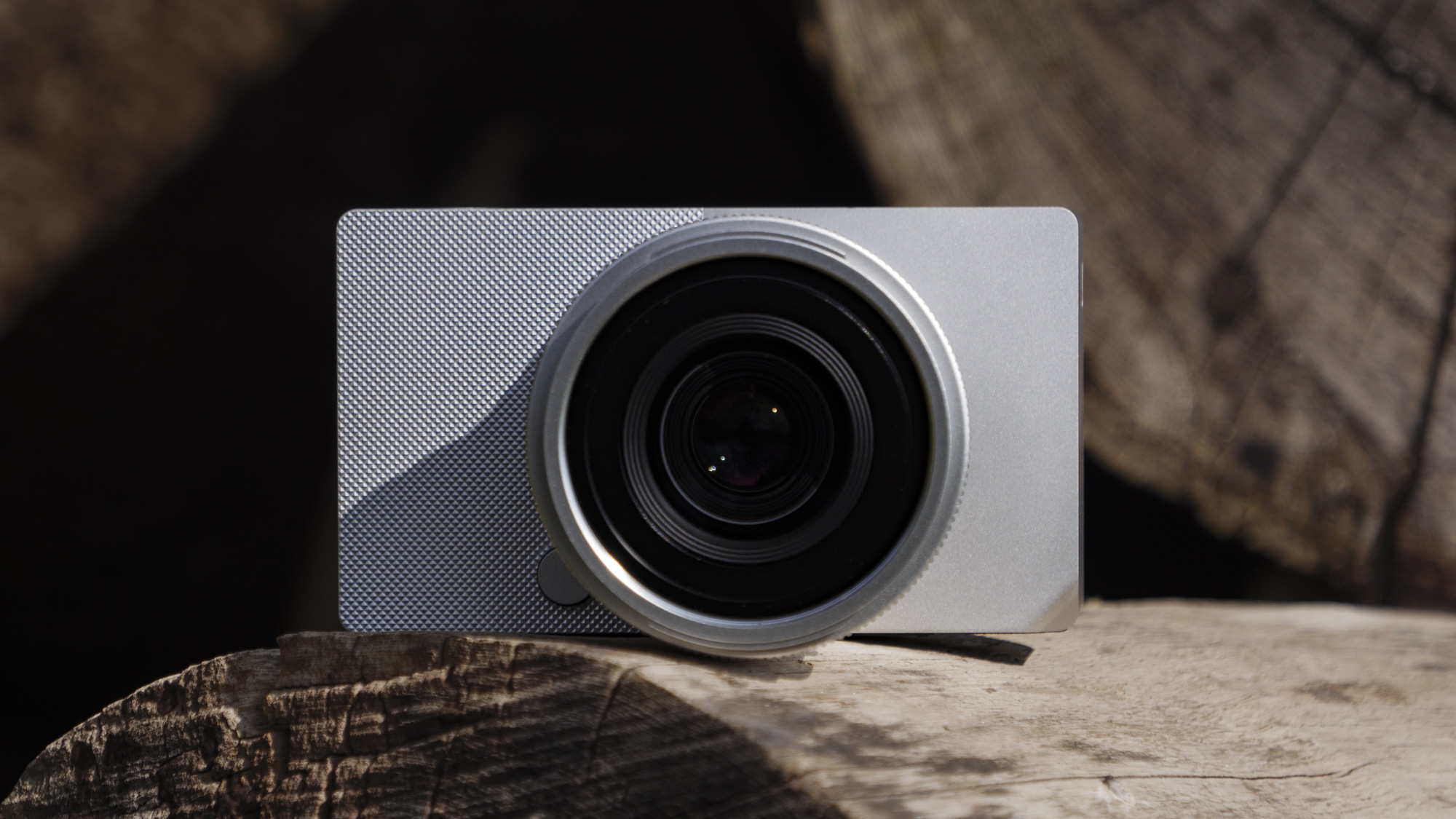
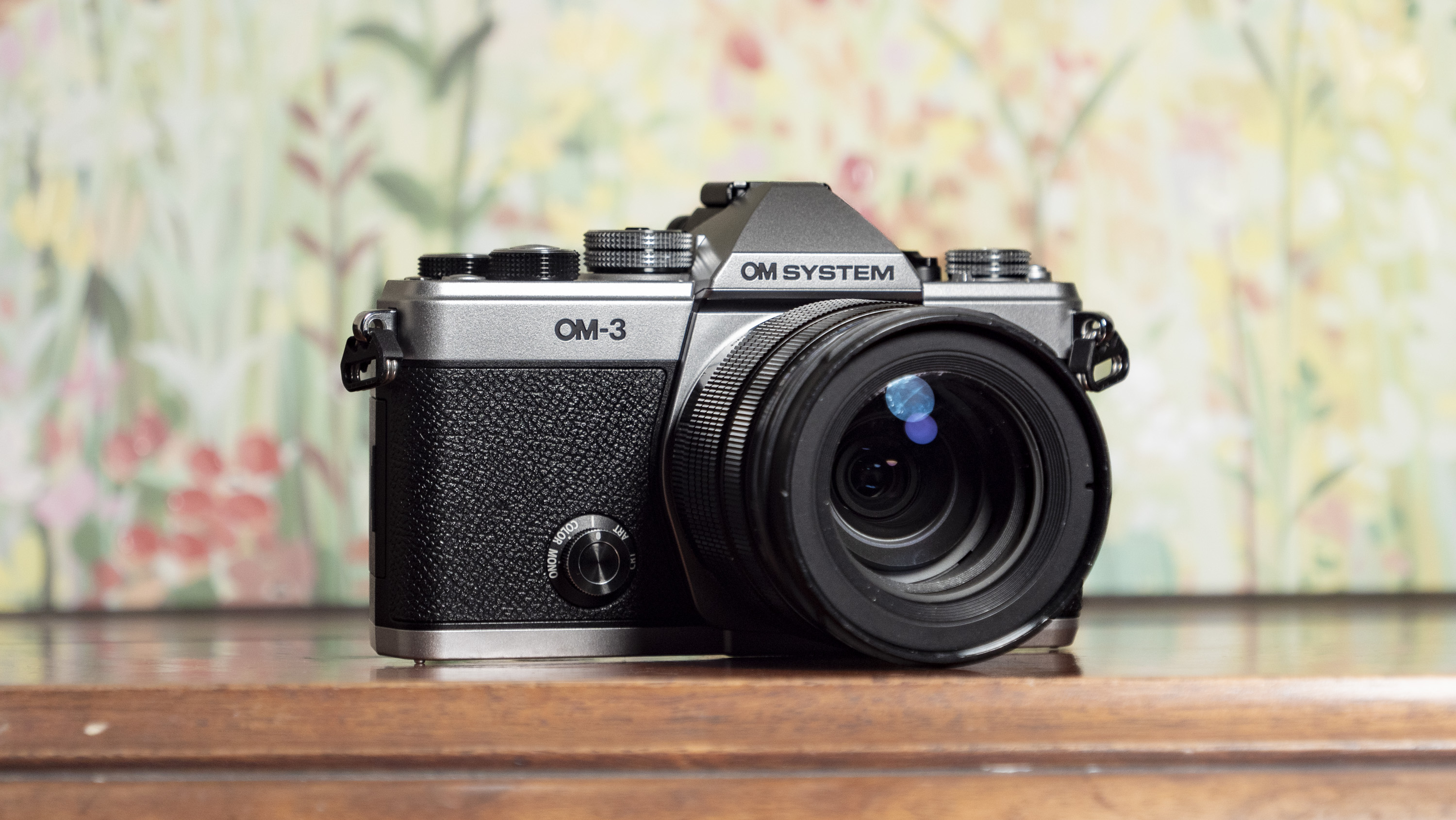
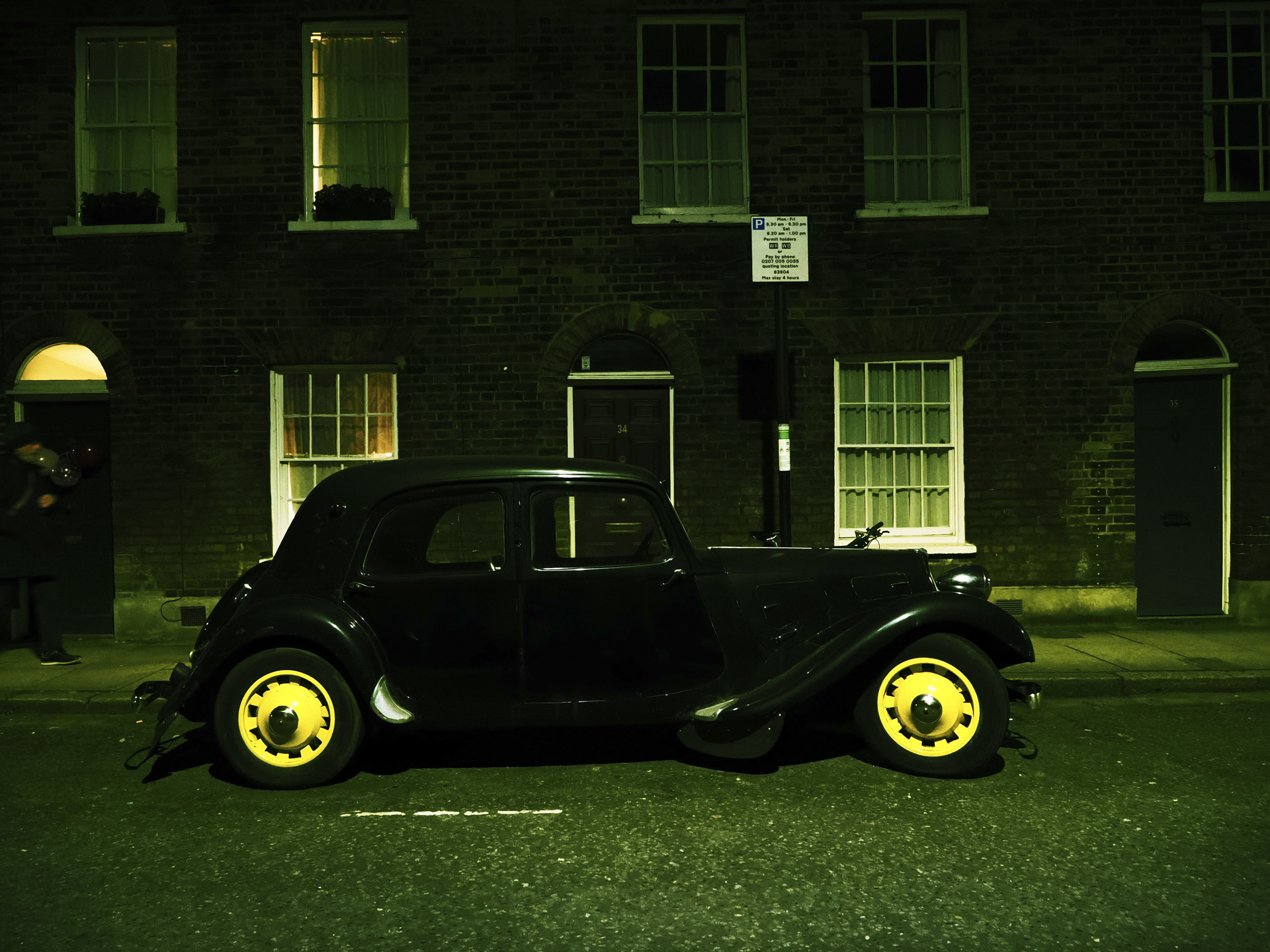
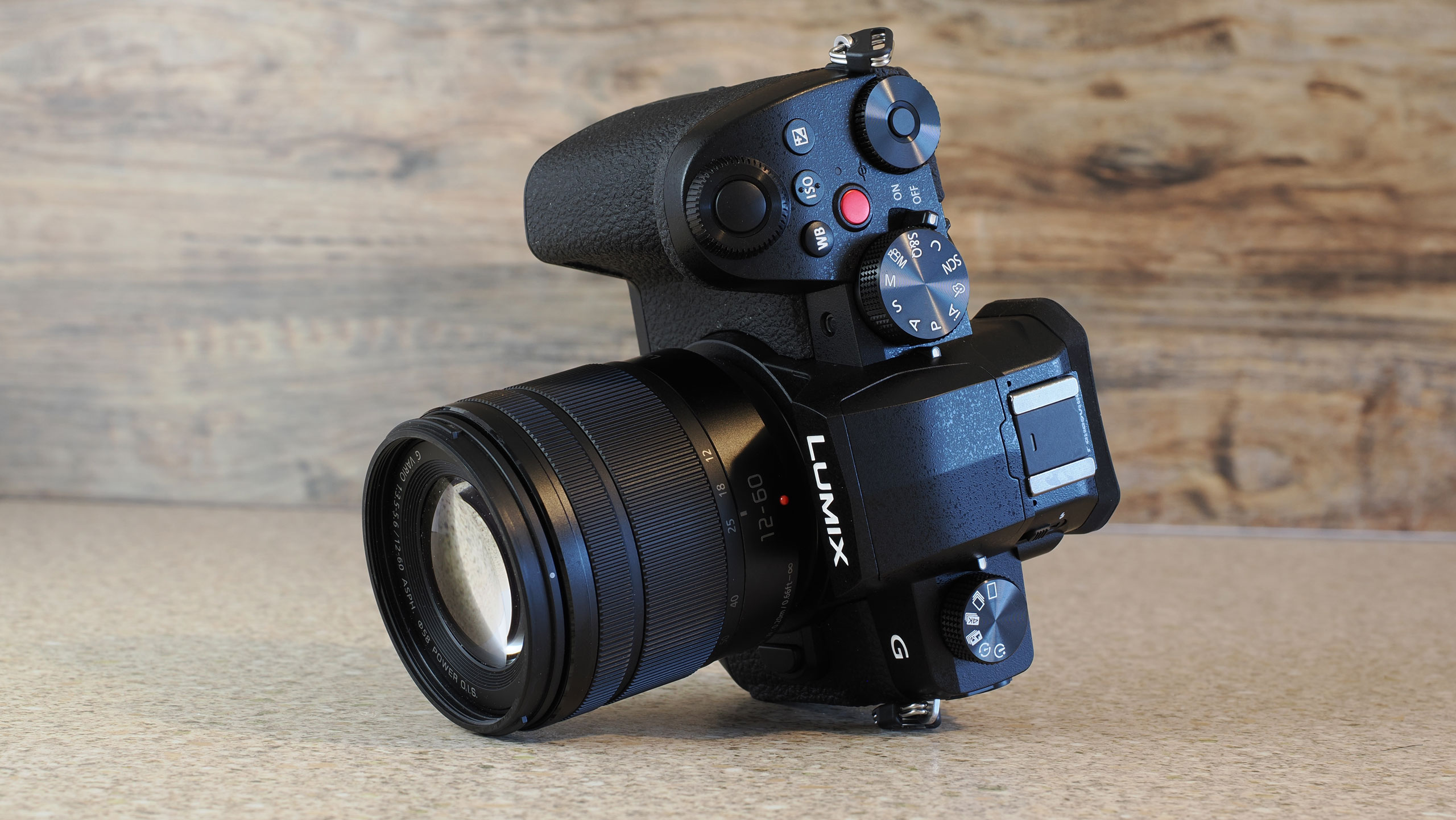
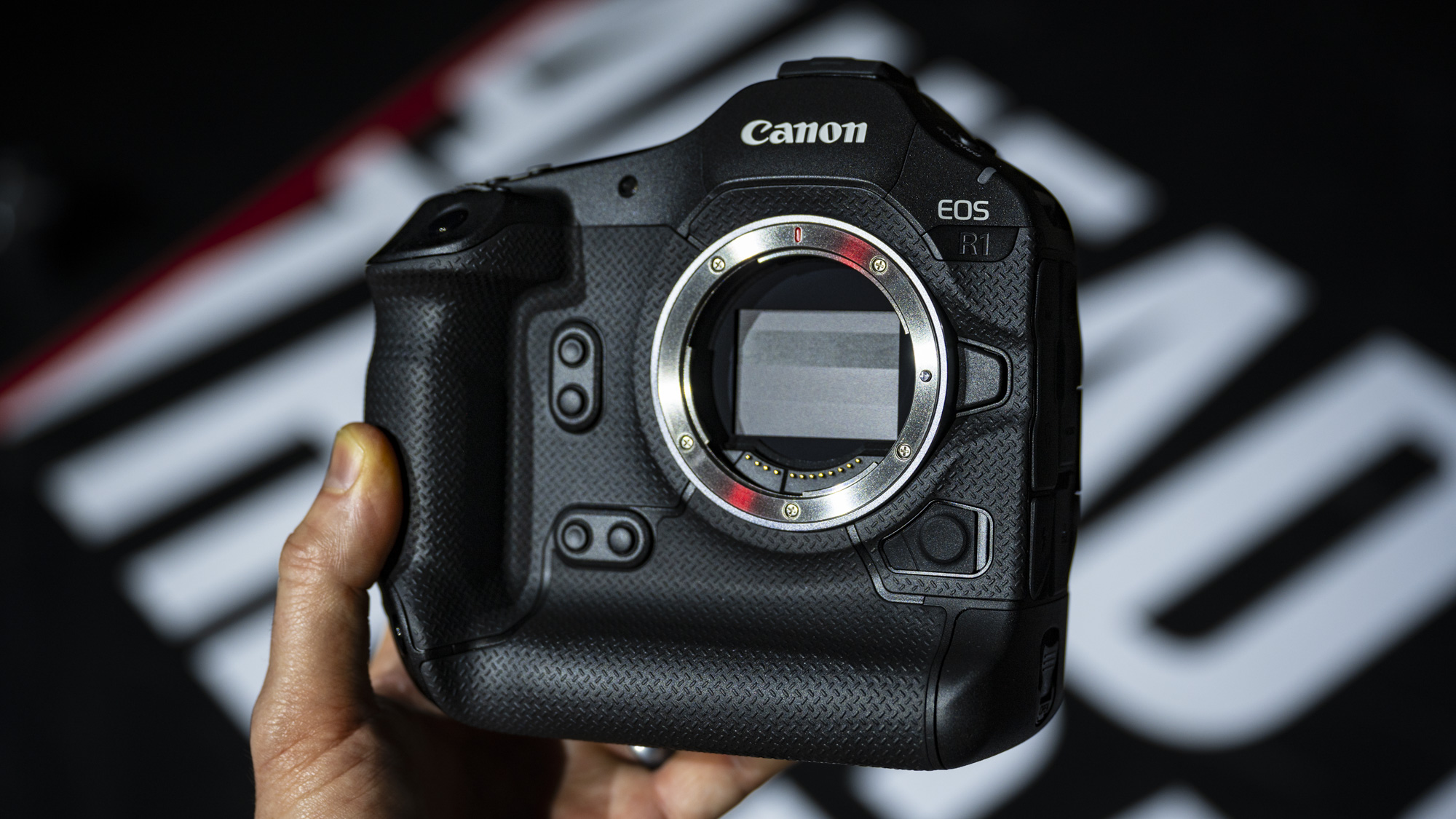
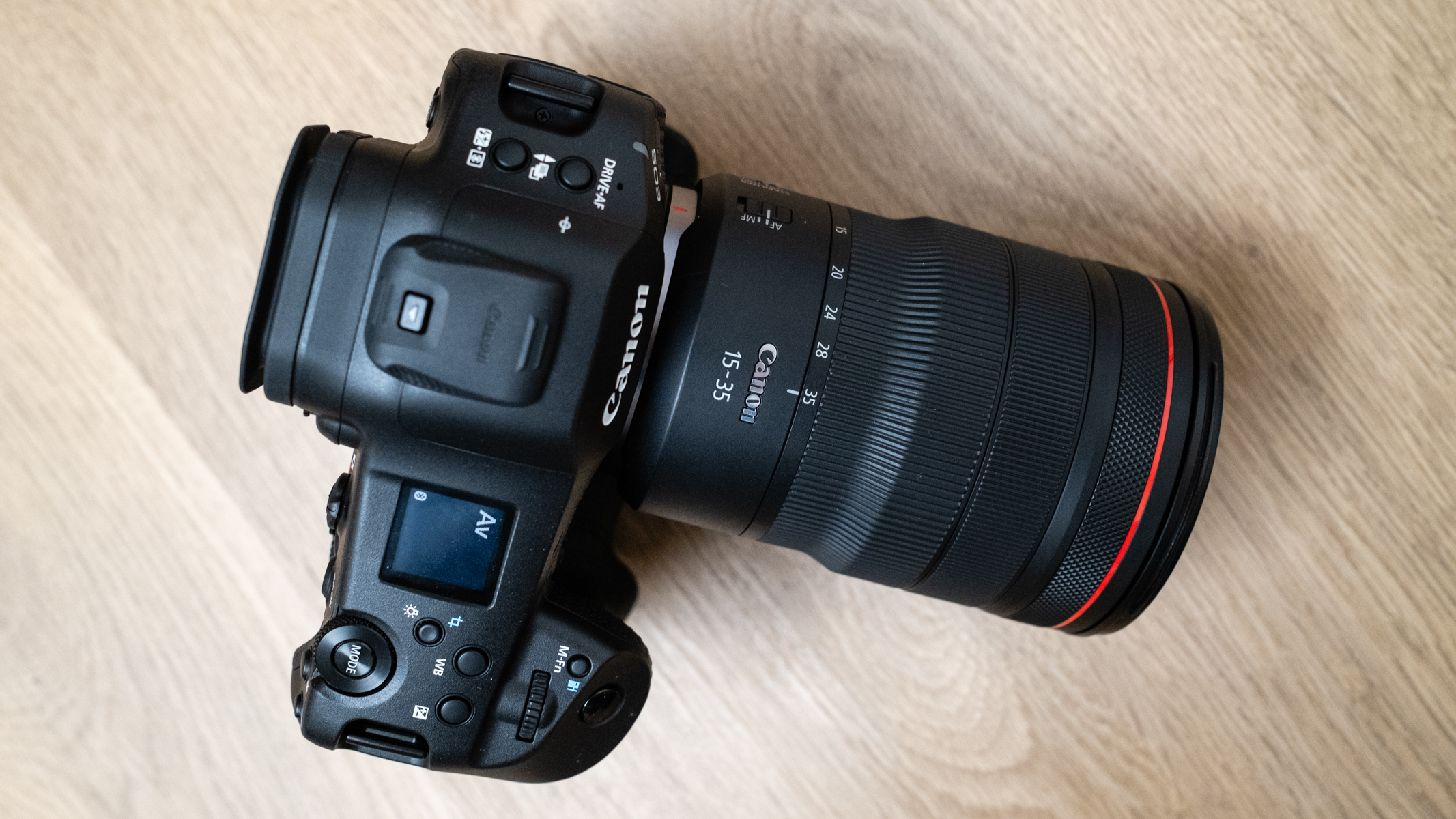
Canon EOS R100: two-minute review
The Canon EOS R100 looks like a pretty dated camera in every sense, and it'll feel alien if you've only used a smartphone camera before. However, don't judge a book by its cover – it actually makes perfect sense for people looking for a cheap camera, especially for the family, and in particular for any budding photographers in the family.
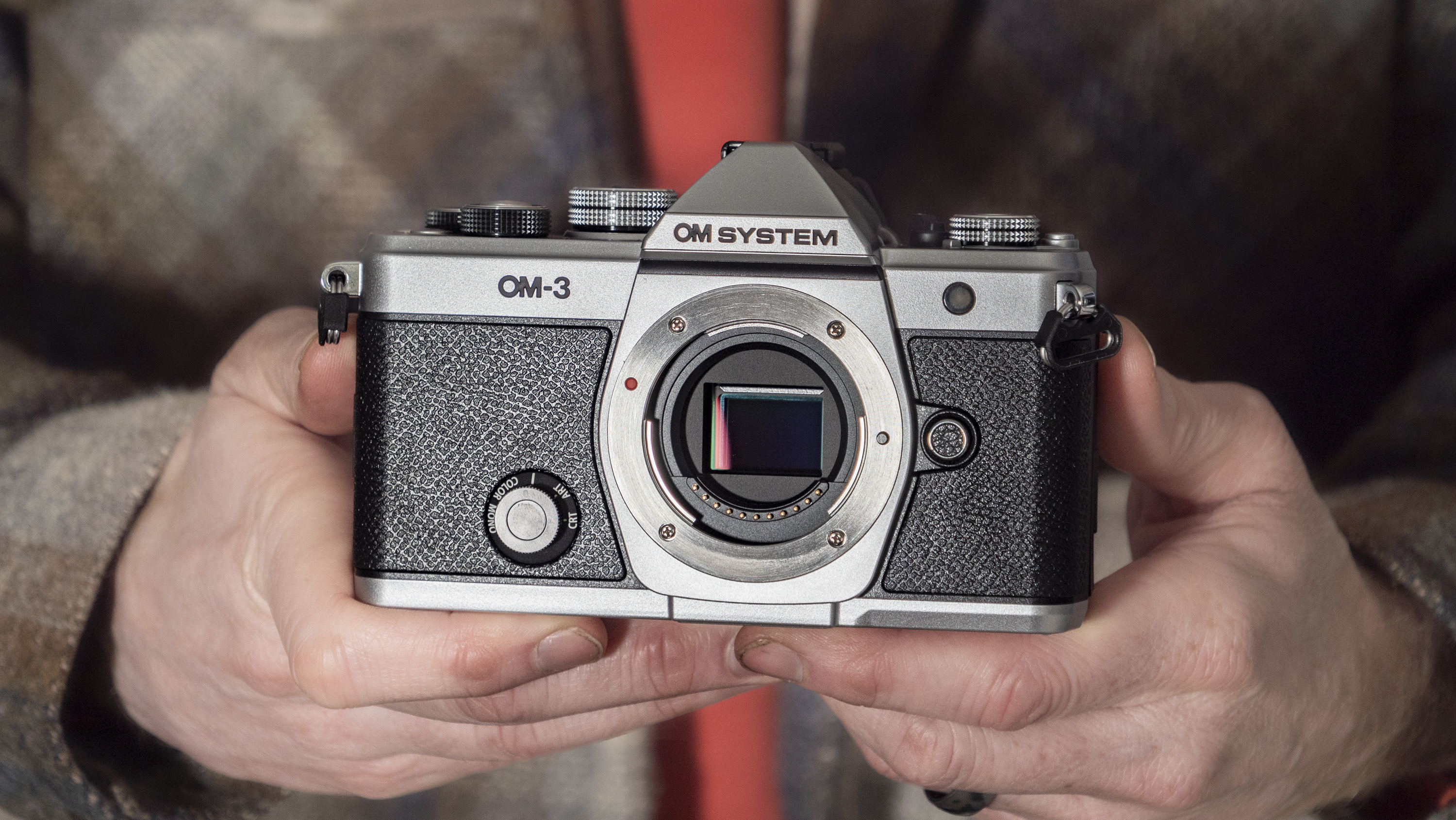
This is the cheapest mirrorless camera that you can buy new, and it's one that utilizes the same 24MP APS-C sensor and reliable dual-pixel autofocus as Canon's pricier models, the EOS R50 and EOS R10.
