Canon claiming they’ve made improvements to the Eye Control AF that makes it easier for people who wear glasses (like me) to use it. Seems like this isn’t an isolated problem as others have reported a similar issue.
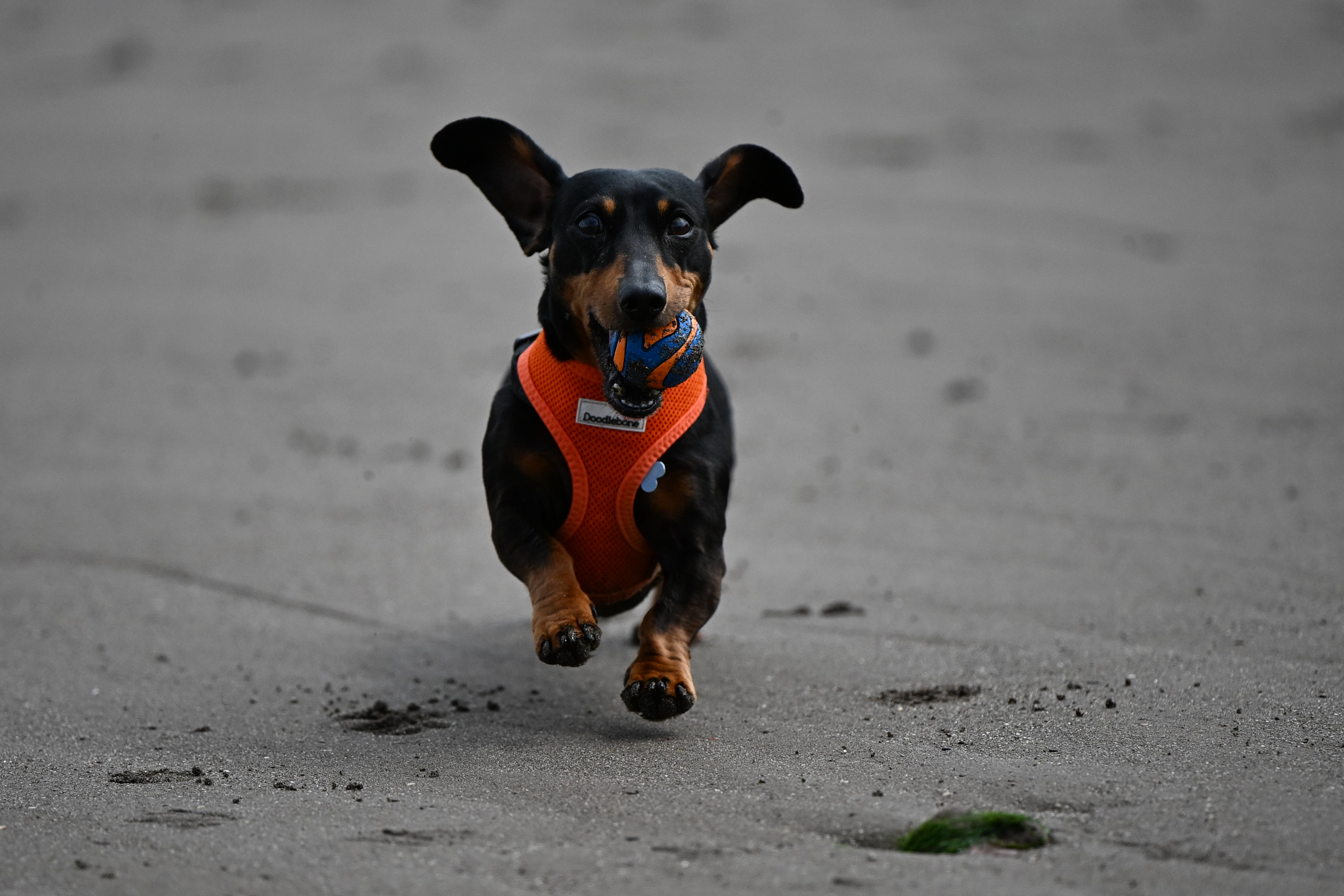
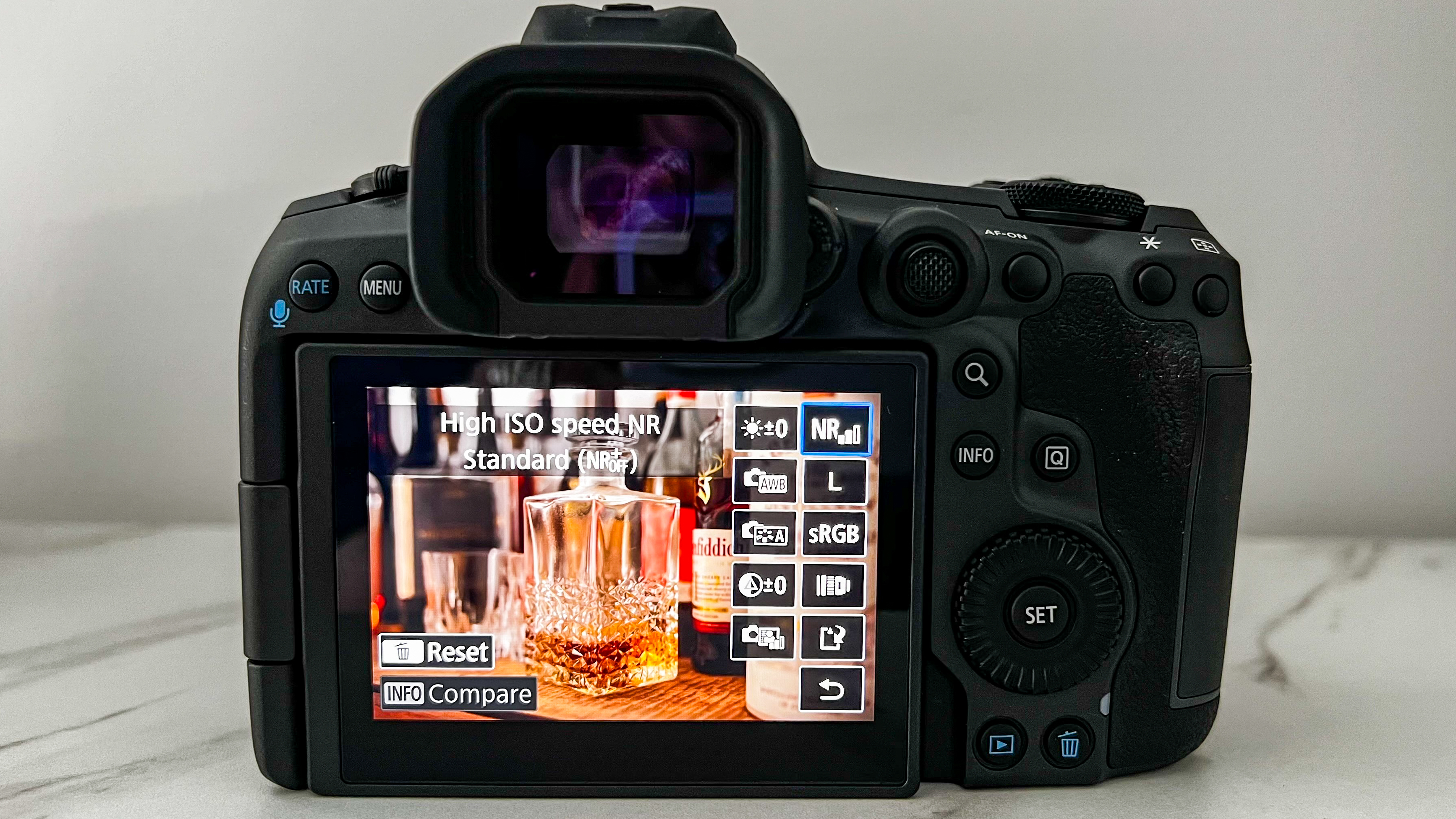
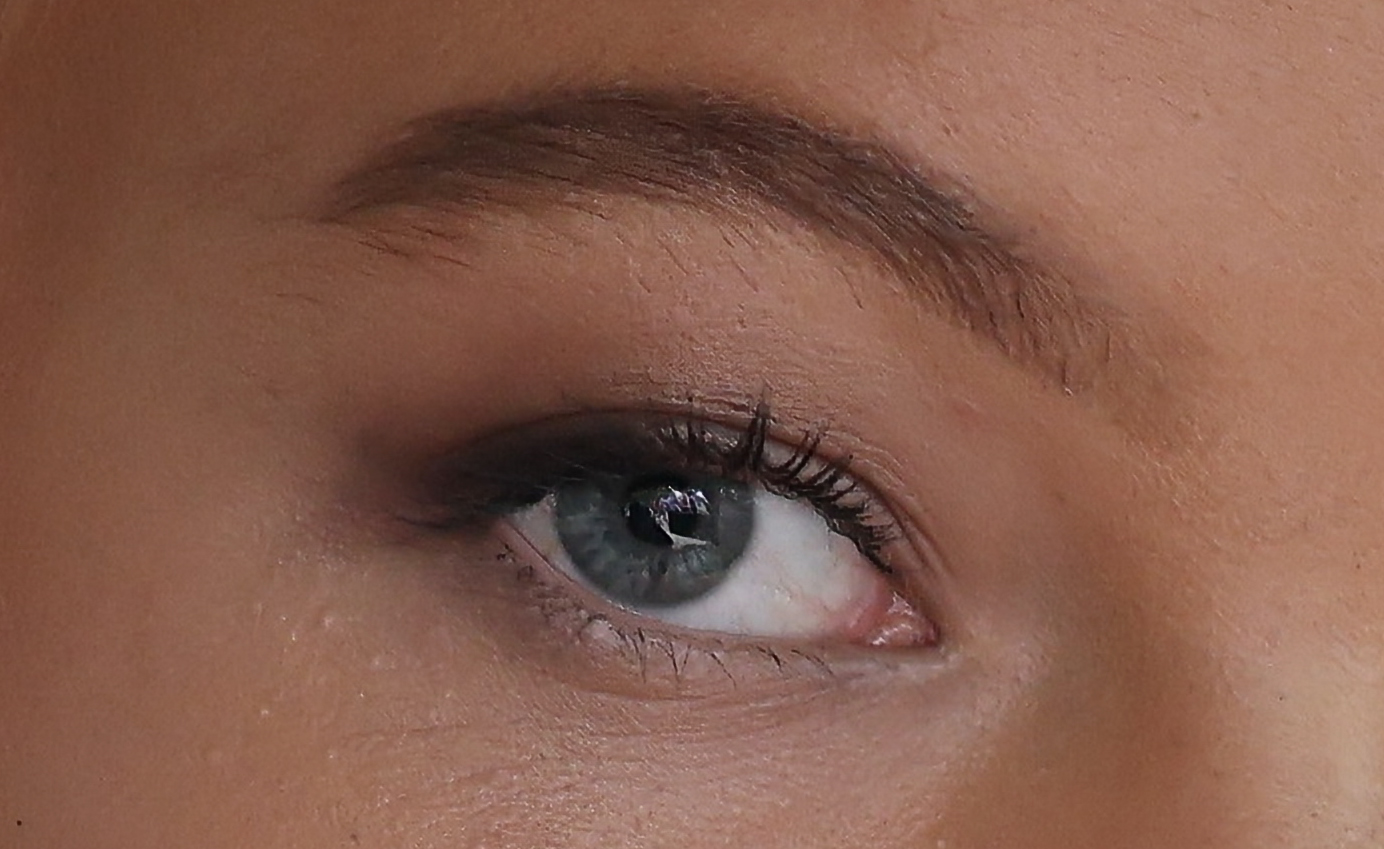
Even without Eye Control AF, the R5 II’s autofocus and tracking is excellent and Canon has improved low-light AF sensitivity to -7.5EV (compared to -6EV in the older model, although the Nikon Z8 is effective at -9EV). The native ISO range remains steady at 100 to 51,200, or 50 to 102,400 expanded. While noise is very well controlled up to ISO 6400, even images shot at ISO 12,800 are usable if you don't need to crop in to zoom. And if noise at this high ISO is an issue for you, Canon’s new Neural Network Noise Reduction feature can help – it can denoise selected images in-camera by up to 2 stops as long as they're RAW files.
