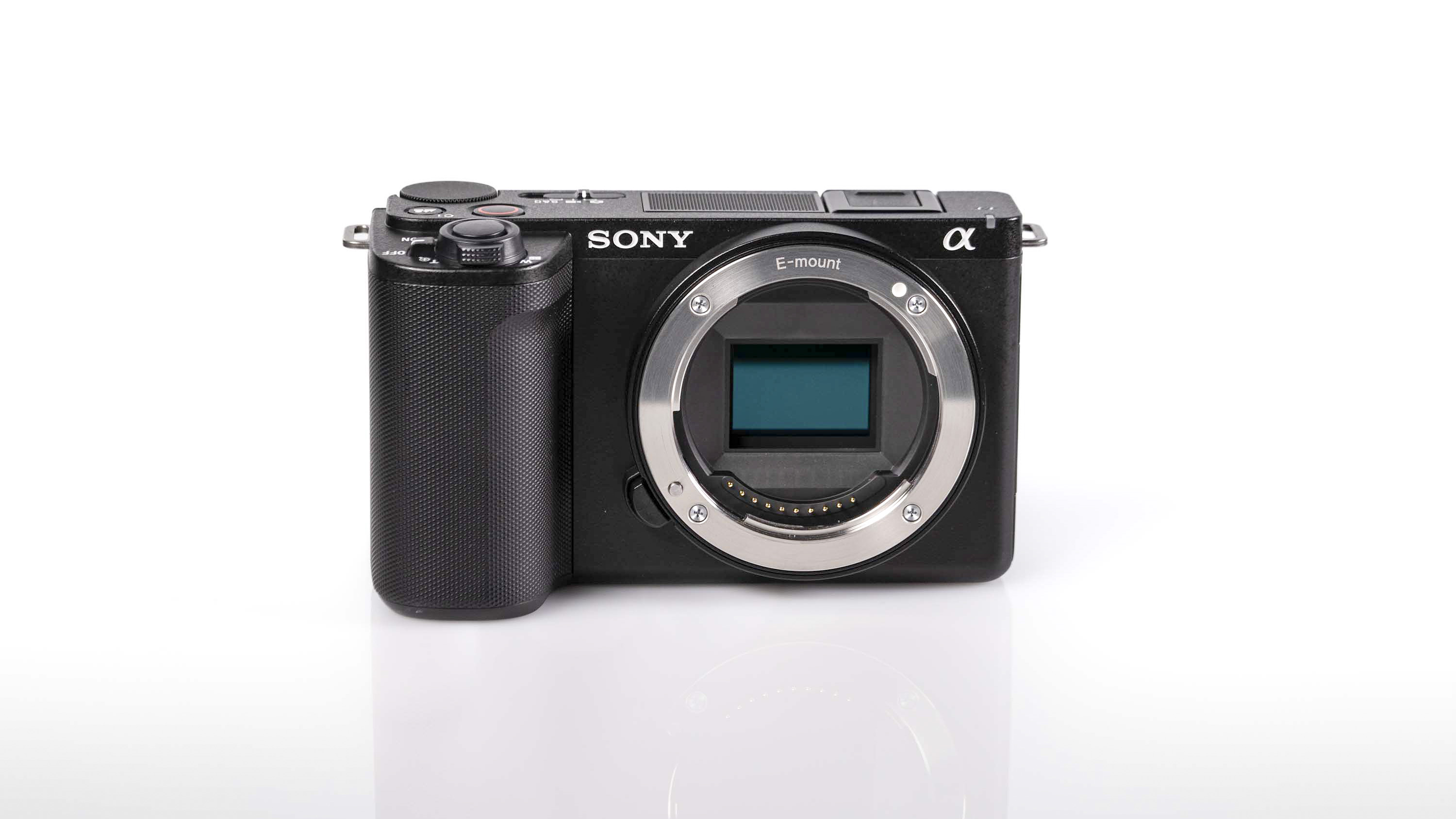
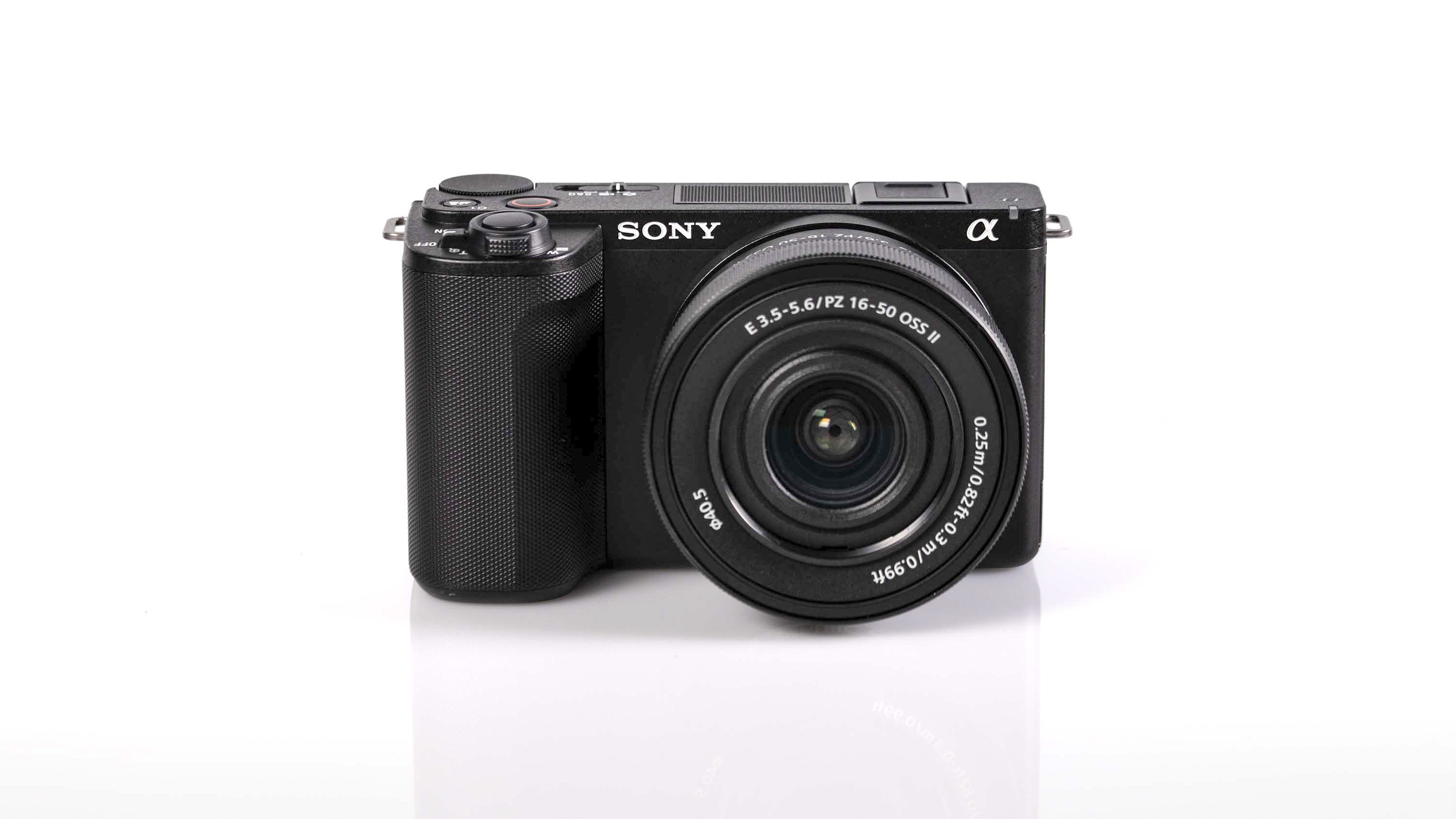
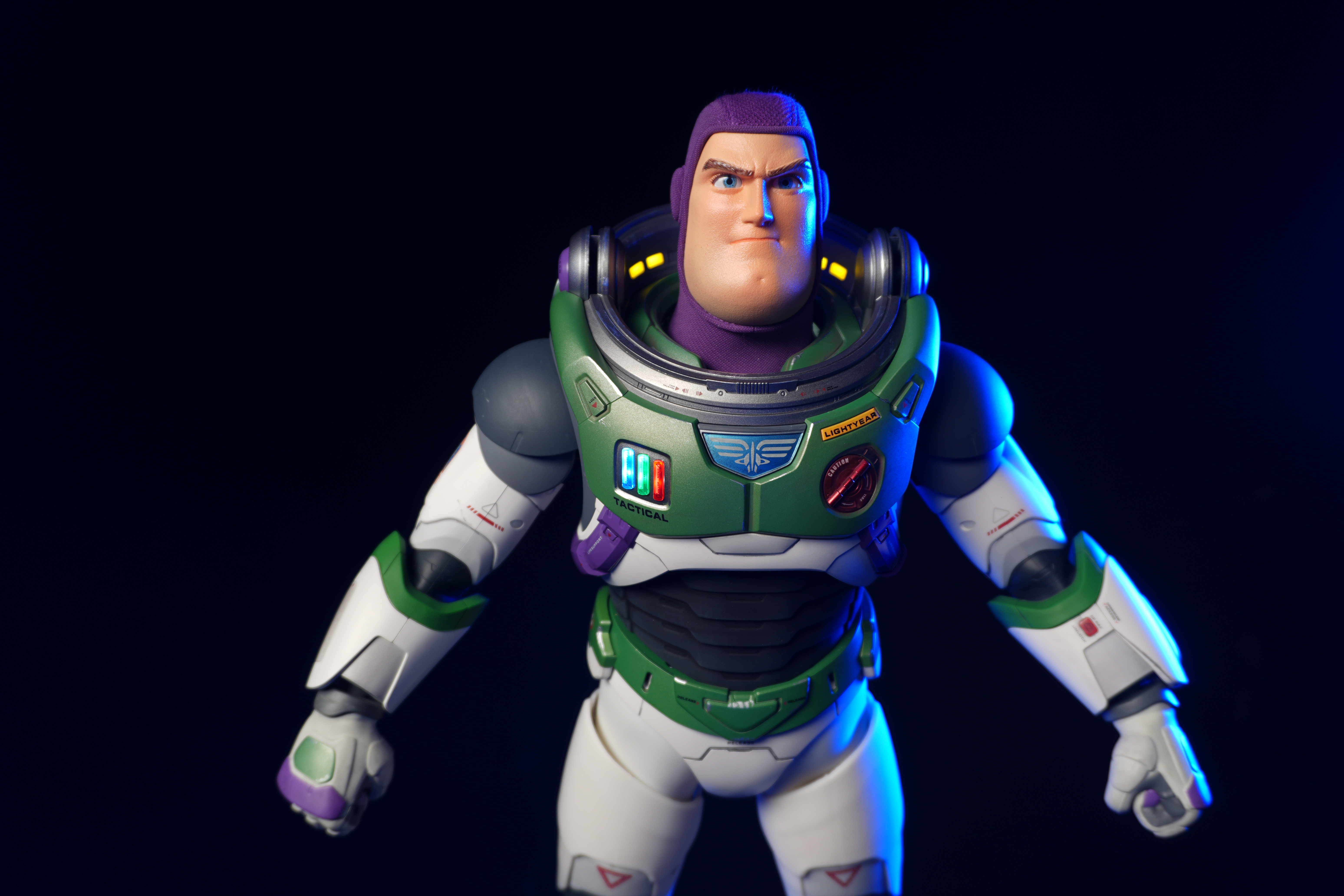
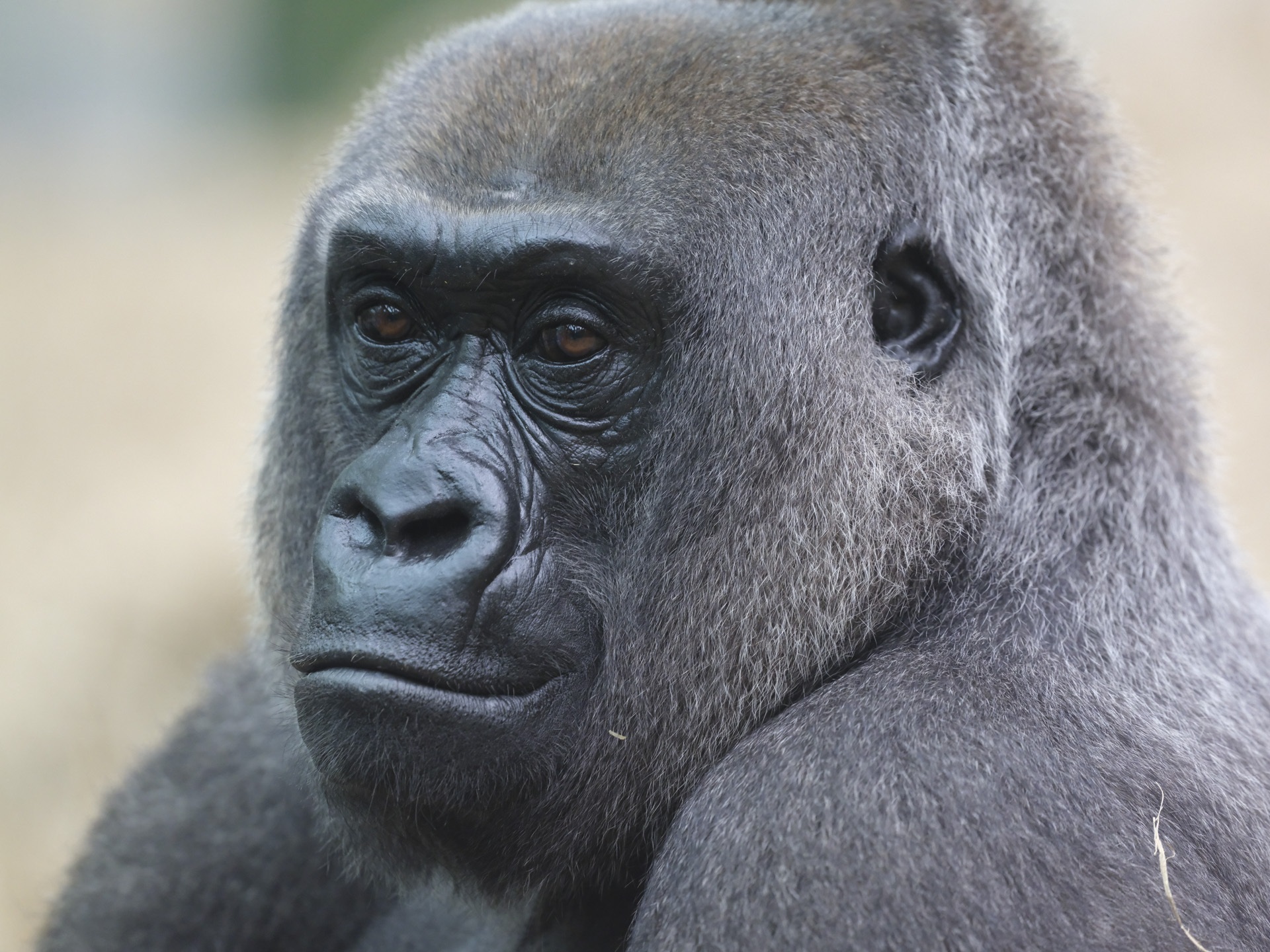
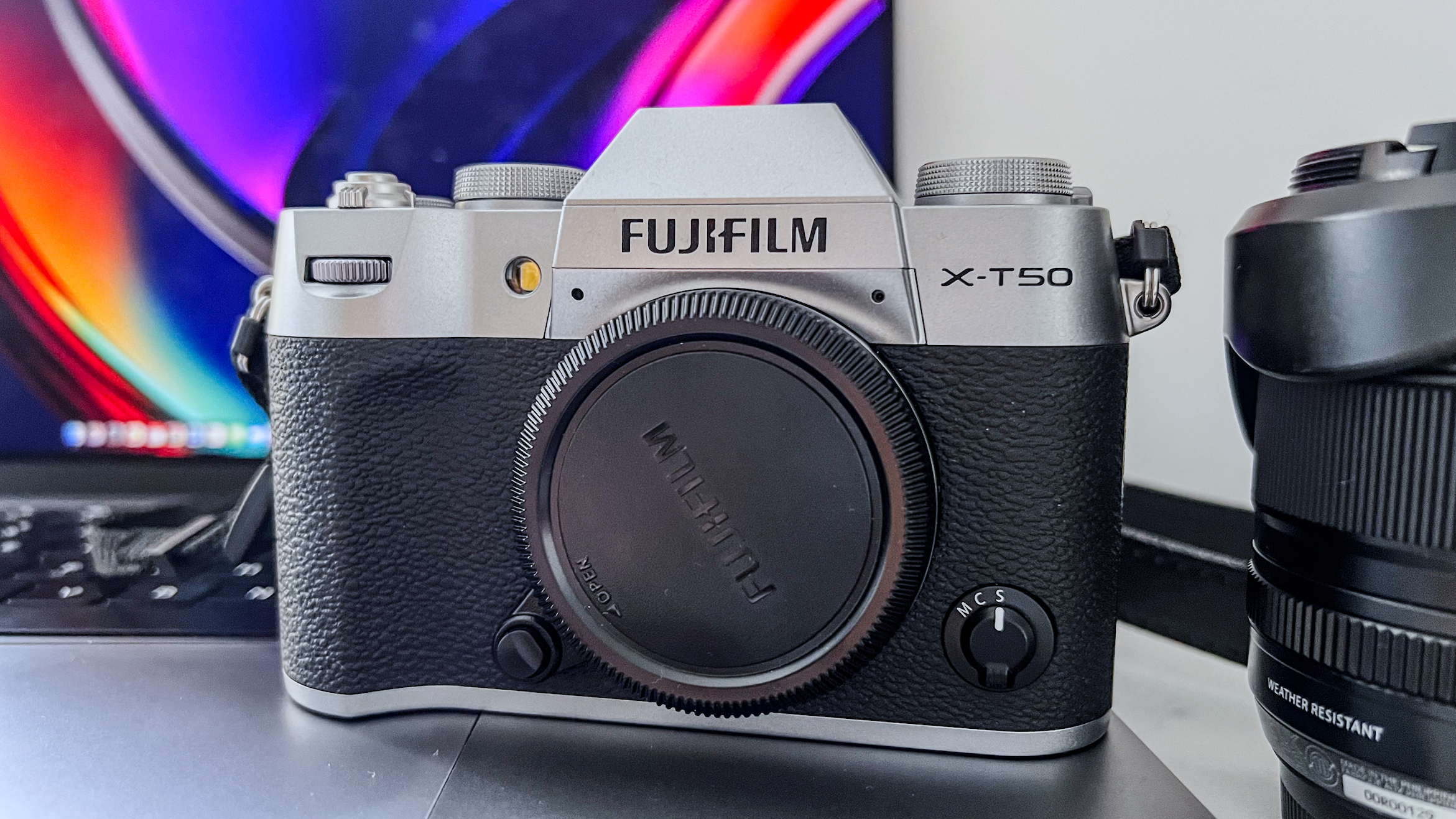
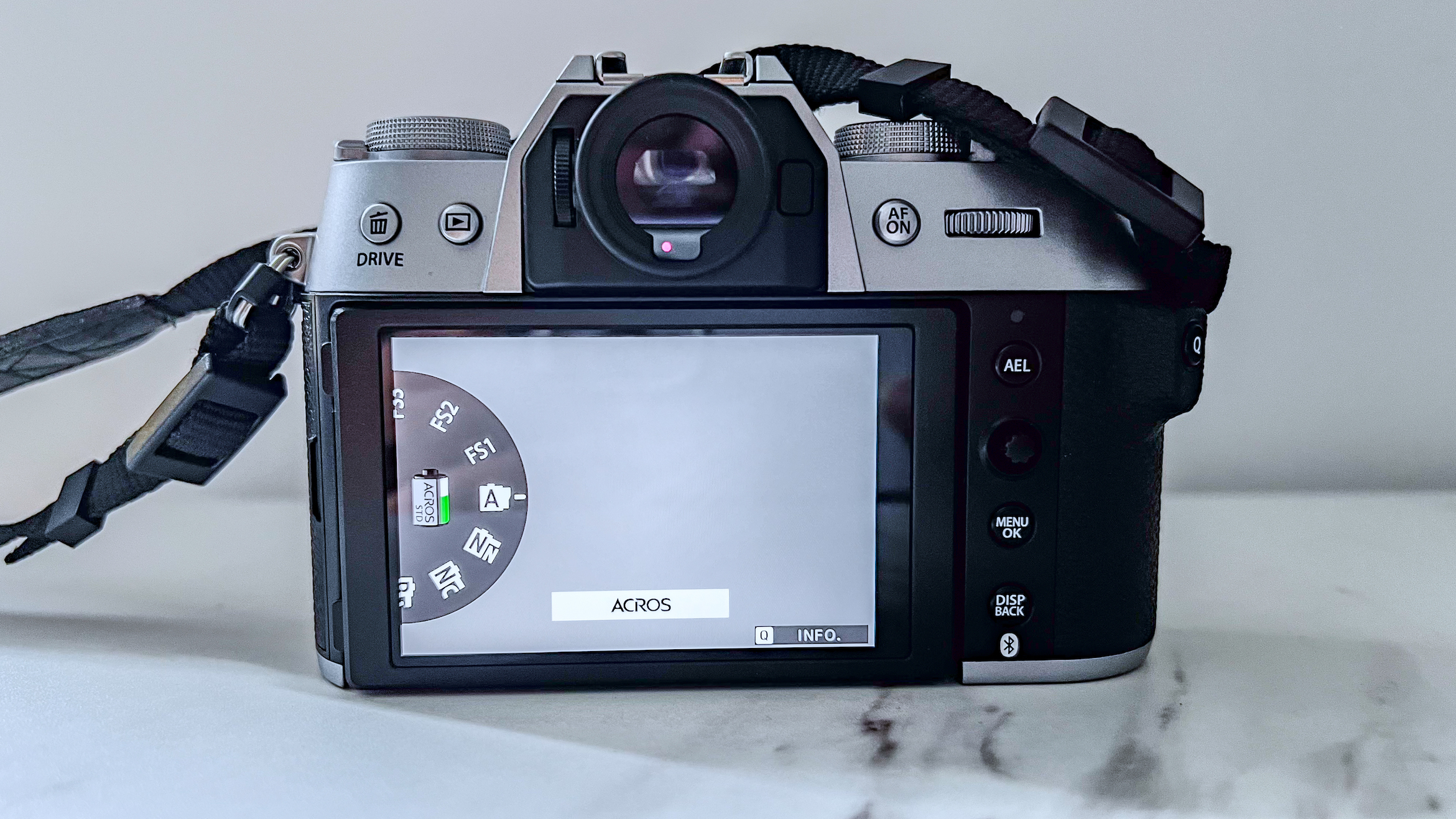
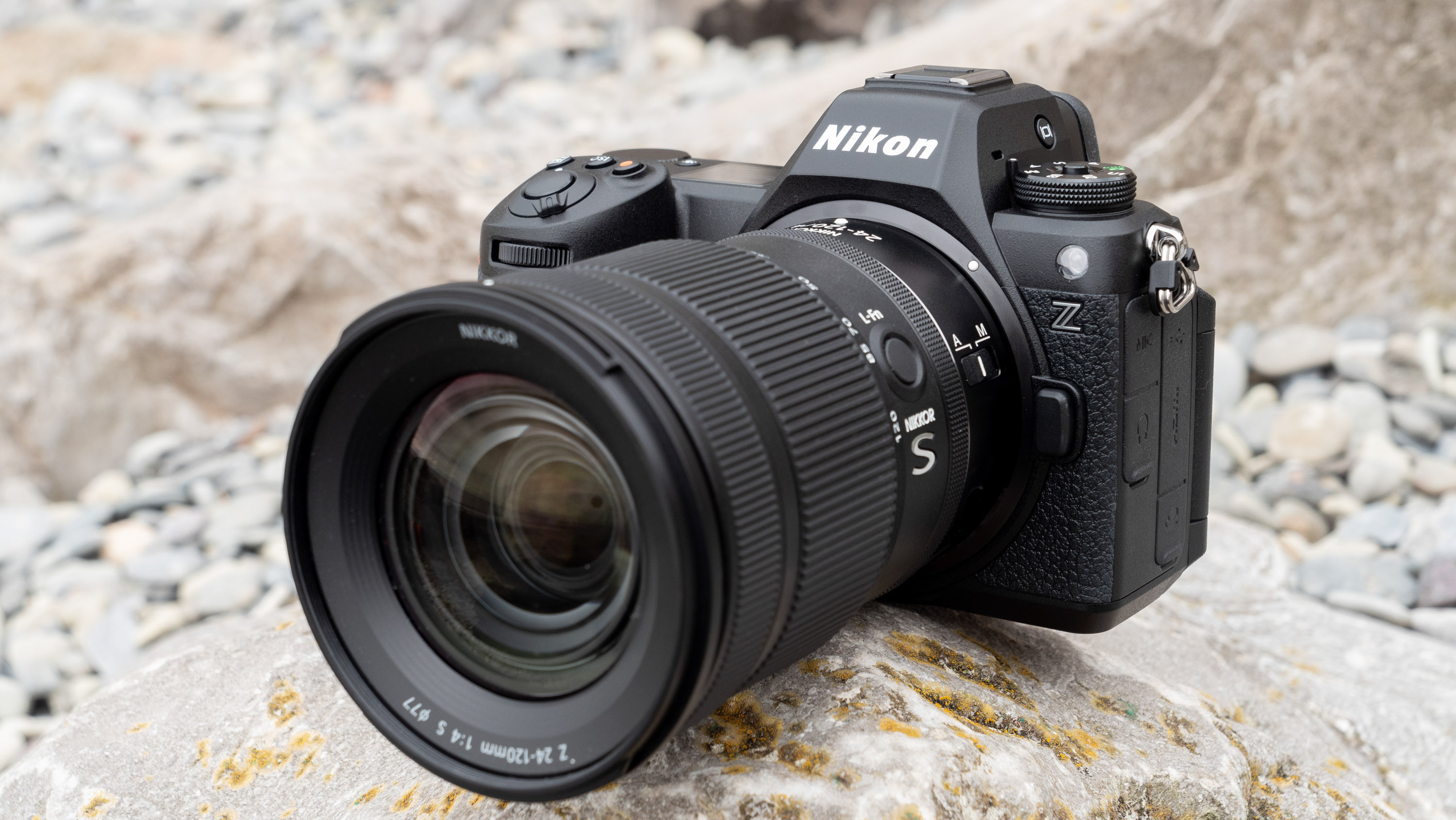
Nikon Z6 III: two-minute review
Sitting at the more affordable end of Nikon’s range of full-frame models, the Z6 III is designed to be an all-rounder, which can tackle a variety of subjects, whether that’s for photo or video.
What makes it more affordable is its 24.5MP sensor, which is just shy of half that of other pricier models in the line-up, including the Z7 II, the Z8 and the Z9. However, it's an