Naturally there are compromises. The build quality is basic, especially the fixed rear screen, which isn't even touch sensitive, and the video specs are dated too.
However, after using the EOS R100 for many months my family has found it to be an excellent little snapper, and a perfect fit for small hands. Furthermore, I actually think the EOS R100's limitations are its strength, especially for first-time photographers.
With its old-school DSLR-style design, a viewfinder, and a rear screen lacking touch functionality the EOS R100 isn't trying to compete with a smartphone, and this has led my kids to explore what each external control does, and consequently pick up some photography basics.
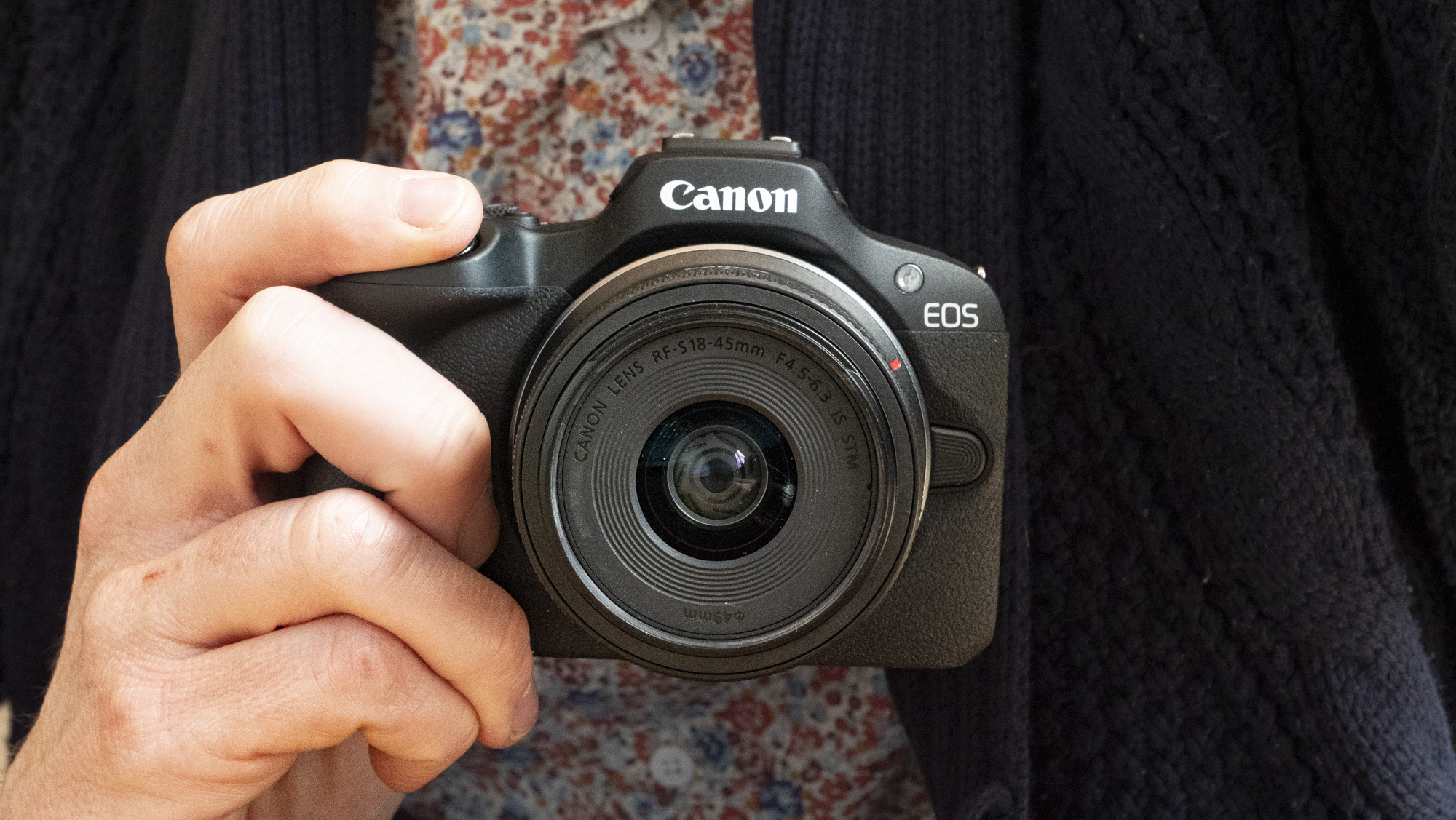

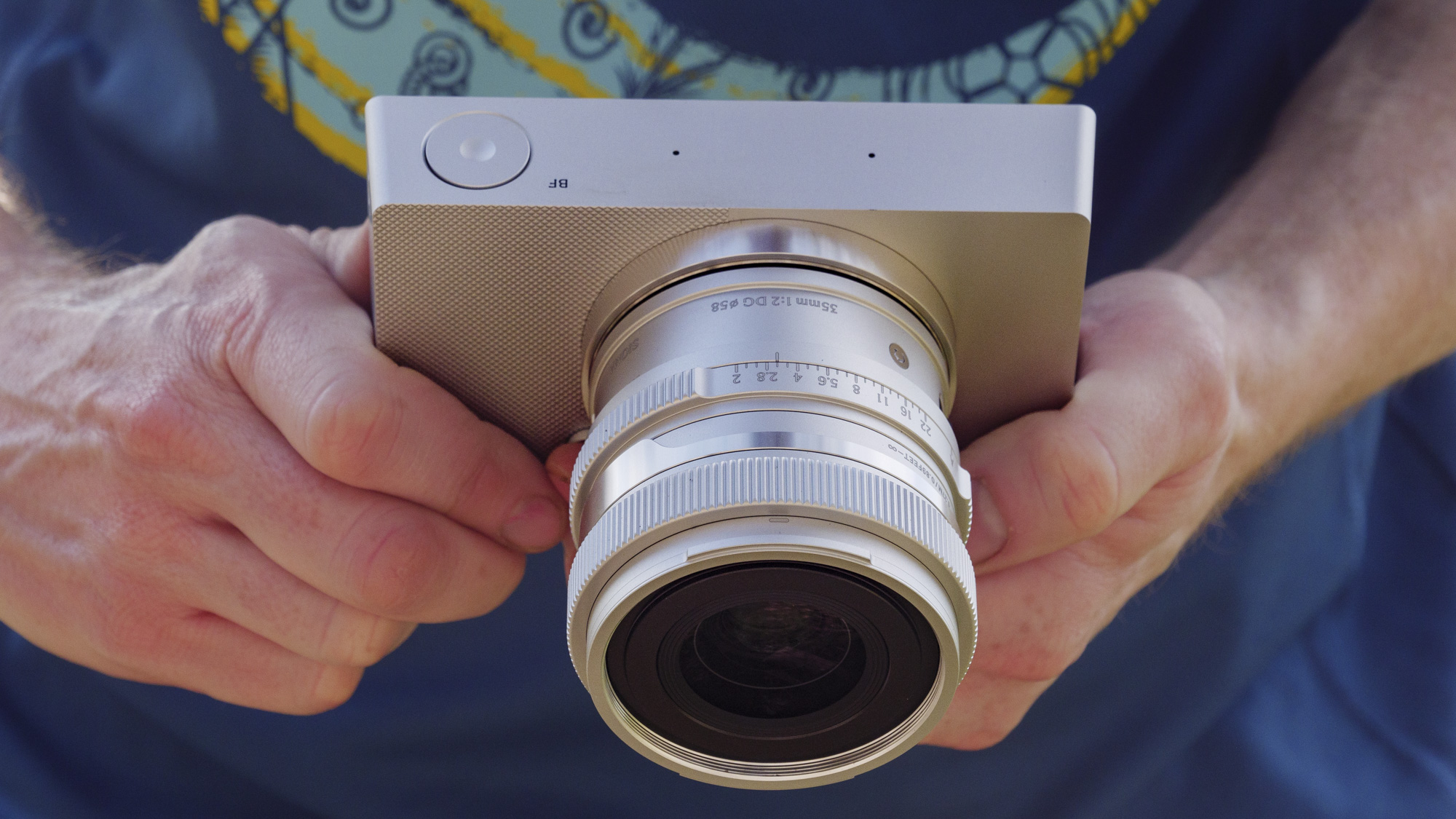
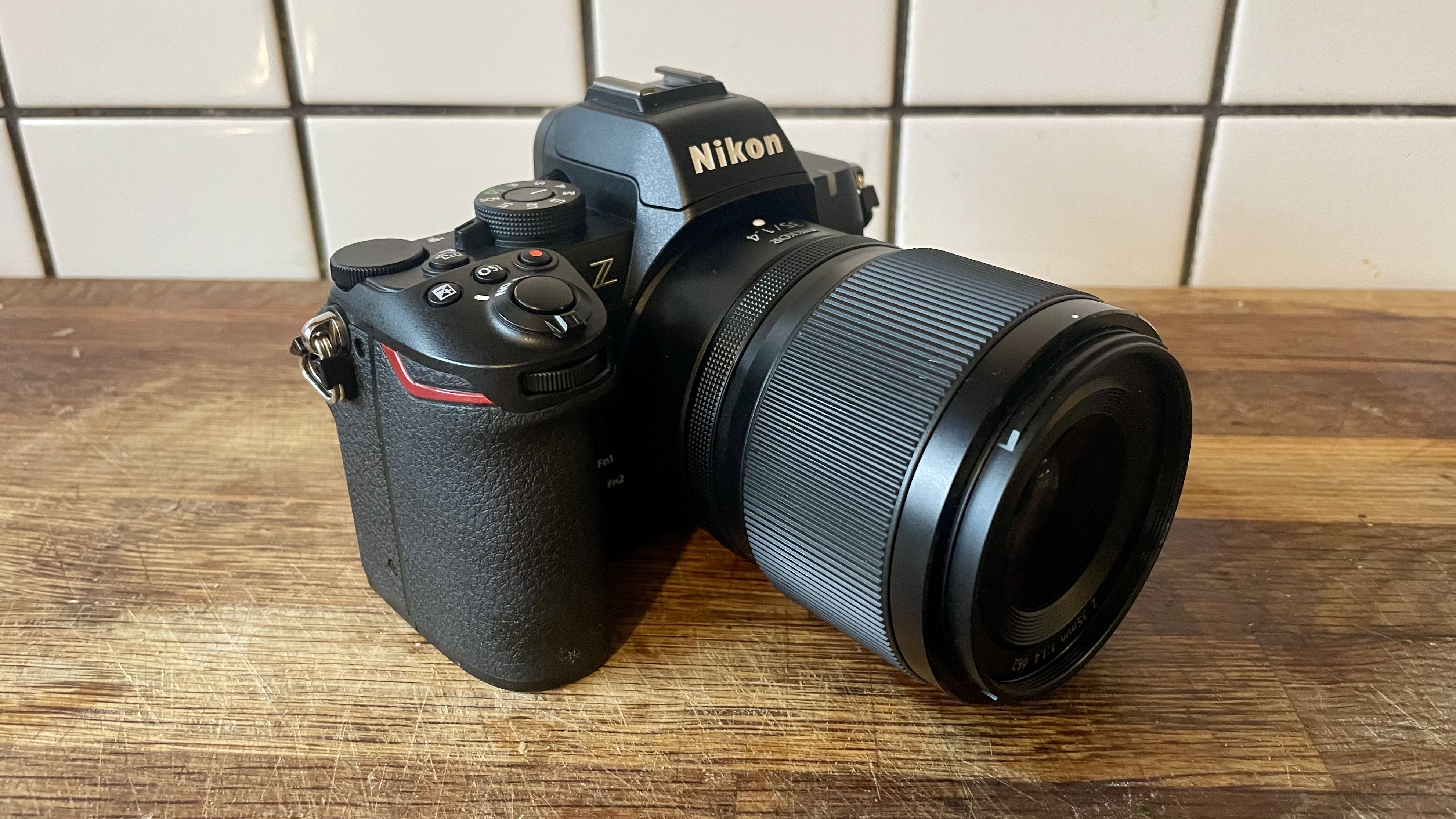
There's been further good news since the EOS R100 launched, too. Canon opened its RF-mount to third parties for manufacturing APS-C lenses, and Sigma has already seized this opportunity, launching RF versions of many of its excellent DC DN Contemporary lenses that enhance the EOS R100's photography chops, where previously lens choice for Canon's mirrorless cameras was severely limited.
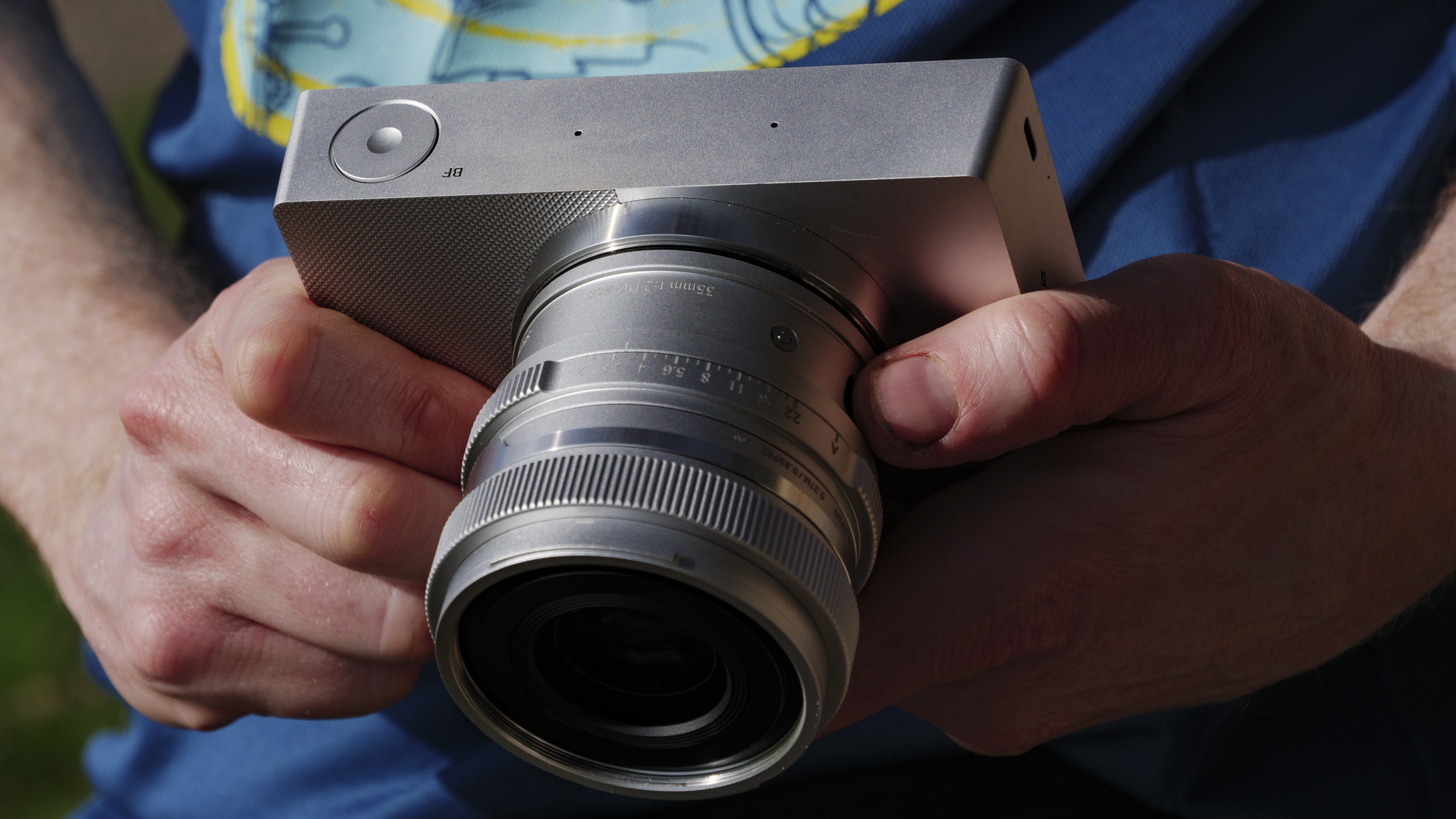
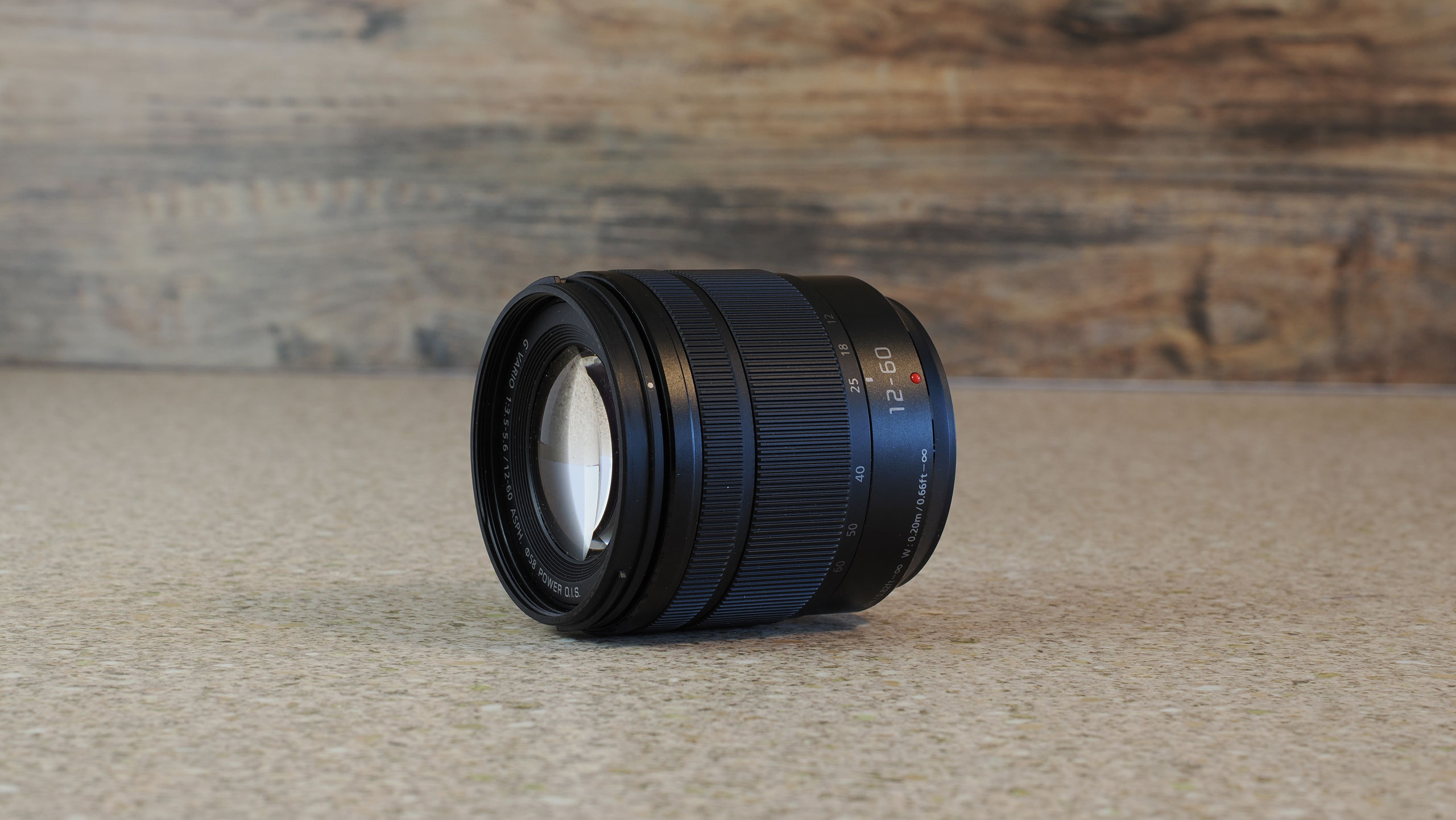
I've particularly enjoyed using a quartet of Sigma f/1.4 prime lenses, which are all compact, lightweight, high quality, and an excellent physical match with the EOS R100 – I'd highly recommend the Sigma 56mm f/1.4 DC DN Contemporary as a second lens after Canon's 18-45mm kit lens, which is pretty basic.
There's a part of me that still can't warm to the EOS R100; but I'm an experienced photographer, and it's not designed for me. It's my family that have really taken to it and actually used it – which is more than I can say for some of the dedicated cheap kids camera we've tested, and pricier alternatives that are complicated to use.
I felt like I can trust my kids with the EOS R100, and they've taken some excellent photos with it, taking the experience to another level by (easily) printing some of their favorite shots using a low-cost Canon Selphy printer. It's this sort of positive engagement with creative tech that I've always hoped my kids would have.
Canon EOS R100: price and release date
- The Canon EOS R100 and 18-45mm kit lens launched for $599 / £669 / AU$1,099
- That bundle now sells for as little as $350 / £410 / AU$800
- It's available body-only too, and in a twin lens kit with the 18-45mm and 55-210mm lenses
I often have friends asking me to recommend a first camera for their young kids / tweens, with a budget around $500 / £500, and naturally they'd rather buy new. That leaves few other options besides the EOS R100.
And that's exactly the point of this beginner mirrorless camera. The design is stripped back, it has basic build quality and some of Canon's earliest mirrorless tech, and it's mass produced, readily available, and sold on the cheap. If general photography is your intended use and you don't need flagship power, the EOS R100 still holds up well today.
The camera was launched in May 2023, and with the 18-45mm kit lens it cost $599 / £669 / AU$1,099. However, since then I've seen some incredibly good deals, especially in the US during Black Friday 2024 and other seasonal sales, during which time the camera and lens price fell to as low as $350 / £410 / AU$800. It costs even less body-only – it's quite simply the cheapest mirrorless camera you can buy new.