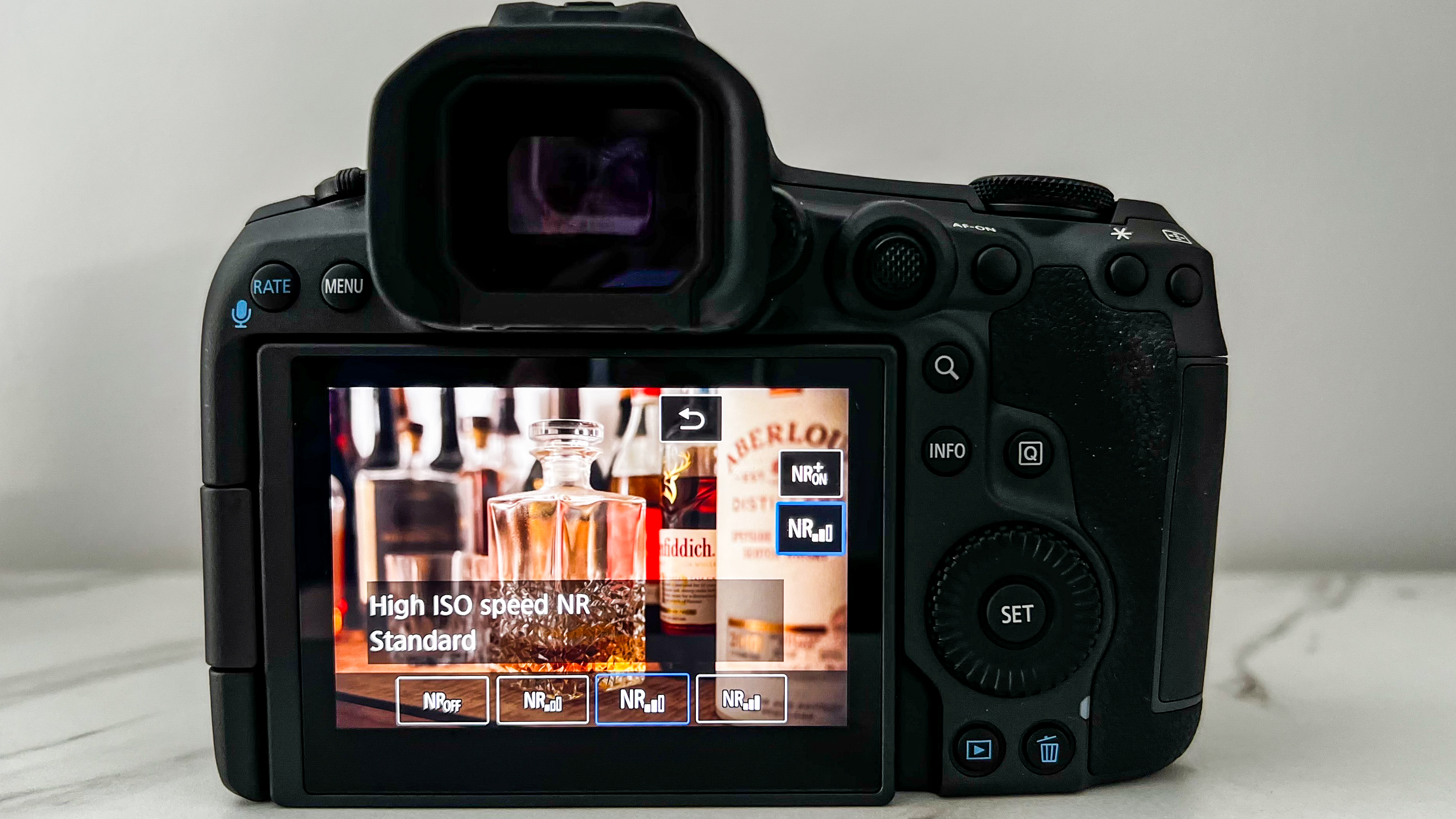
Within the Playback menu settings is the option to Process RAW Files, where the noise reduction editing feature is nestled. There are three options to choose from – Low, Standard and High – and they can be utilized in a pinch to cut down on some grain. The processed file is then saved as either a JPEG or HEIF.
I'm uncertain why Canon choose to enable this processing for RAW files only, and I'm hoping a future firmware update will allow for JPEGs/HEIFs to also be edited in-camera in the same way.
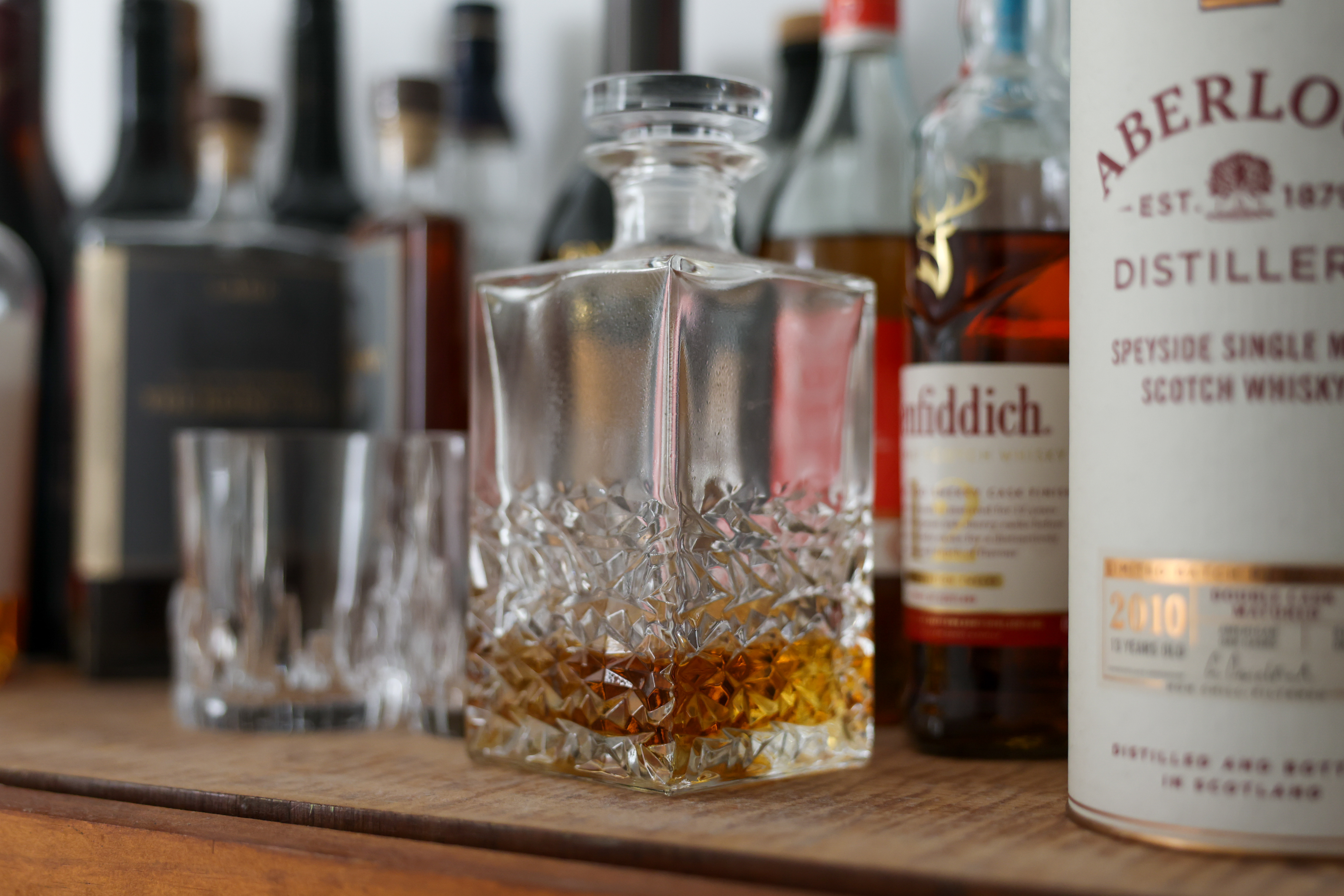
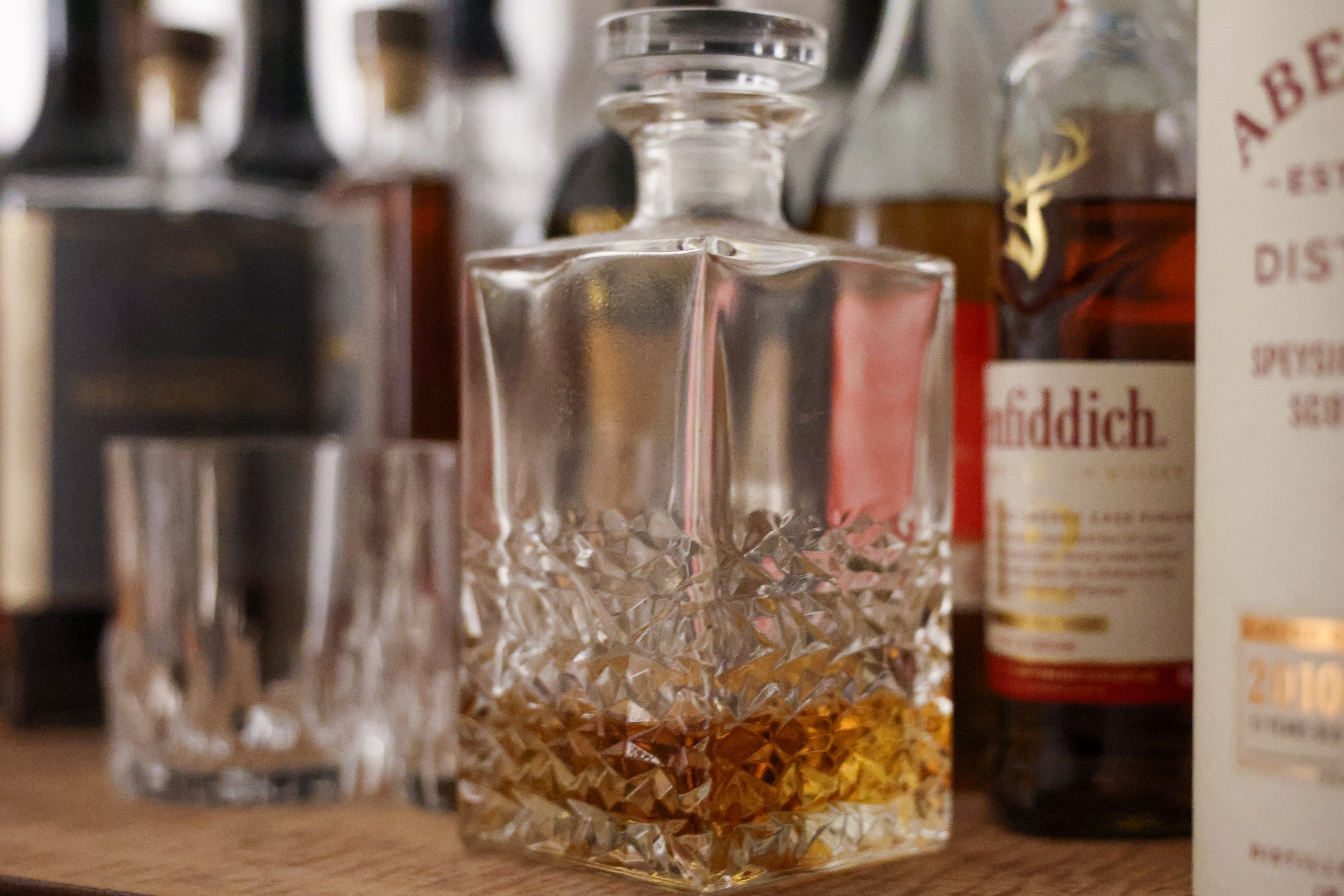
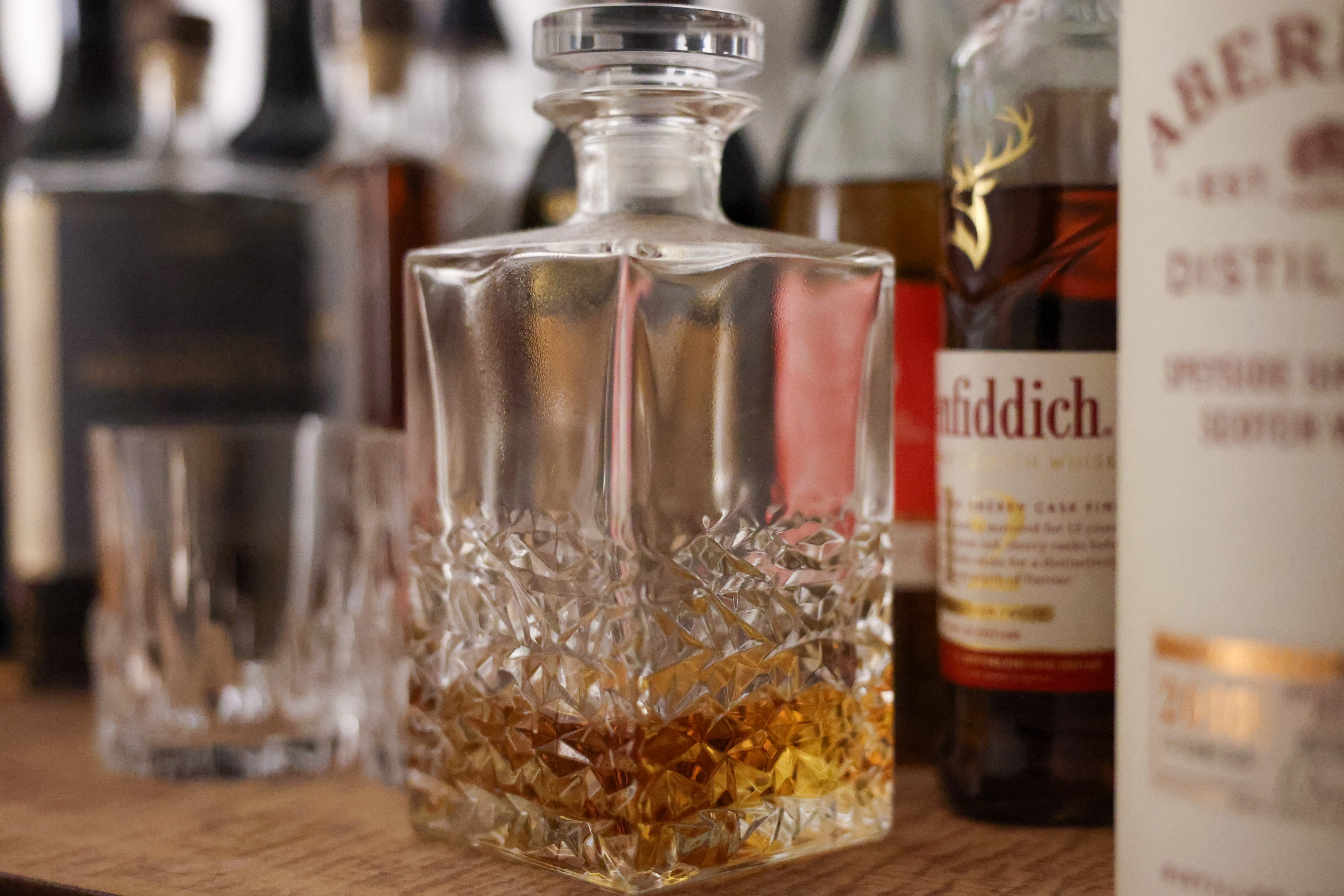





In a similar vein, if you want a higher resolution version of a particular image, you can upscale it in-camera to add up to 4x the pixel count using AI to extrapolate the image’s EXIF data, creating stills of up to 180MP from the original 45MP shot. While this is an excellent option for landscape photographers, it turned out to be rather impractical when shooting bursts. Pro sports and wildlife photographers will end up with so many shots that it could be hard to find the specific one you want to select to be upscaled.