exciting new “partially stacked” sensor, which unleashes ultra fast shooting speeds available, making this a real powerhouse when it comes to sports and action - and marking a major improvement on its predecessor, the Z6 II.
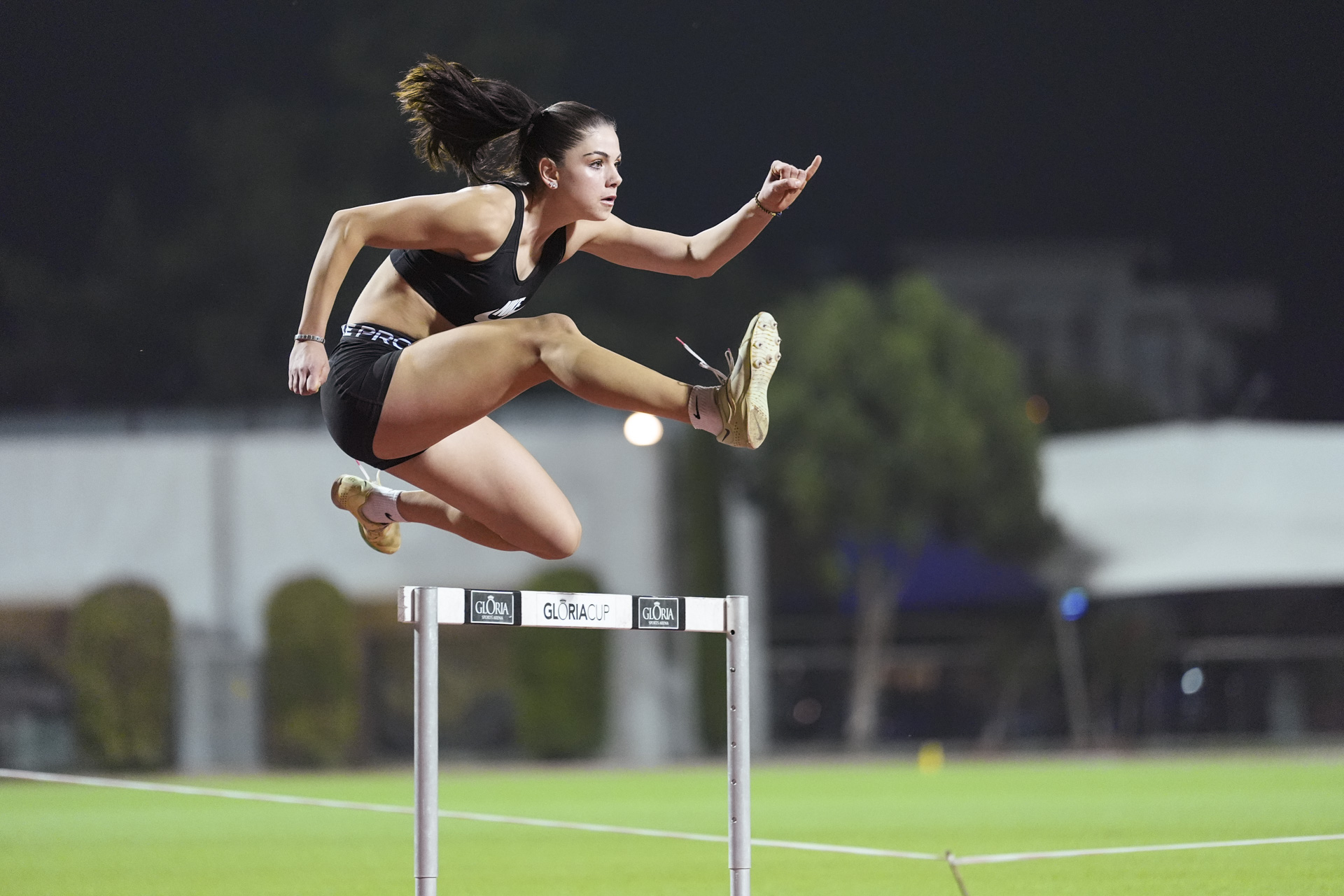
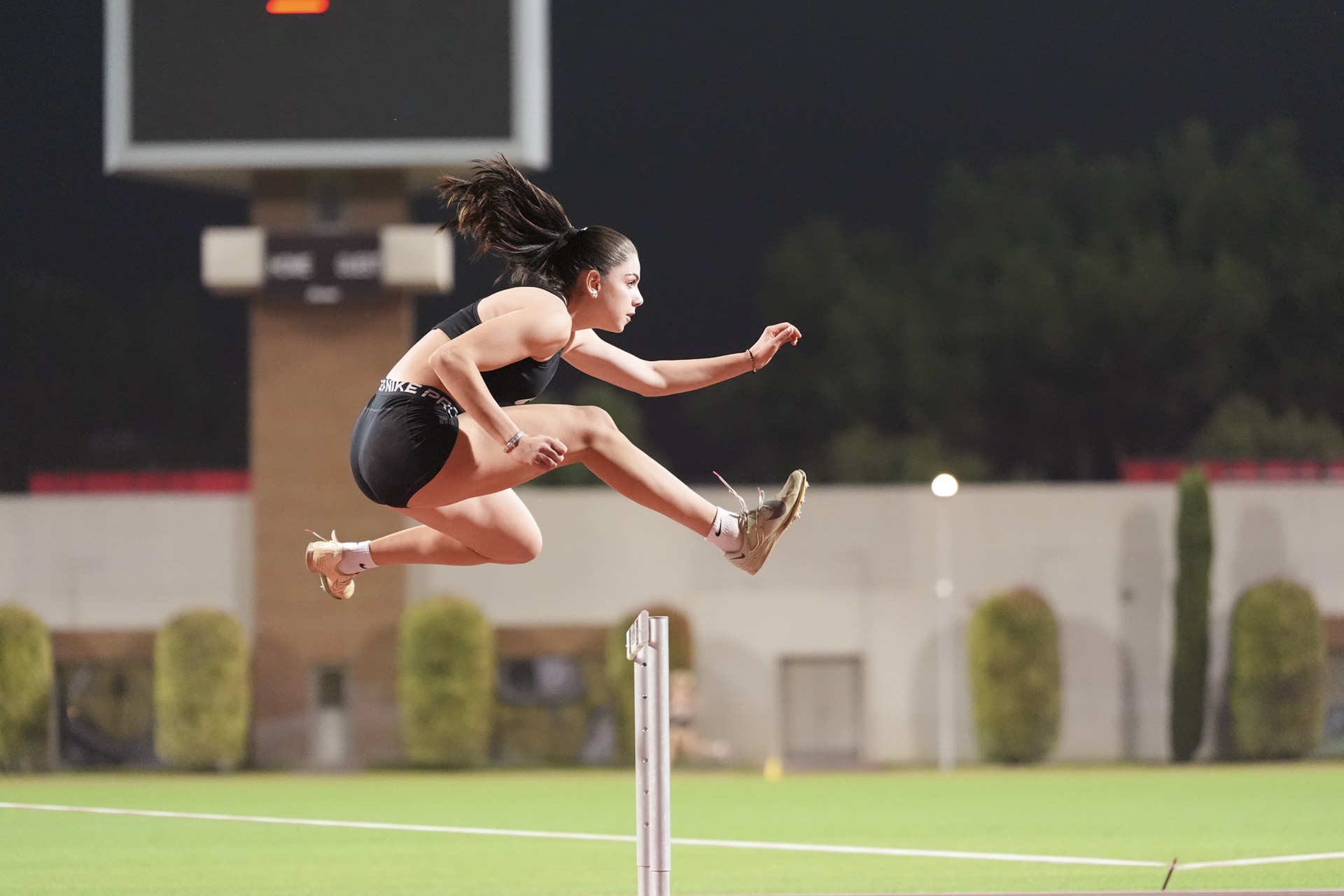
There’s up to an incredible 120fps shooting available - with some big caveats - but up to 20fps at full resolution in raw with full AF/AE. In practice, this turns out to be more than you’ll need for most types of action and returns a fantastic hit rate where almost every shot is in focus thanks to the superb autofocusing system which has been brought over from the Z8 and Z9 cameras.