- Price score: 5/5
Canon EOS R100: specs
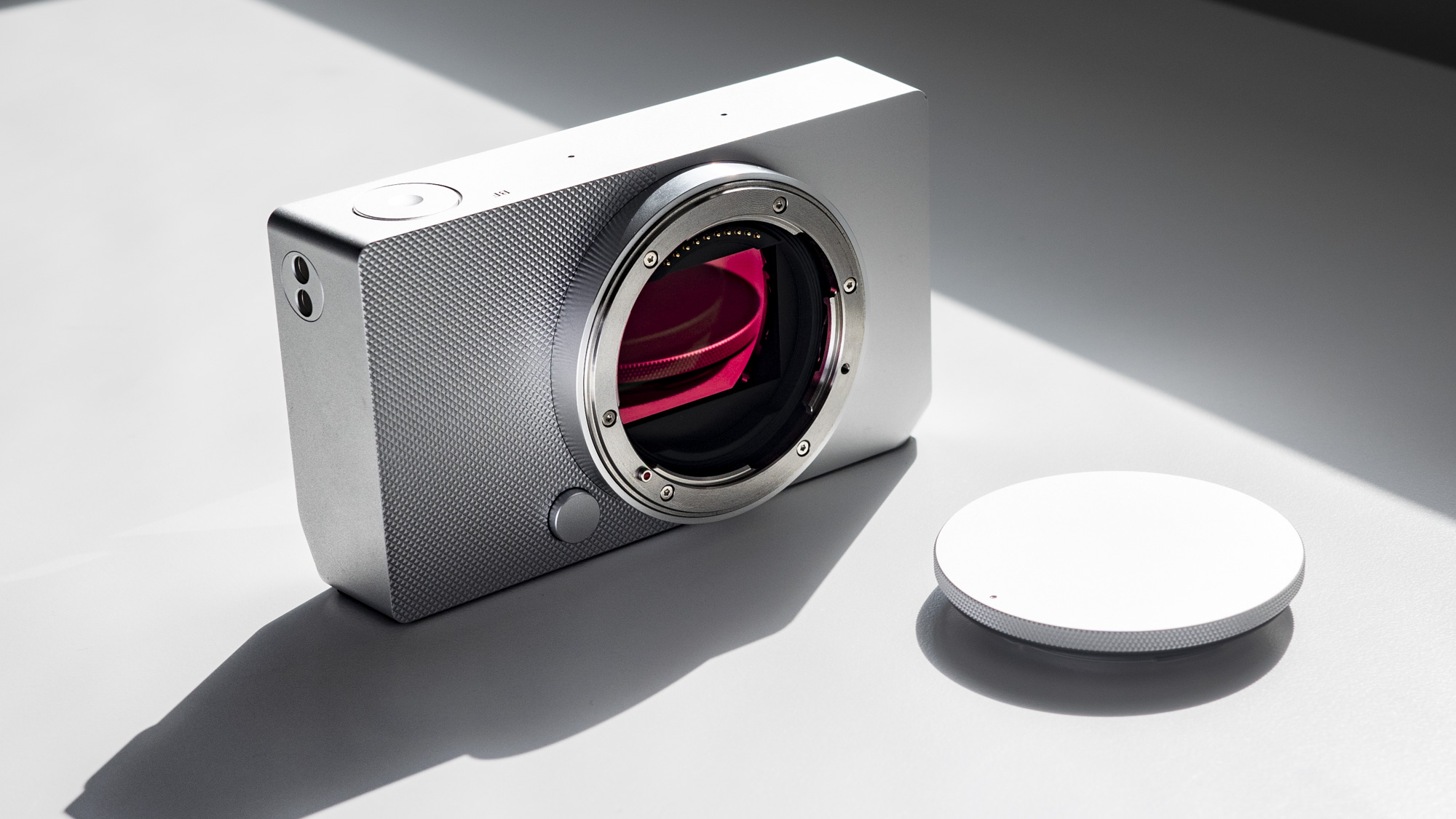
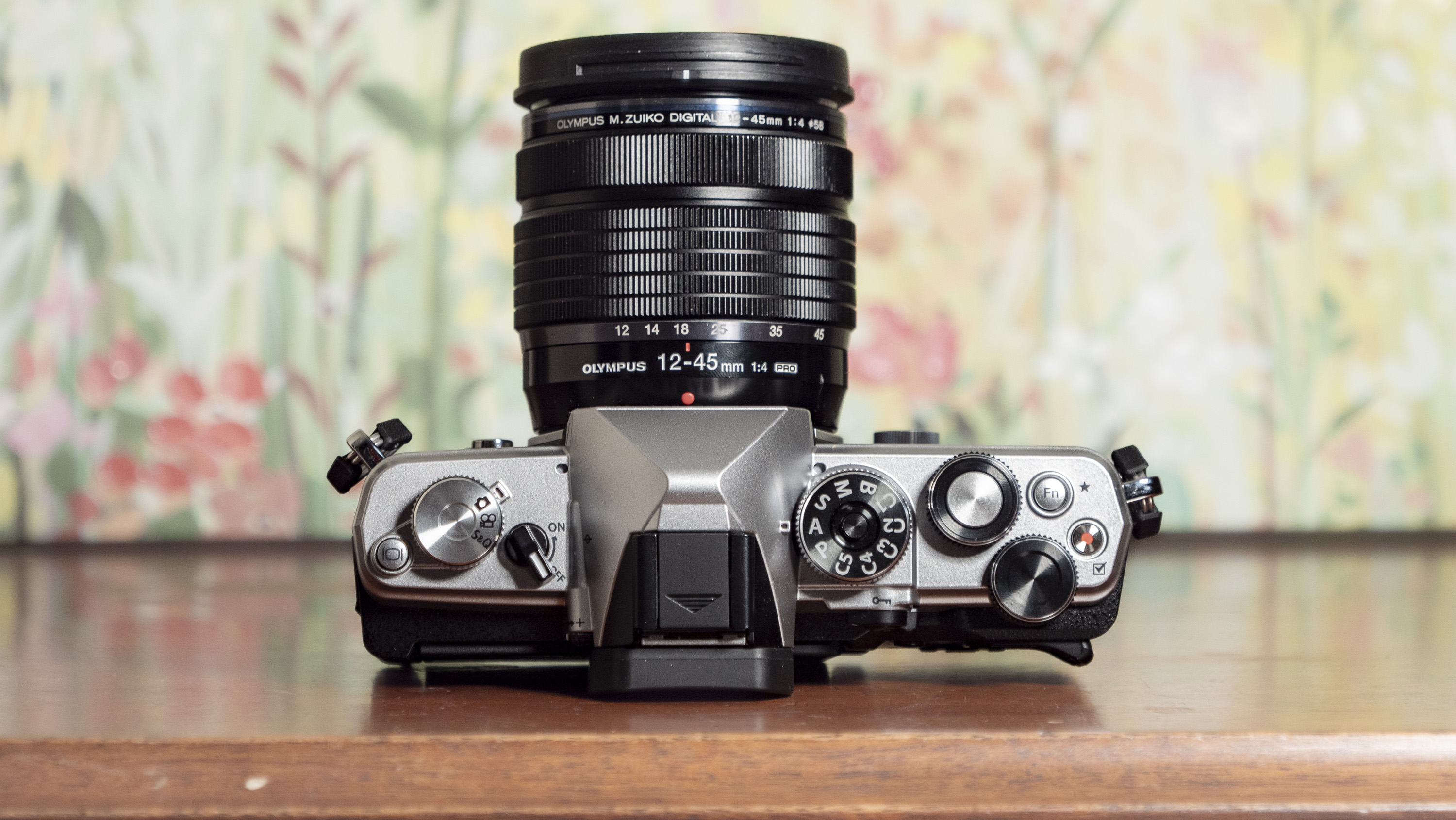
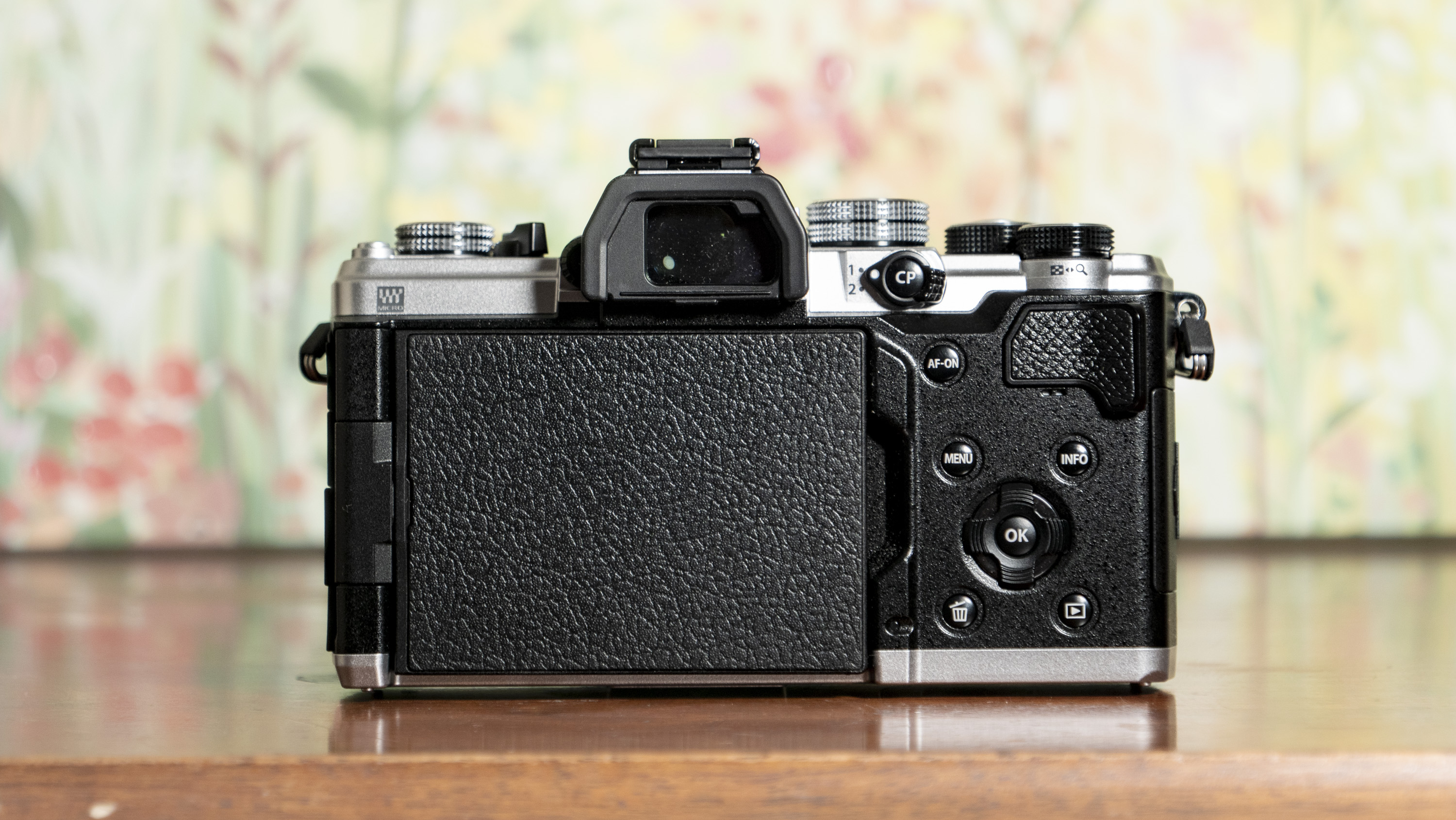
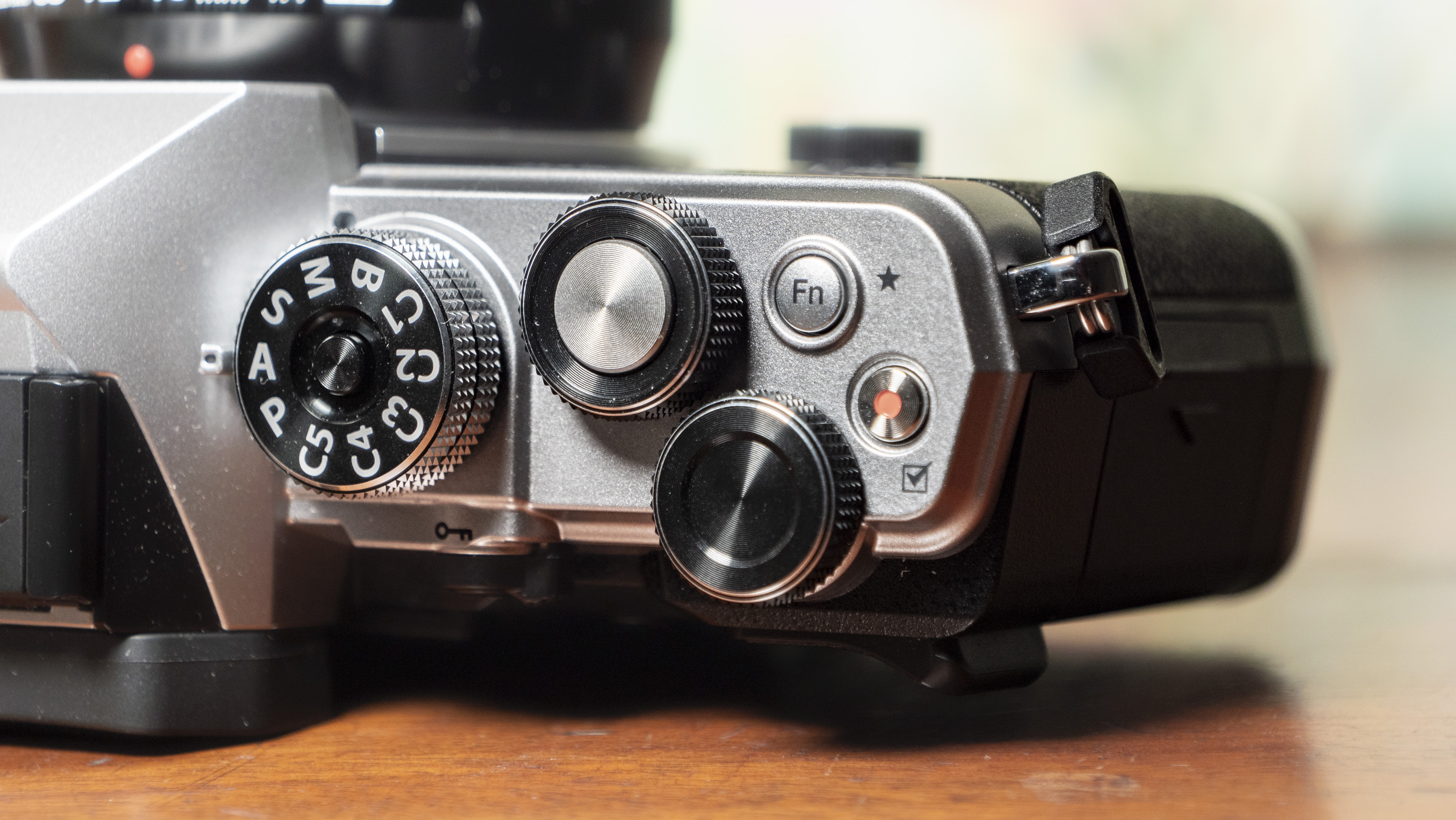
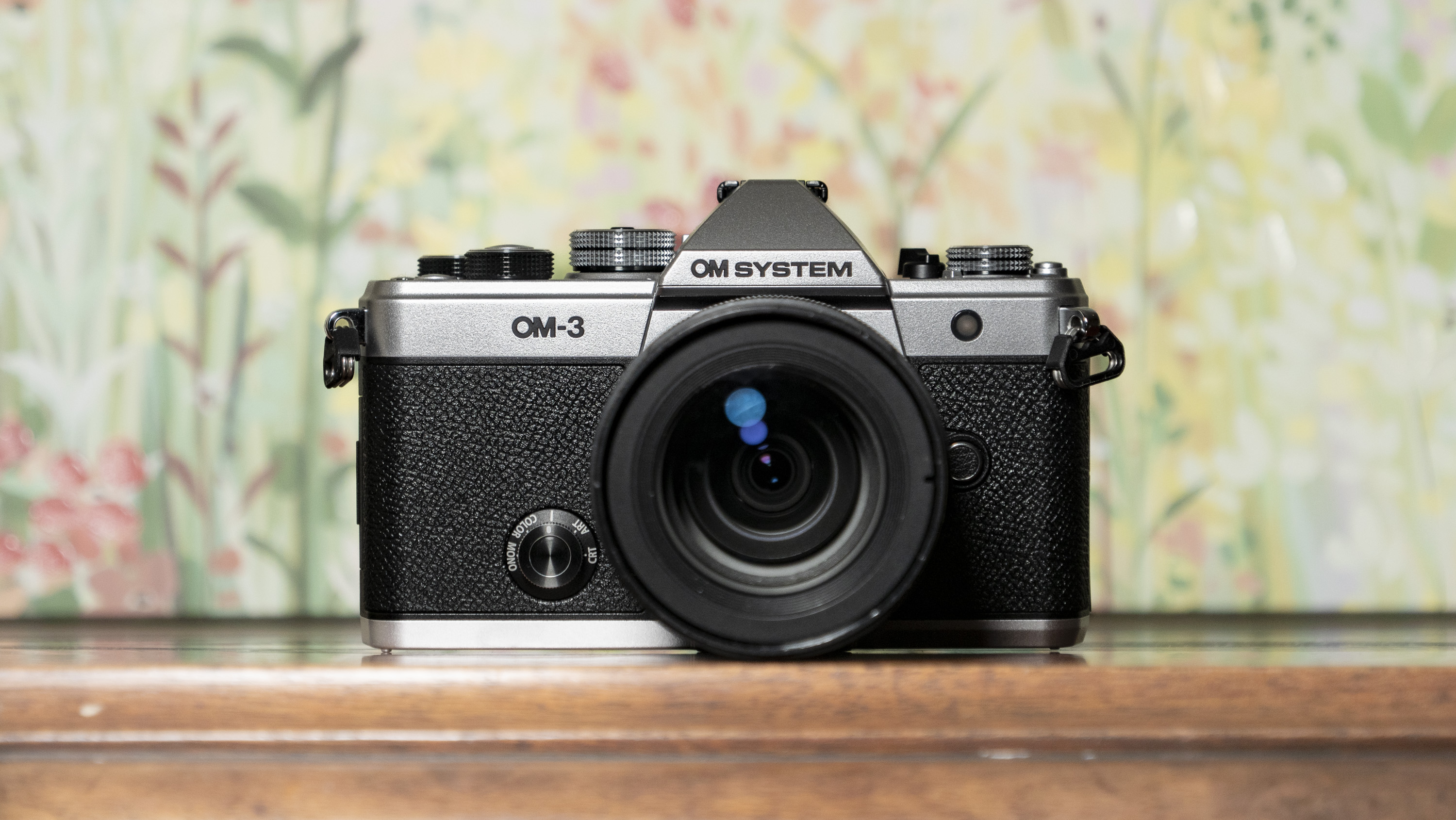
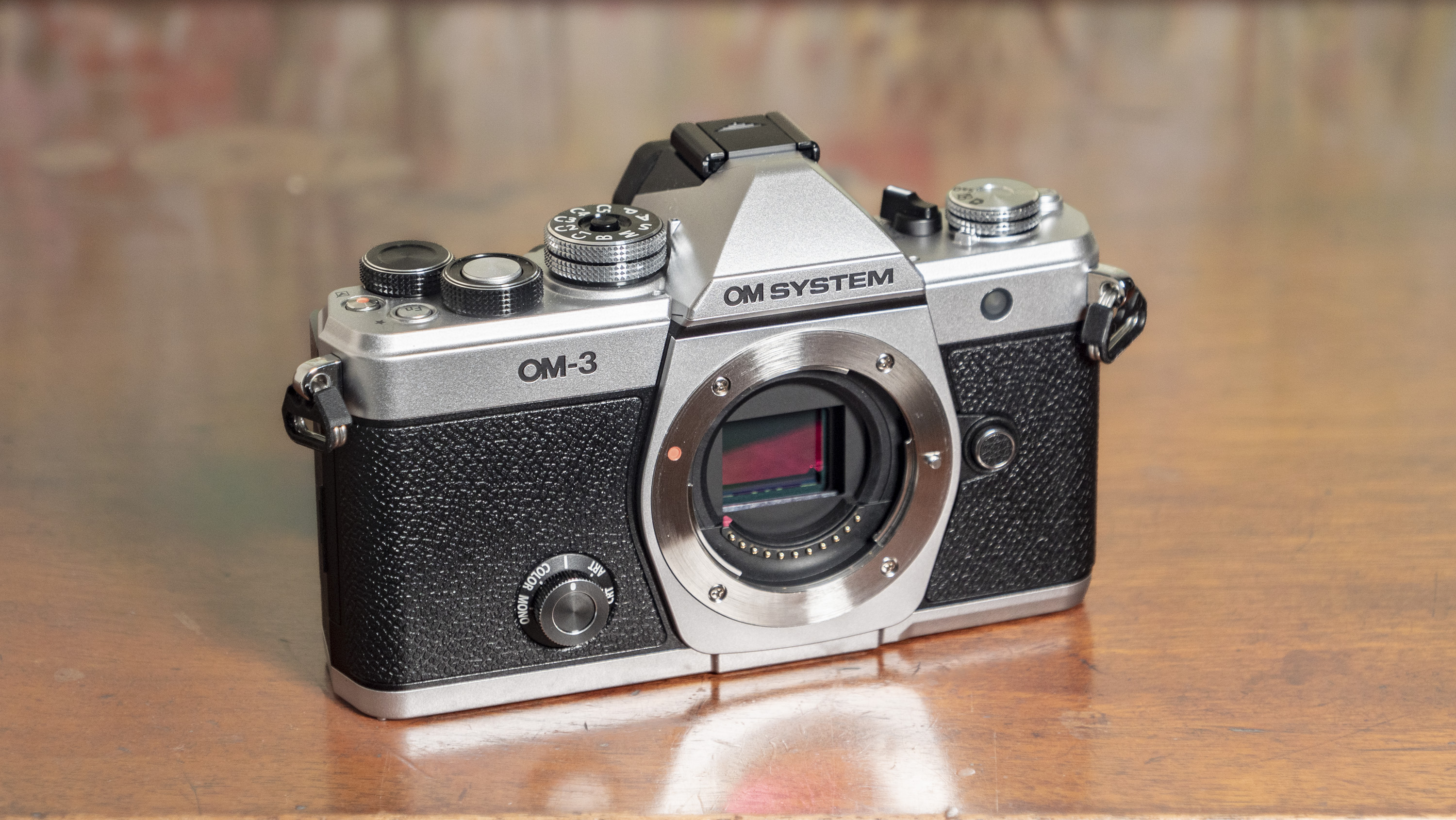
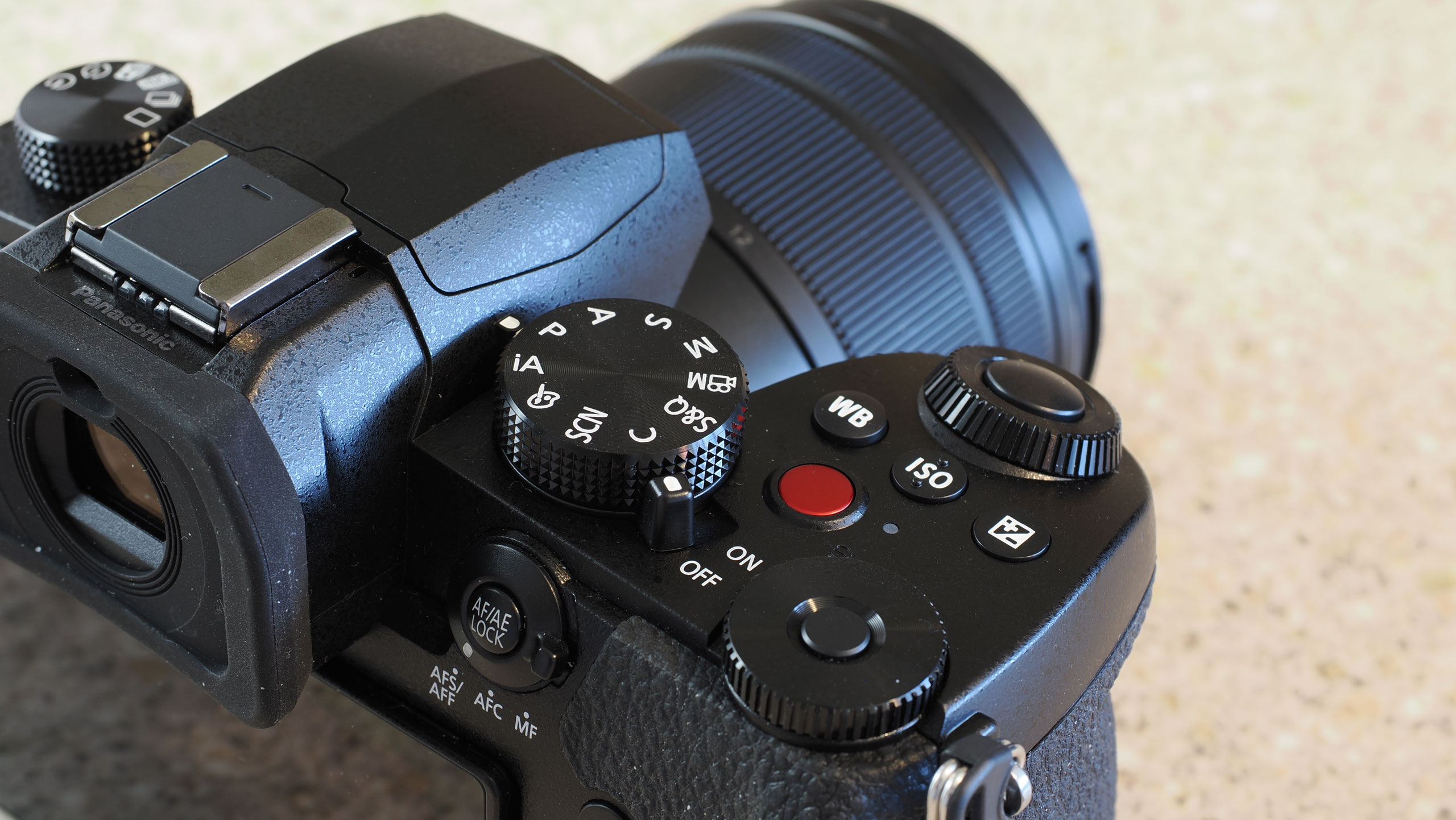
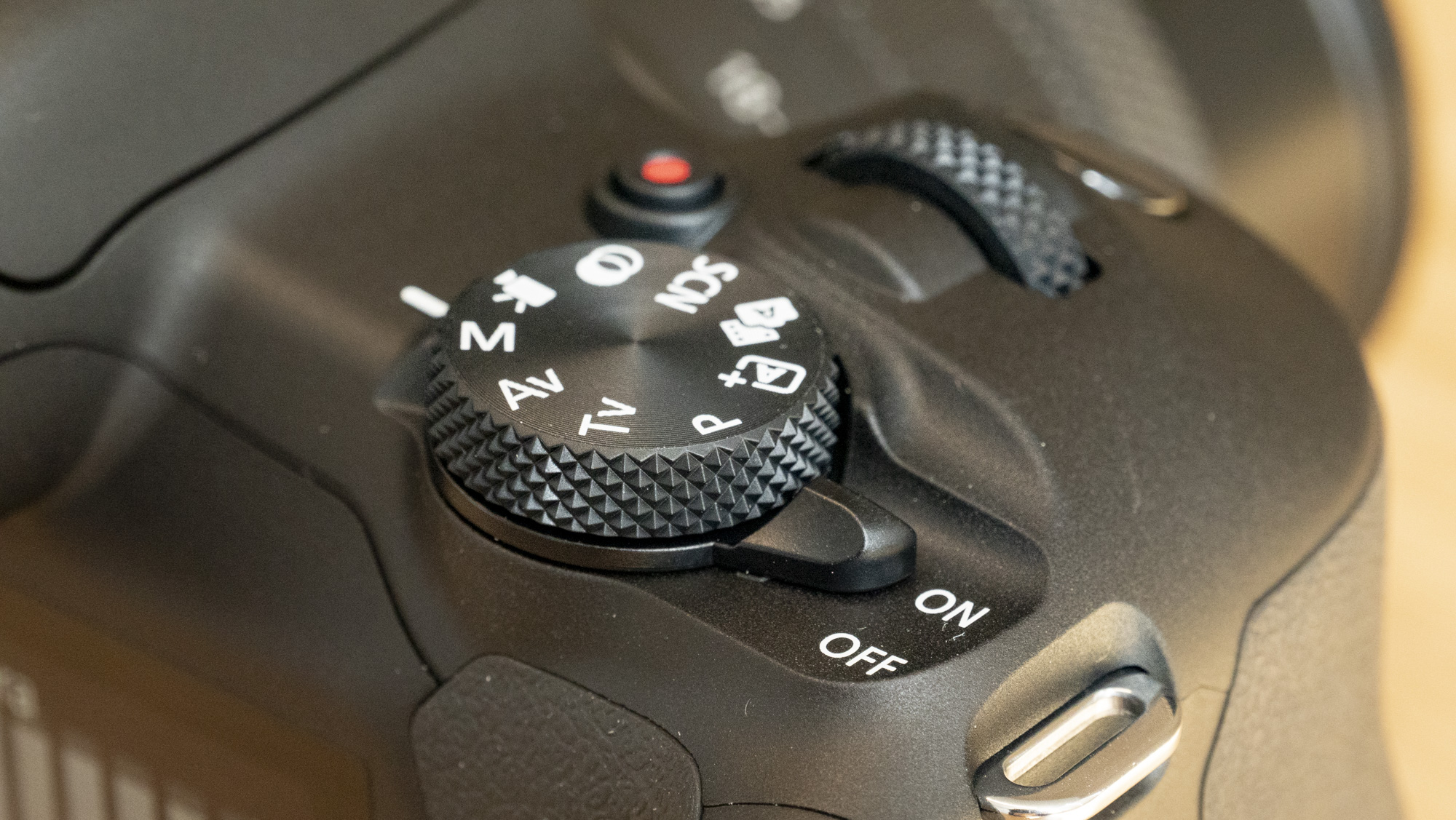
Canon EOS R100: design and handling
- Canon's smallest mirrorless camera, and an ideal fit for smaller hands
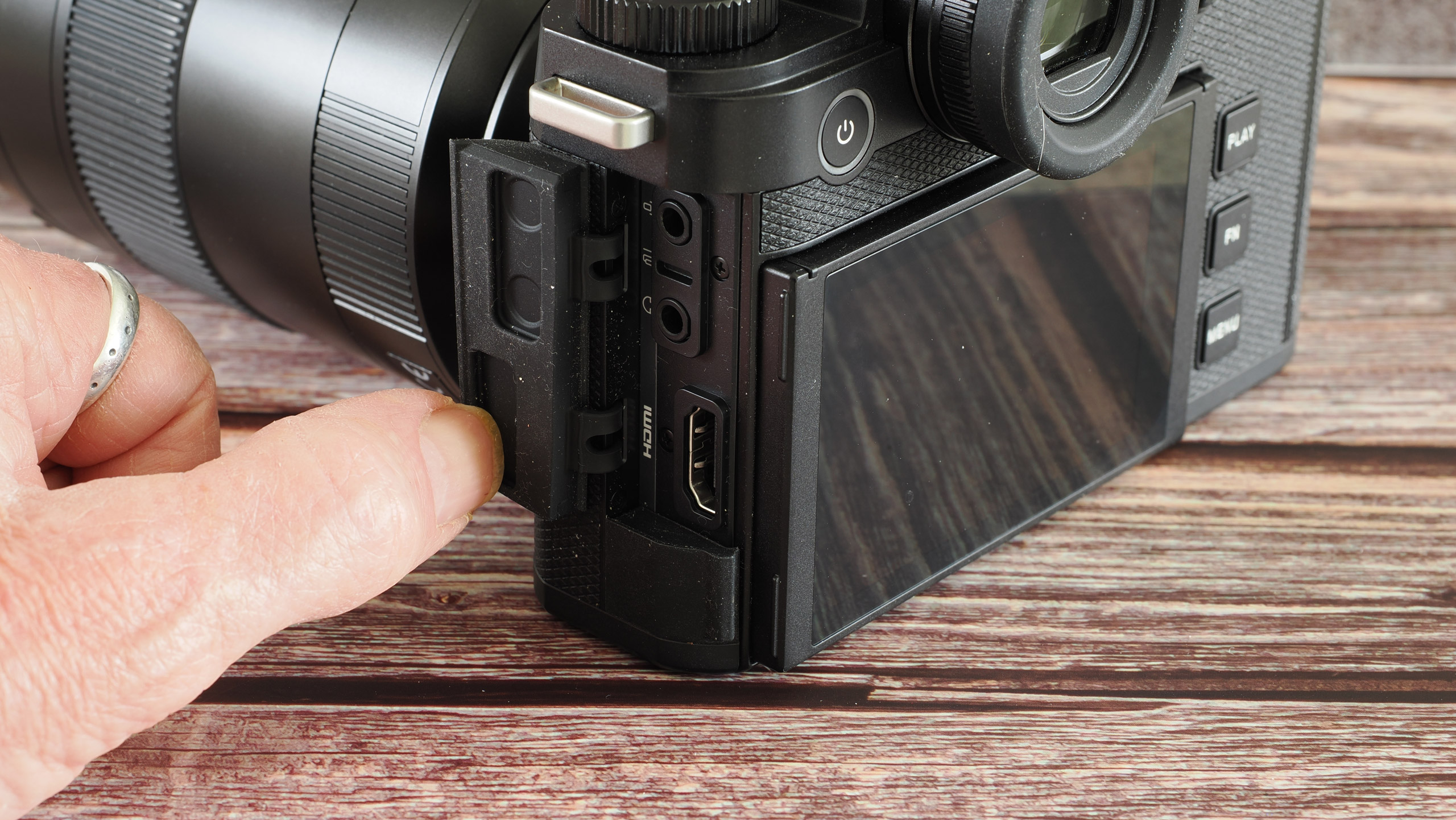
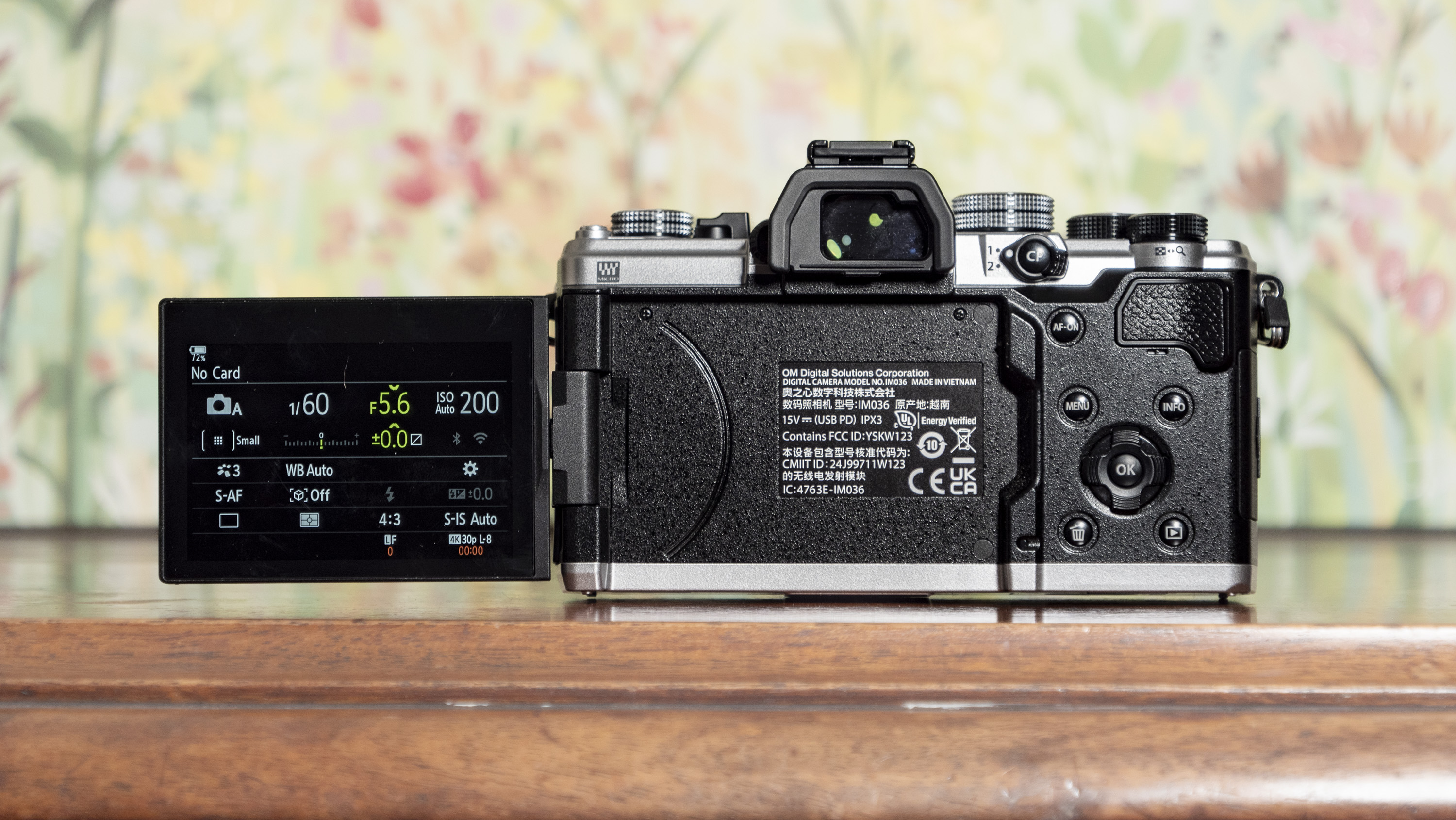
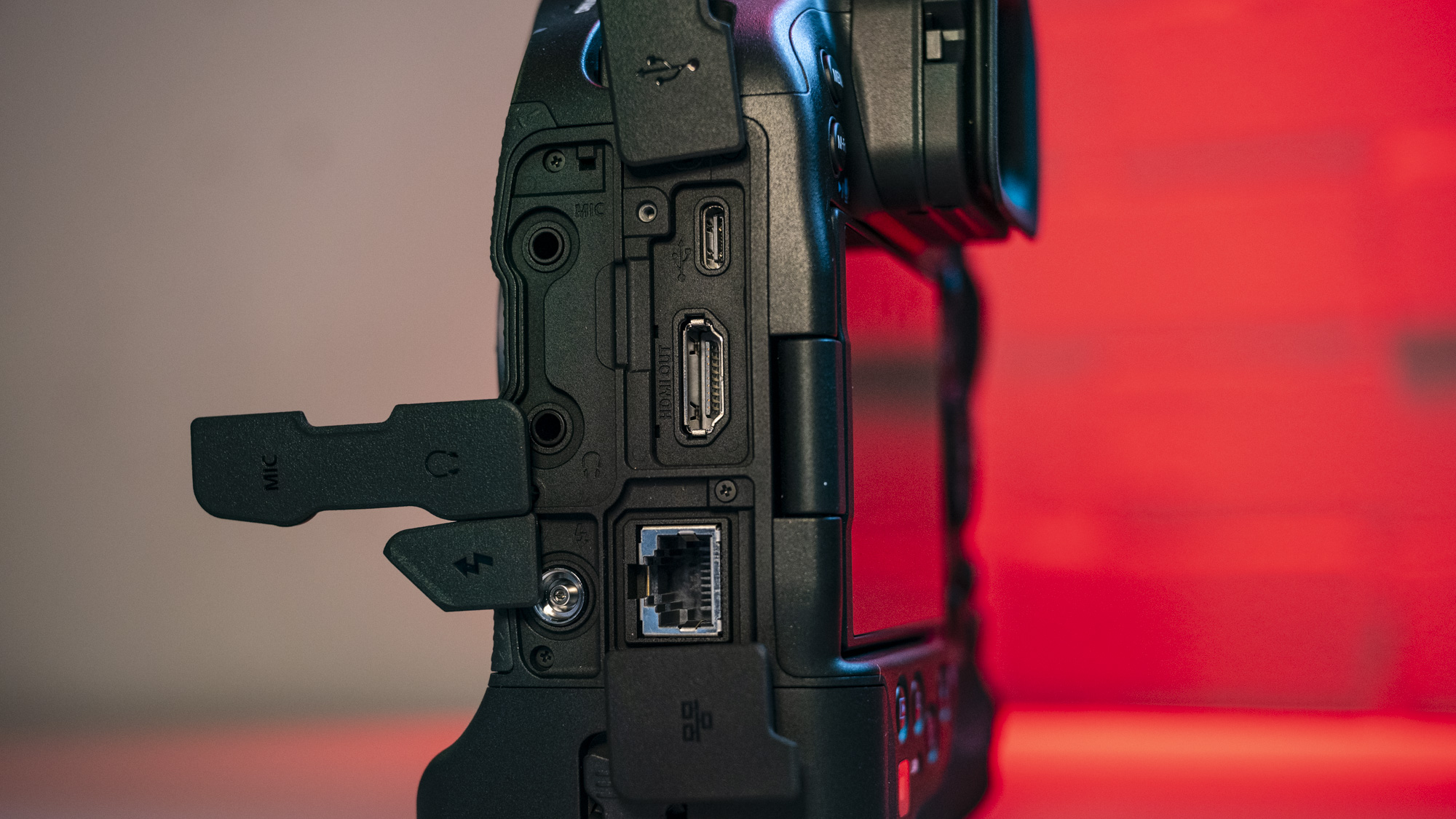
- It features a viewfinder and a fixed rear screen that's not touch sensitive
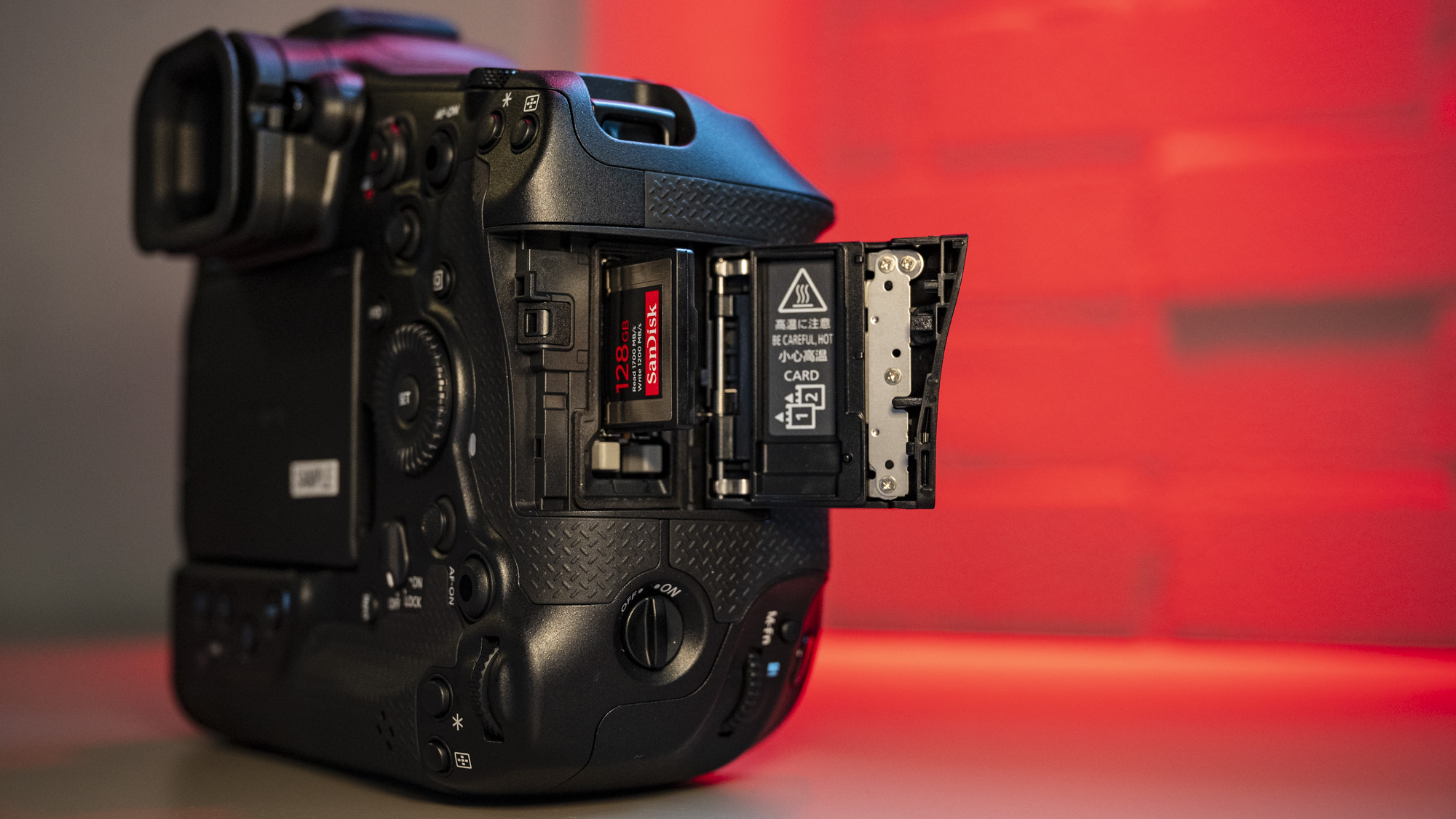
- Images are recorded onto a single SD card
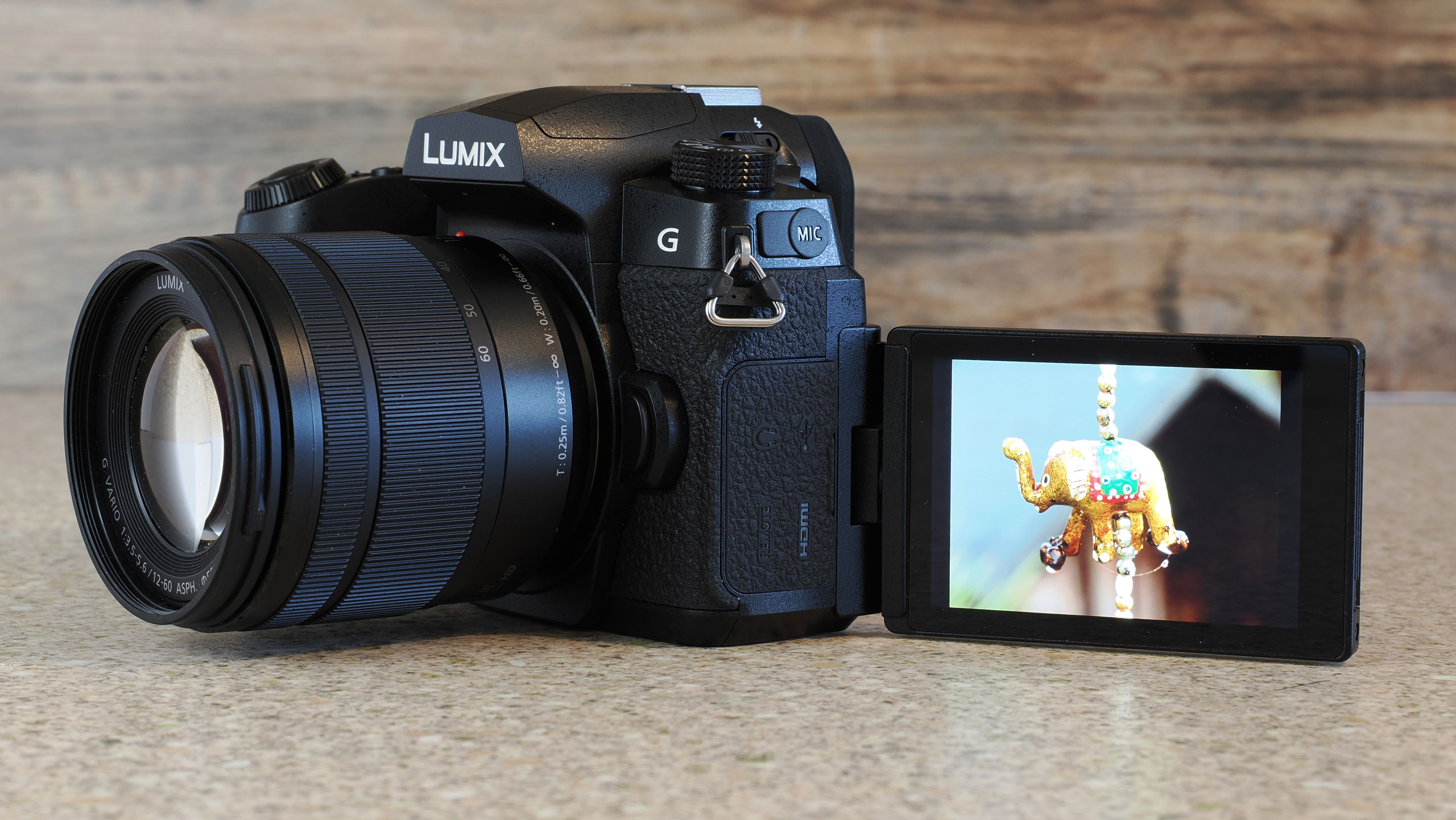
The EOS R100 feels like a shrunken-down version of Canon's DSLRs of old, only with mirrorless tech under the hood.