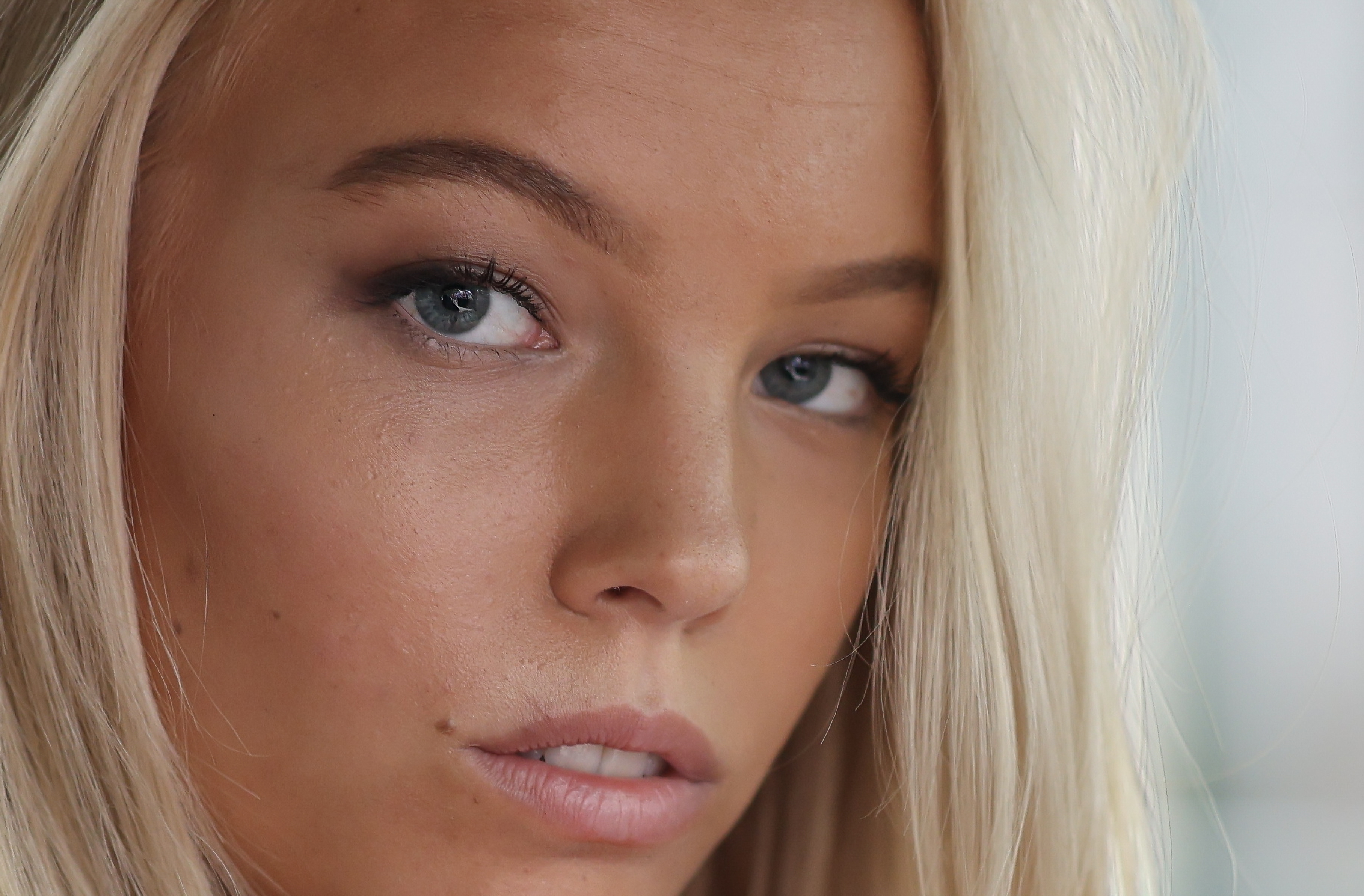





Thankfully Canon has thought of that and you can select a range of images to upscale, but that will eat into your memory card’s free storage. Moreover, I found that Lightroom (my go-to image editing software) struggled with the larger files, crashing four times before I was able to view them – and this is on a MacBook Pro equipped with Apple’s decently powerful M3 Pro processor.
The main caveat for this feature is that it only works for JPEG/HEIF files and not RAW. Perhaps this will change down the line via future firmware updates, but it's still handy to have.

In terms of video, the R5 II is a powerhouse, with better heat management than its predecessor. Without the Cooling Fan Grip, Canon says the R5 II can shoot up to 18 minutes in 8K/60p RAW internally when ambient temperature is about 23ºC / 73ºF, although during my testing I managed about 4 minutes before I got the temperature warning, then another 2.5 minutes before the temperature gauge went into the red. Another minute later, the camera stopped recording with the warning that no more footage could be captured until the camera cooled down. That’s just 7.5 minutes but, to be fair, the ambient temperature was 26ºC (78.8ºF) and I was standing in direct sunlight.
Recording times increase as the resolution is lowered, with the possibility of up to 45 minutes when shooting 45K/60p without the fan. If you invest in the Cooling Fan Grip, there is theoretically no recording time limits with the fan set to high.
While not all the exciting features on the R5 II work as well as Canon would like us to think (I’m referring to Eye Control AF here), and there are dedicated hybrid cameras that handle pro filmmaking better, it’s really hard to fault the R5 II when everything else makes taking great shots really easy.
• Features & performance score: 5 / 5







Canon EOS R5 Mark II review: Image and video quality
- Gorgeous colors but slightly lower dynamic range
- Great details and sharpness, even in shadows
- Top notch video results
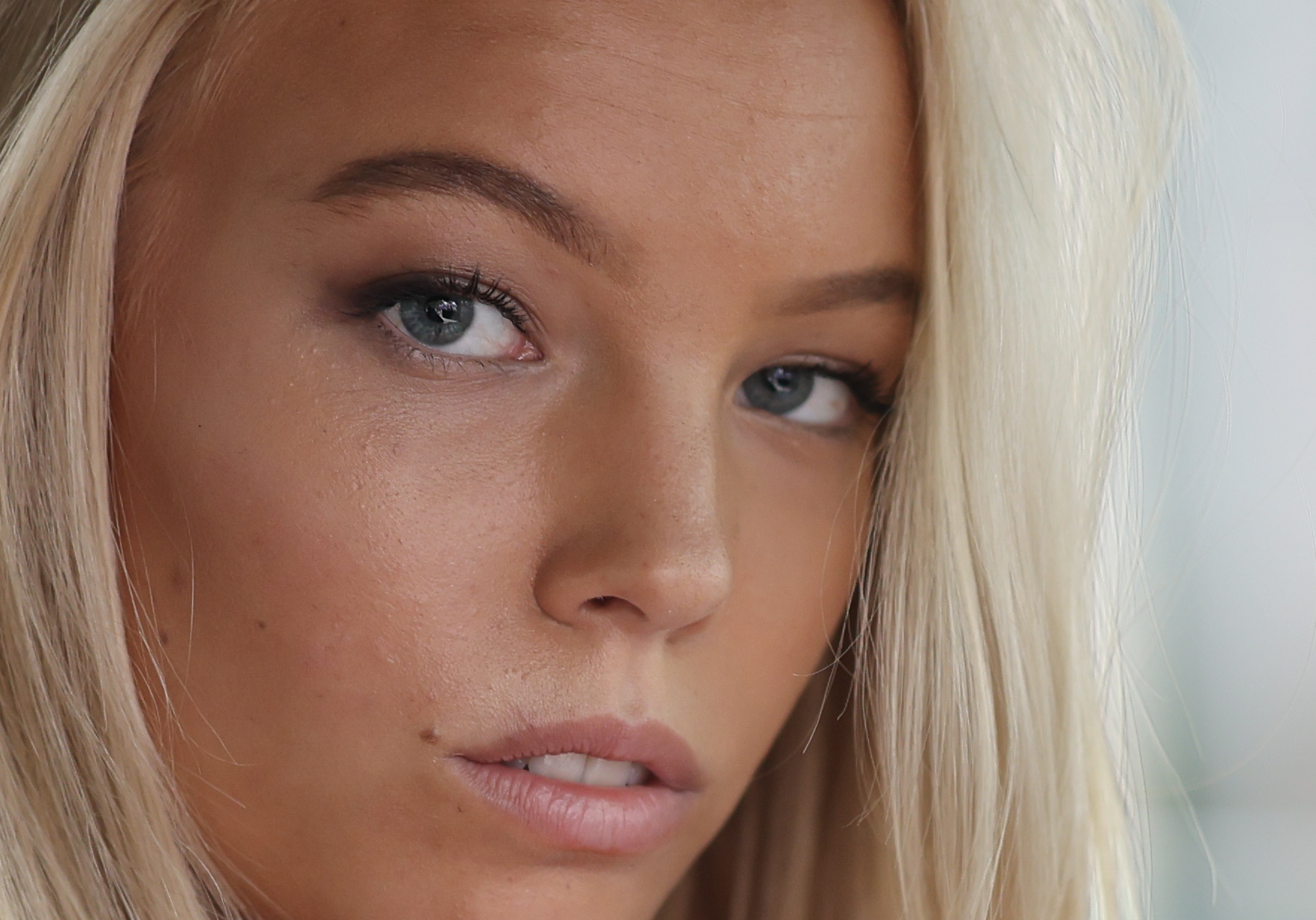
Not everyone needs a high-resolution camera but many prefer it. With 45MP on tap, there's more than enough sensor resolution here to suit most photographers, and having fewer pixels compared to the 61MP Sony A7R V and the 45.7MP Nikon Z8 means the Canon can handle speed better than some of its competition.
Even on a pre-production model of the R5 II, I was able to get excellent results, with colors that I personally find pleasing, plus focus and subject tracking practically pinpoint perfect. And that performance was just as impressive when I tested the final production model.