For video, there’s now 6K up to 60fps available, as well as 4K at a range of frame rates up to 120fps. Being able to create oversampled video at 4K thanks to its 6K shooting ability will be appealing to lots of content creators, and gives you scope to get more shooting angles from whatever lenses you have.
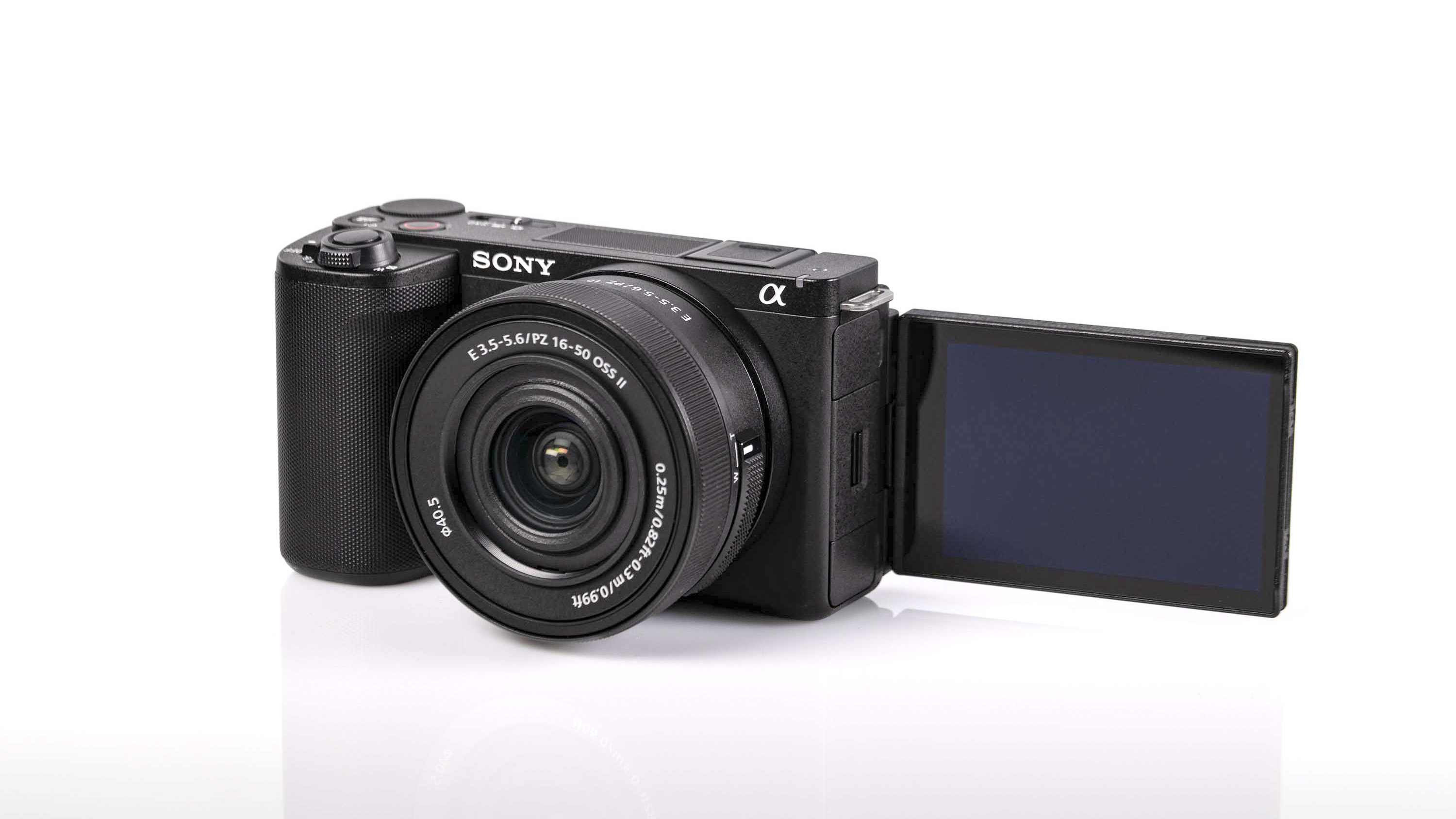
In terms of body design and layout, much has stayed the same or similar since the Z6 II, however the III is now toting a fully articulating screen, making it far more suited to video work than ever before.
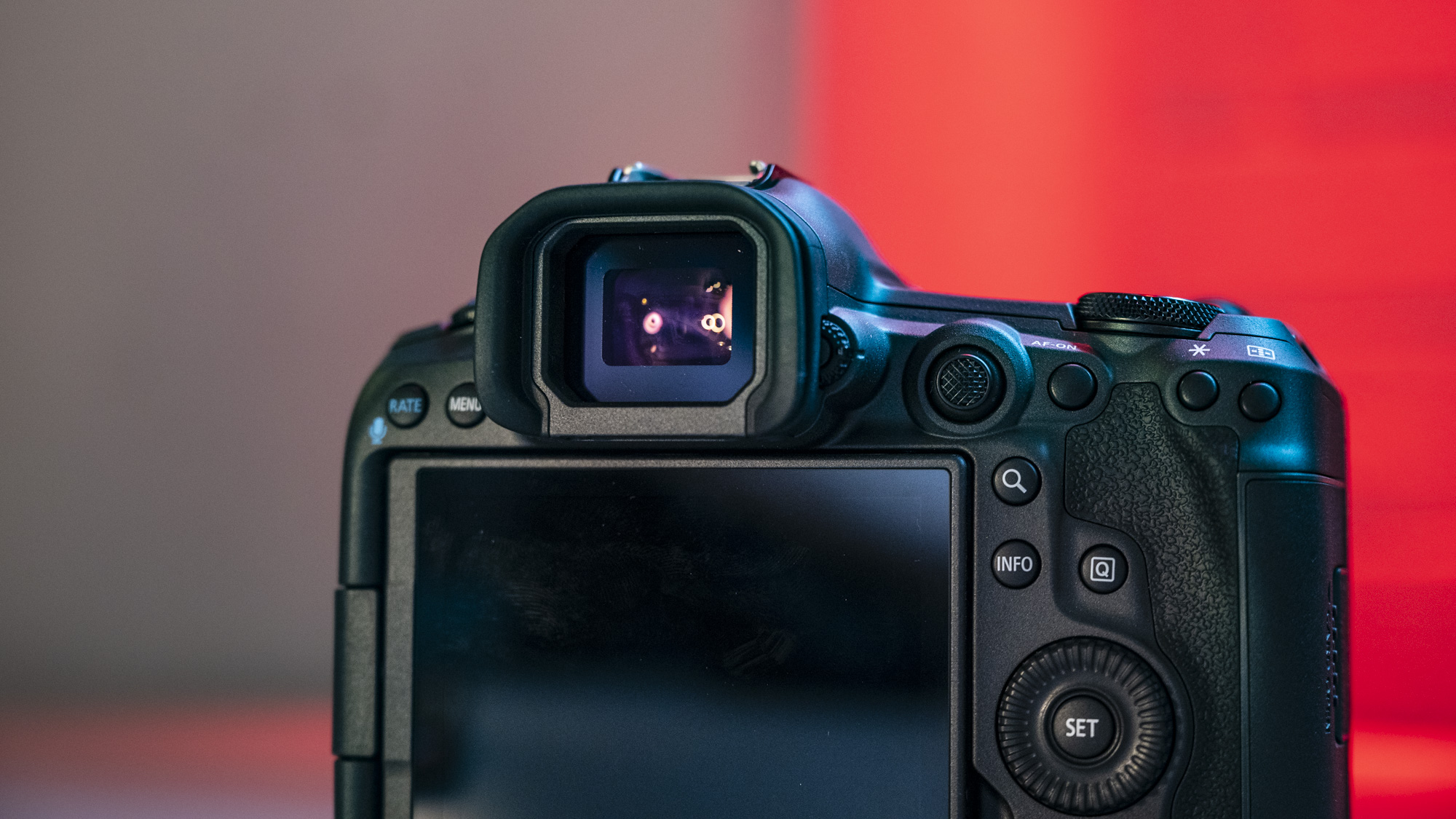
We’ve also got a brand new viewfinder and it's Nikon's best yet, with a 5,760k-dot resolution and an ultra-wide color gamut, plus a 60fps refresh rate. These specs all combine to make the Z6 III’s viewfinder one of the best experiences on the market.
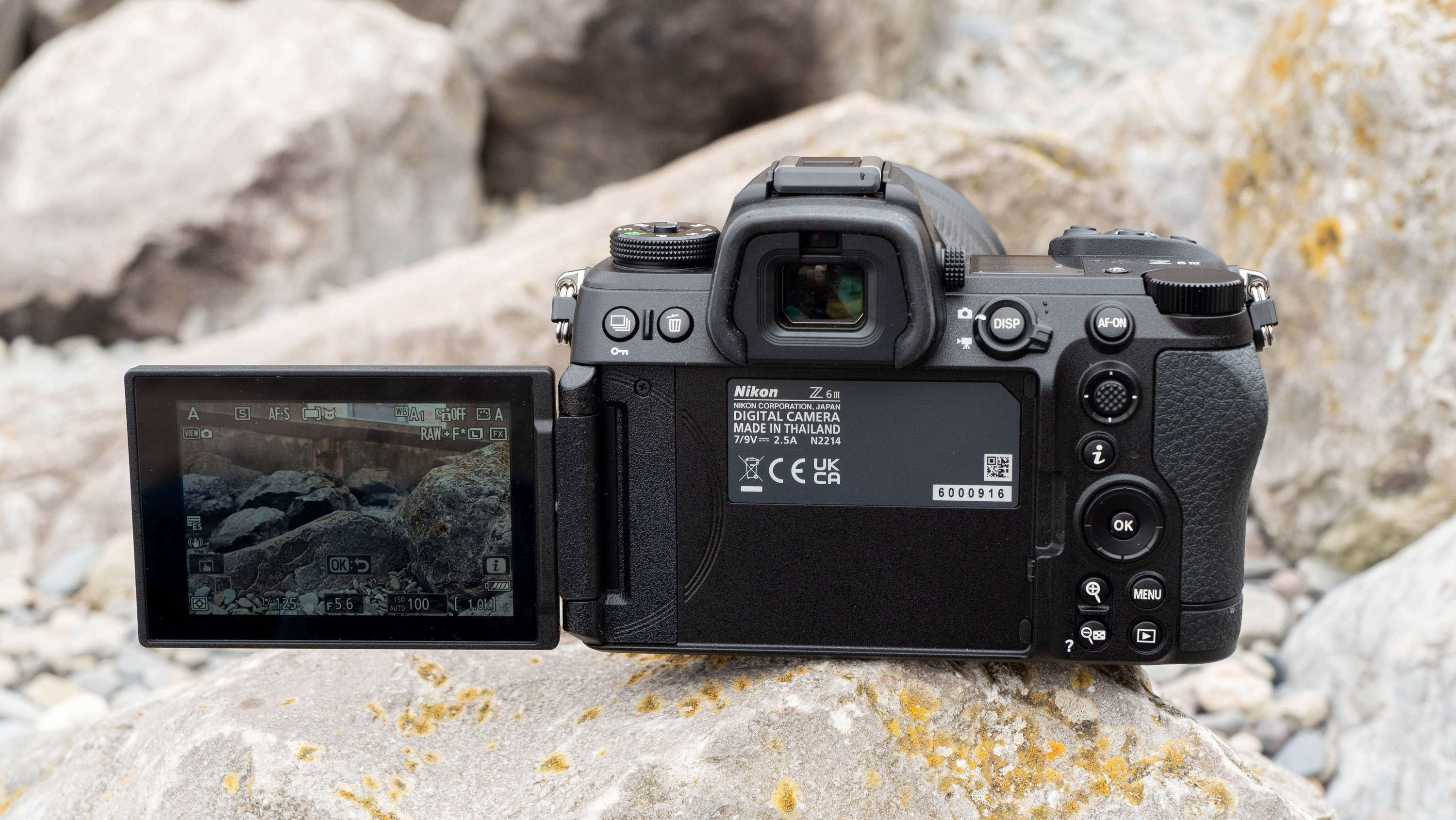

Image quality doesn’t show a revolutionary improvement from the Z6 II, which is pretty much as we’d expect. However, it's easier to get the shots you want thanks to improved autofocus and burst shooting performance, so while individual shots might not be an improvement in terms of things like dynamic range, color and detail, the fact that you can get more shots in focus is what makes the big difference. Video quality is also great.
When it comes to pricing, the Z6 III is more affordable than the Z8 and Z9, but you will be paying a premium for how much better it is than the Z6 II, especially considering that camera is now on sale since the Z6 III was announced. In fact, you’ll also be paying a premium right now over the high-resolution Z7 II. Between those two cameras, it’s up to you to decide whether you want high resolution at the expense of speed, or the other way around.
If you mainly shoot landscapes and other still subjects, the Z7 II might be the better choice, but if you ever shoot anything moving - or at least think you might - then the Z6 III is a much better choice.
Nikon Z6 III: release date and price
- Body only price is $2,496 / £2,699 / AU$4499
- Available now
The Z6 series has always been on the more affordable end of Nikon’s pro-spec line-up. Although it’s higher in value than the Z5 series, it’s generally cheaper than the Z7, Z8 or Z9 cameras. That said, the feature-packed Z6 III will set you back more than its predecessor did at launch by around 25%, and with the Z6 II on sale, the Z6 III is £1000/$1000 more expensive for the body only version at the time of this review. Right now, the Z6 II feels like a comparative bargain, especially if you can live without some of the Z6 III's improved autofocusing and burst rates.
The Z6 III is also currently more expensive than the Z7 II, so if you need higher resolution, you might opt for that model instead - again though, you’ll be missing out on things like fast shooting. If Nikon hasn't given up on the Z7 series, we could see a speedier Z7 III, but that would be treading a little too close to the Z8 and we think a new Z7 model is unlikely.
Perhaps the best thing to compare the Z6 III within Nikon’s own line-up is the Z8, with which it shares similar focusing capabilities. Here you’ll need to fork out an additional £600, and use a larger and heavier camera - but you do get higher resolution.