It's comfortable to hold thanks to a pronounced grip, and its diminutive proportions are a perfect fit for little hands – my kids, aged between five and 12, could all hold the camera comfortably and easily take photos with it.
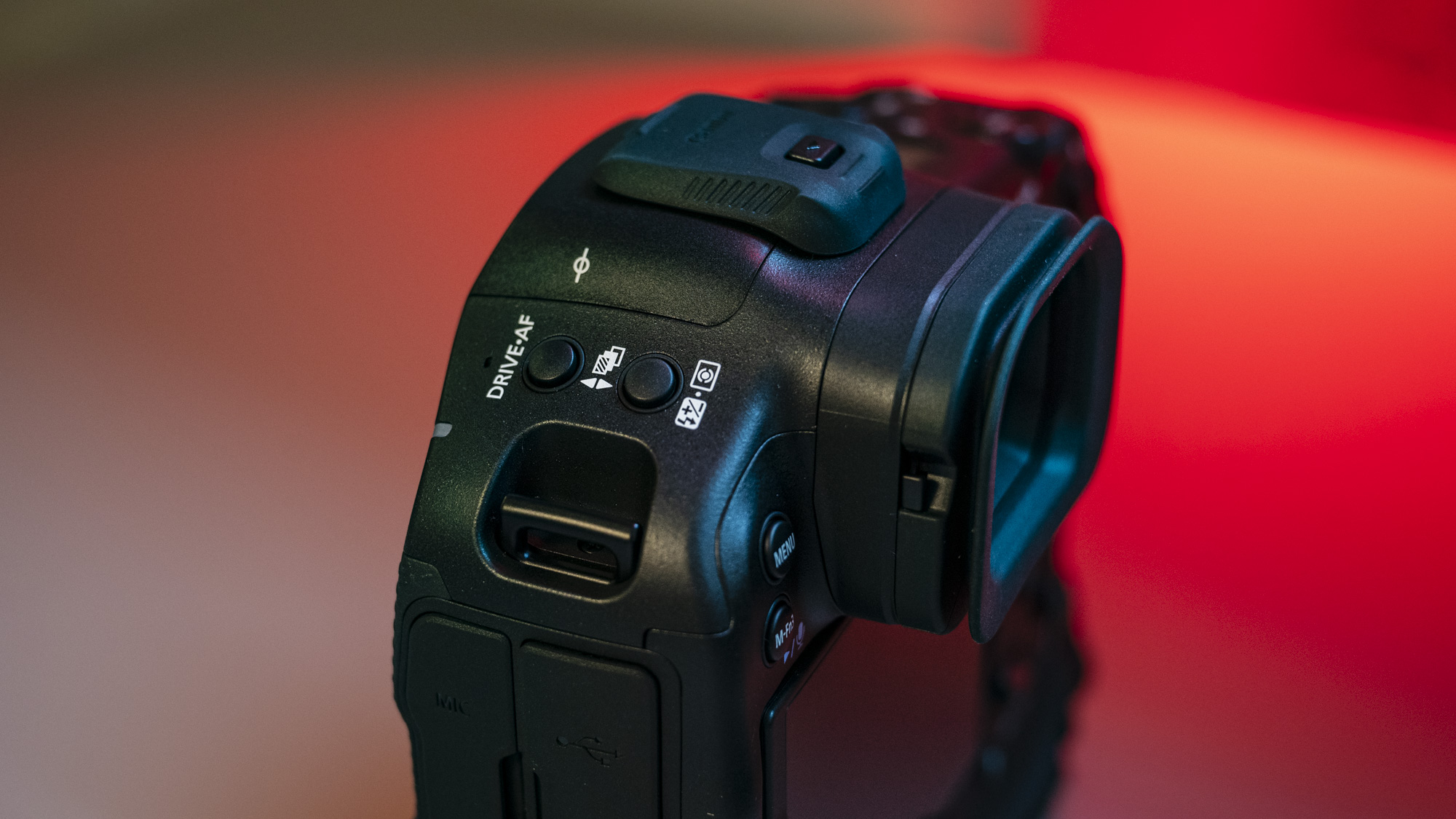
A dinky viewfinder provides a clear view of your scene for when it's otherwise tricky using the rear screen, such as in bright daylight.
Personally, I'd rather the rear screen at least tilted for easy viewing from awkward angles – the slightly pricier EOS R50 features a vari-angle touchscreen – although the fixed screen was less of a limitation for my kids, whose knees are rather less creaky than mine.
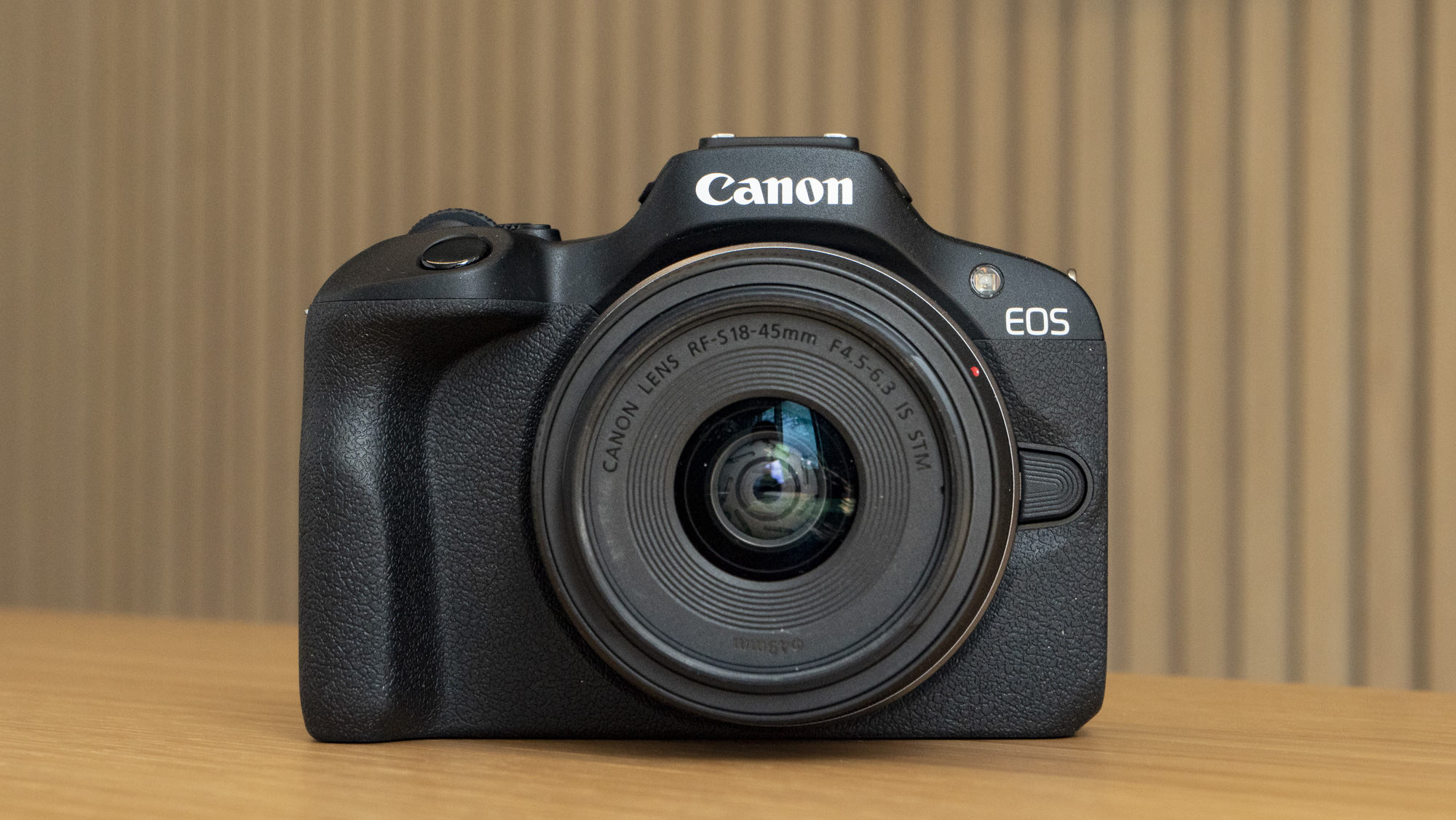



At first my kids were thrown that the rear screen didn't respond to touch – they've grown up with tech and are familiar with smartphones, and the camera's screen felt alien to them.