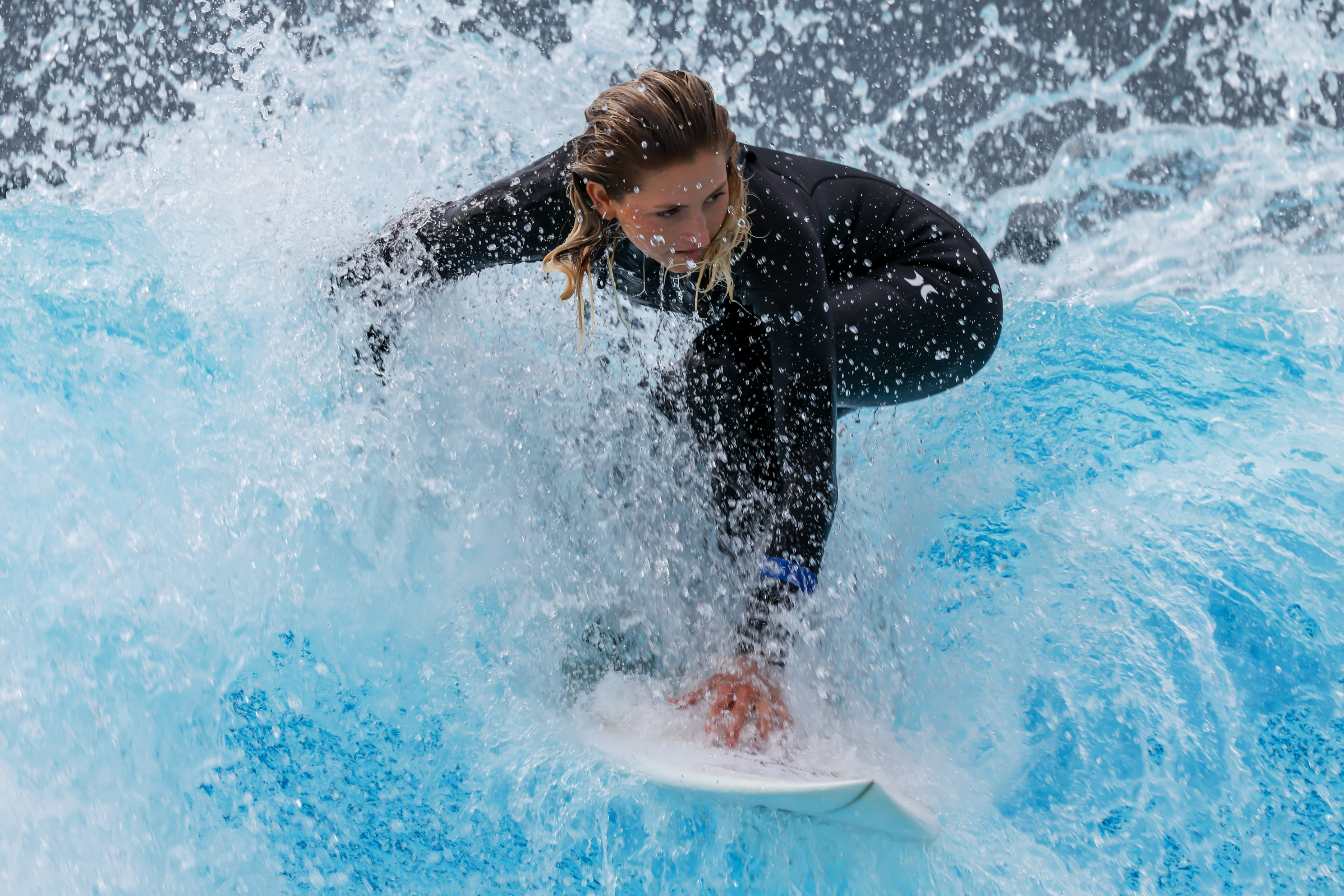
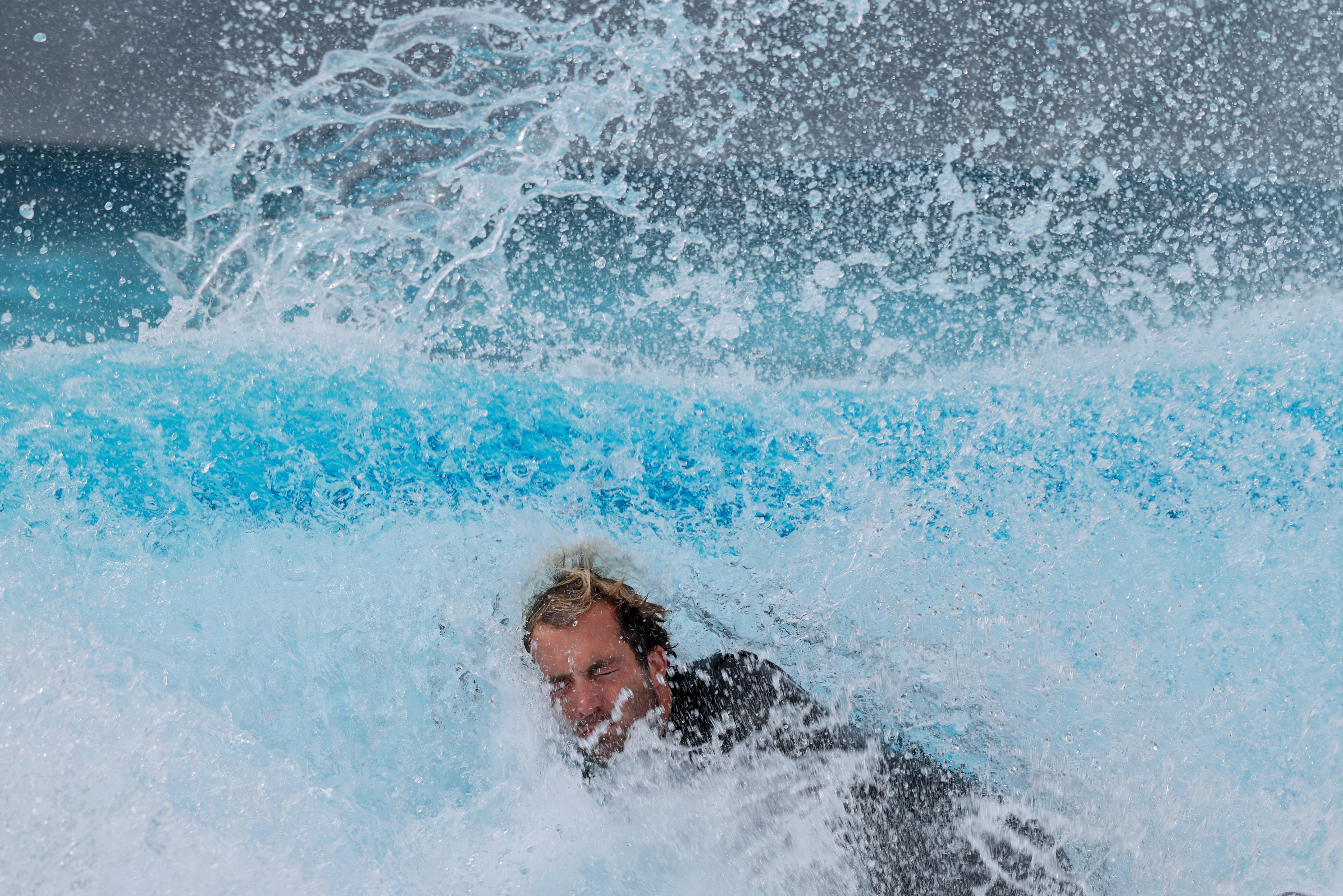



It’s been really hard to find fault with the results of the R5 II, despite the limitations of its stacked sensor design. As I’ve mentioned previously, this gives the camera its speed but comes at the cost of a little bit of dynamic range. I didn’t have the older R5 with me to do a direct comparison but, in my real-world testing, I found this compromise to be so small, even when shooting with the electronic shutter, that it’s hardly worth commenting on. Unless you plan on significantly cropping an image, the resulting noise in darker areas will not be a problem because of the lower dynamic range.
Otherwise, images shot using the R5 II are sharp, with very reliable autofocus and subject tracking performance – meaning all a photographer needs to think about is composition.



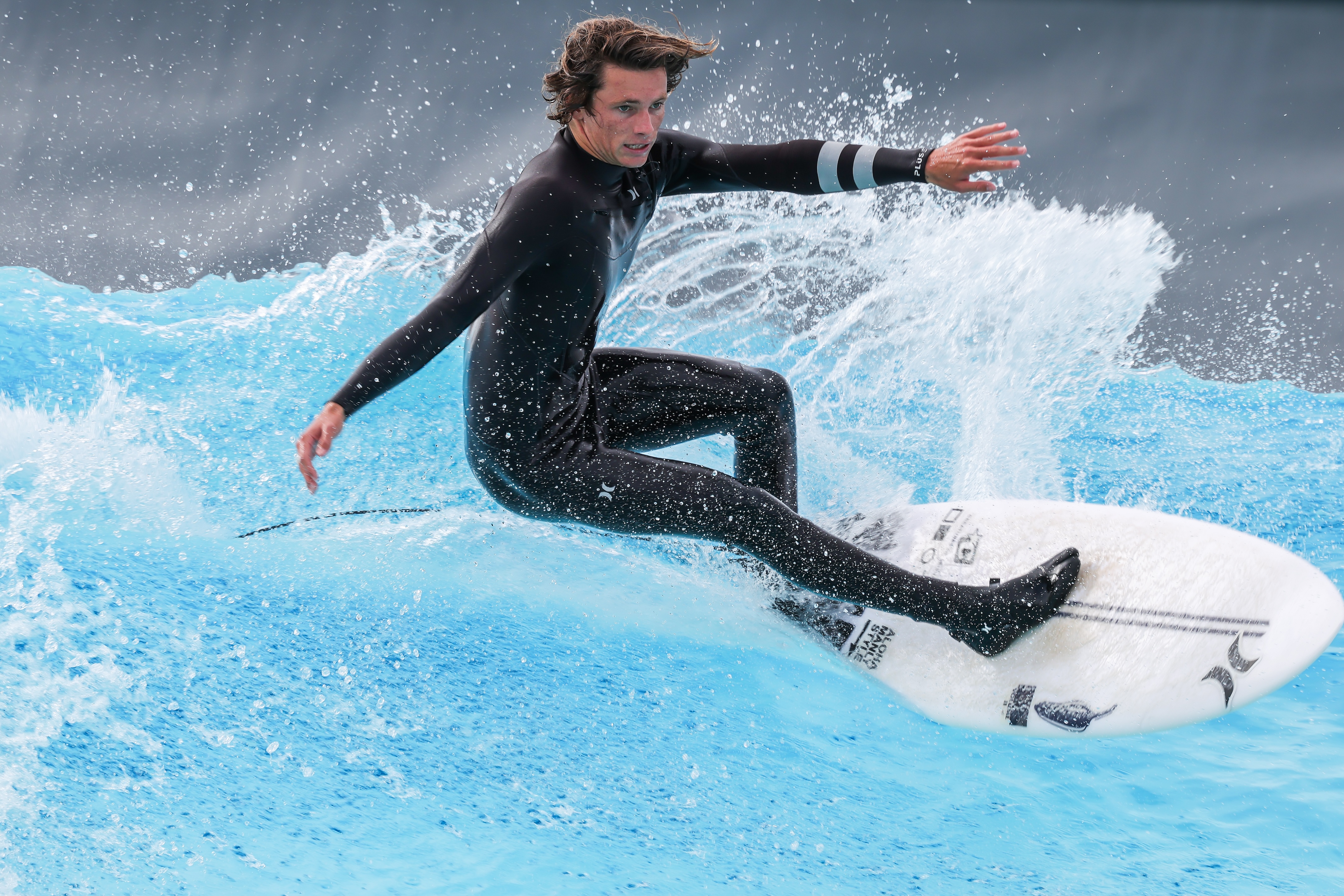
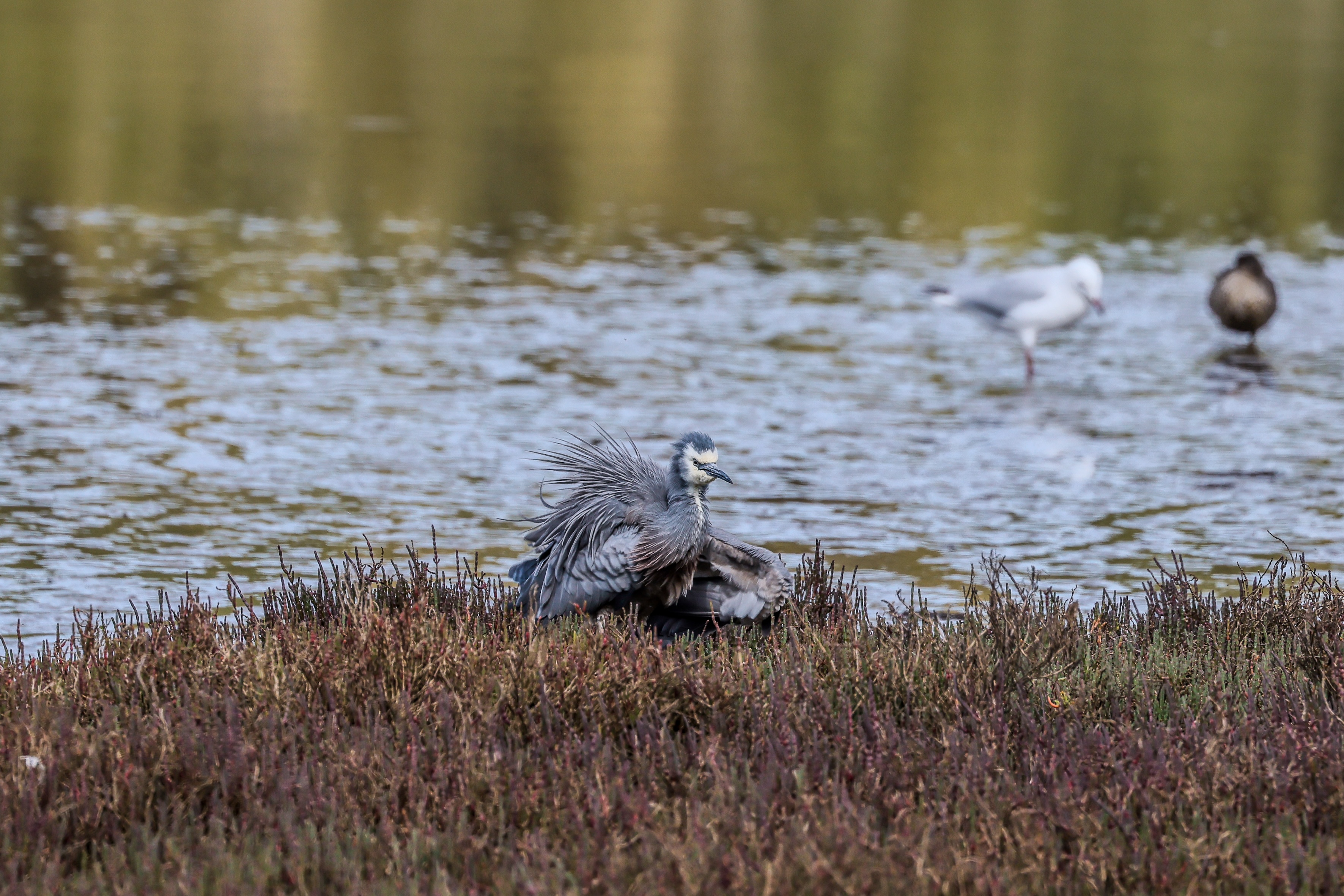
I also pushed the R5 II’s ISO sensitivity to see how well it holds up at the higher end of the spectrum and was suitably impressed. While there is some noise at ISO 6400, it’s hard to discern unless you crop significantly. Even at ISO 8000 or 12,800, the noise is decently controlled and, if in a pinch you think there’s too much visible graining, the option to use the Neural Network Noise Reduction feature is there… as long as you’re shooting RAW. And there are always photo editors like Topaz Photo AI that will help reduce the grain.