In the end, it likely comes down to speed vs resolution. If you need speed, go for the Z6 III, if you need resolution, the Z7 II or the Z8 if you can stretch to that is the best choice.
What about compared to other brands? Well, the Z6 III is significantly more expensive than its current main competitors, the Canon EOS R6 II, or the Sony A7 IV - both models which are also ripe for an upgrade. Although more expensive, you will get more for your money from the Z6 III, so if you’re particularly after some of its impressive features, then it’s likely to be worth the extra expense.
- Price score: 4/5

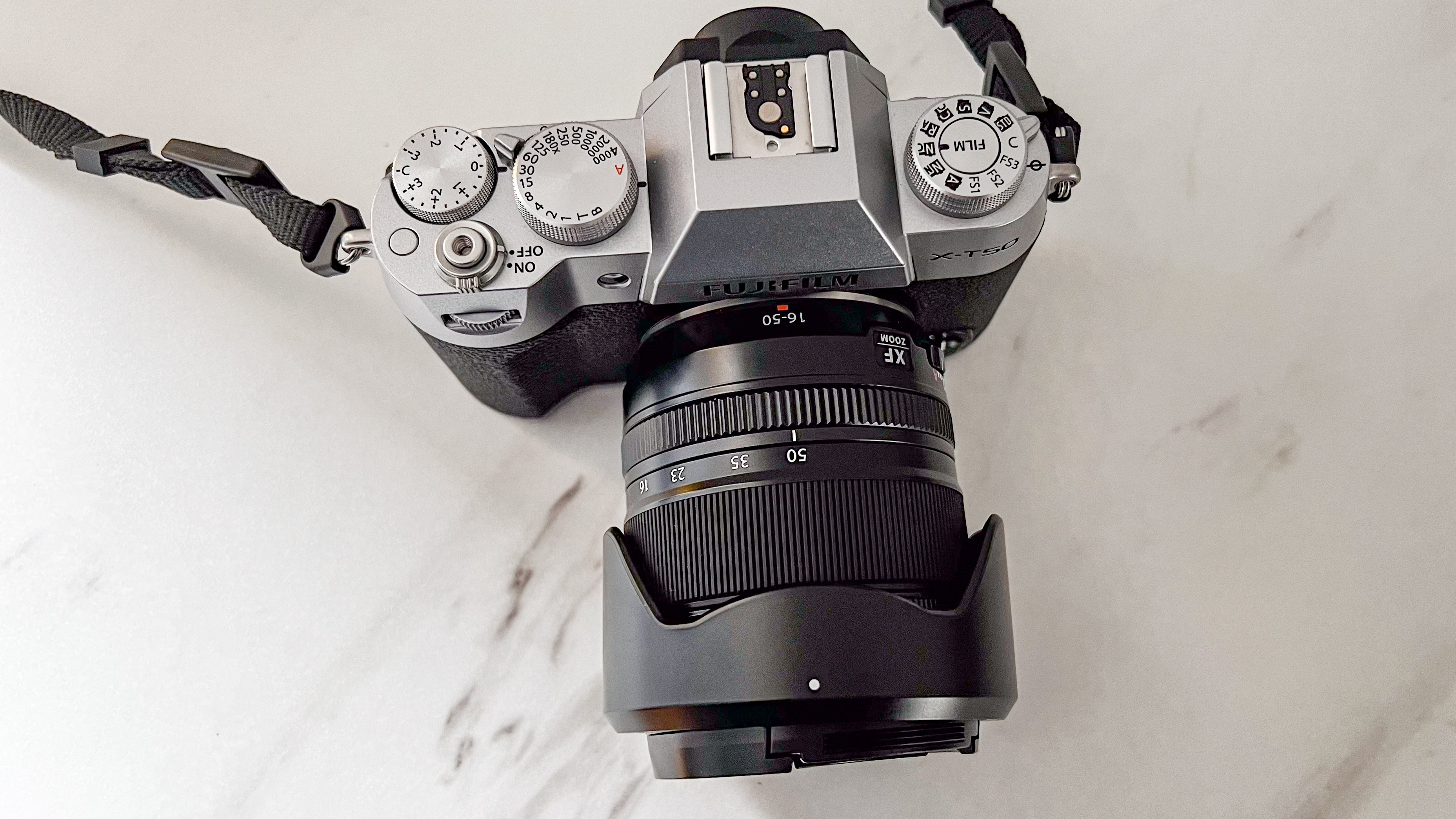
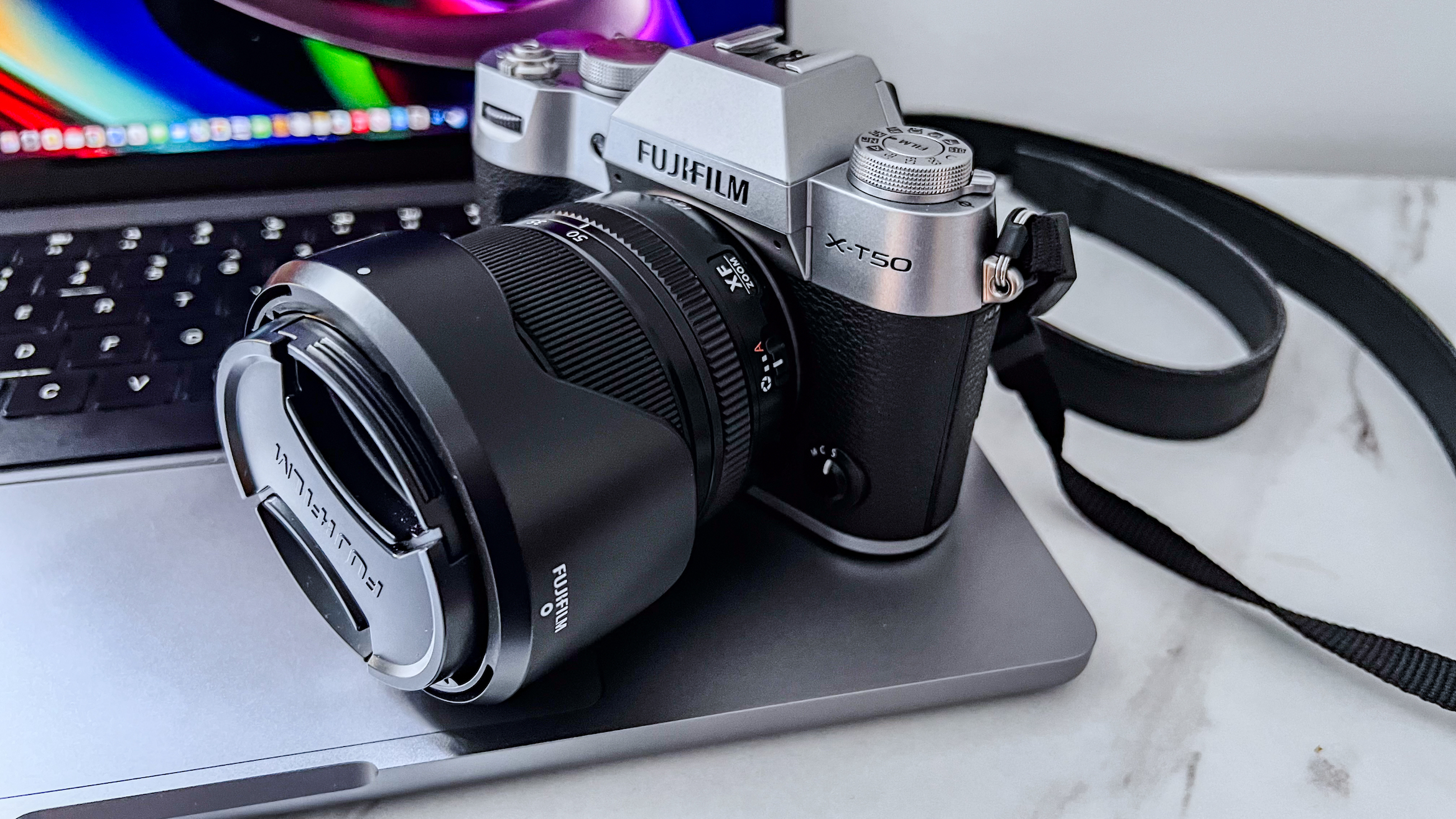
Nikon Z6 III: design and handling
- New vari-angle touchscreen
- Super high-res EVF