Eventually, however, the lack of touch functionality caused them to turn their attention to the EOS R100's physical controls, and I felt like this encouraged them to they explore the camera more, figuring out what each control and button did.
I initially called the camera 'out of touch' with beginners, precisely because of its old-school design and non-touch screen, but after extended use I've changed my mind – this is in fact an ideal camera with which to learn photography basics.
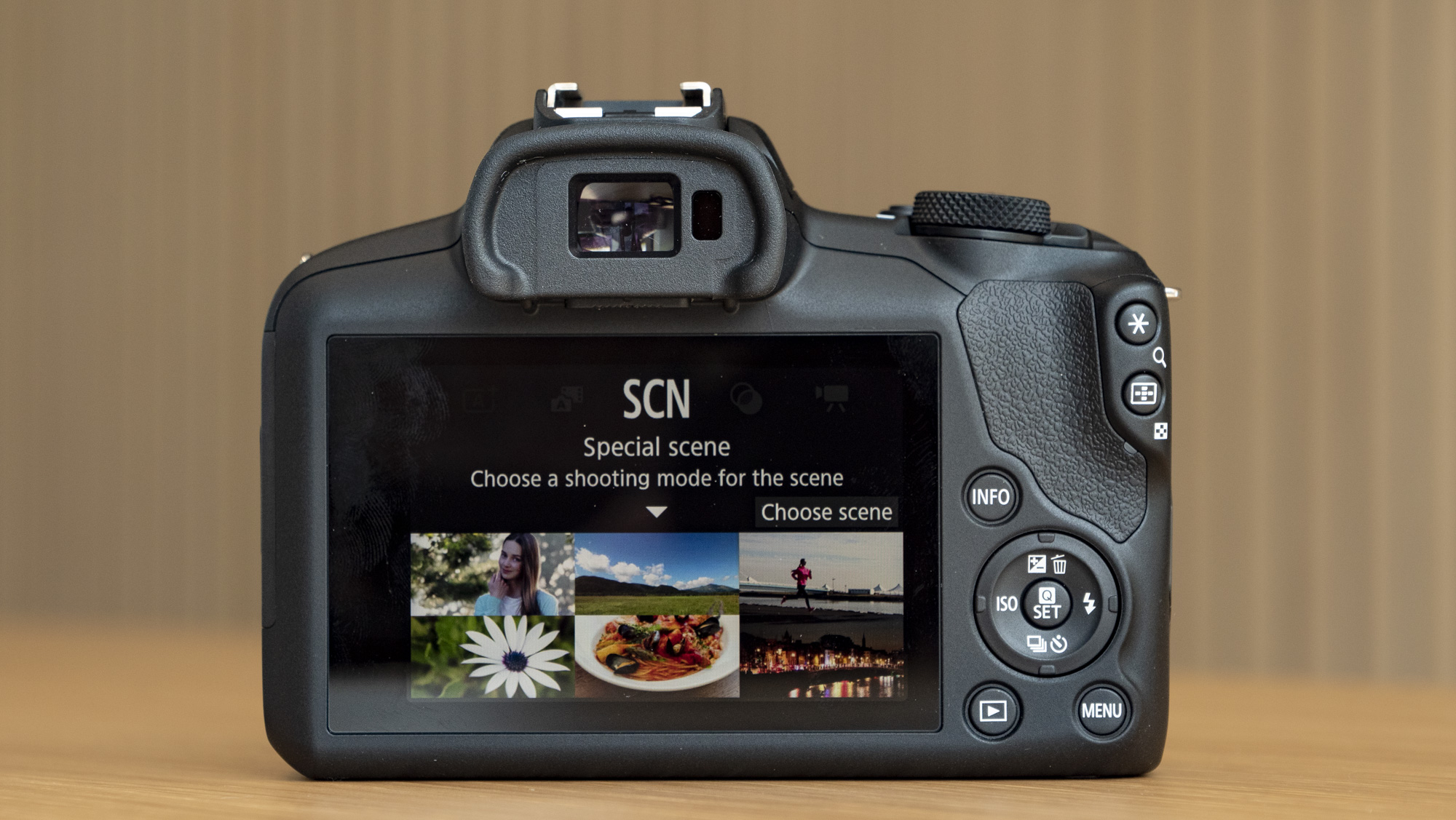
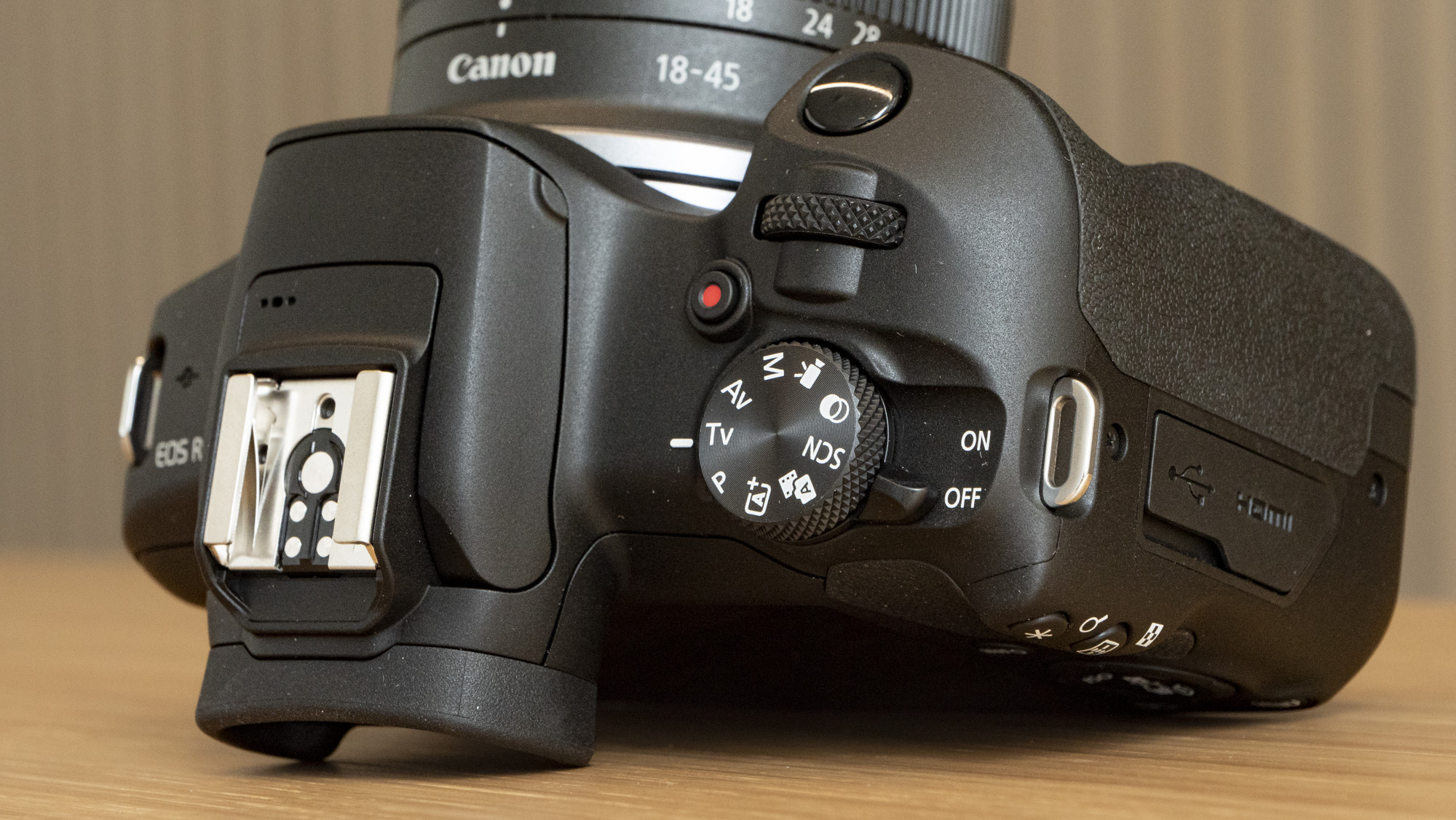





The body is built from a sturdy plastic. It's not weather-sealed, but as it's cheap and feels solid I felt comfortable letting my kids get on with using it without intervening too much, although I was also conscious of its potential vulnerability in inclement weather and dusty outdoor areas.
As I'm an experienced photographer, the EOS R100 isn't enough for me – there would be far too many occasions when I'd miss having a certain control or a feature at my fingertips. However, for beginners the EOS R100 makes a lot sense.
- Design score: 3.5/5
Canon EOS R100: features and performance
- Canon's original dual-pixel autofocus is snappy for general photography
- Burst speeds are a fairly average 6.5fps for continuous shooting
- Video specs are basic – this is primarily a camera for stills
As you can imagine, Canon's cheapest mirrorless camera is fairly stripped back when it comes to features, and limited when it comes to outright speed.
It does, though, feature Canon's dual-pixel CMOS autofocus with face detection and human subject-tracking autofocus, which I found to be really sticky and reliable for portraiture.
Should you wish to employ a different autofocus mode, such as spot AF, the convoluted process involves diving into a menu, while there's no joystick for speedily selecting focus points manually.
Canon's latest autofocus system in the pro EOS R5 Mark II is another level, with a range of subject-detection modes for animals and vehicles, sports priority, the option to store specific people to prioritize, plus Eye Control AF – the two cameras are worlds apart. However, for general photography, the EOS R100's autofocus is very good.
The EOS R100 has rudimentary burst shooting speeds of up to 6.5fps, with sequence lengths up to 97 JPEGs or just six raws – an action photography camera this is not.





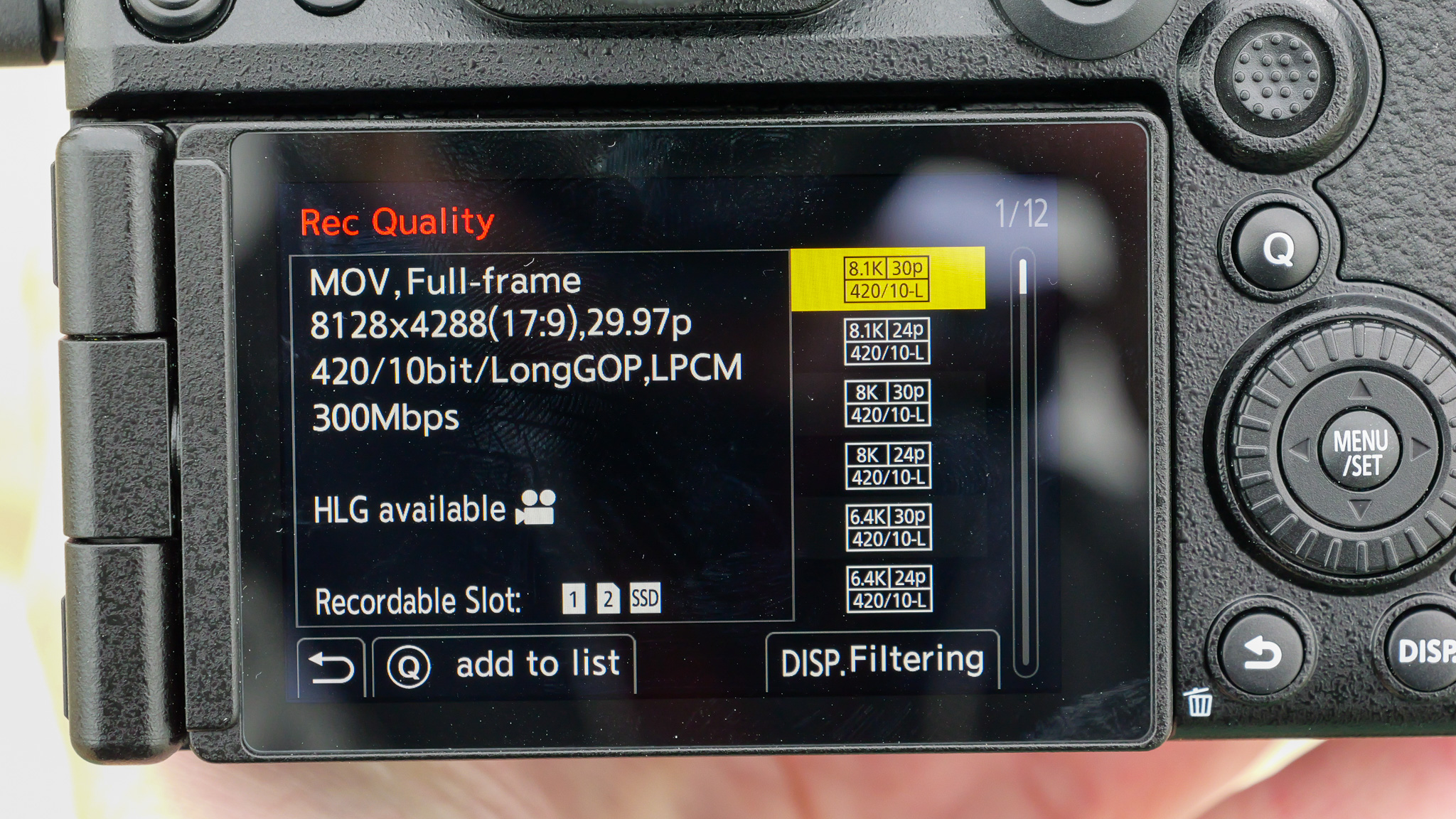
Video recording options include 4K up to 30fps, plus Full HD up to 60fps; that's the minimum I'd expect for a video-capable camera launched in 2023. Dig deeper into the specs and you'll find that video recording is in 8-bit color, which is much less color-rich than 10-bit.
The camera has a hotshoe for attaching accessories such as a flash gun. It's the more basic 5-pin type, meaning not all of Canon's flash guns are supported by the EOS R100, so if you're looking to purchase such an accessory check that it's compatible with the camera first.
- Features and performance score: 3.5/5
Canon EOS R100: image and video quality
- Same trusted 24MP APS-C sensor as pricier Canon cameras
- 4K video recording up to 30fps, 8-bit color
- No C-Log color profile or 'recipes'
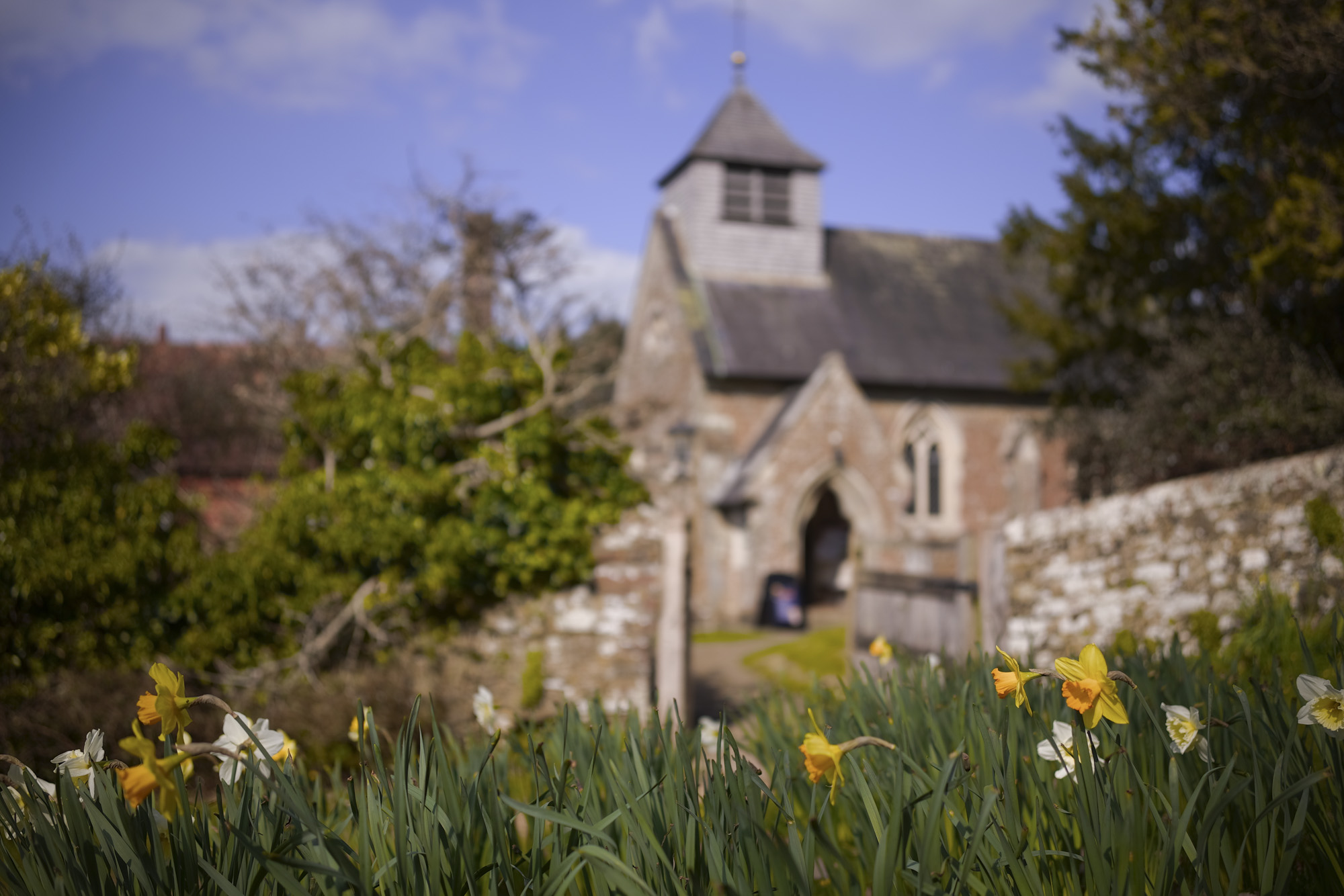
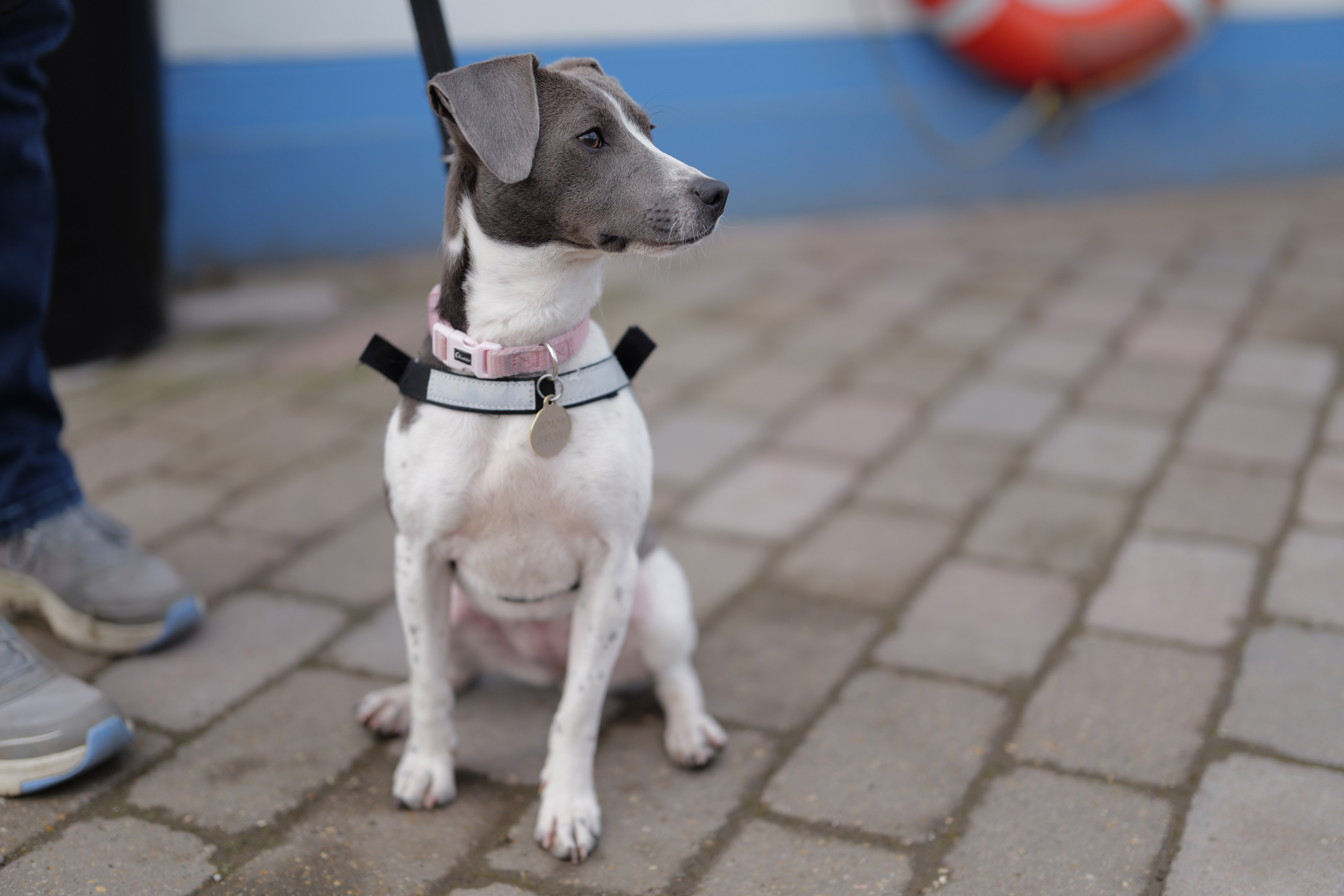
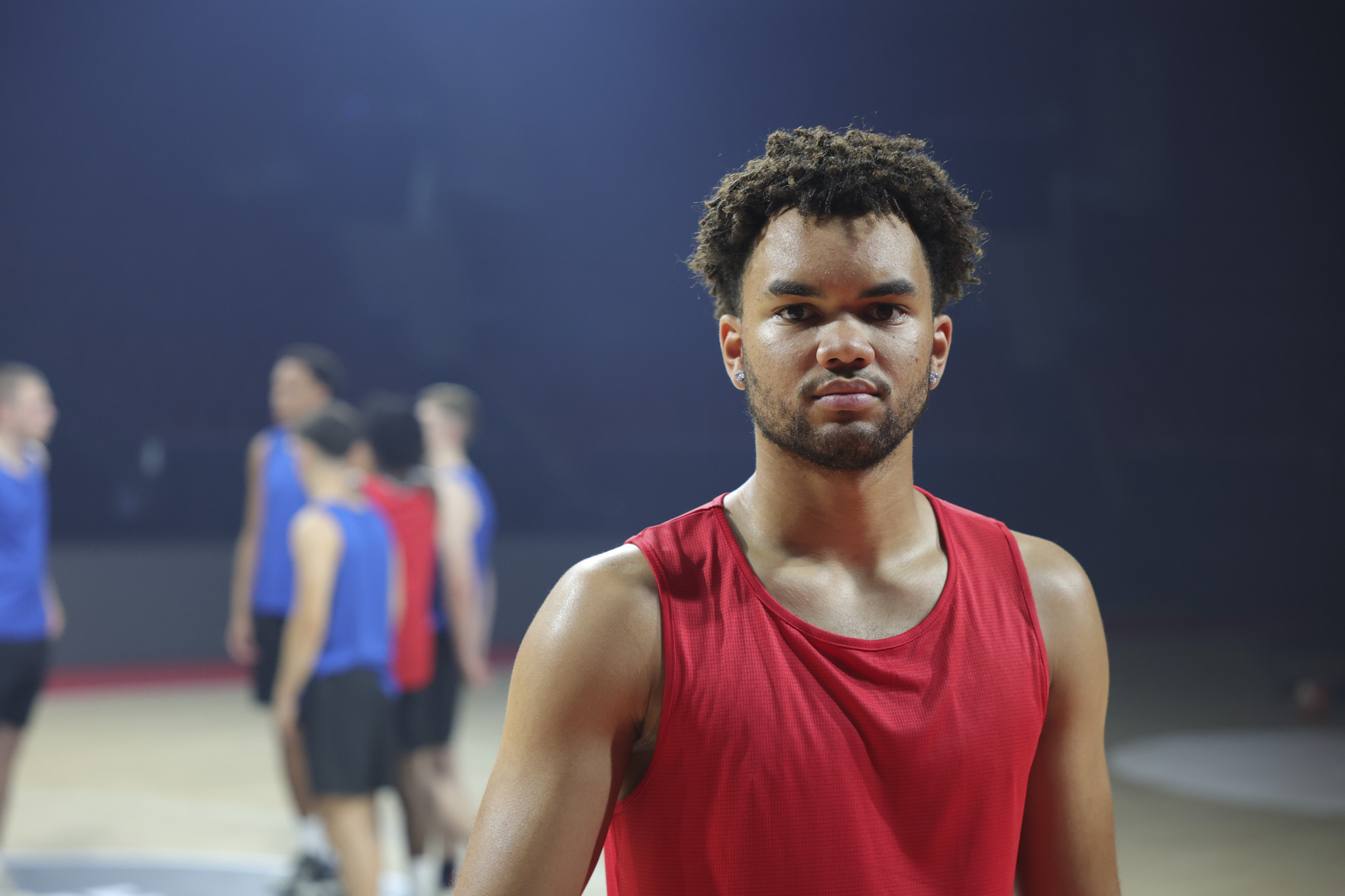
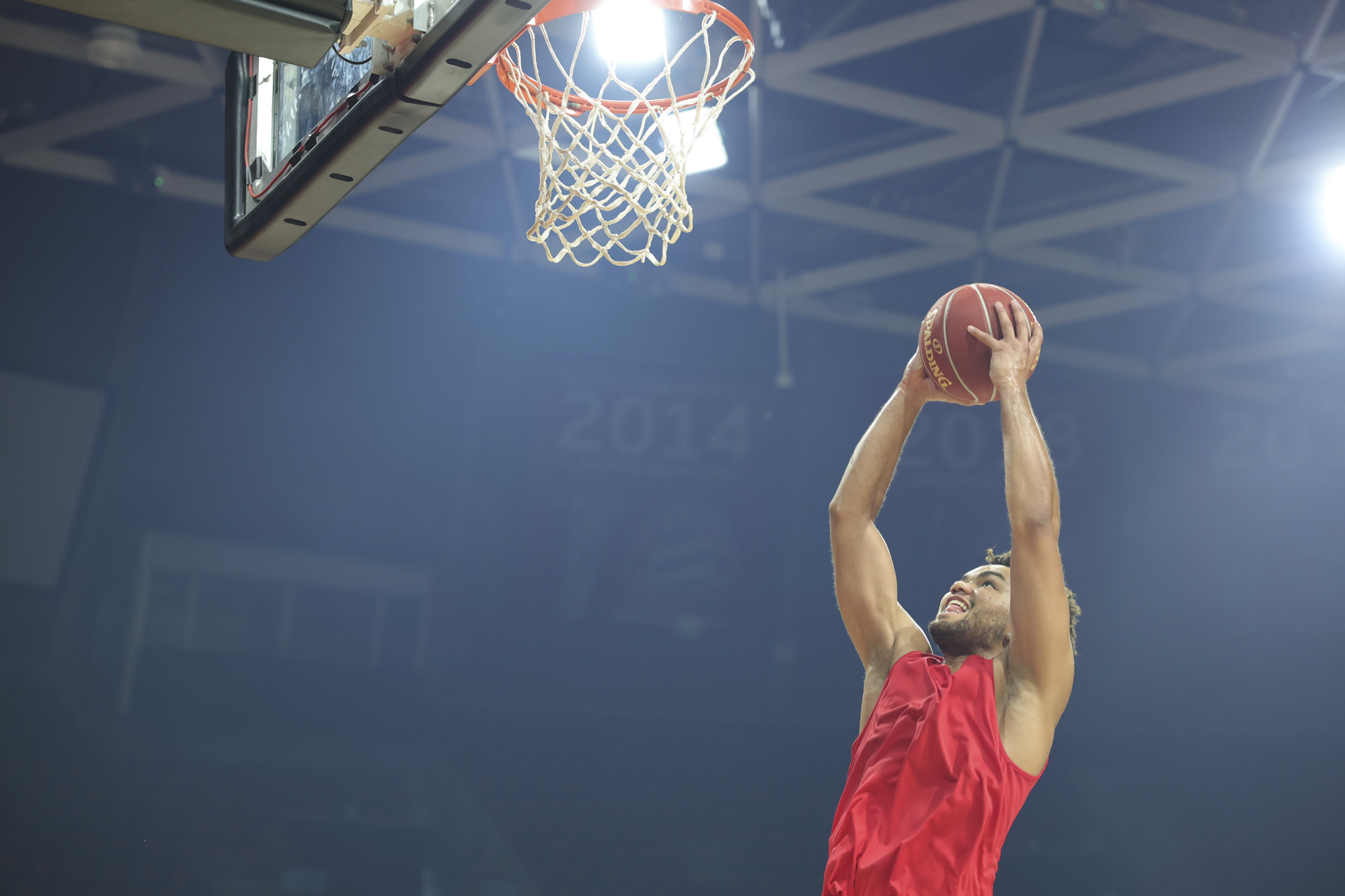
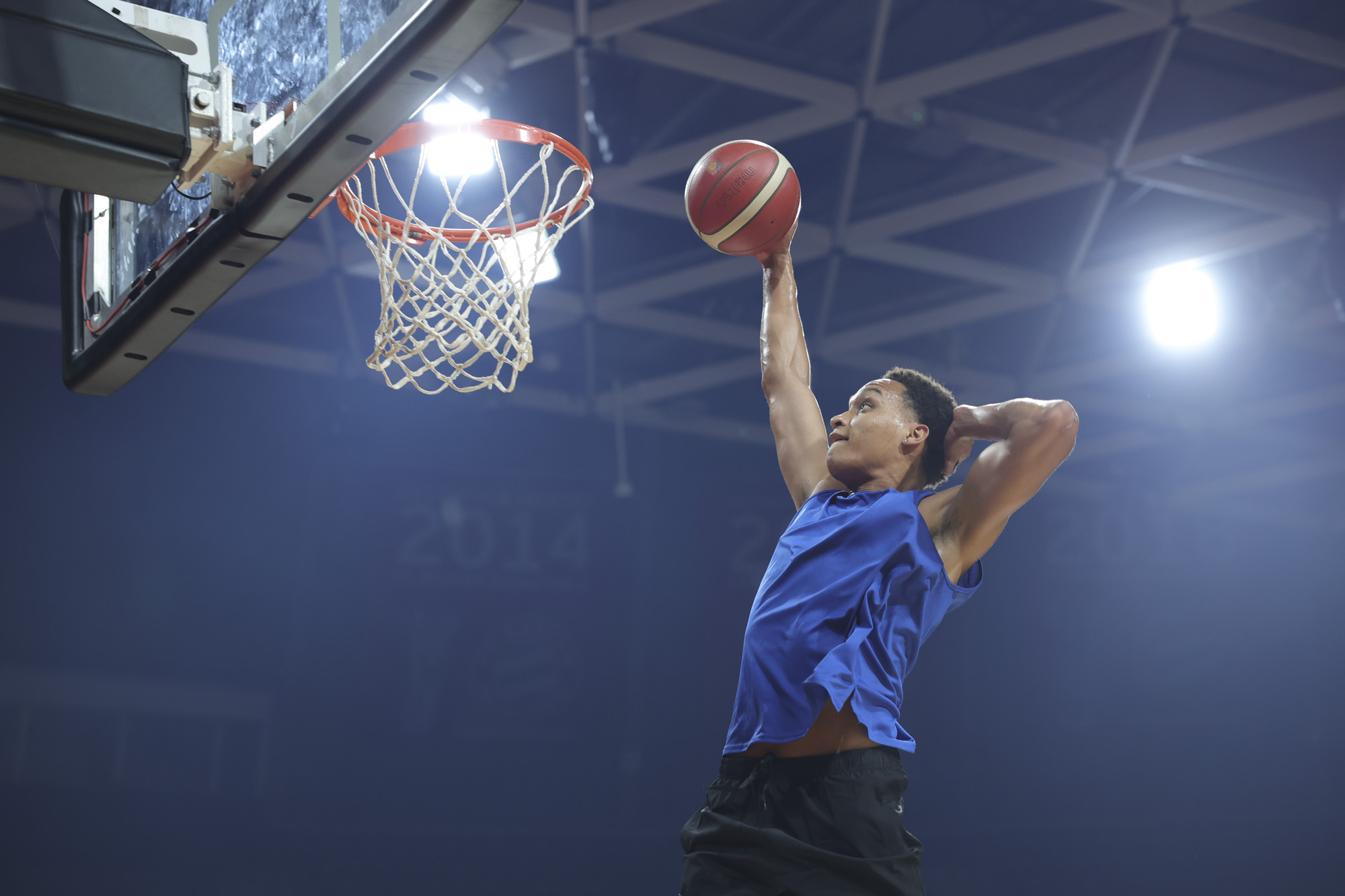
There's not too much more to say about the EOS R100's image and video quality that hasn't already been covered in our EOS R10 review – it has the same potential for natural-looking photos with Canon's lovely color profiles.