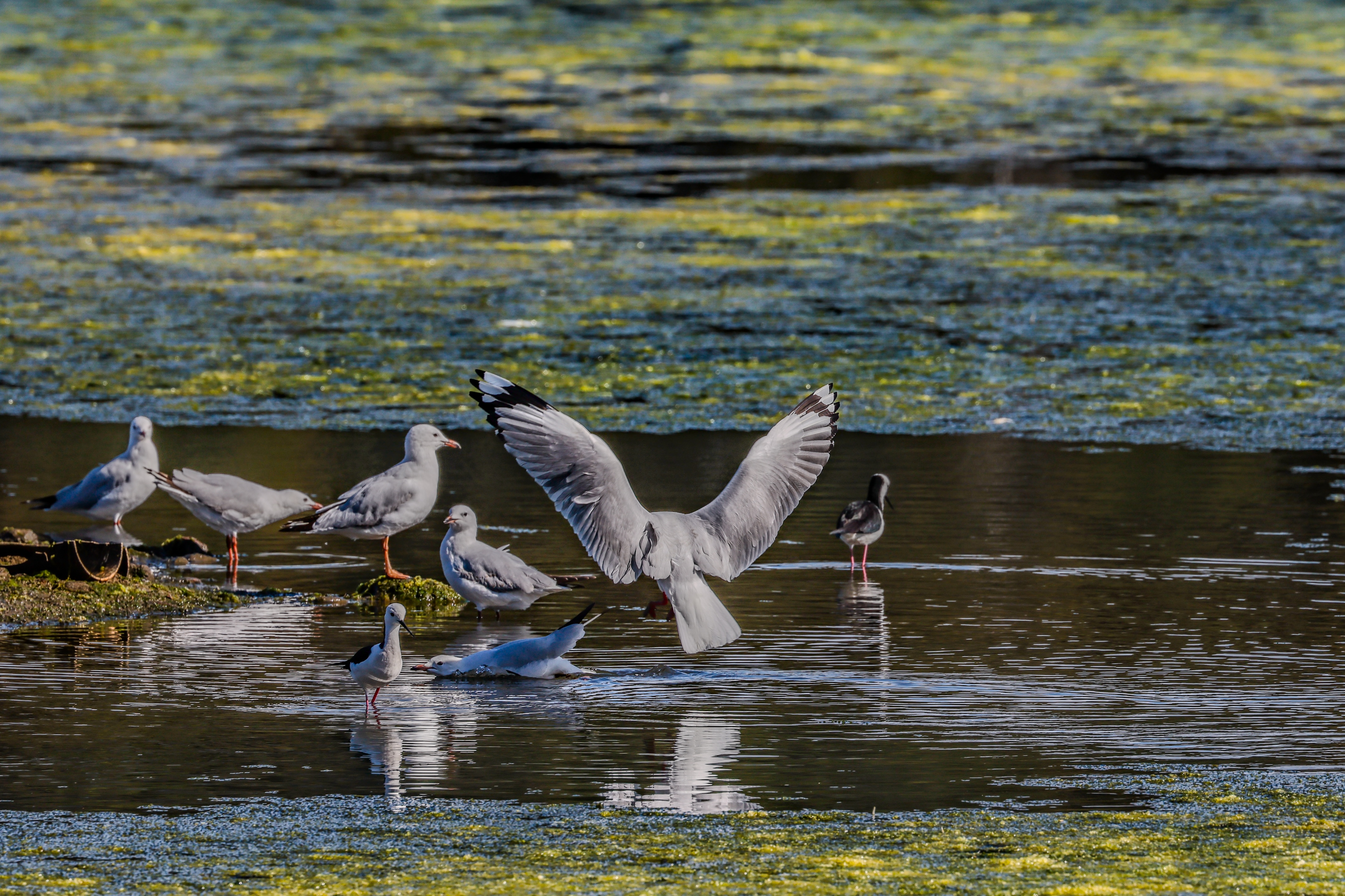
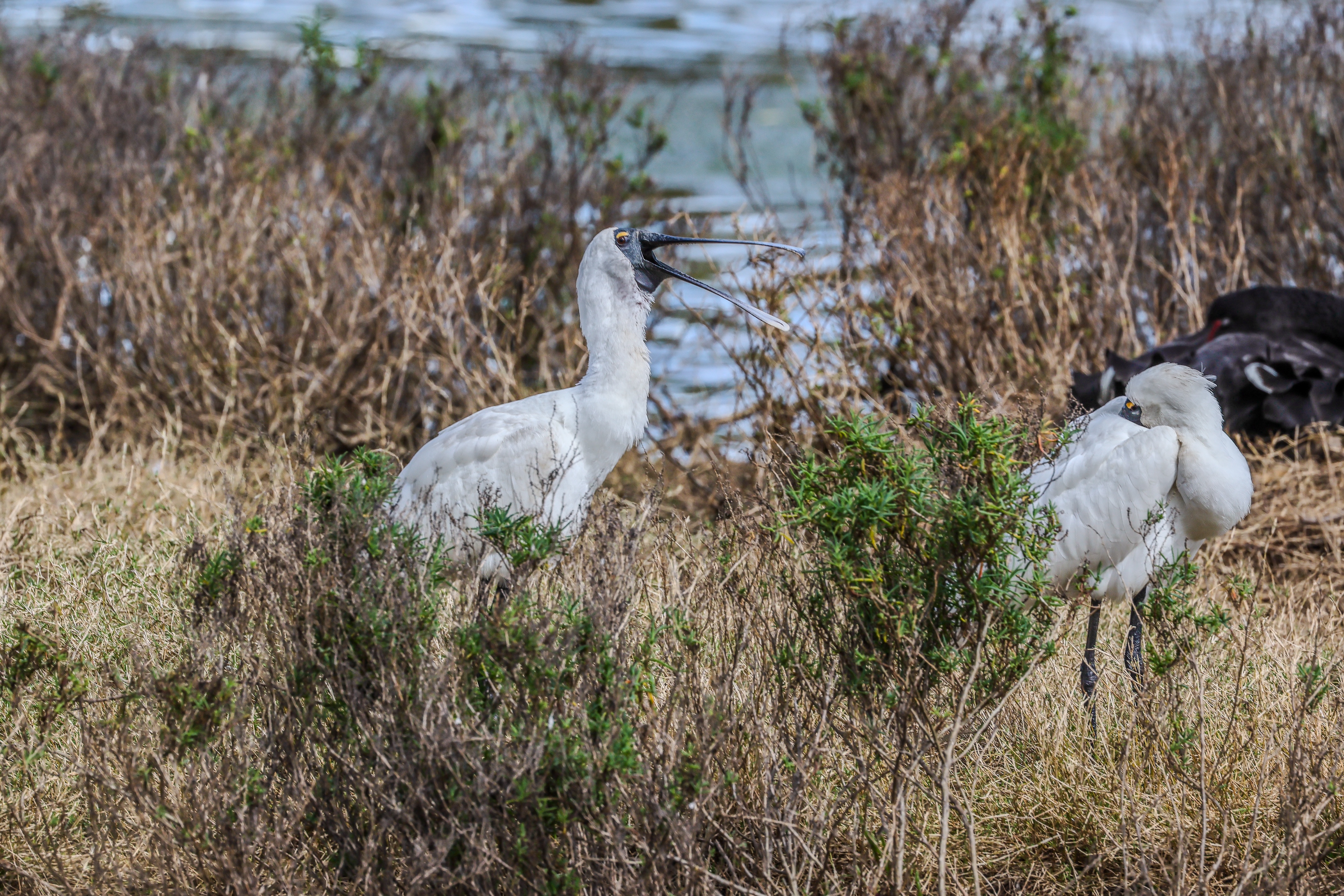
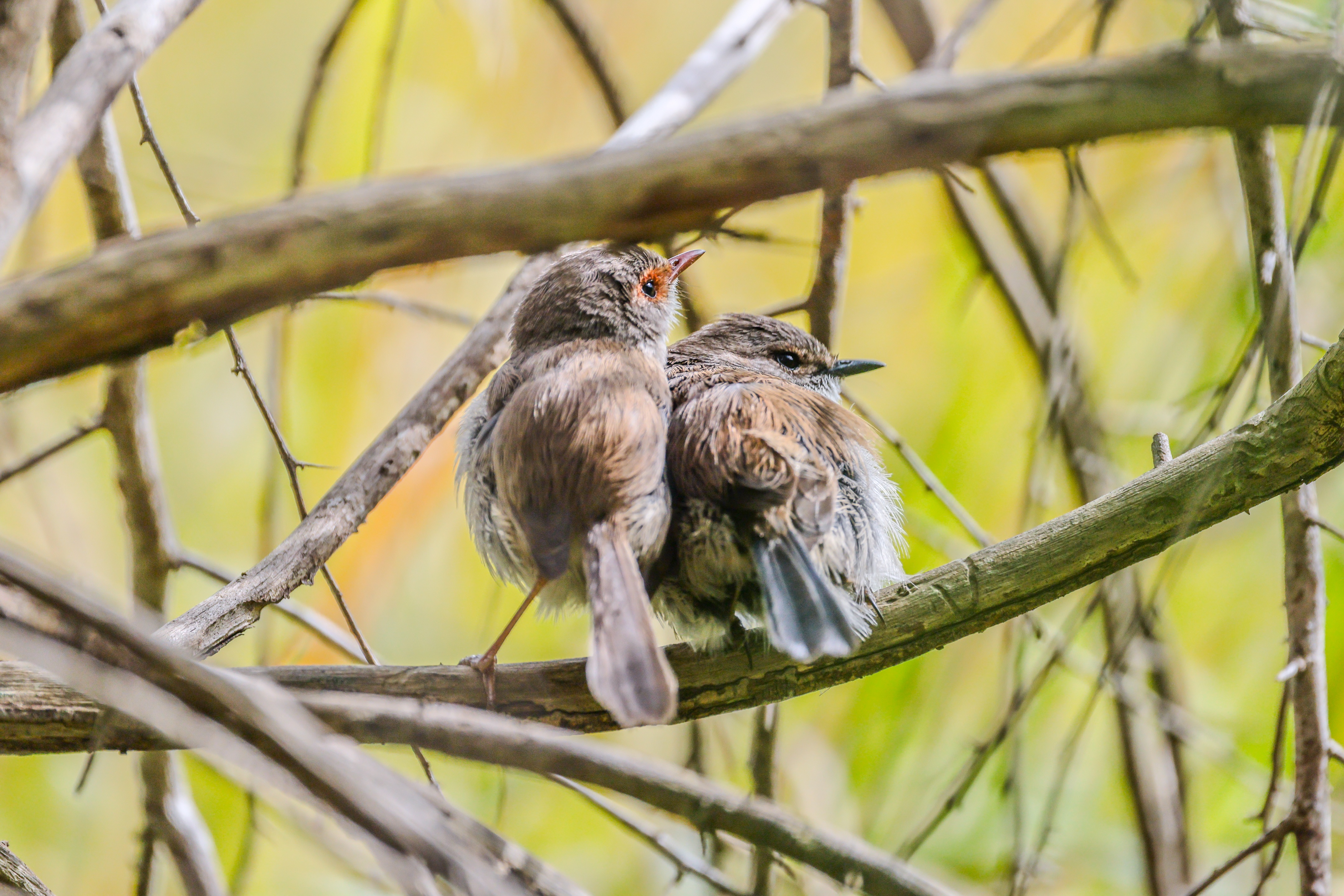
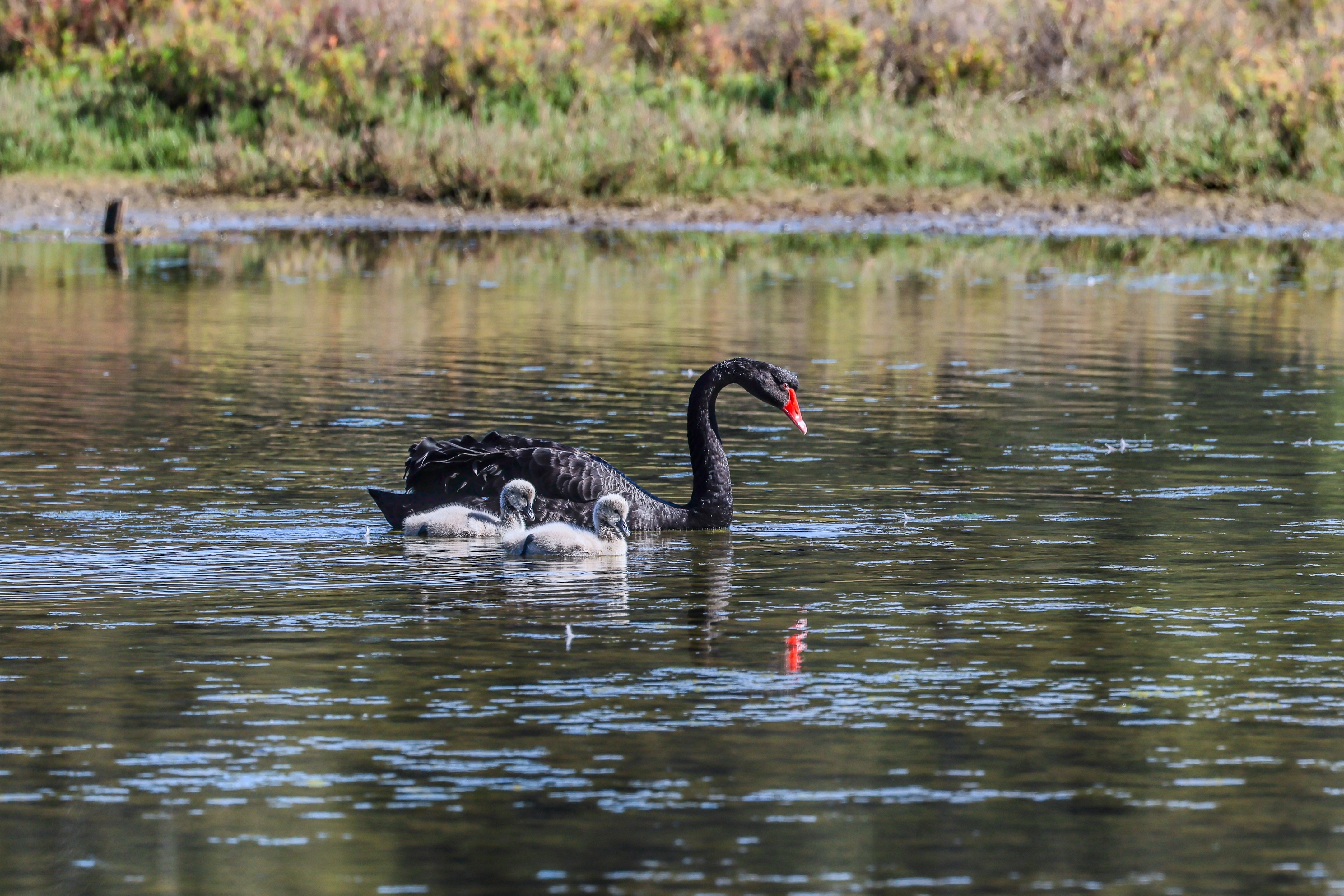
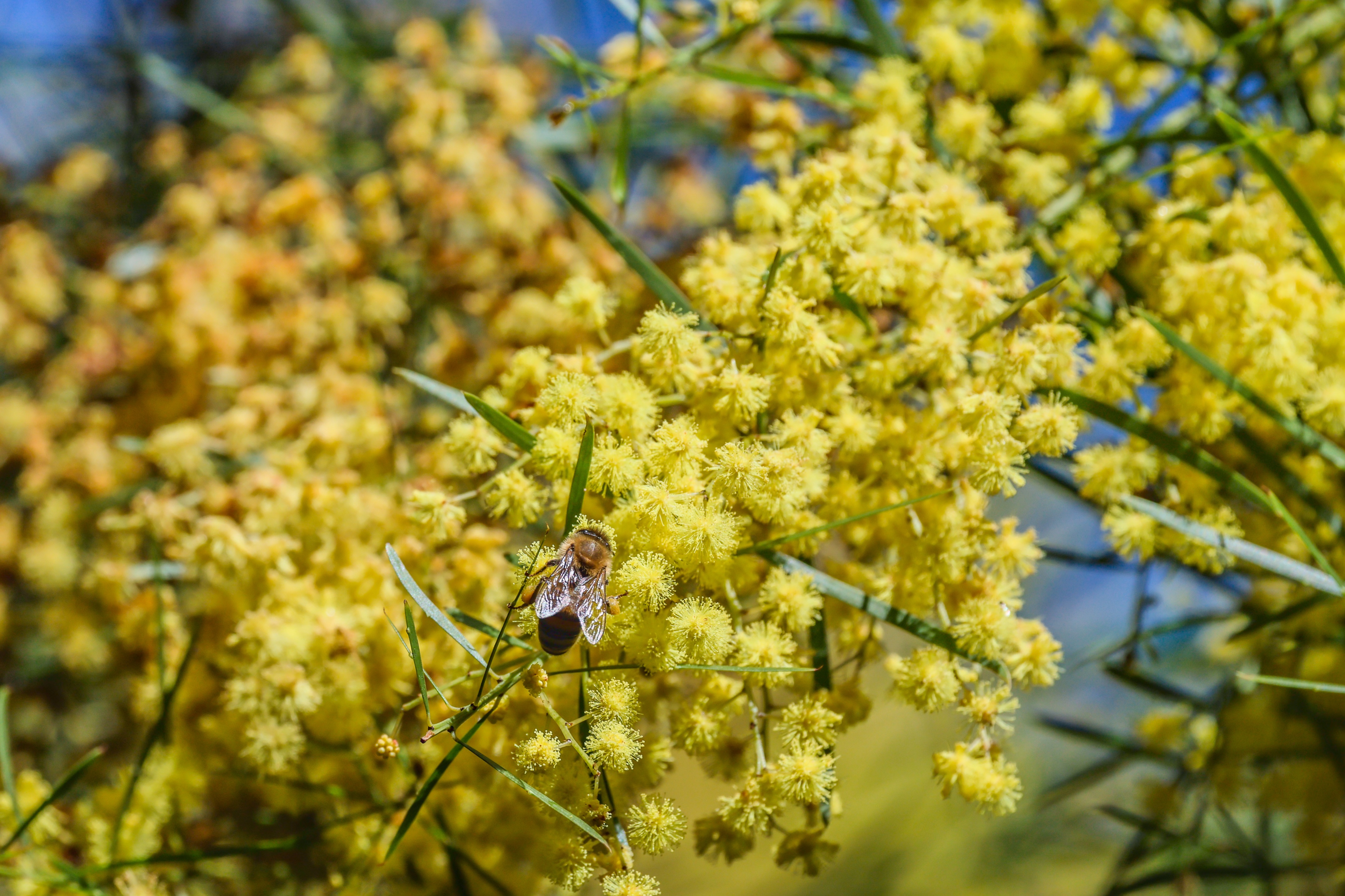






While video quality is also very good, I doubt pro creators will opt for the R5 II – there are other hybrid cameras, like the Panasonic Lumix S5 II or the Sony A7S III that would be better suited for professional videography. Still, if it’s 8K video that you’re after, I think it’s as good as the Nikon Z8 / Z9, if not better. And with better recording times out of the box than its predecessor, the R5 II can be a worthy investment for hybrid work.
It uses the full sensor to shoot 8K/60p and 12-bit RAW footage internally, but there are a few different resolutions and frame rates to shoot from if 8K is overkill for your needs. You can shoot in either DCI (17:9) or UHD (16:9), with a bunch of codecs to choose from. Perhaps the best news for videographers is the addition of Canon’s C-Log 2 custom picture profile. This has, so far, only been available on Canon’s EOS cinema cameras, but it offers better dynamic range and more natural colors compared to C-Log 3, which makes it easier for video creators to color grade and produce more appealing visuals.
There is now no 4GB video recording limit and, during my testing, I had no issues with heat buildup with video clips of 50 seconds to 1-minute in duration when shooting in 4K. the temperature gauge, however, will appear on the display (or EVF), which I found handy, as it's a visual indication of how warm (or hot) the camera is getting with use.