- Chunkier grip
- New additional battery grip
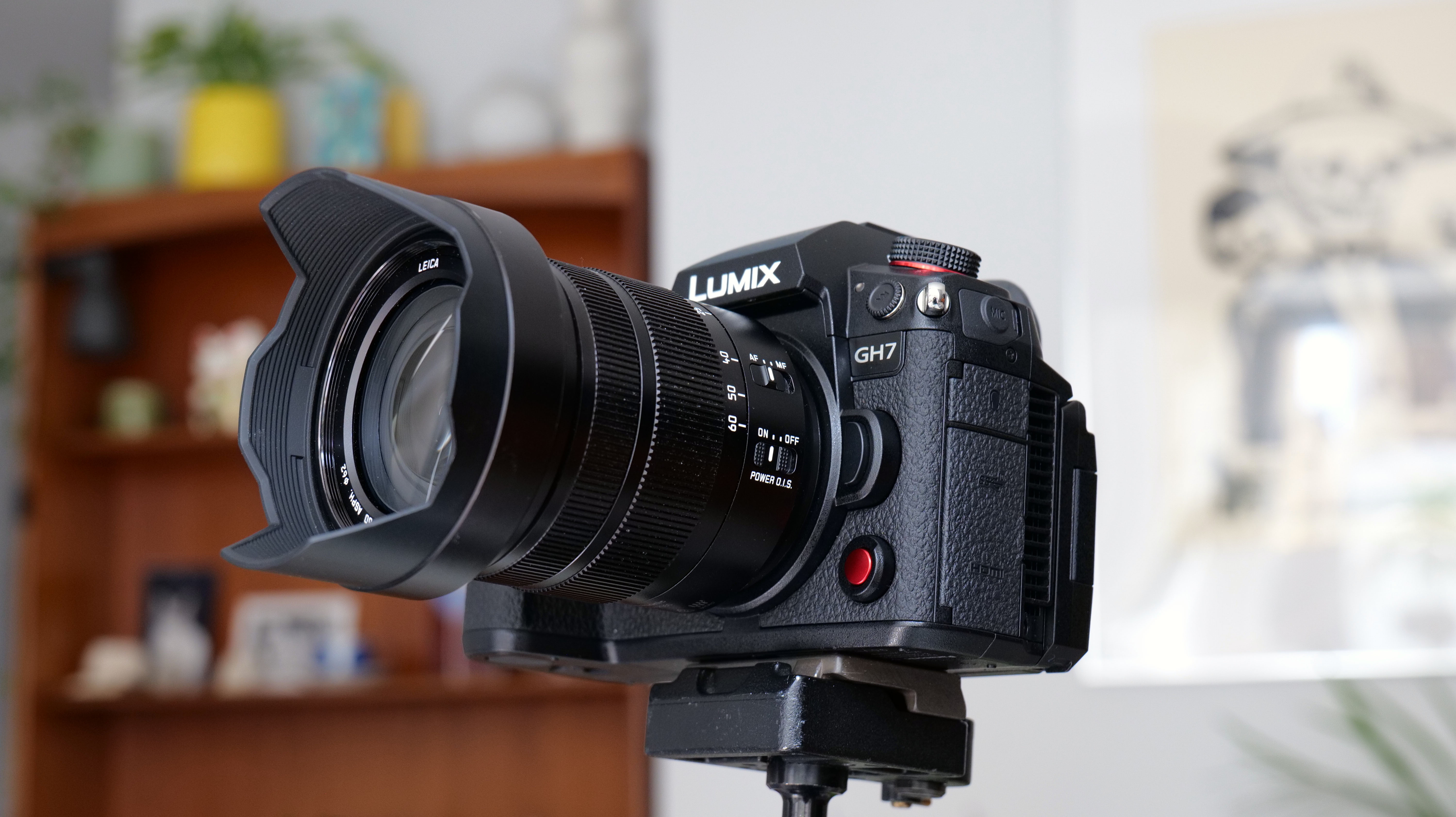
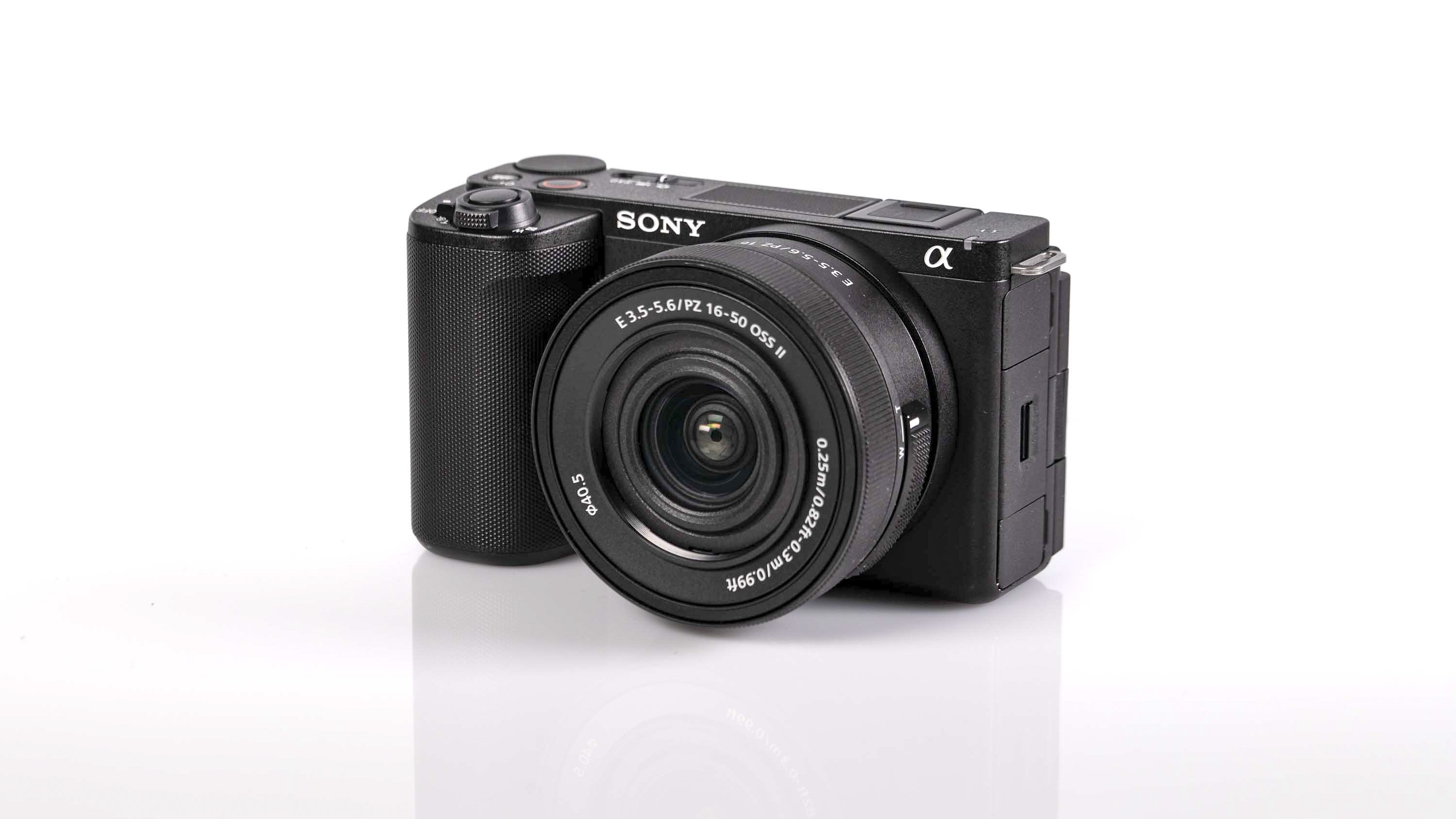
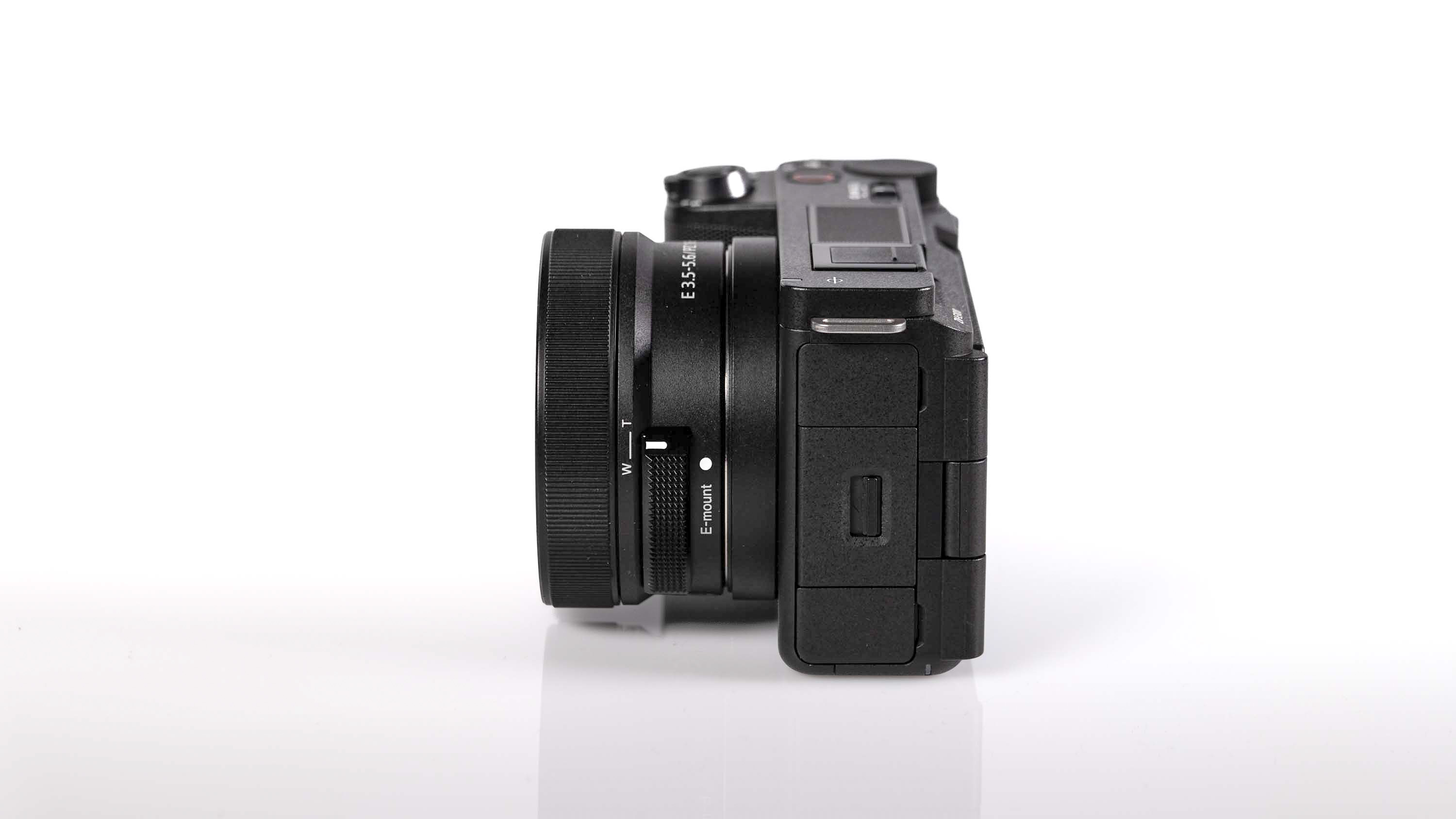
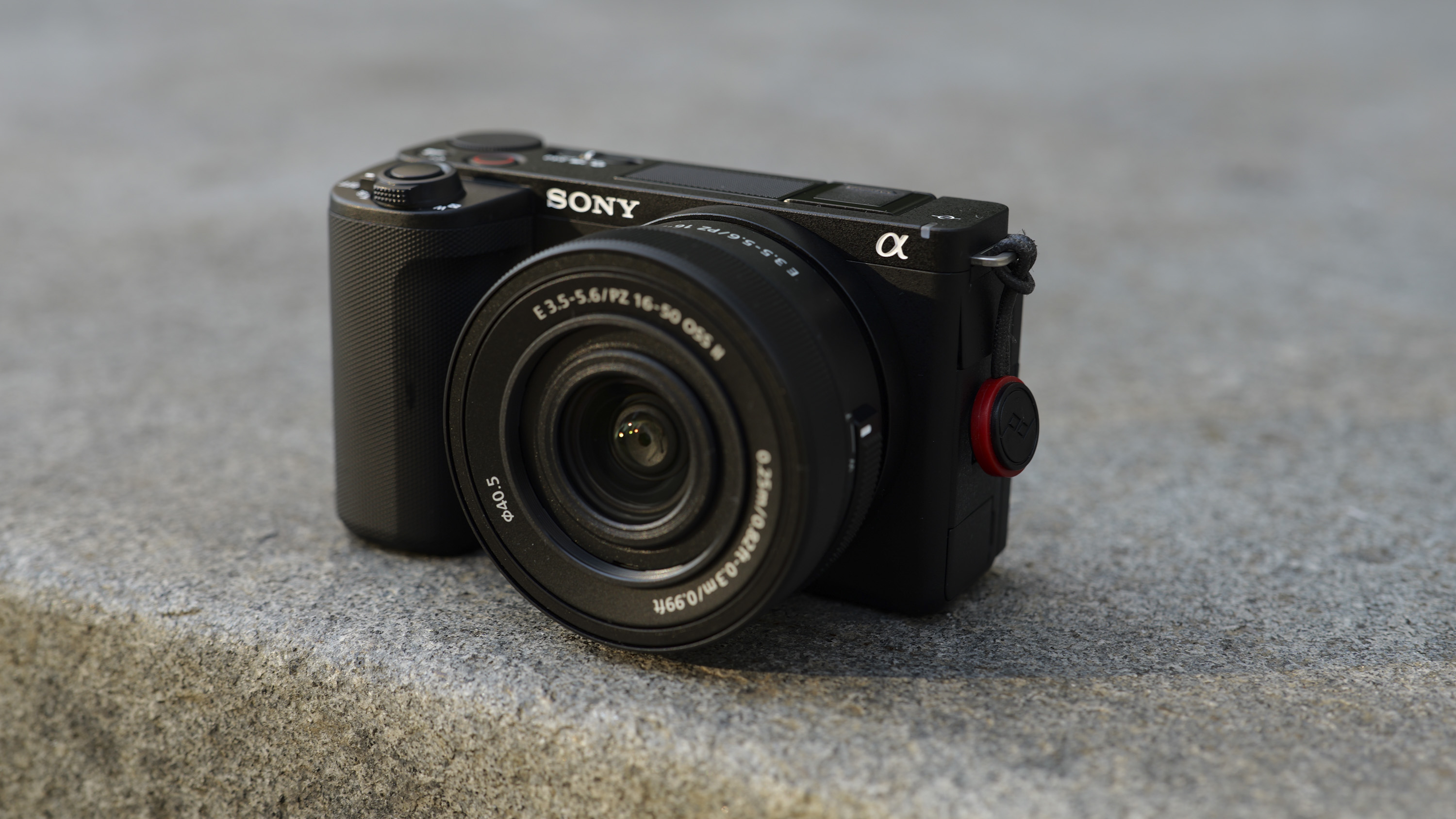
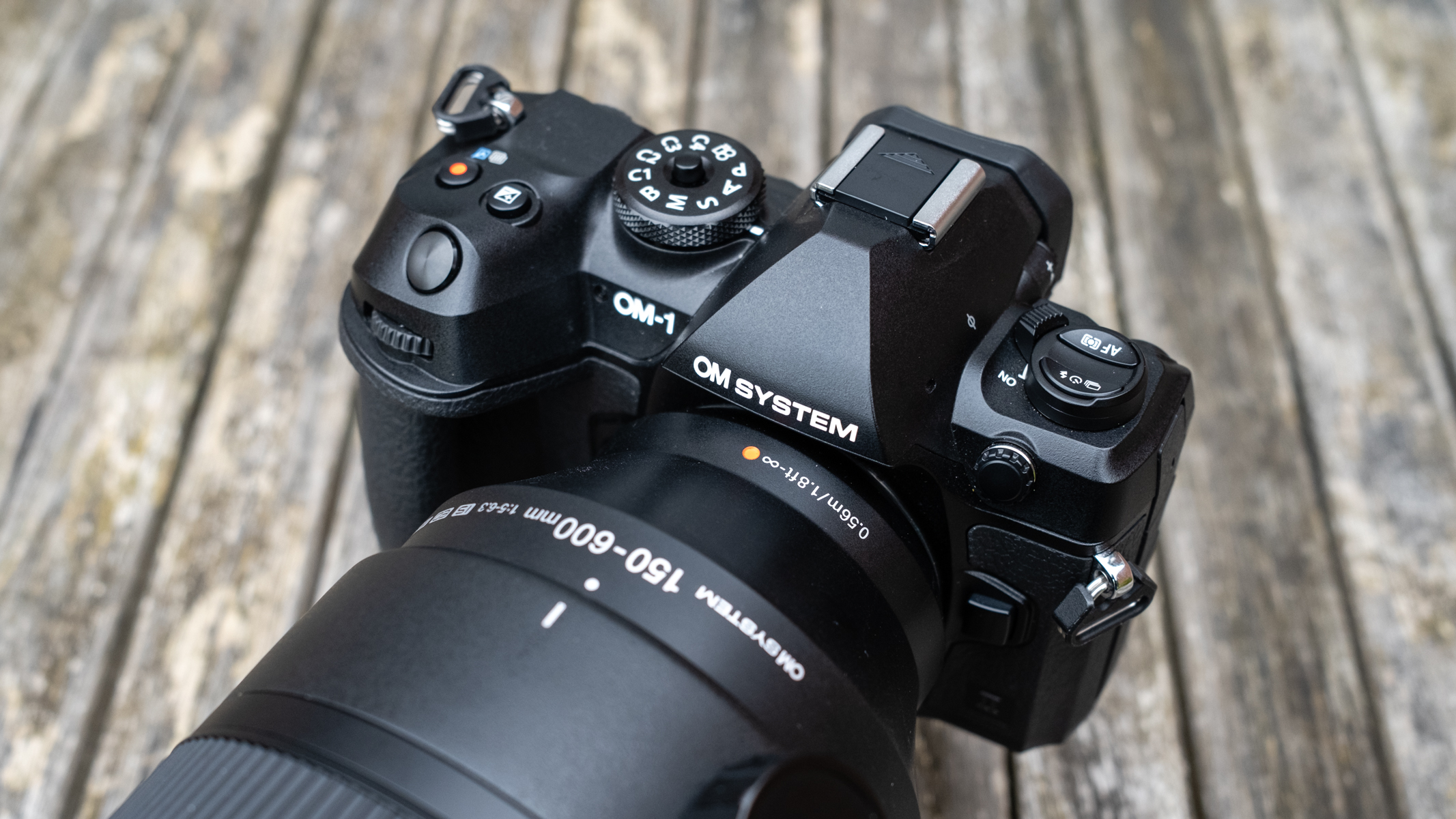
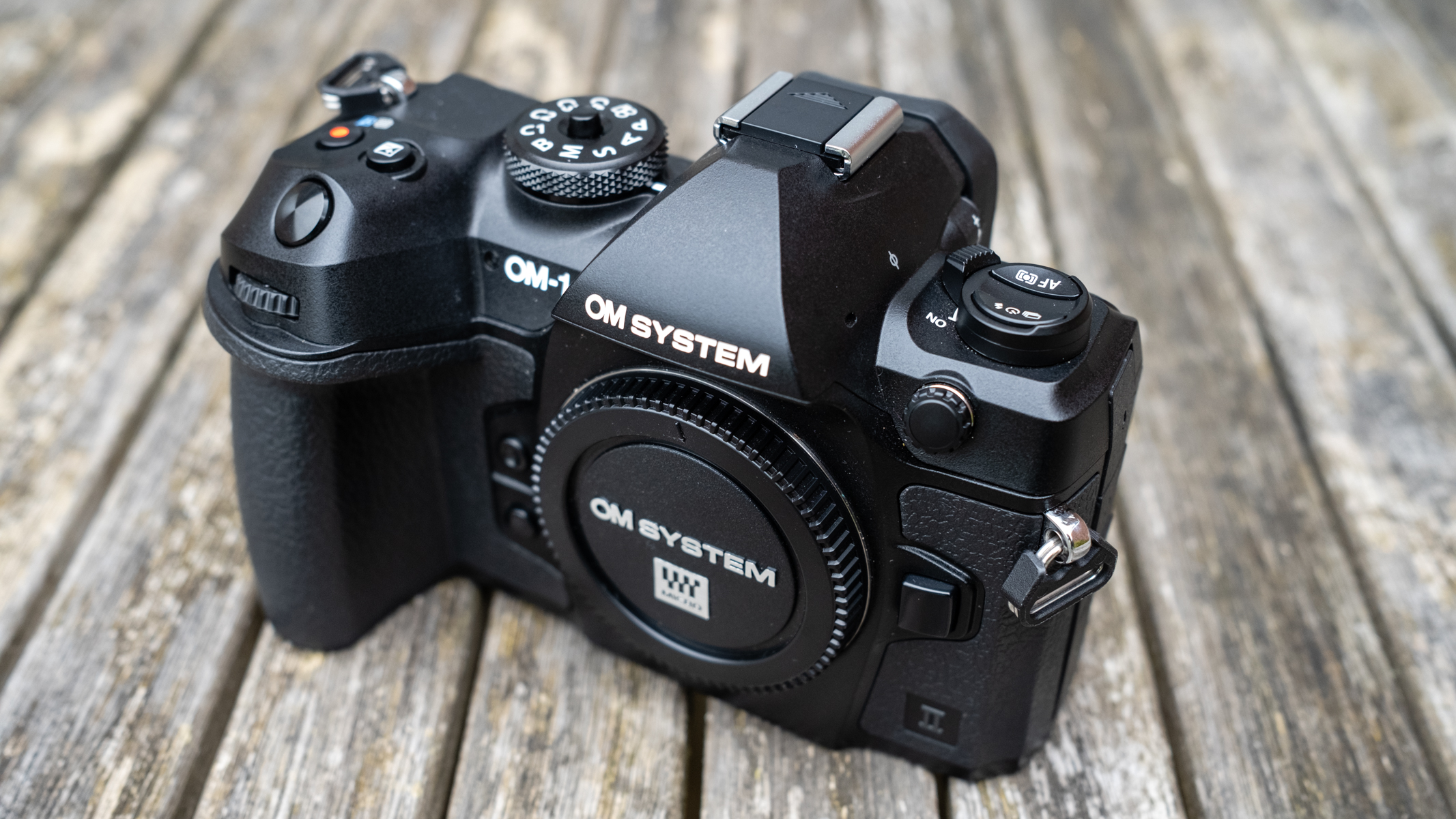
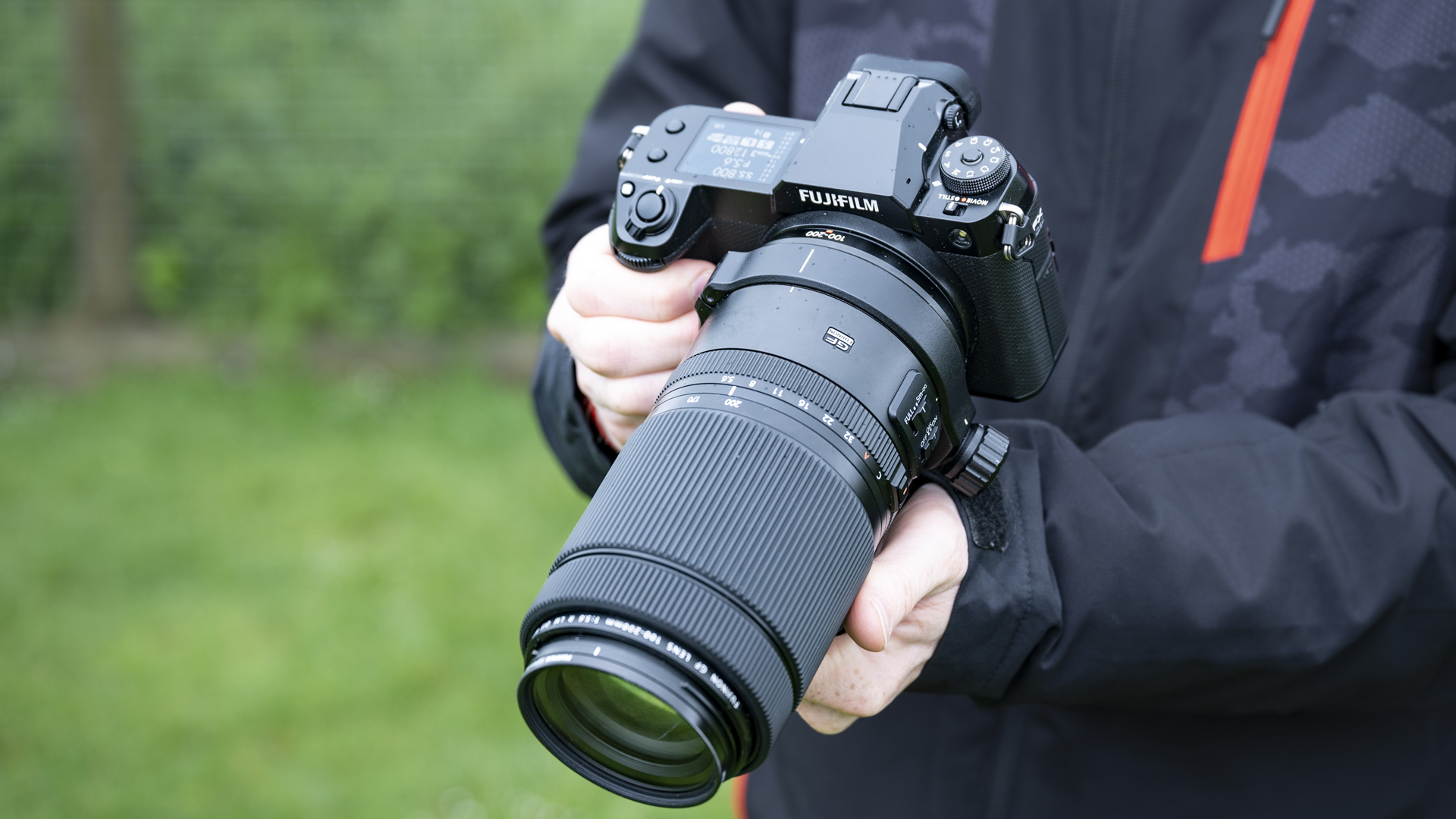
If you’re looking for a fast Nikon, then you might have had your head turned by the Nikon Z8 or even the Nikon Z9, but then been quickly put off by the size of either of those models. The Z6 III is a a much more easy-to-manage size than either the Z8 or the Z9, although it's little heavier than its predecessor (760g vs 705g body only) – that's mostly down to the chunkier hand grip which I'm all for because it gives a secure hold.