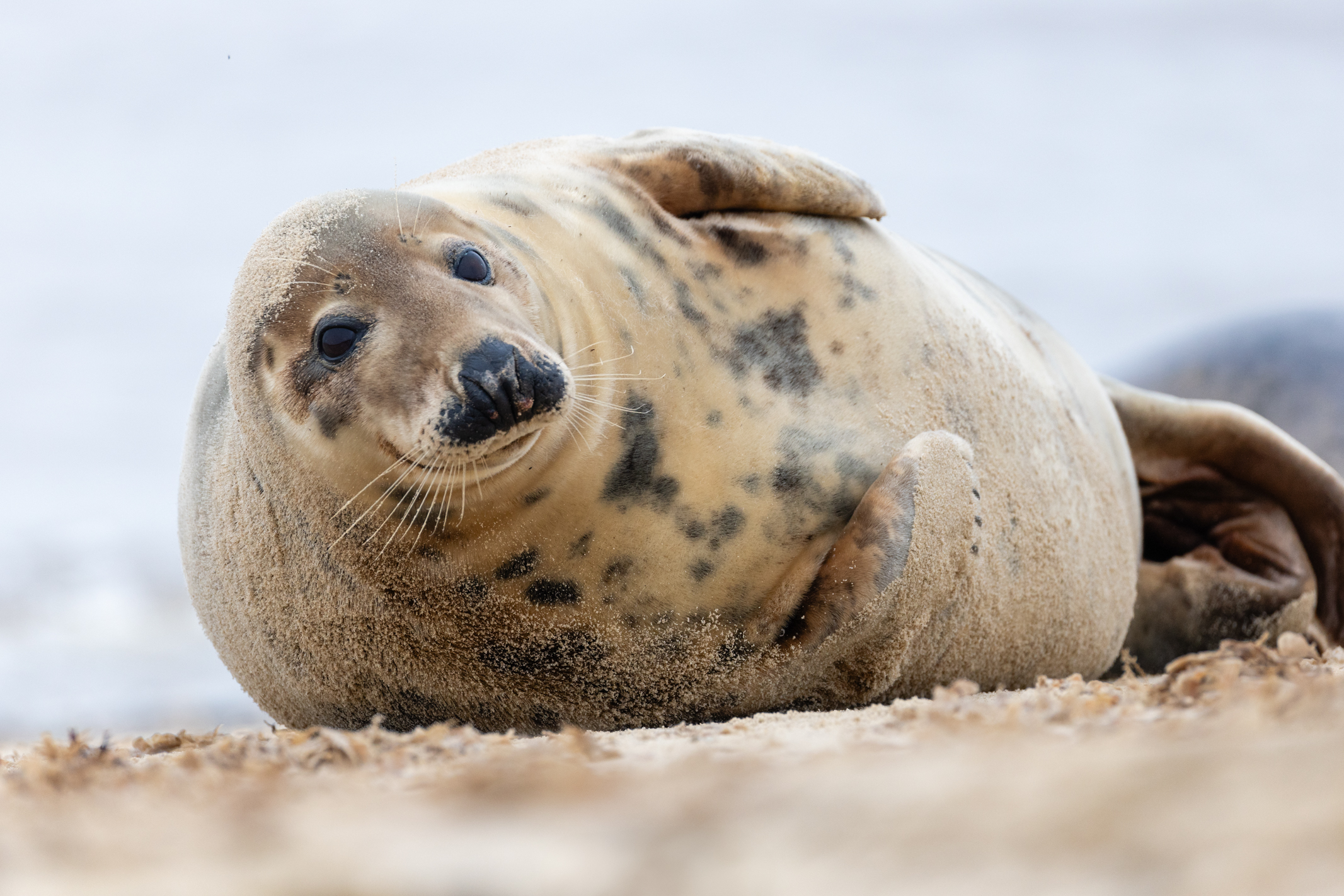
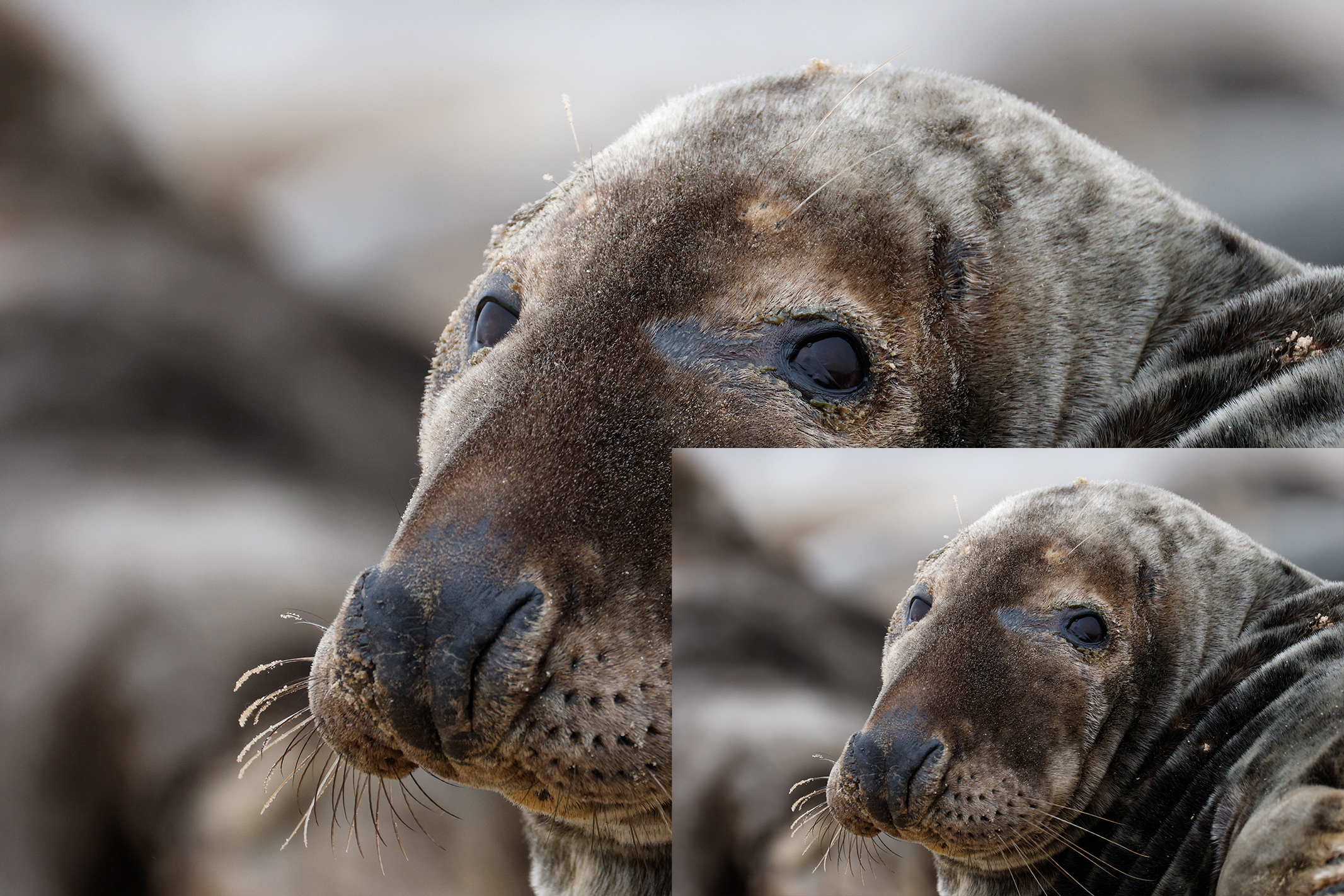
This also means the EOS R100 can grab detail-rich photos of similar quality to the likes of the Sony A6100, Nikon Z50 II and Fujifilm X-T30 II, all of which utilize a sensor with a resolution around the 24MP mark, which is impressive considering that the EOS R100 is a much cheaper camera.
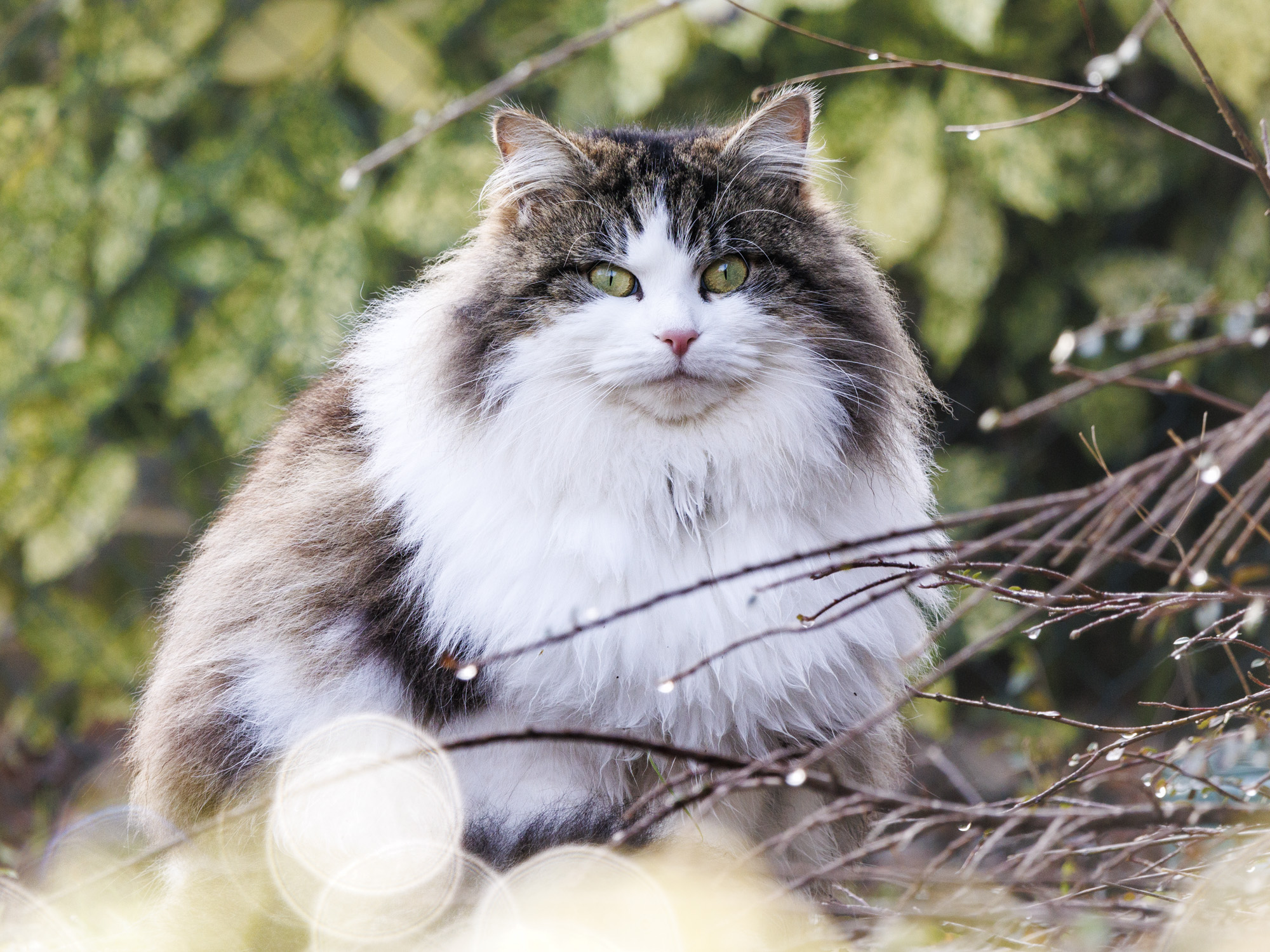
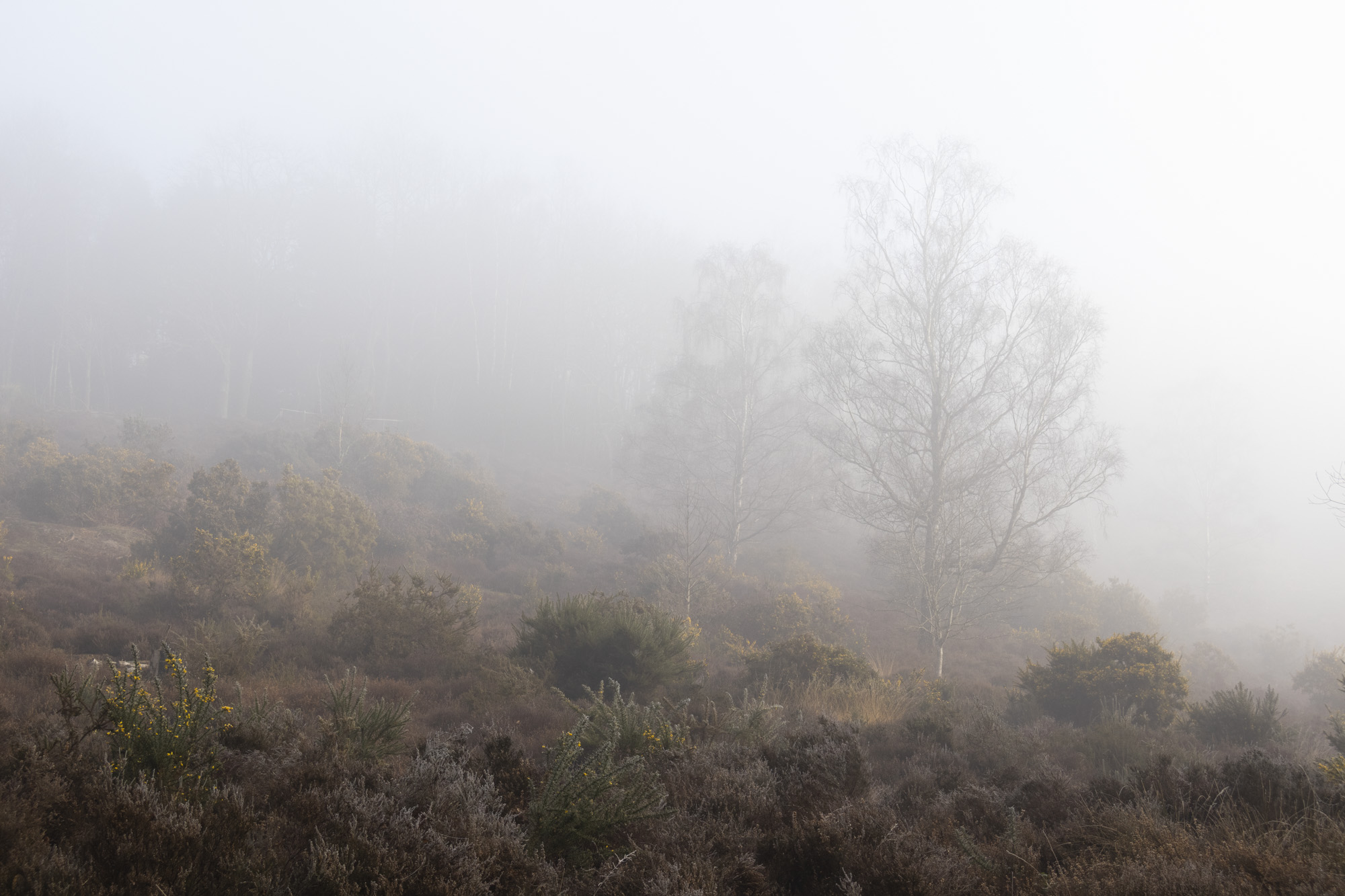
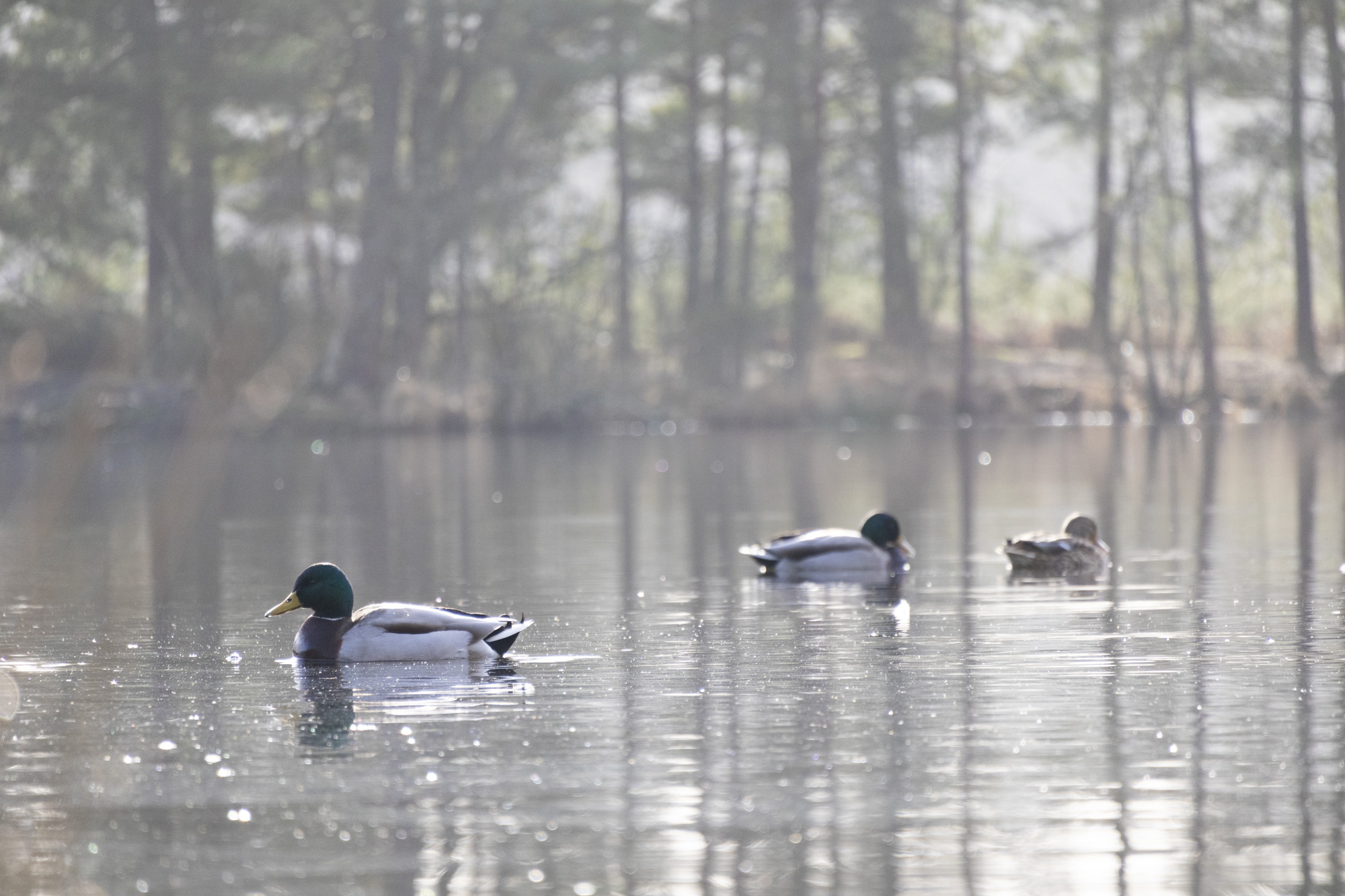











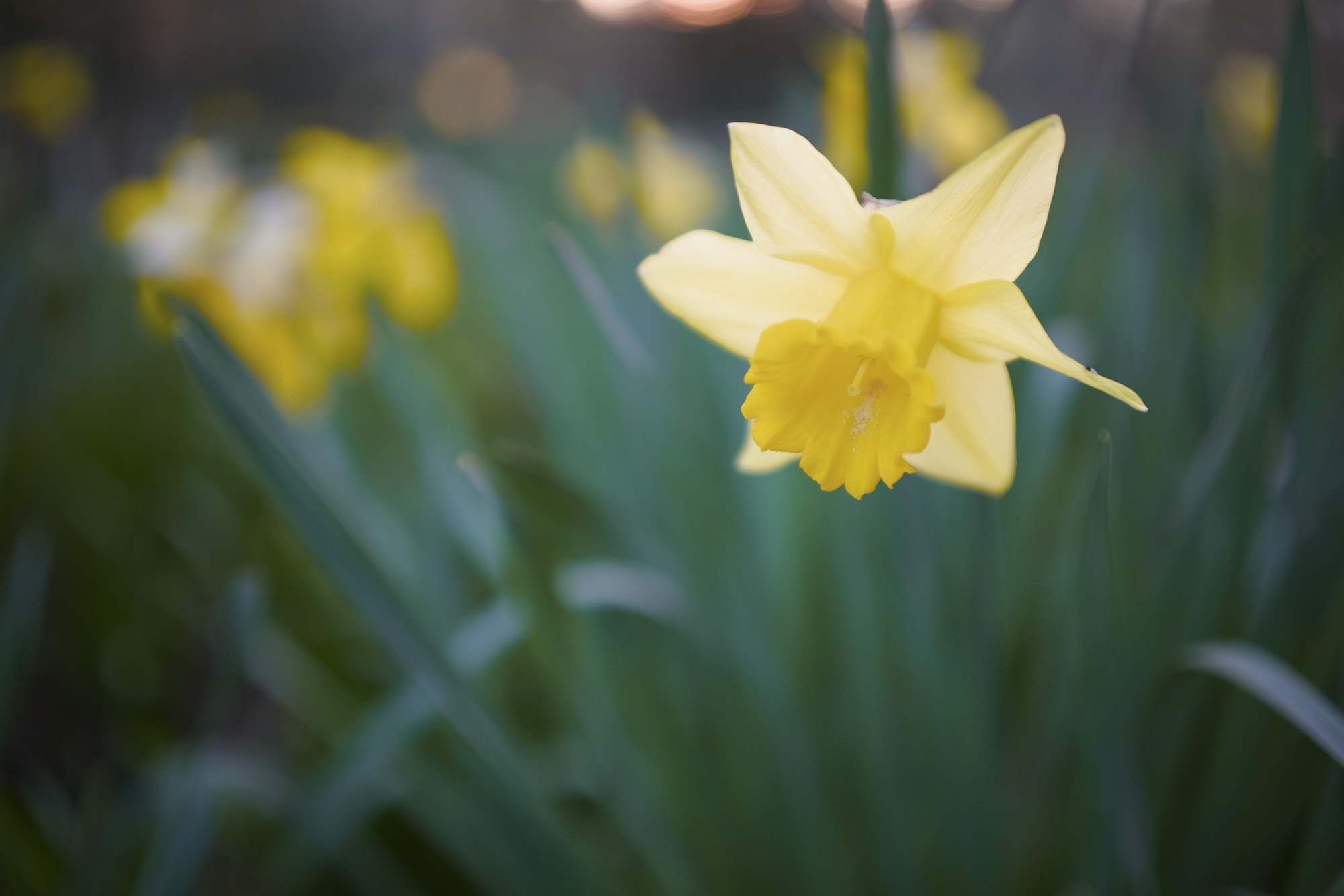
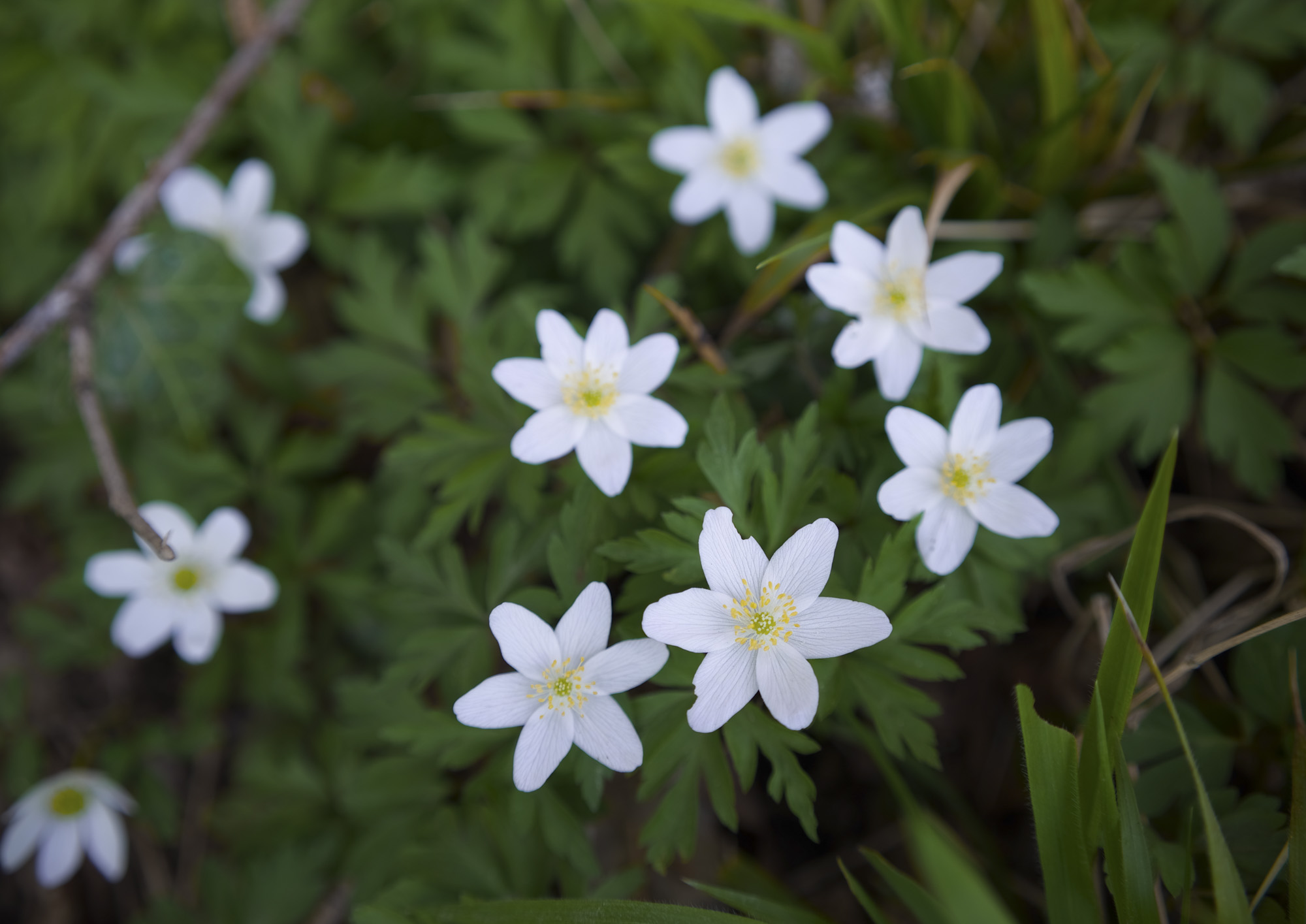
All of the photos above were taken with either Canon's RF-S 18-45mm or RF-S 55-210mm.
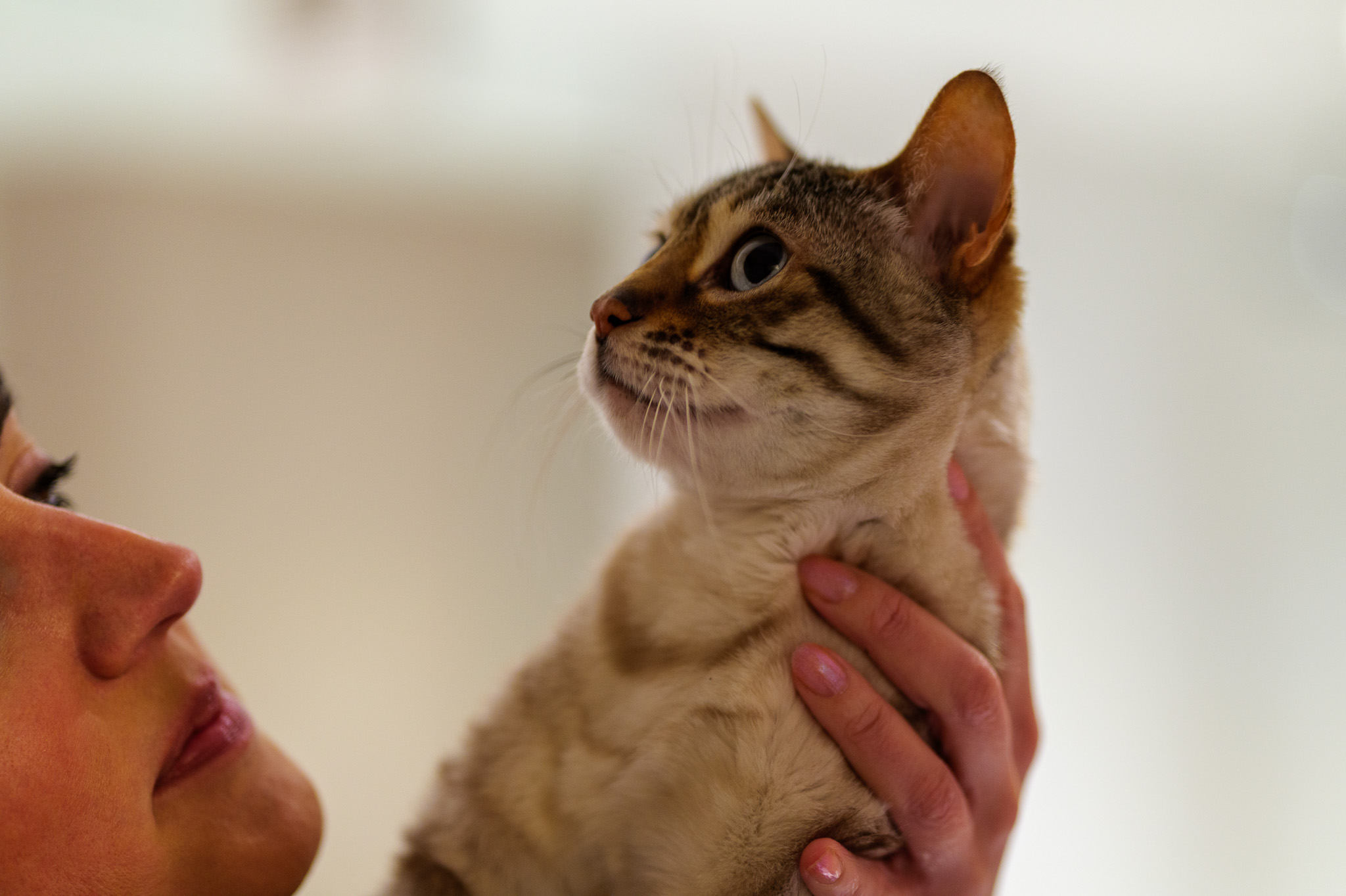
Canon's RF-S 18-45mm kit lens doesn't quite match the quality of Nikon's 16-50mm kit lens, while the RF-S 55-210mm lens, which is available in a twin-lens kit with the EOS R100, is decent without overly impressing; detail is a little soft in the images of ducks, above, while bokeh in the cat portrait has an onion-ring effect.
To truly elevate image quality, I would recommend buying another lens. The photos included in the first gallery directly below are made with some of Sigma's DC DN Contemporary f/1.4 primes – the 16mm , 23mm and 30mm. In the second gallery below, all the photos are made with Sigma's 56mm lens, which is ideal for portraits.
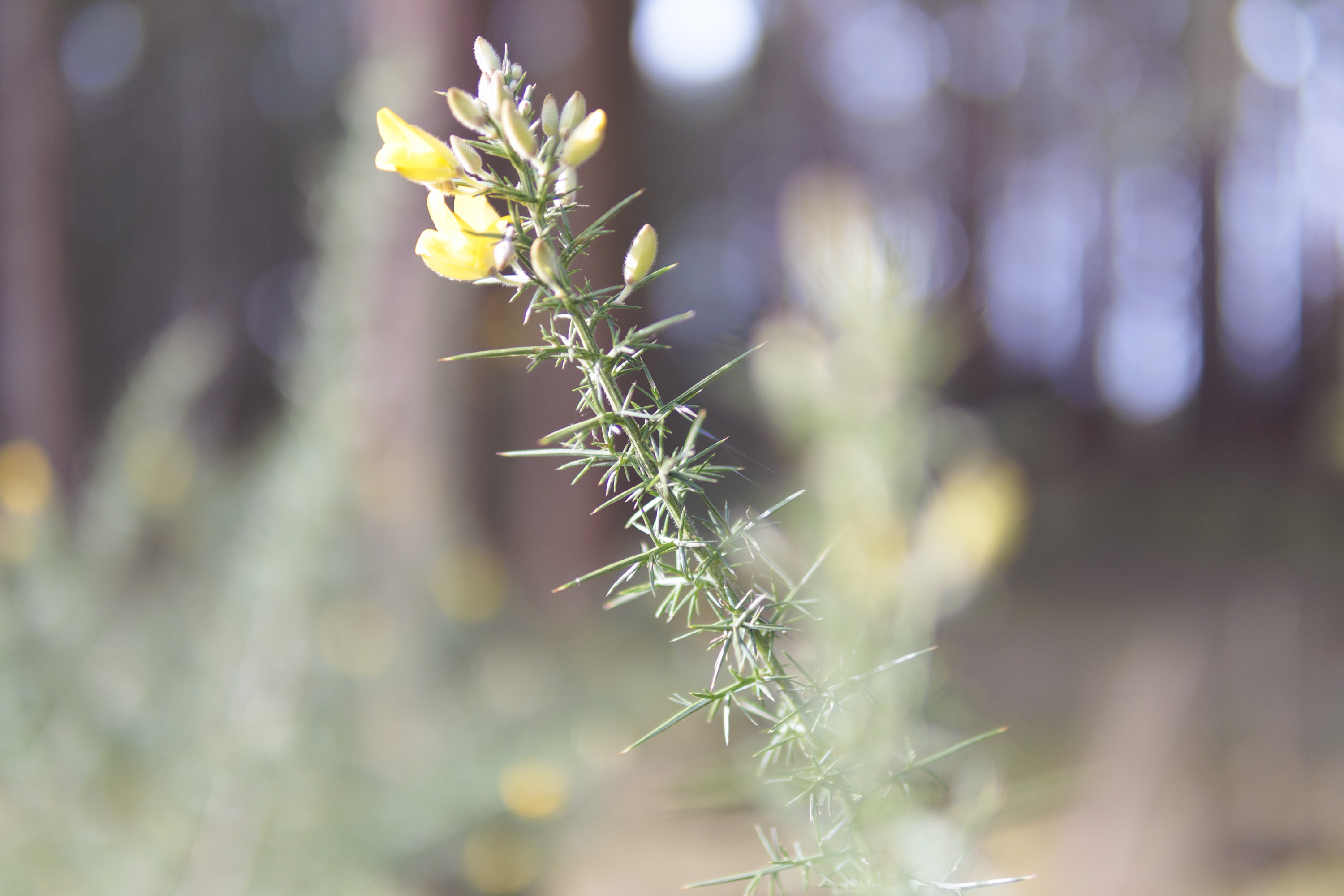
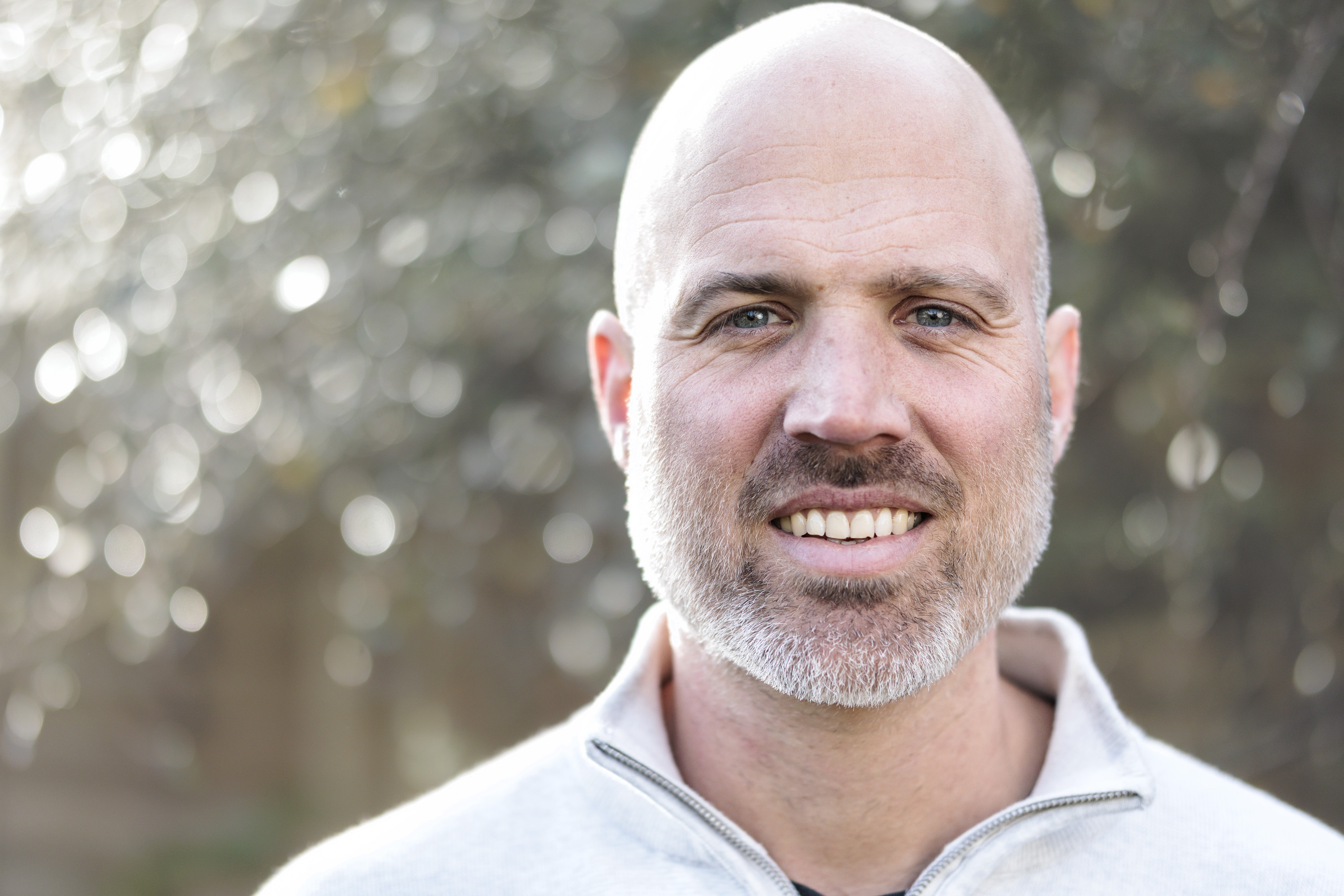
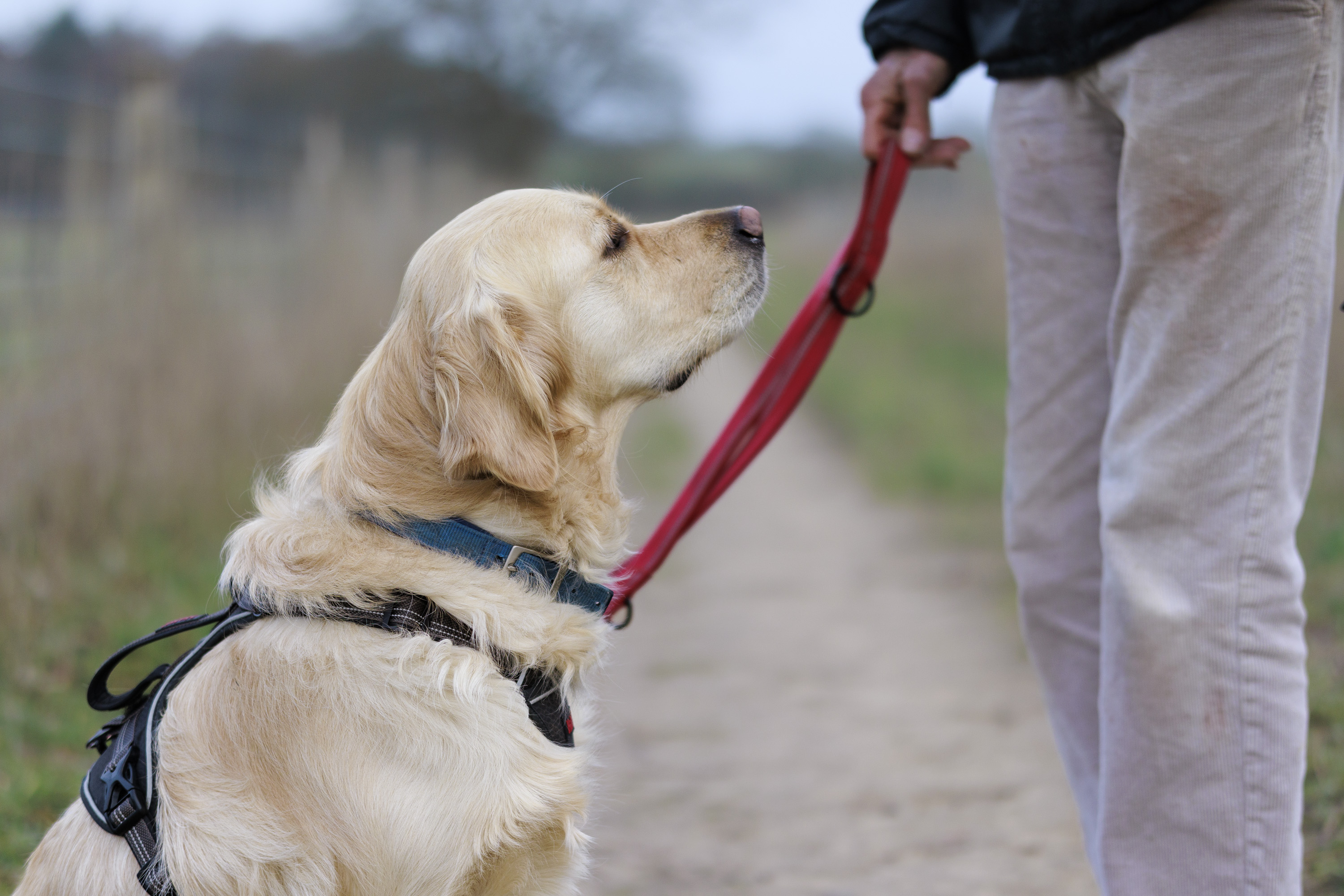
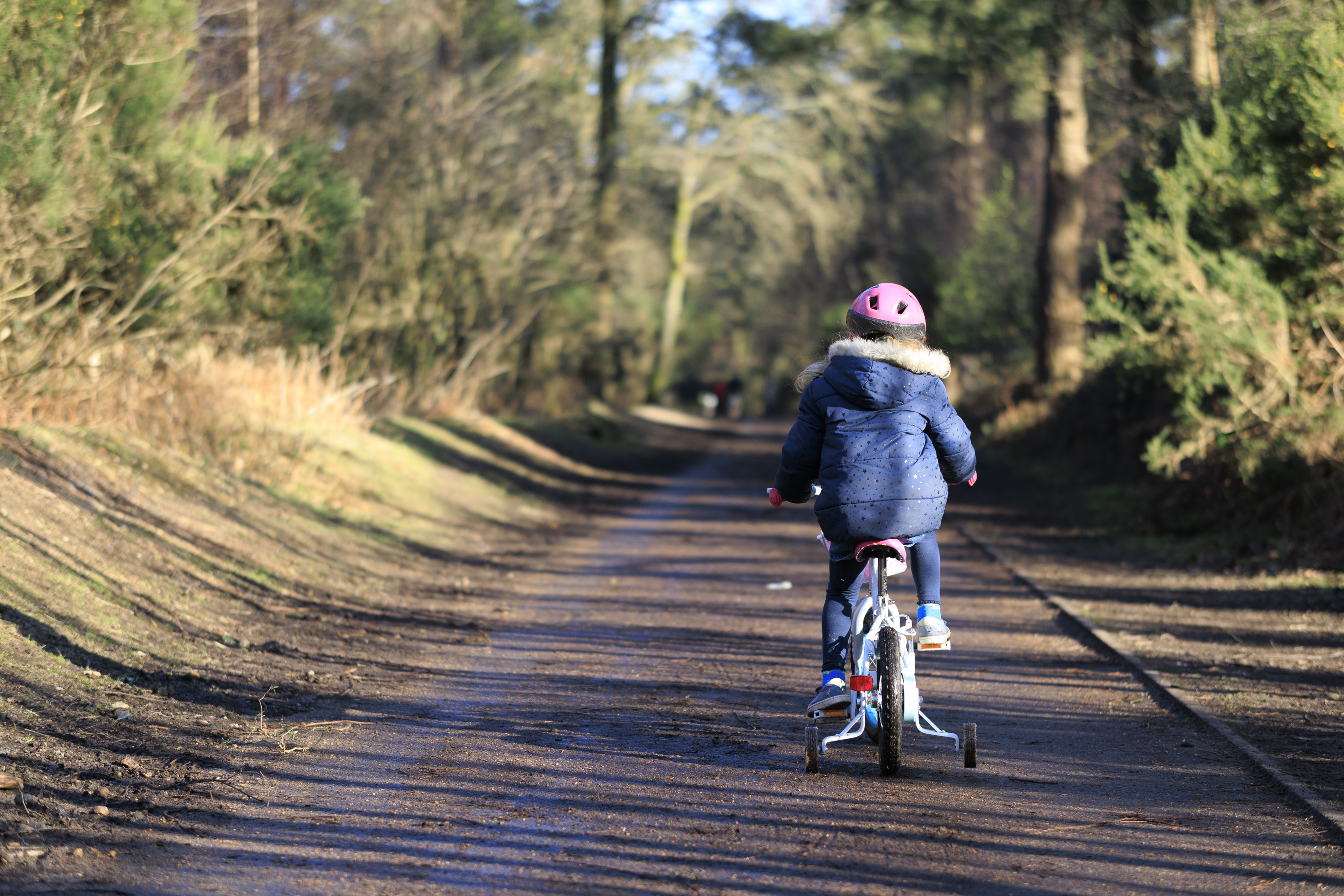
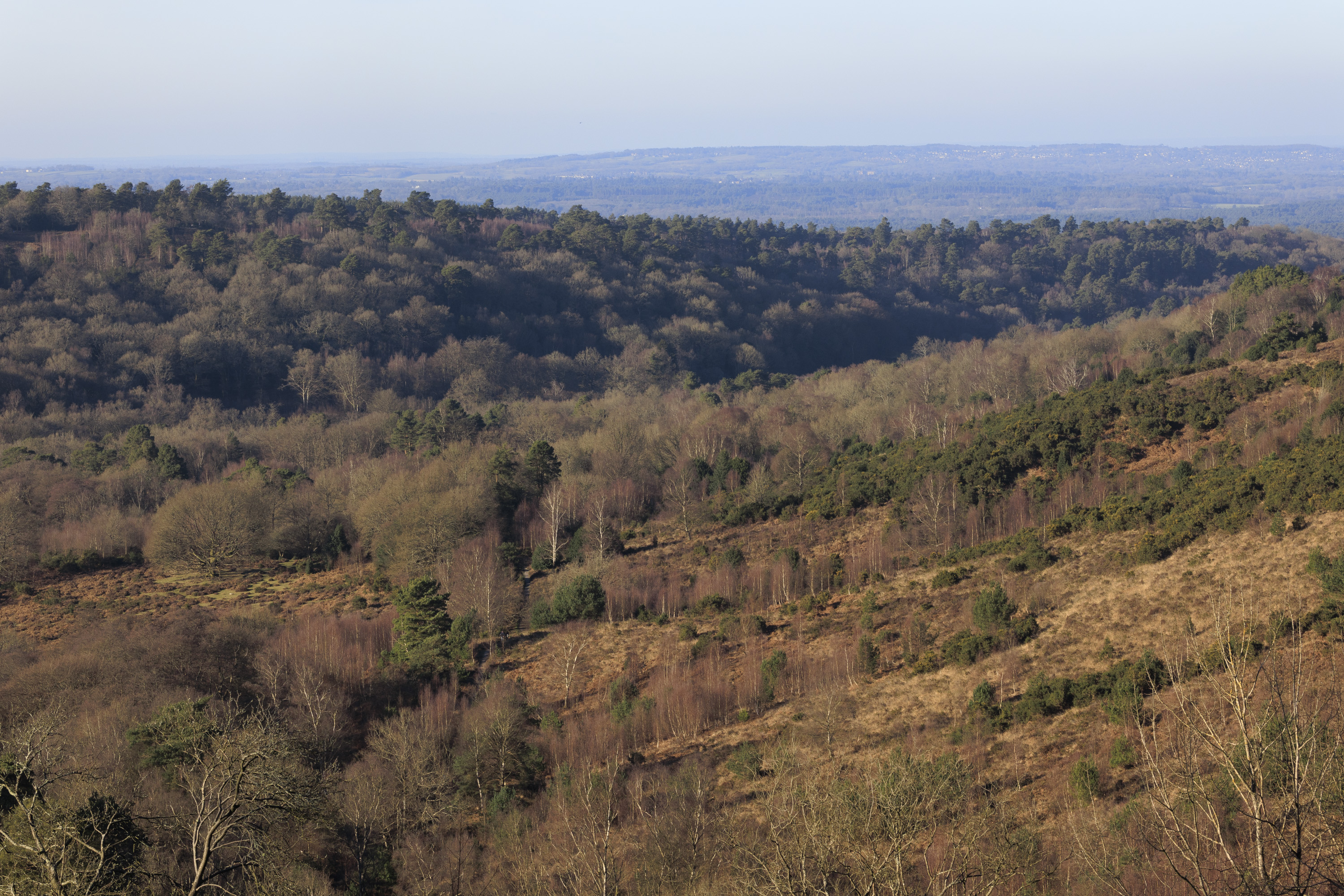
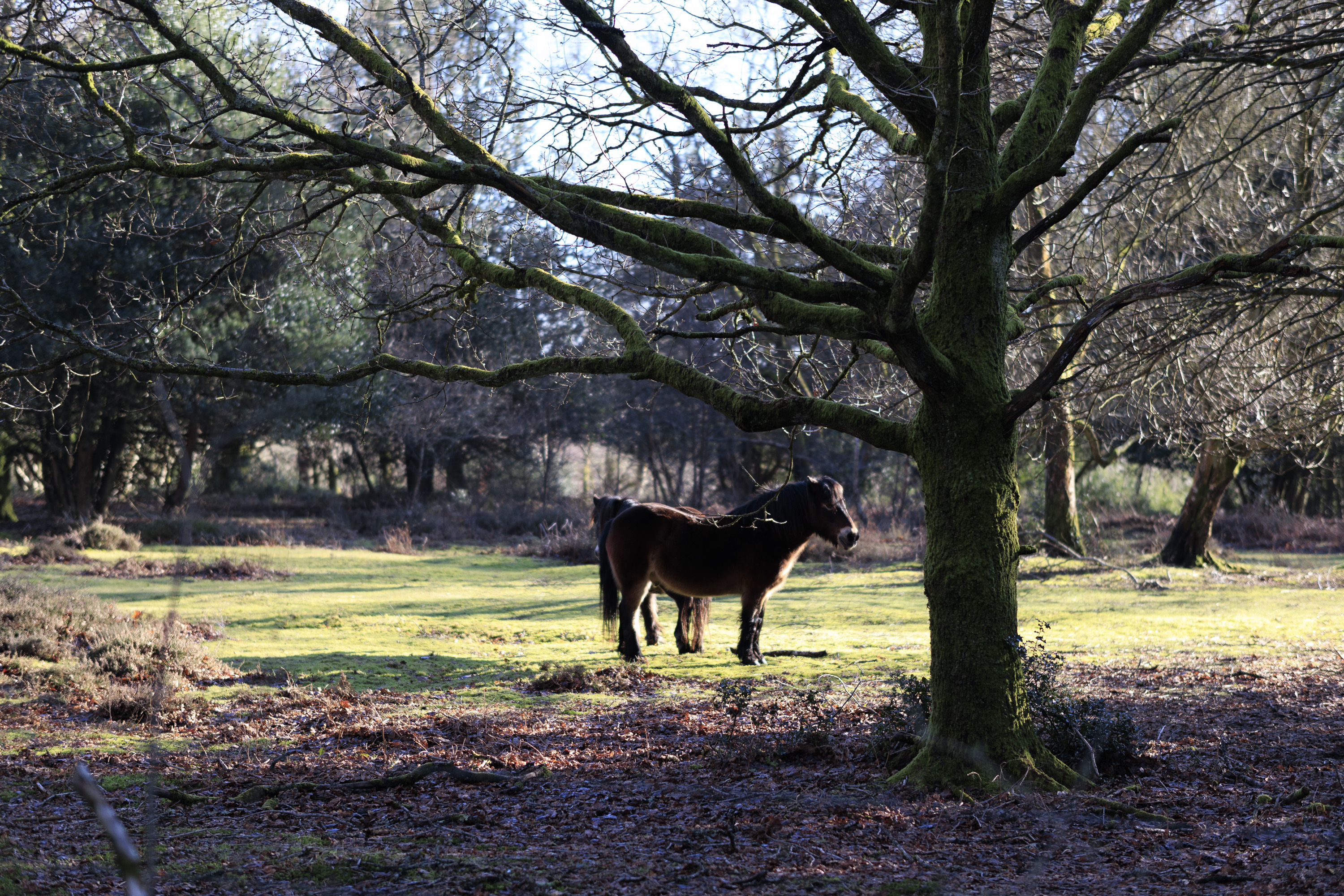