Image stabilization for video and stills is also quite impressive. While I’m not a good videographer at the best of times, I struggled to hold the R5 II steady with the RF 100-500mm f/4.5-7.1L IS USM telephoto lenses at 500mm for durations of over 10 seconds, but found it a little easier to handle at 300mm.
• Image & video quality score: 5 / 5
Should I buy the Canon EOS R5 Mark II?
Buy it if...
You’ve been holding out for a great full-frame high-res camera
Whether you want to upgrade from your Canon EOS 5D Mark IV DSLR or any of the older EOS R-series cameras – or even just keen to change systems – it’s really easy to recommend the R5 II.
You want an easy-to-use pro camera
Its fast and accurate performance aside, the R5 II has very intuitive physical controls and the menu system is simplified, making this pro camera really easy to wrap your head around.
You want a versatile camera for any kind photography
While its in-camera editing features have some caveats, the R5 II will be as comfortable shooting landscapes and nature as it would be in a sports arena or a war zone. It has the chops – and then some – to handle it all, plus even some decent video skills.
Don't buy it if...
You’re a pro video content creator
It might have good video prowess but, if filmmaking is your priority, you might be better off with a camera that was designed specifically for video.
You don’t want to drain your savings
While the R5 II is well priced compared to its predecessor and the competition, I wouldn’t call it ‘affordable’ or ‘cheap’. If money is a constraint, you could consider dropping a sensor size and yet retain high resolution if that was important to you.