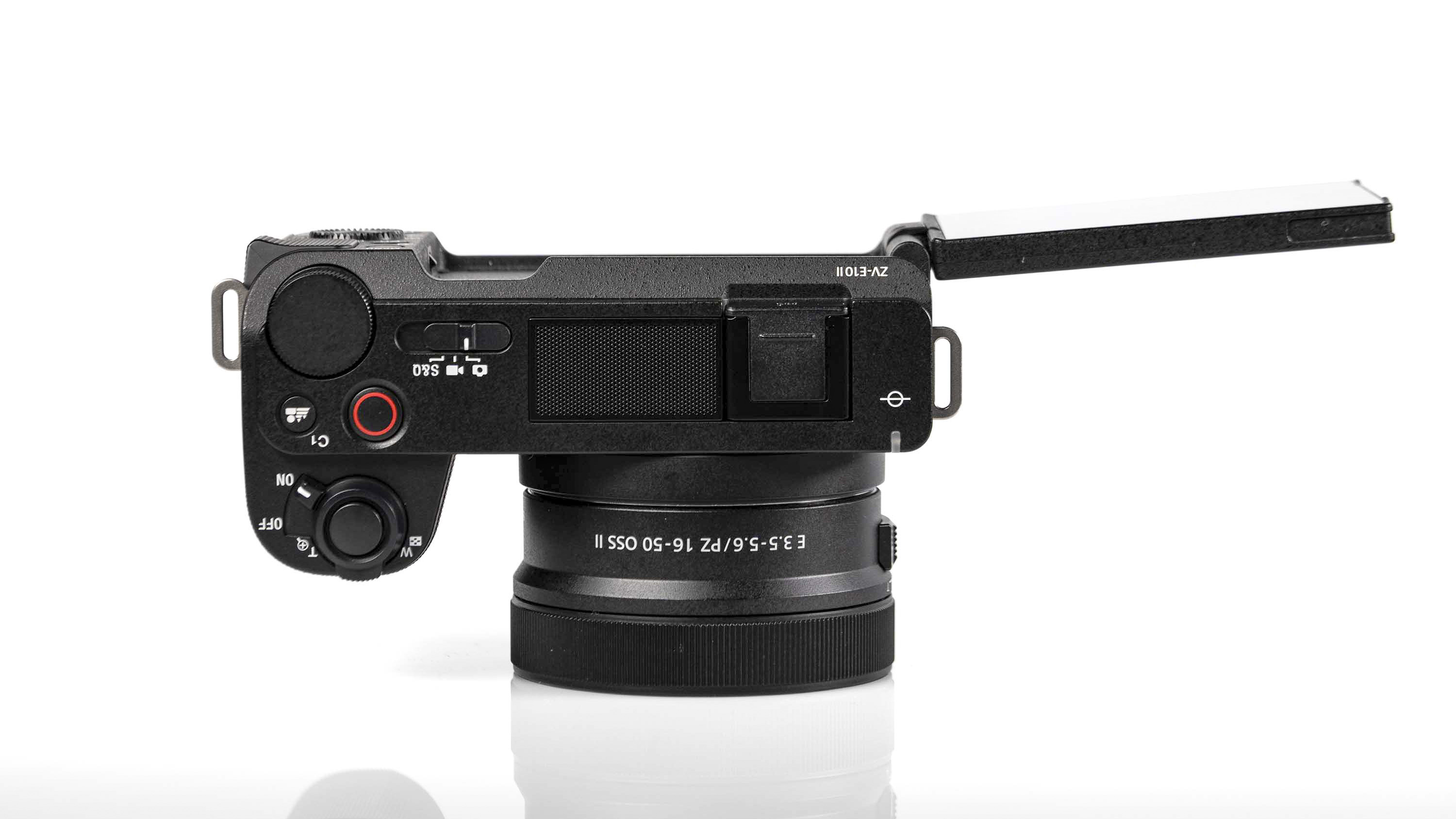
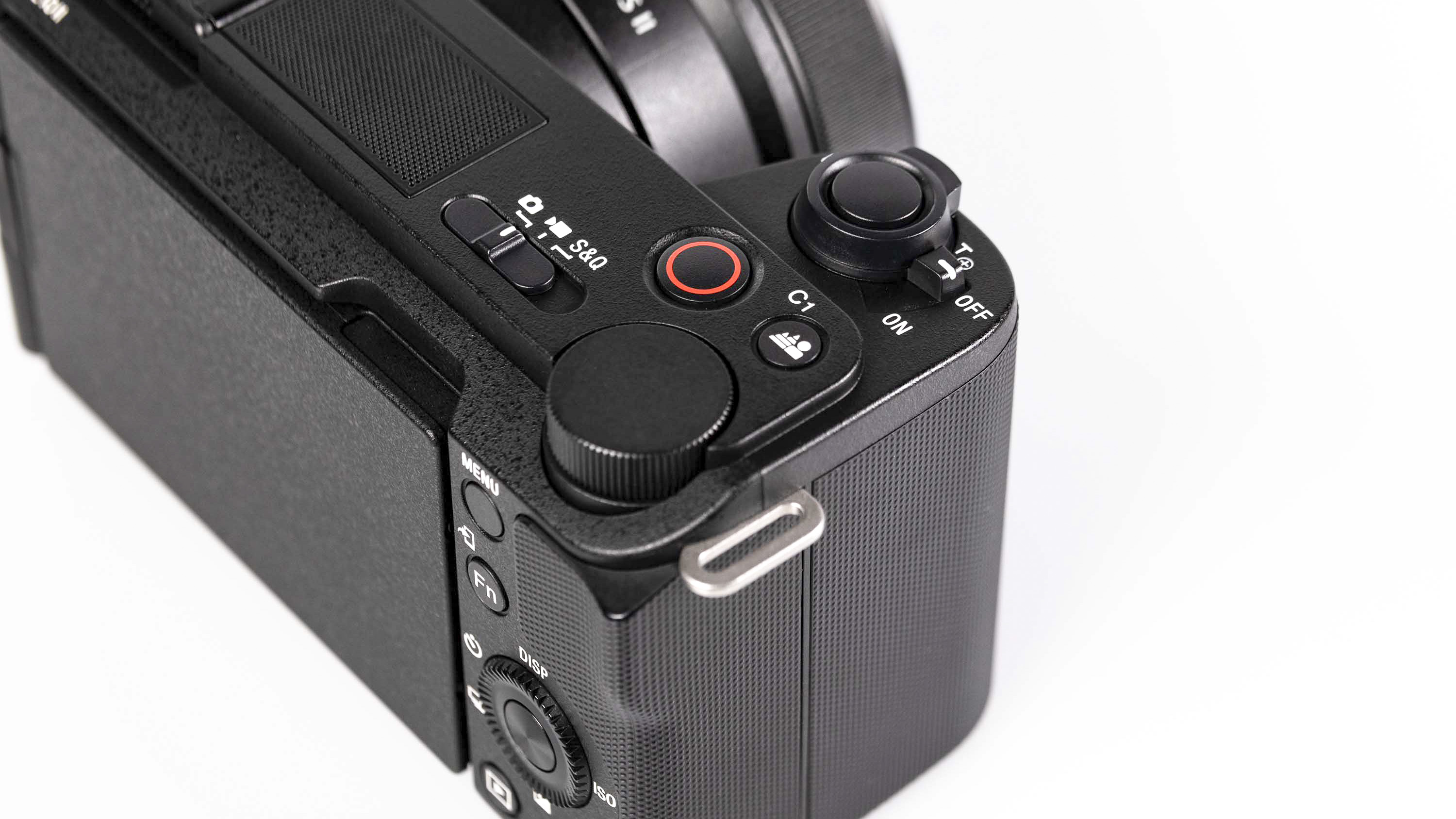
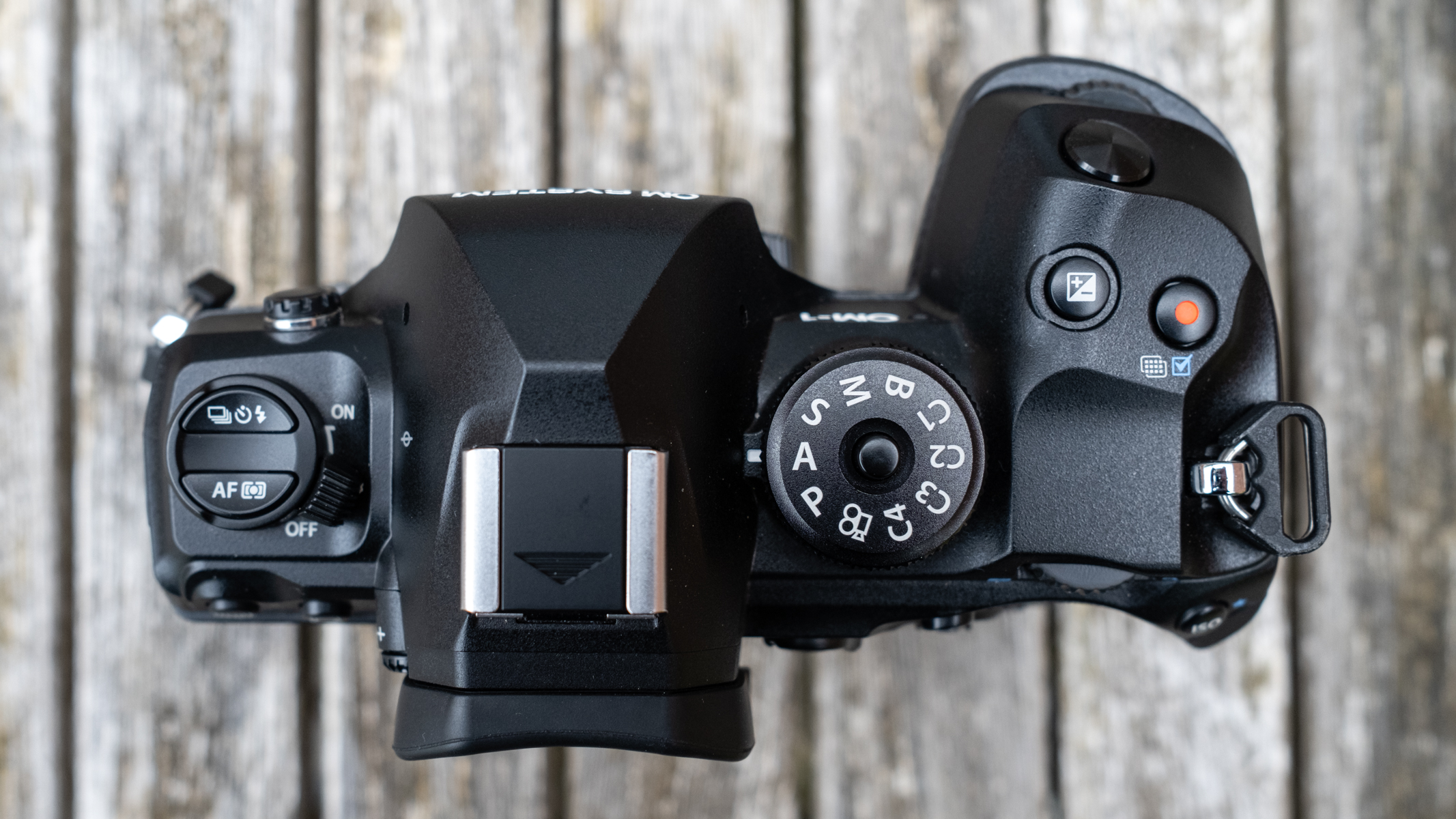
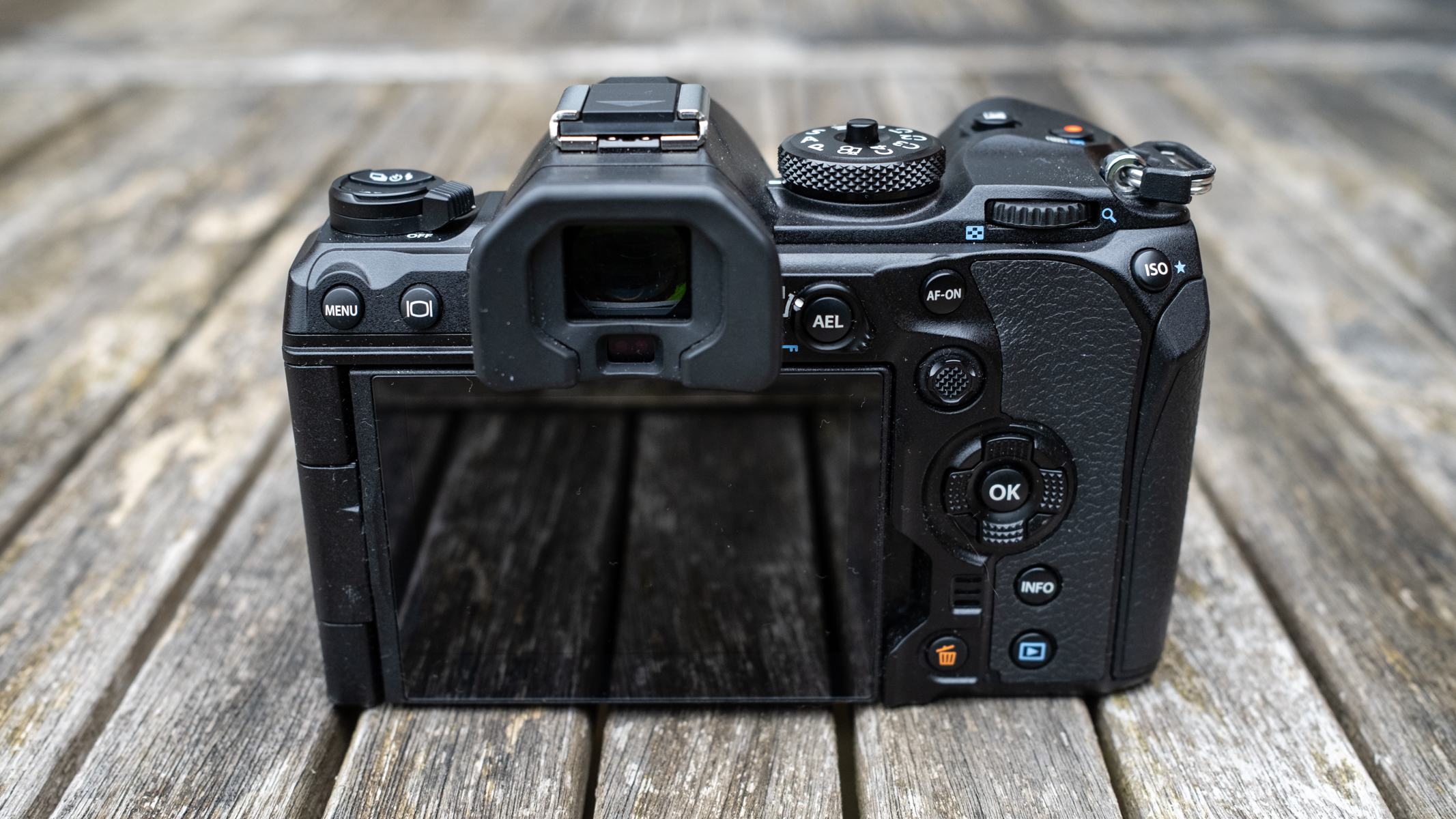
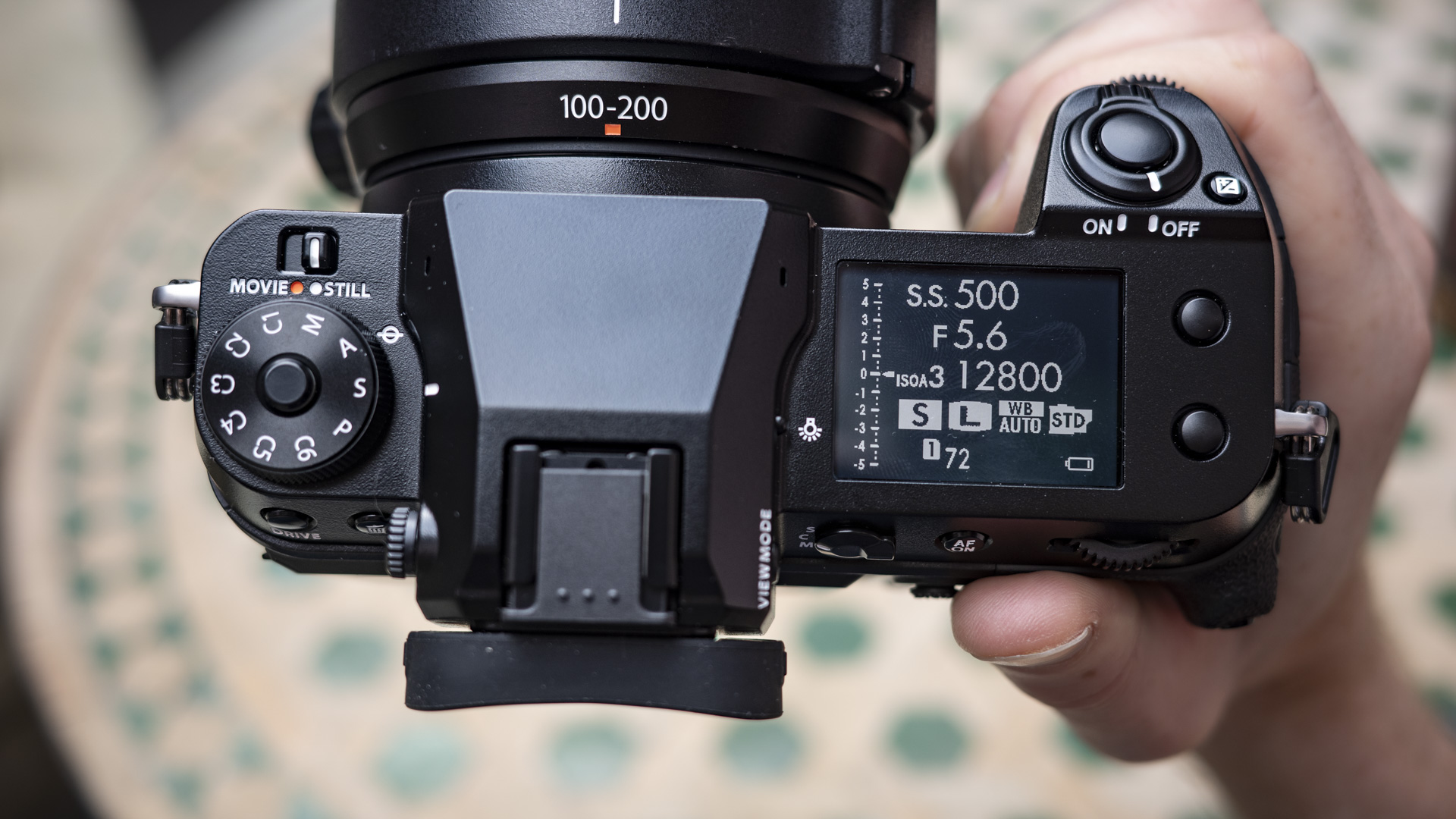
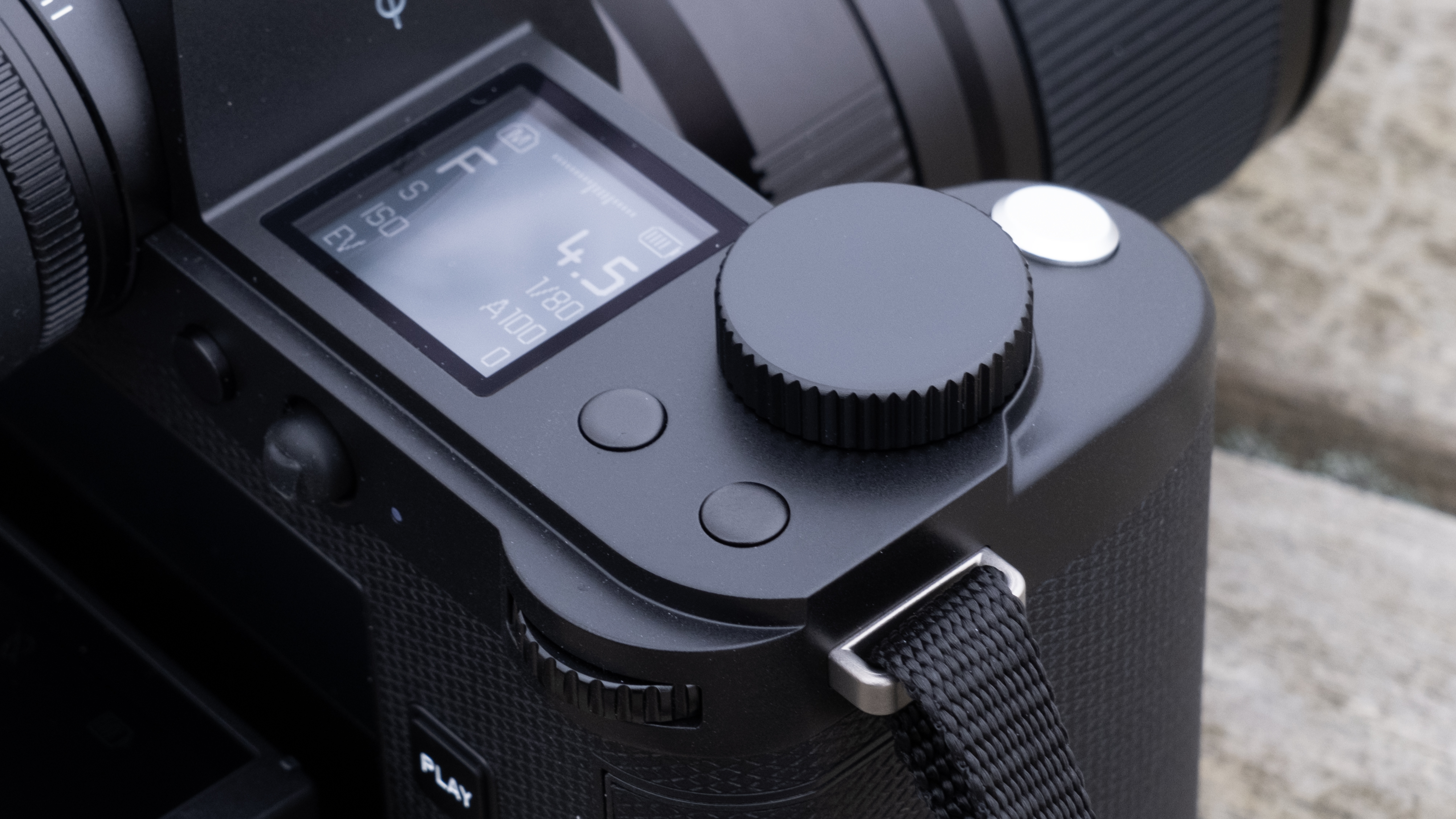
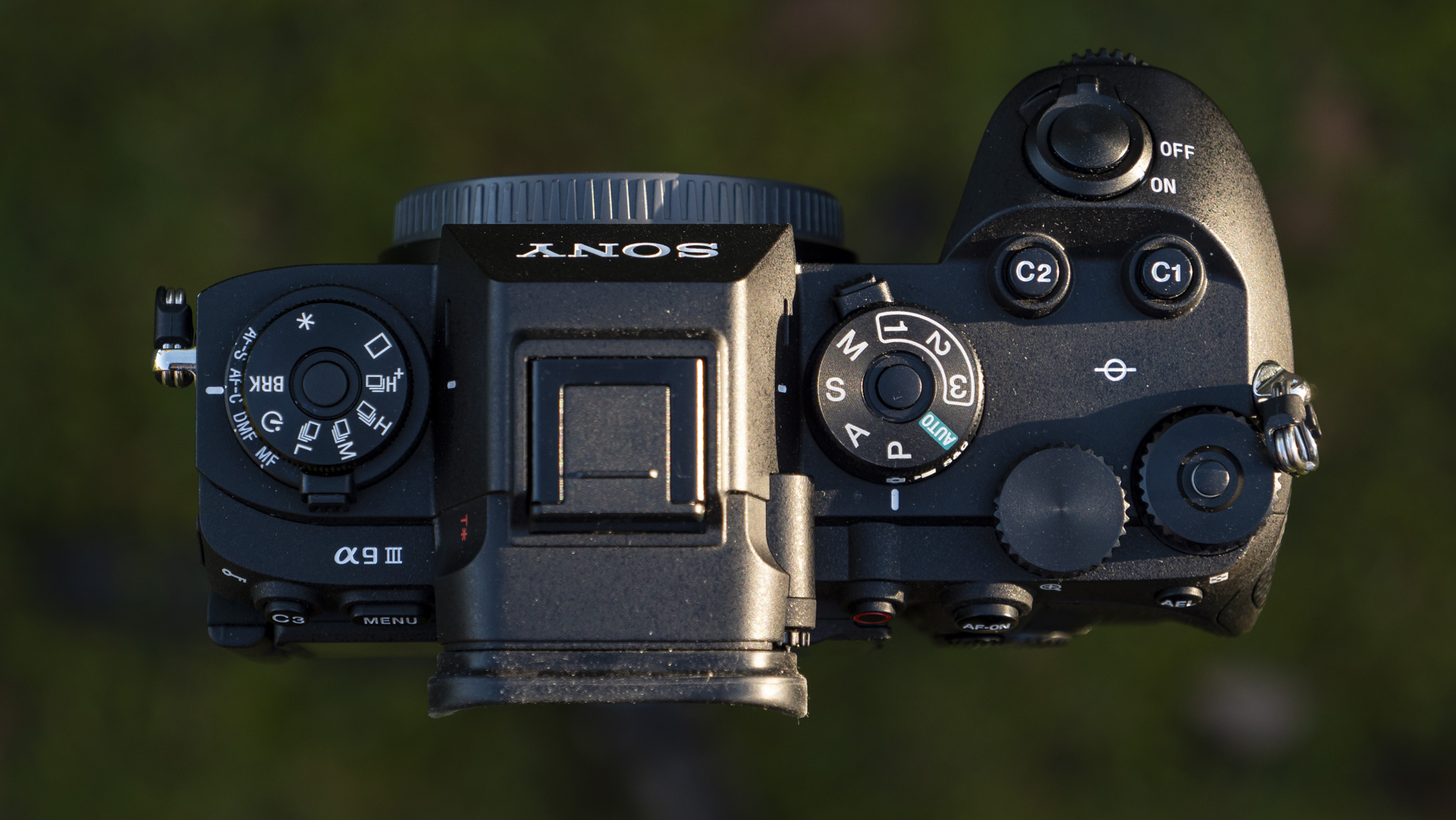
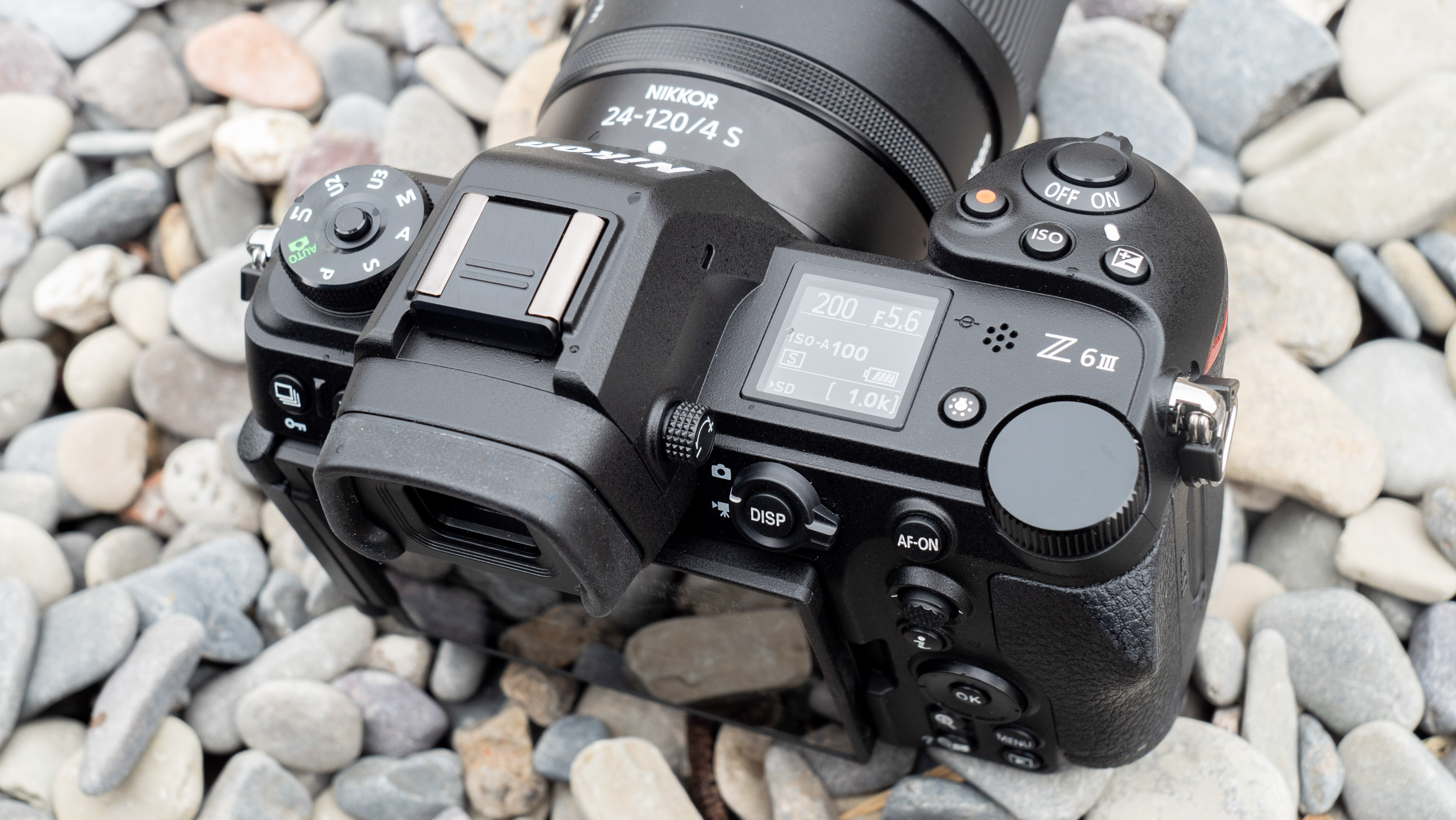
Layout and button placement remains largely unchanged from the Z6 II, with a mode dial to the left of the viewfinder, plus all of your regularly used buttons and dials on the right hand side. A relatively minor tweak, but one which makes a decent bit of difference, is the drive mode and playback buttons have been swapped over. This means you can hit playback with your right thumb, rather than having to bring in your left hand to quickly scroll through the images you’ve just taken. I find this particularly handy when I’m shooting and want to have a quick check in the viewfinder that whatever I’ve just photographed is in focus - then I can have another go if something hasn’t come out quite right.