Video quality is rudimentary. Yes, the EOS R100 can shoot 4K, but only up to 30fps and with 8-bit color depth, which isn't as rich as 10-bit, which cameras like Fujifilm's X-M5 offer.
Flat color profiles for video, which would give color graders more to work with when editing, are missing too, as are custom profiles that can be uploaded to the camera, something that's available with the Nikon Z50 II via Nikon's Imaging Cloud
None of this is surprising given the EOS R100's price point and target user, though, and we're left with Canon's familiar range of color profiles which, thankfully, are better than most.
- Image and video quality score: 3.5/5
Canon EOS R100: testing scorecard
Should I buy the Canon EOS R100?
Buy it if...
You're looking for a first 'proper' camera
With its small form factor, comfy grip, decent photo quality and changeable lenses, the EOS R100 is an excellent camera for budding photographers.
You want a cheap camera
The EOS R100 is not only Canon's cheapest mirrorless camera, it's the cheapest mirrorless camera from any brand – and there are usually superb deals during seasonal sales that further lower the price.
Don't buy it if...
You want versatile handling
The EOS R100's basic build quality and fixed rear screen with no touch functionality do limit where and how you can shoot.
You shoot photo and video
The EOS R100 has decent photography credentials, but its video specs are limited by today's standards.
Canon EOS R100: also consider
The Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark IV is arguably the best-value beginner mirrorless camera available, with its retro-styling, a capable 20MP sensor and superb image stabilization. As it's a Micro Four Thirds camera an enviable selection of lenses are available, and despite being launched in 2020 its tech is of a similar era to the EOS R100's.