You exclusively shoot landscapes or architecture, or do mostly studio work
If you aren’t going to put the R5 II’s speed and accuracy to good use, it might be overkill for your needs. Moreover, some photographers who do more studio work – like portraits or product shots – might be better served with a medium format sensor, and it’s now possible to get one for about the same price or lower.
Also consider
Nikon Z8
In direct competition with the R5 II, the Nikon Z8 is arguably the easiest alternative to recommend. While the physical setup is different to Canon's, and it might lack the new autofocus and in-camera editing features, the Z8 is a superb shooter that offers just as much speed (even more, in fact, if you're willing to forgo some resolution). It even allows you to shoot with a crop (DX) if you want more reach.
Read our full Nikon Z8 review
Sony A7R V
If resolution is important to you, then the 61MP sensor in the A7R V might be just what you're after. While you won't be able to get the speed, you will gain Sony's rather good autofocus system with its own nifty AI features, like knowing exactly what to focus on and where. It doesn't have the video chops as the R5 II or the Z8 listed above, but landscape photographers might prefer this high-res shooter.
Read our in-depth Sony A7R V review
Fujifilm GFX100 II
Again, if resolution is more important and money isn't an issue, the GFX100 II is arguably the most powerful medium format camera on the market. It can handle both stills (102MP shots at up to 8fps) and video (8K/30p) well, although the lens options will be limited if AF speed is important.
Read our full Fujifilm GFX100 II review
How I tested the Canon EOS R5 Mark II
- Tested over a period of three weeks; paired with RF 24-70mm f/2.8L and RF 100-500mm f/4.5-7.1L IS USM lenses
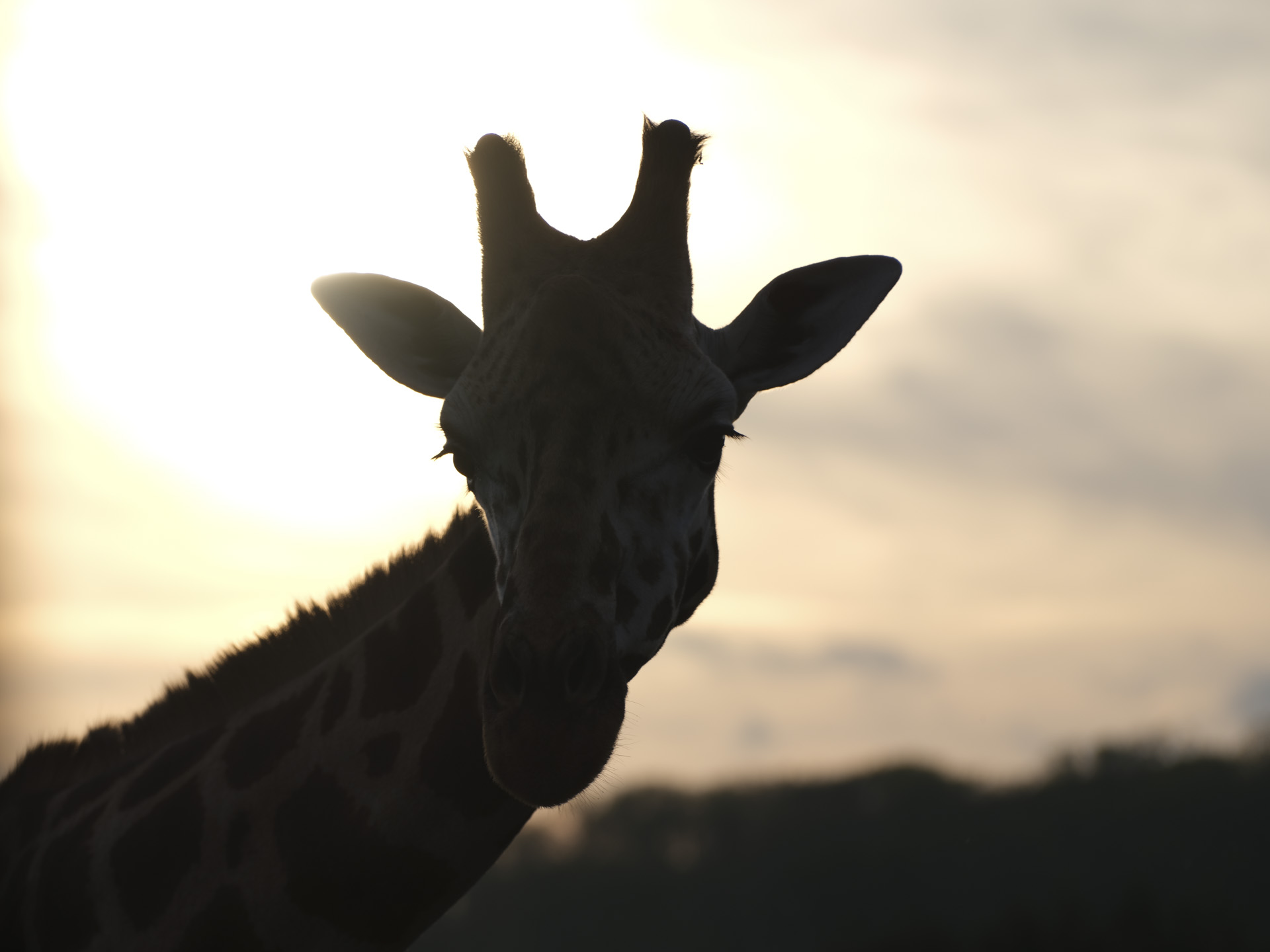
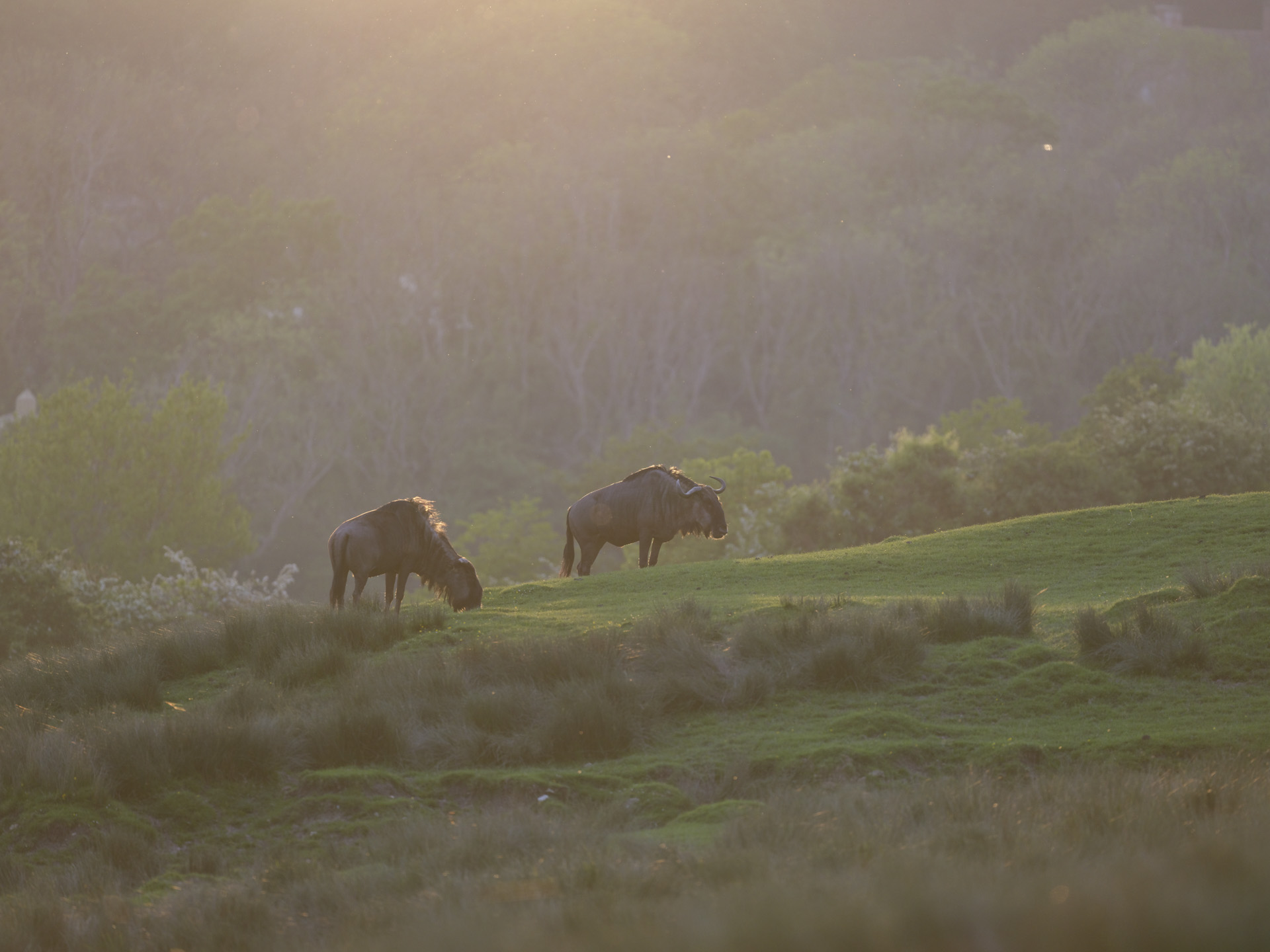
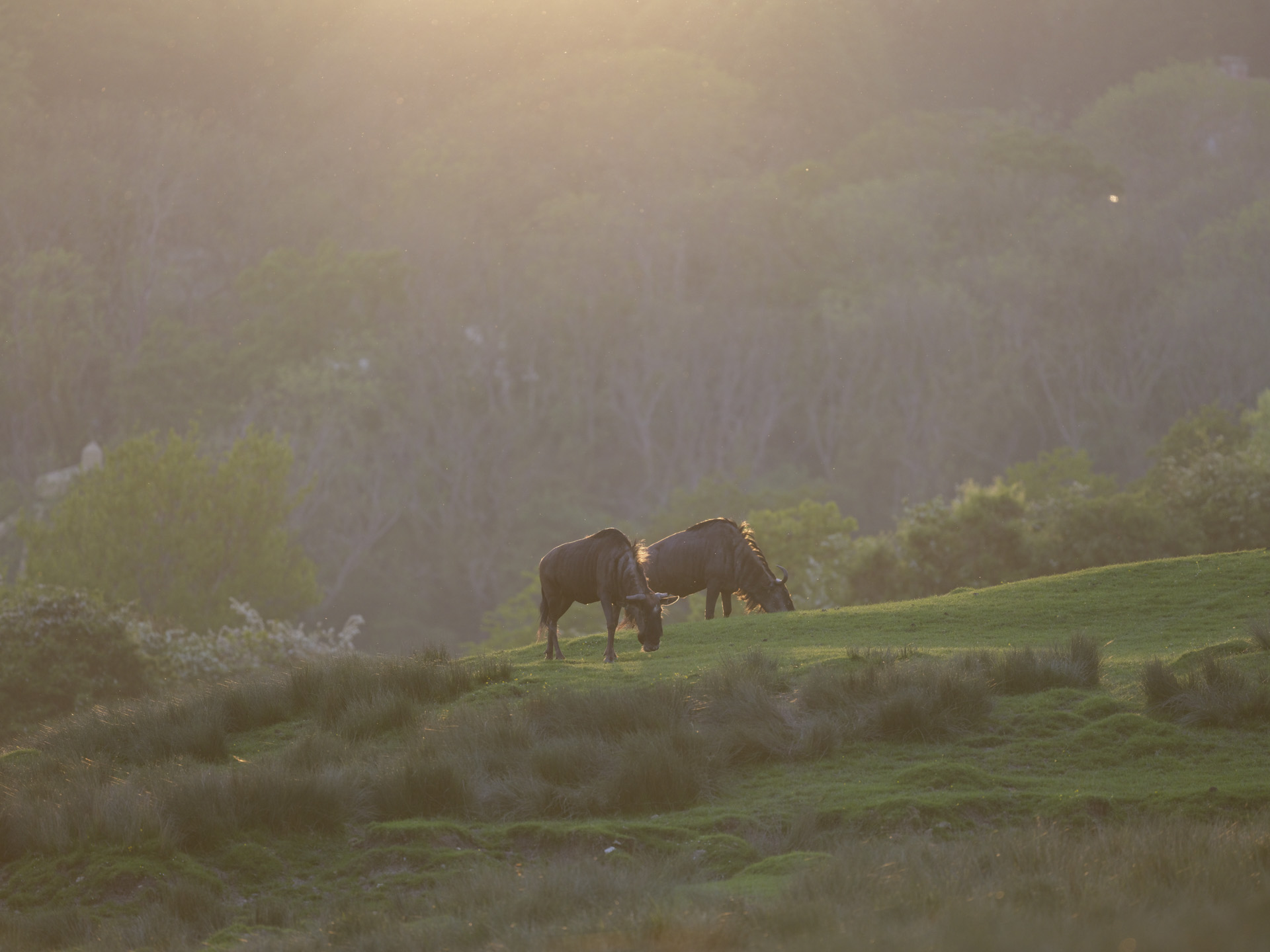
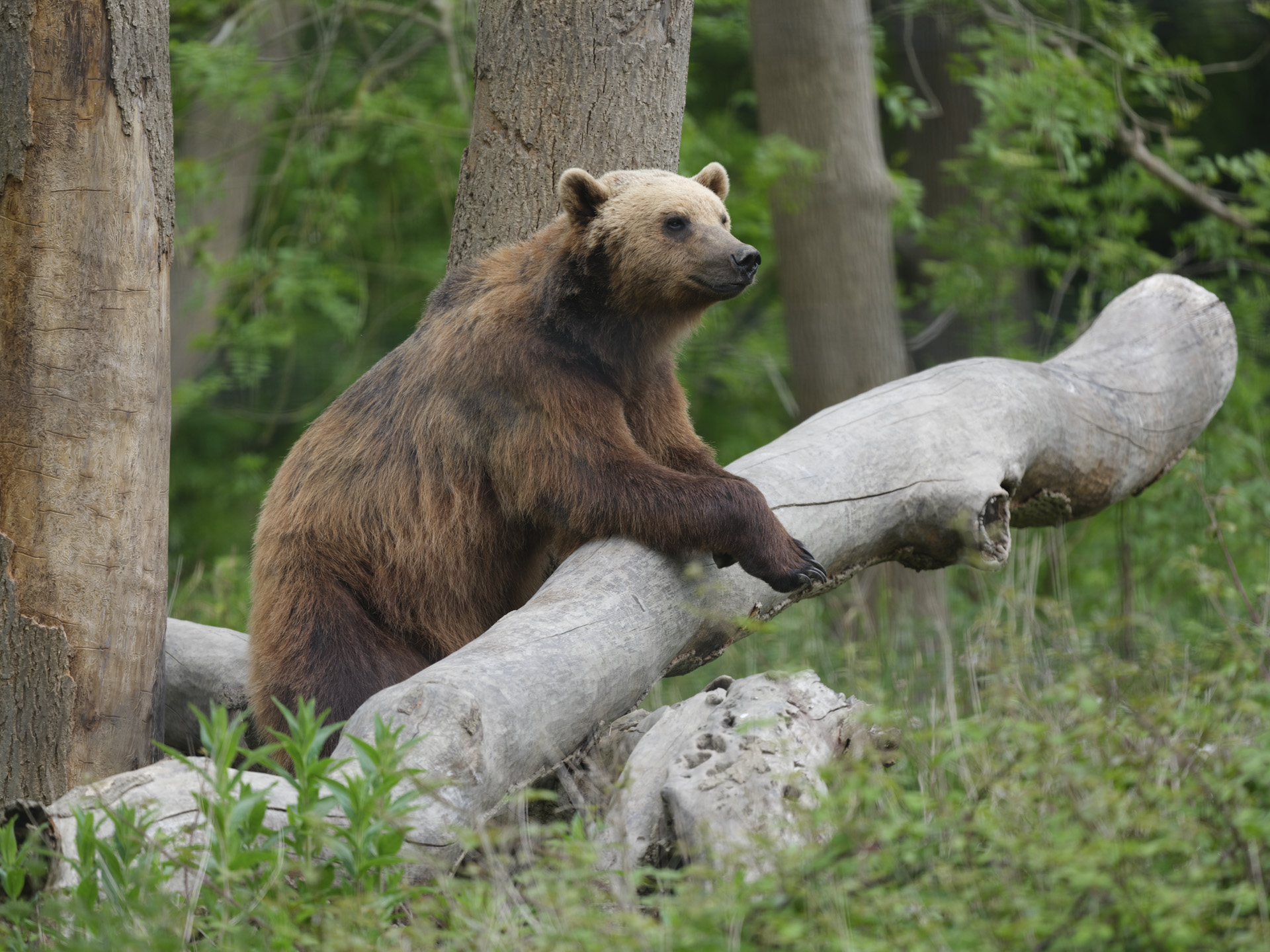
- Used to shoot mostly wildlife with high-speed bursts and Servo AF engaged
- Captured several video clips to test frame rates and resolutions
Having already tested the original R5, and as a current Nikon Z8 user, I am in a unique position to judge the R5 II as it gives me a couple of different points of comparison.
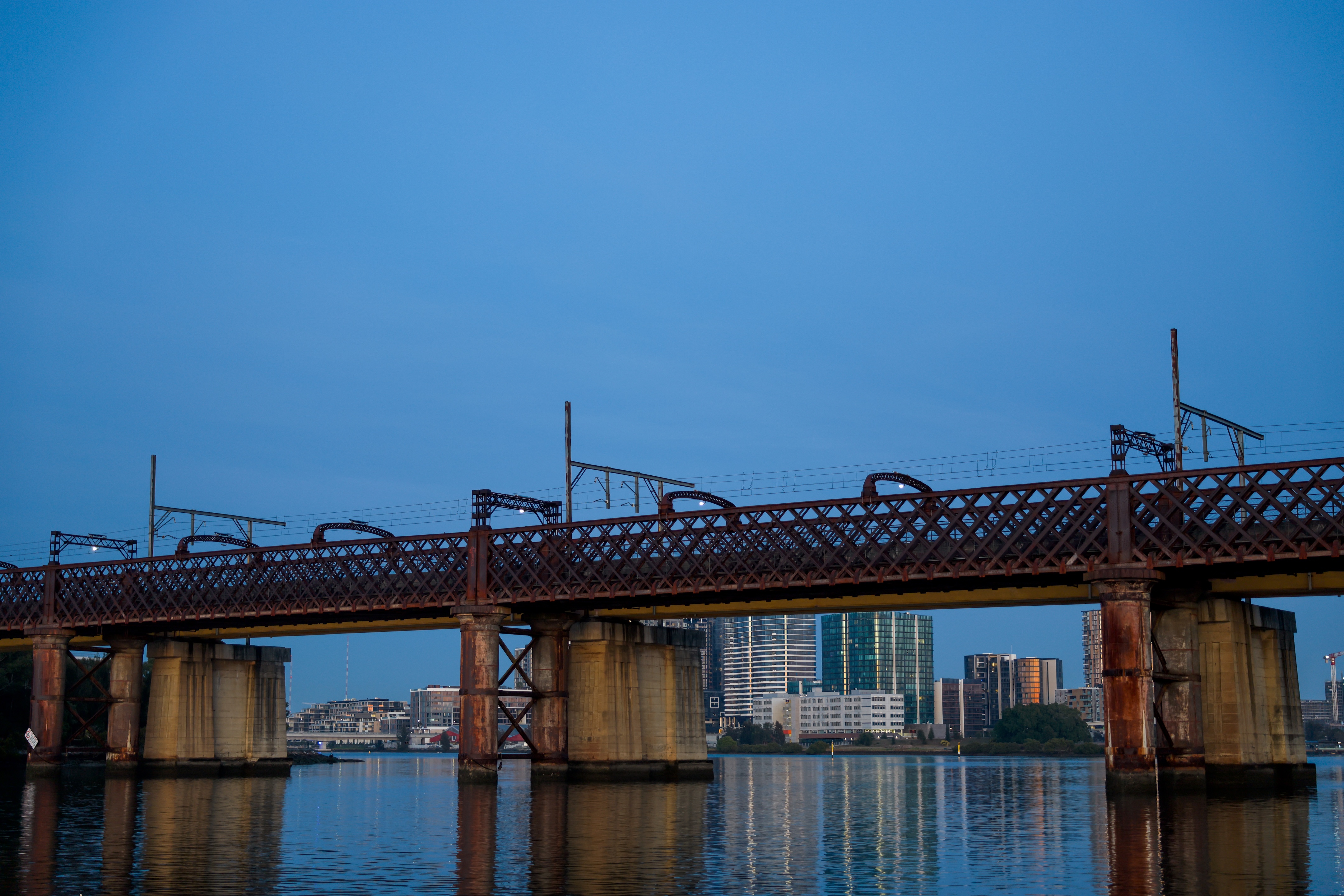
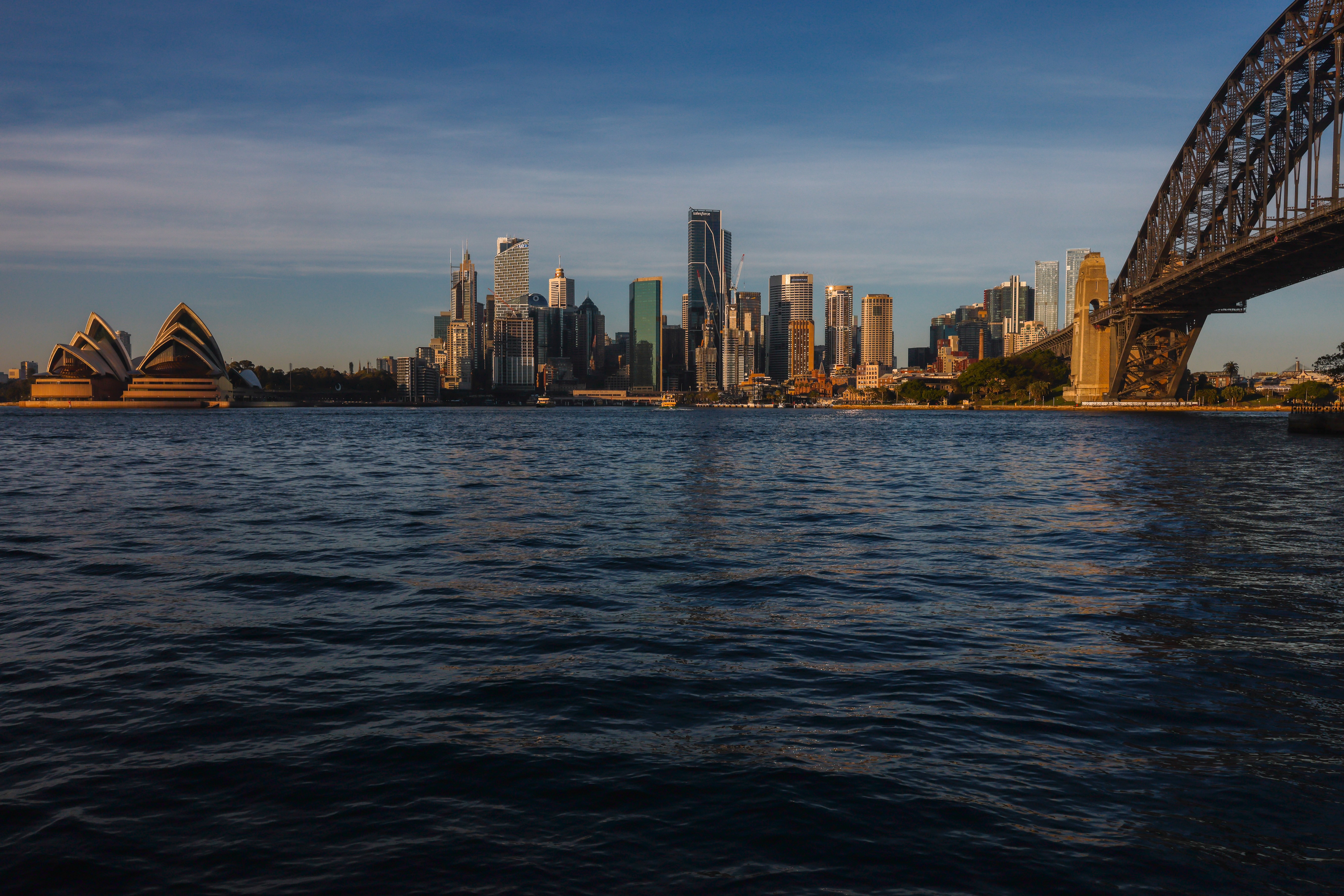
I had the Canon EOS R5 Mark II for about three weeks for this review and did my best to try it out in different scenarios. While there weren't any local sports to capture during my testing period, I pushed the camera's speed limits by capturing birds at a waterbird refuge. I also took the camera on a whale-watching cruise (sadly the humpbacks weren't very active on that day).
This was done with the camera set to capture at 30fps using the electronic shutter and Servo AF engaged. I used some of these images to test the upscaling feature.
The waterbird refuge is also where I did most of the video testing, using the birds as my subjects.
I also captured some urban landscapes as single shots. My testing of the stills including some indoor captures to test the ISO performance, and I used this to see how well the camera's built-in noise reduction feature works.
Read more about how we test
[First reviewed September 2024]