Read our in-depth Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark IV review
For an additional outlay, the Fujifilm X-M5 is a superb alternative for beginners who want to shoot video and much as photos. The X-M5 is tiny, is supported by a superb selection of lenses, and comes with a 26MP sensor that delivers 6K video. However, like most other beginner mirrorless cameras, it's about twice the price of the EOS R100.
Read our in-depth Fujifilm X-M5 review
How I tested the Canon EOS R100
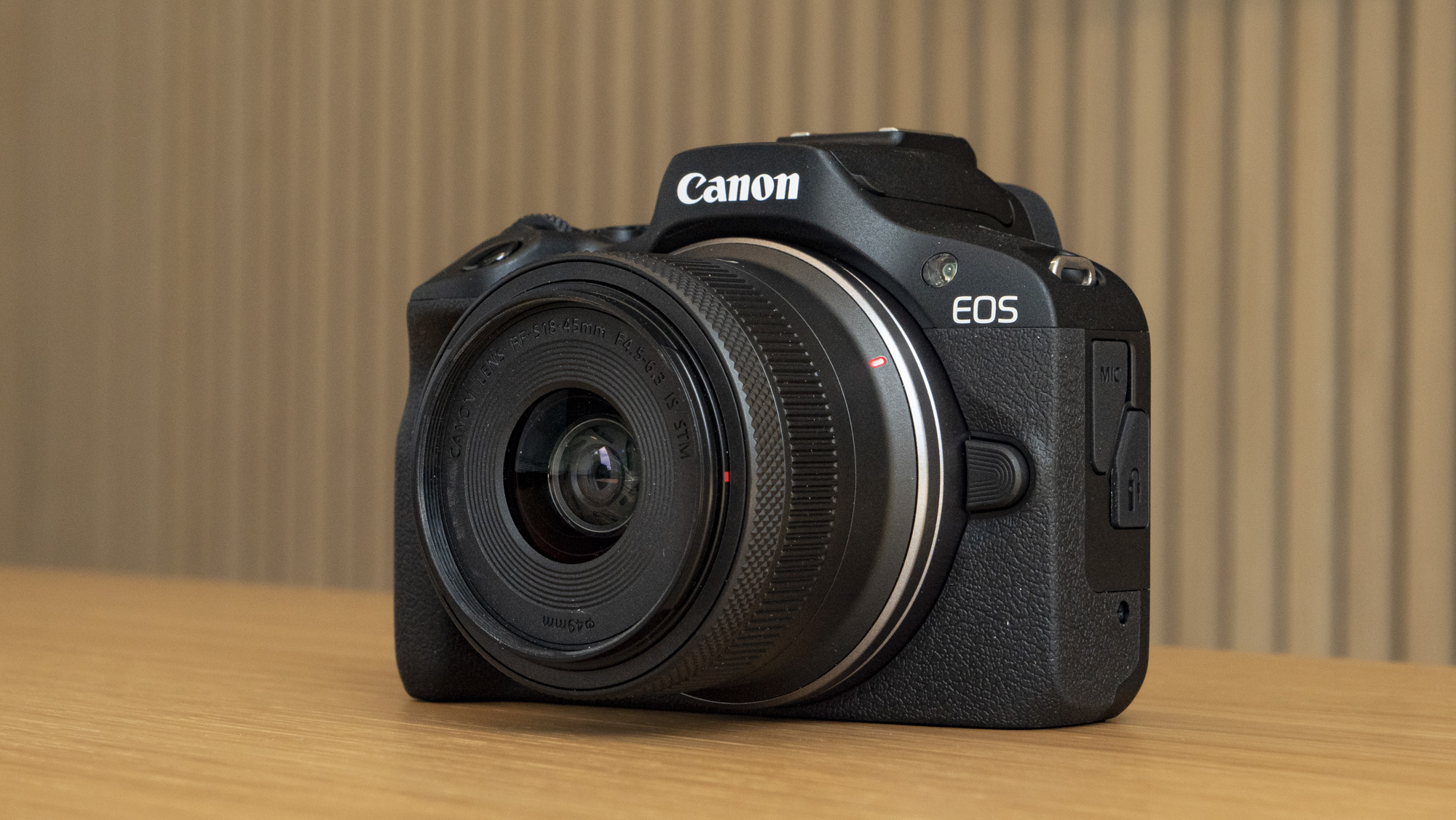

- I picked up the EOS R100 more than six months before writing this review
- During that time both I and my children have used it regularly
- I've paired the camera with many lenses, primarily the RF-S 18-45mm kit lens, but also third-party ones
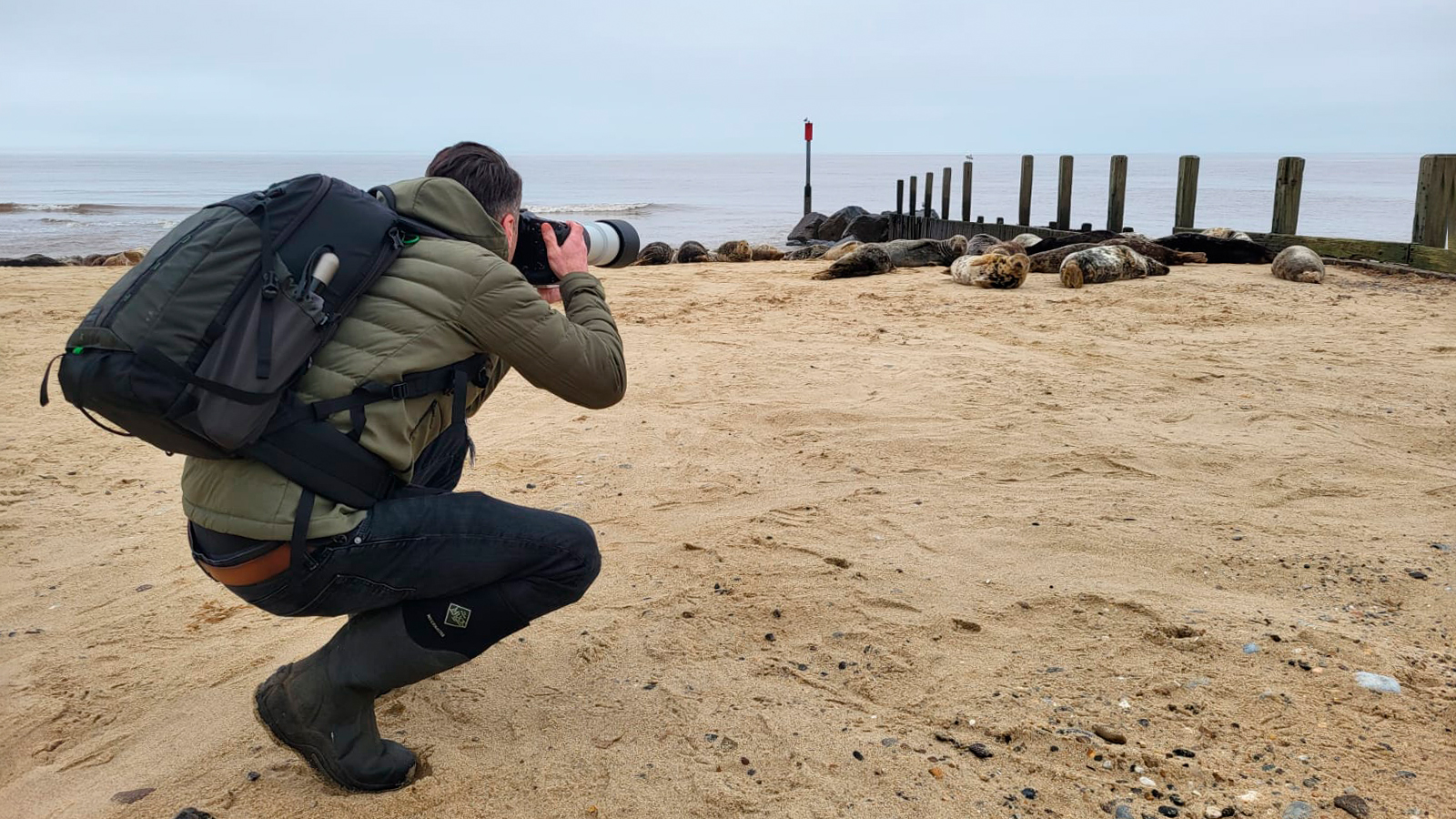
This review is a reflection of long-term testing over many months. And it's not just my thoughts and testing of the camera that have informed my thoughts, as my kids have taken a keen interest in the camera too.
Initially, I used the camera with just the RF-S 18-45mm kit lens, but we've also tried out Canon's RF-S 55-210mm telephoto zoom, plus four Sigma Contemporary lenses – 16mm, 23mm, 30mm and 56mm f/1.4 primes.
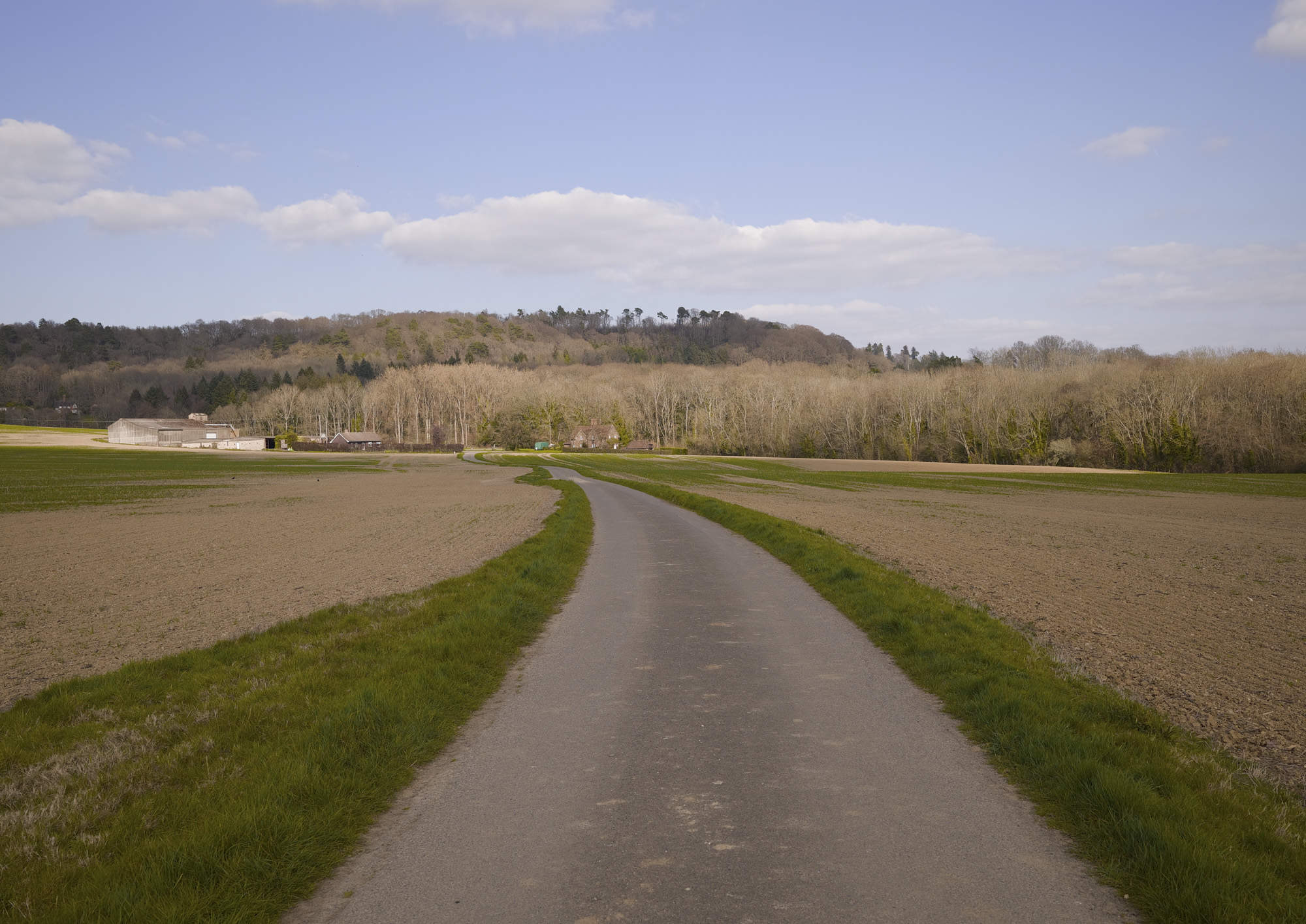
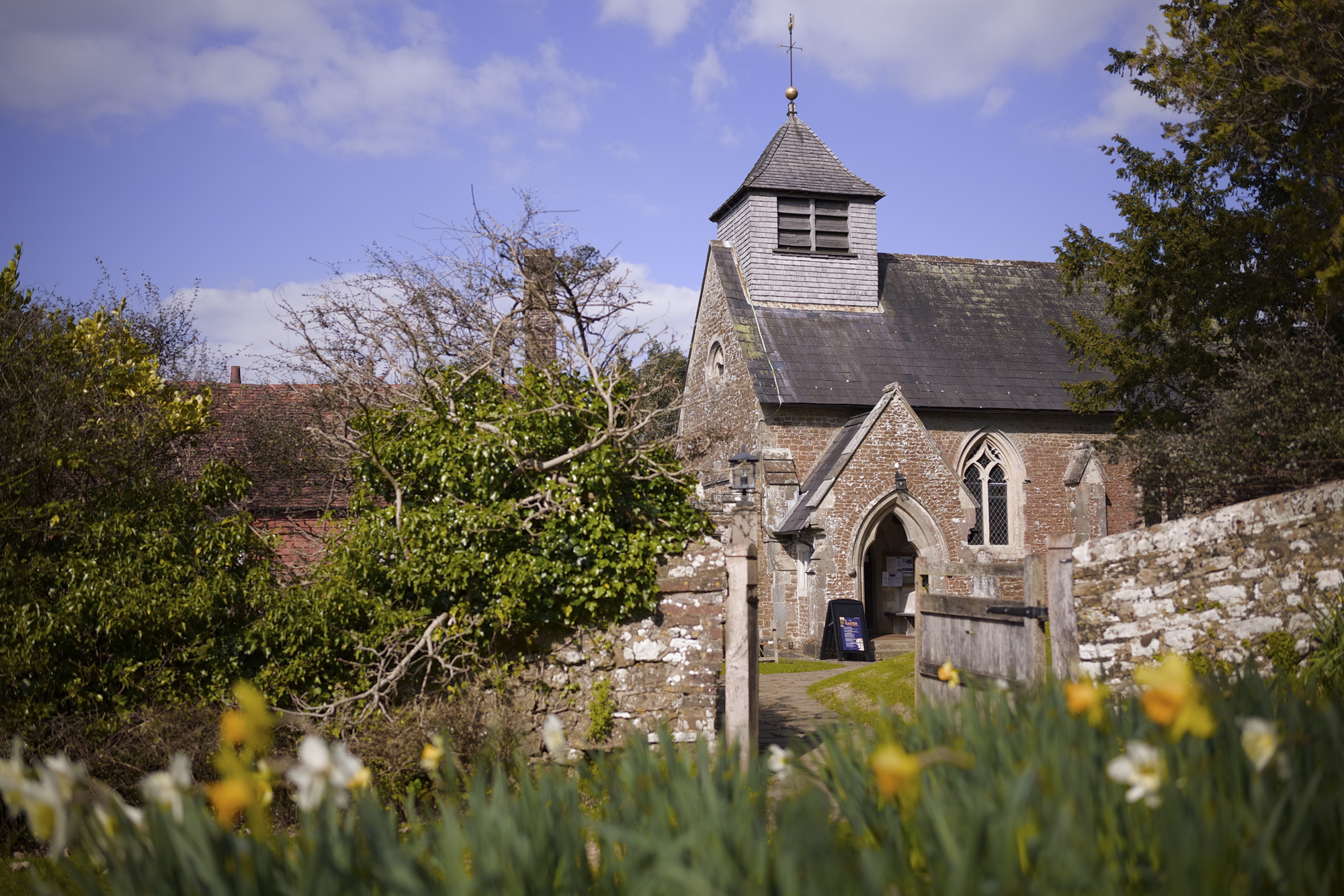
We've primarily used the camera for taking photos rather than video, shooting landscapes, portraits, wildlife, pets, closeups and more.
First reviewed April 2025