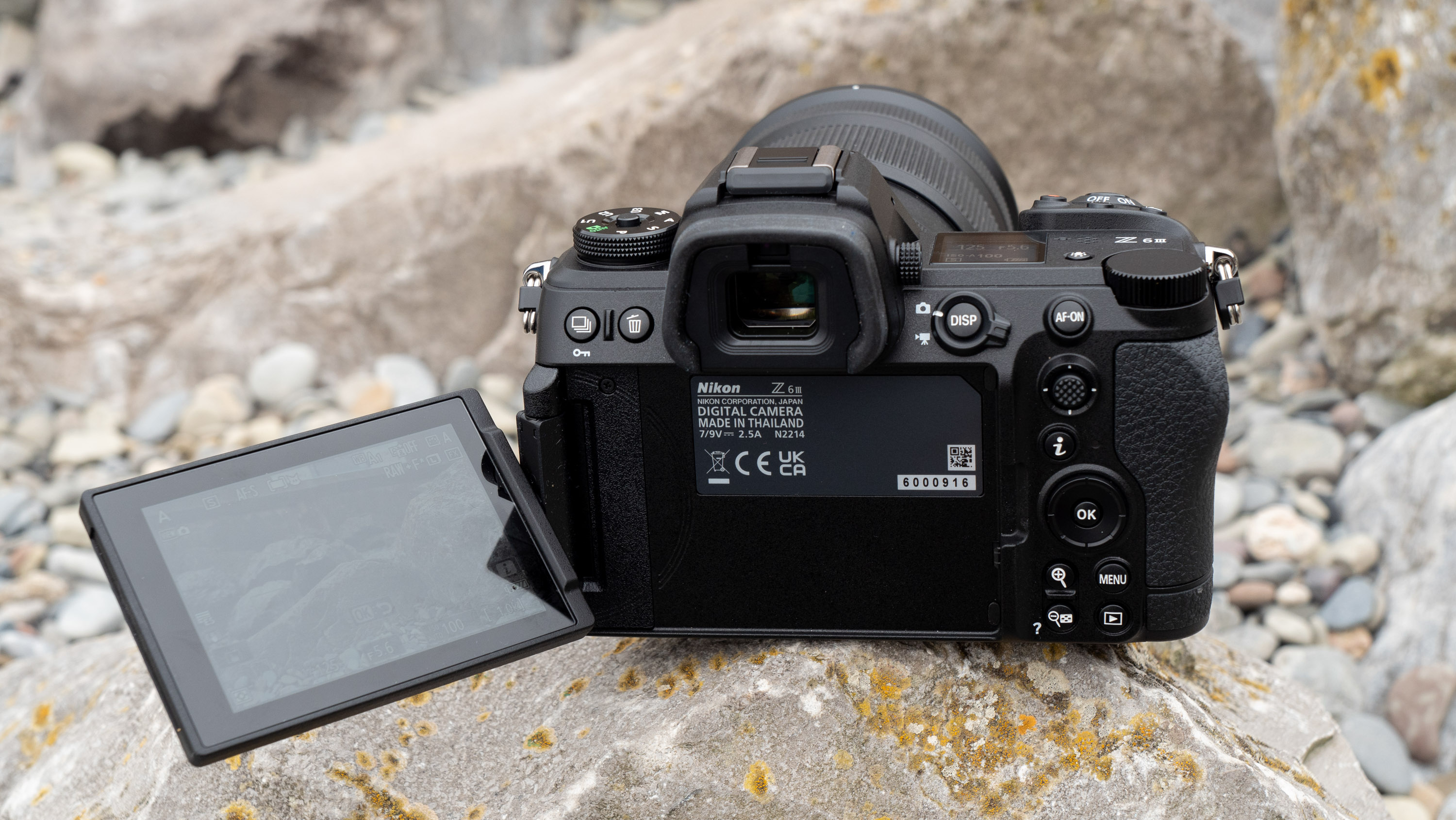

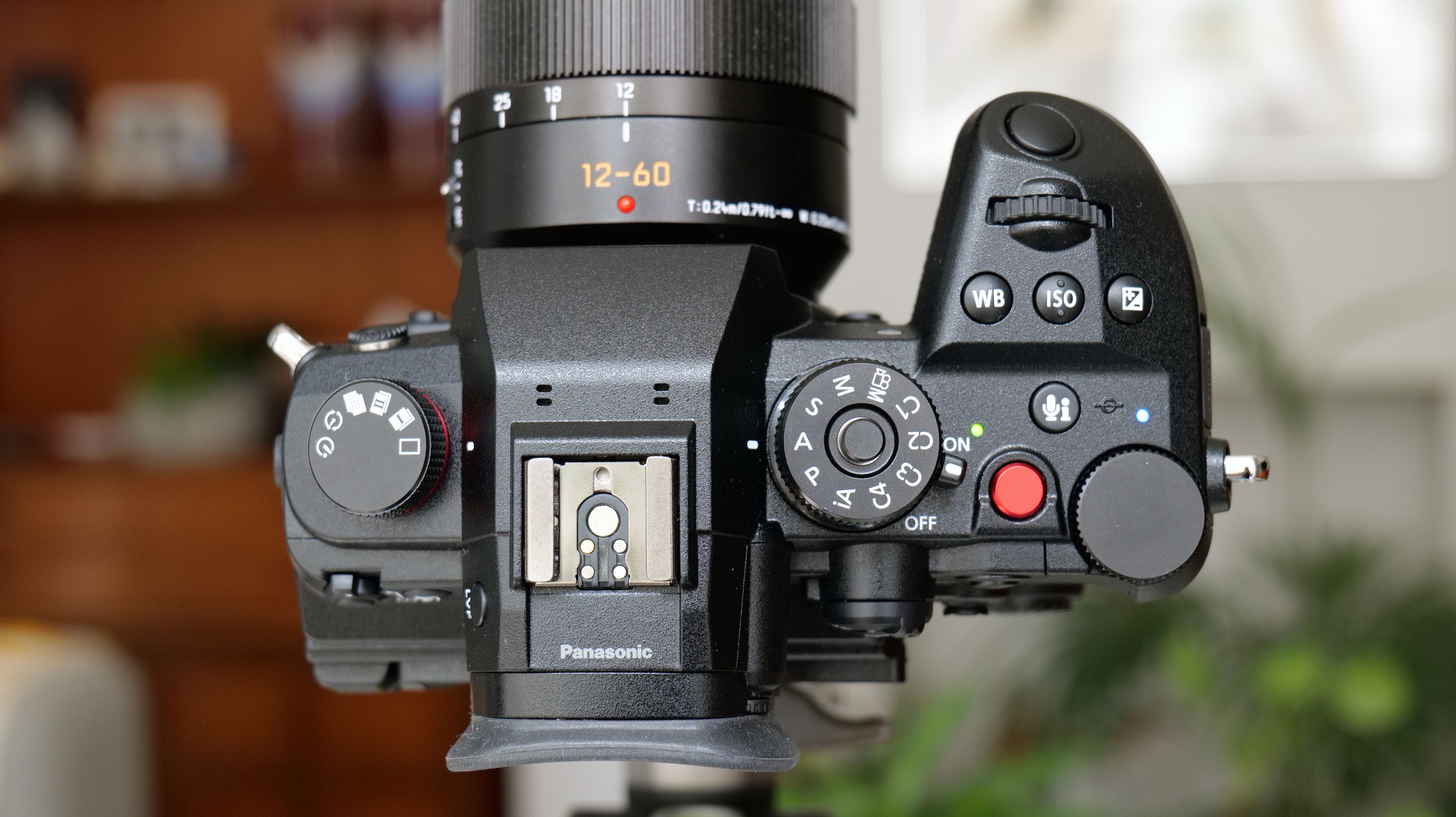
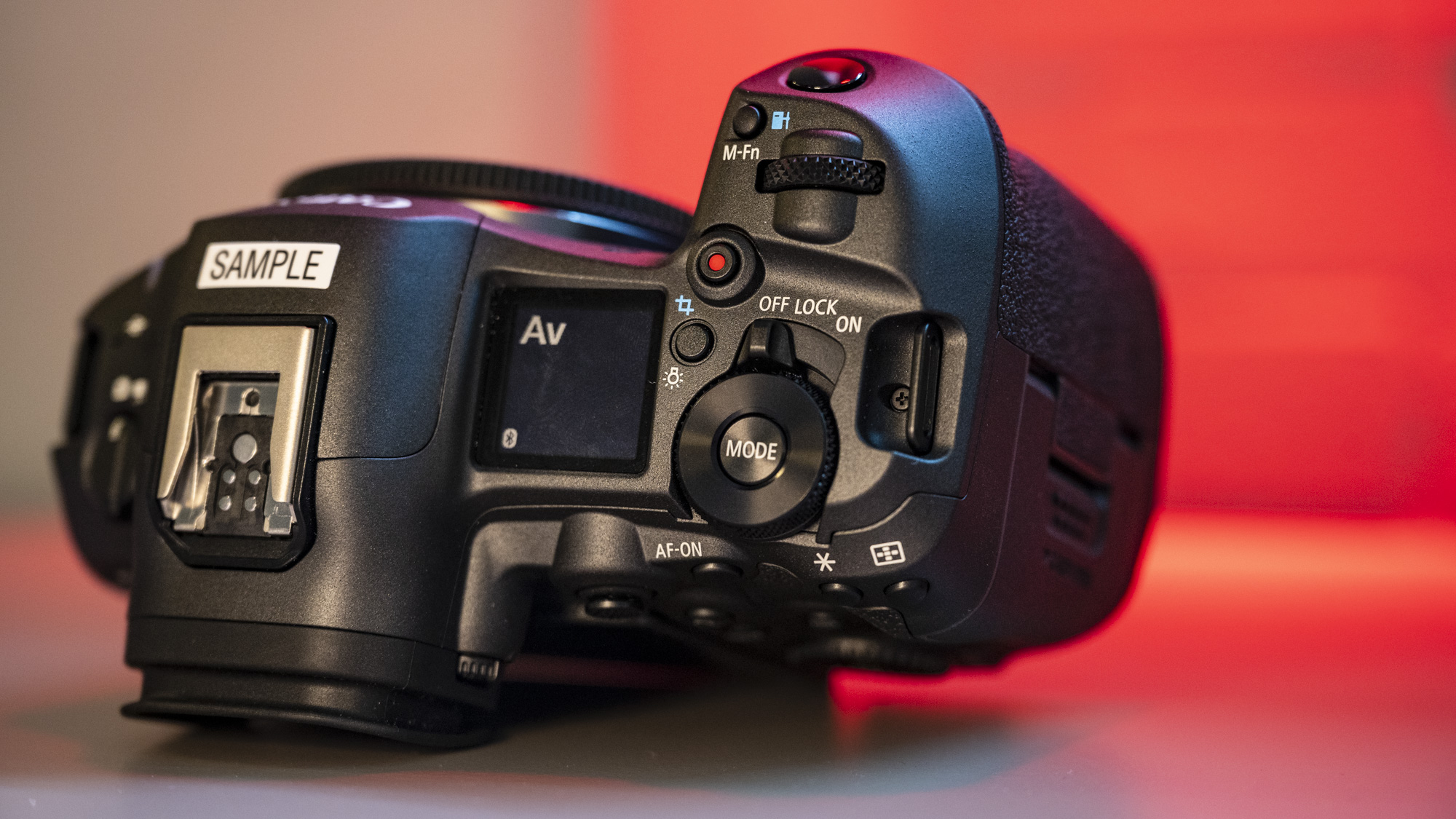
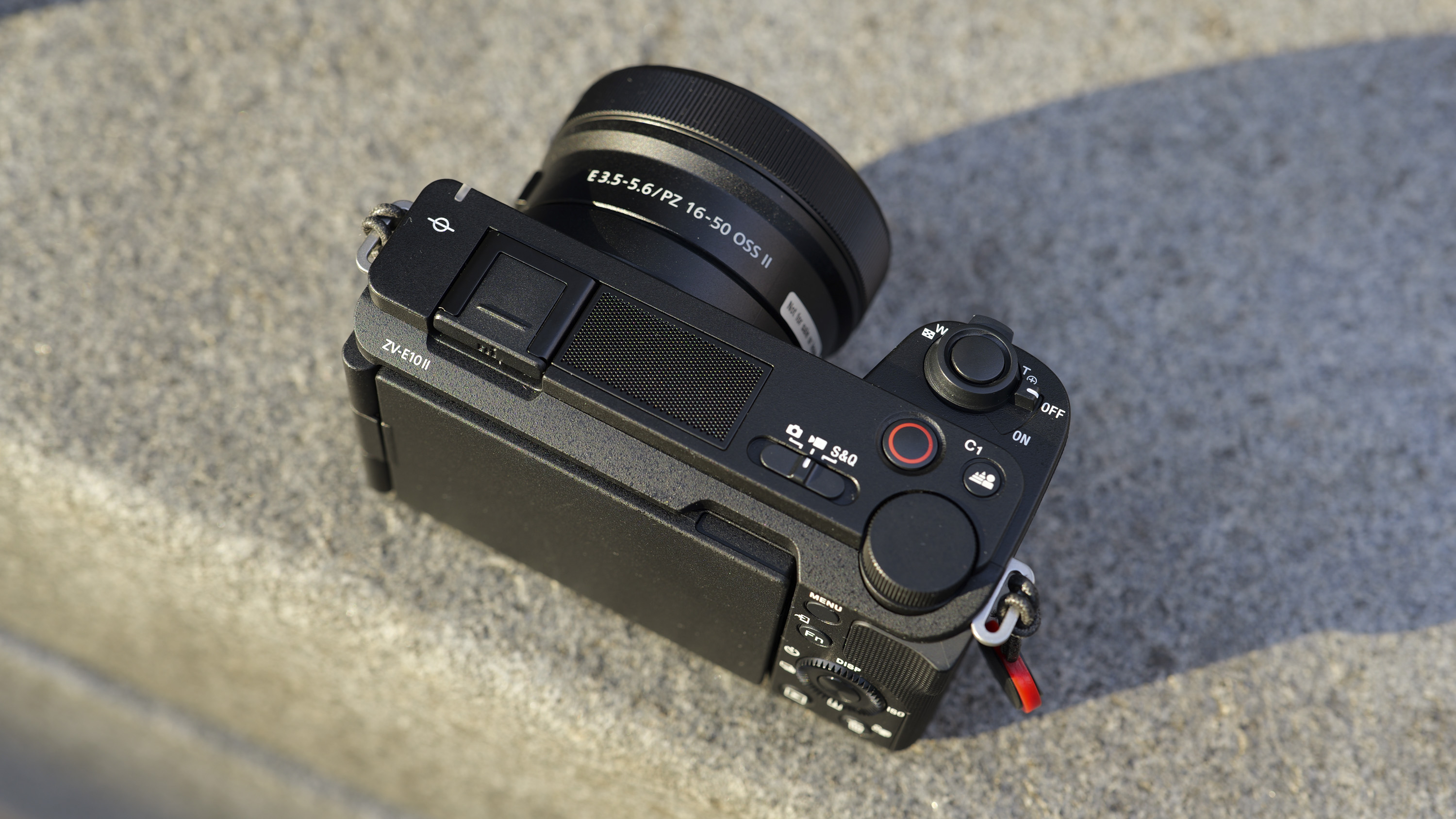
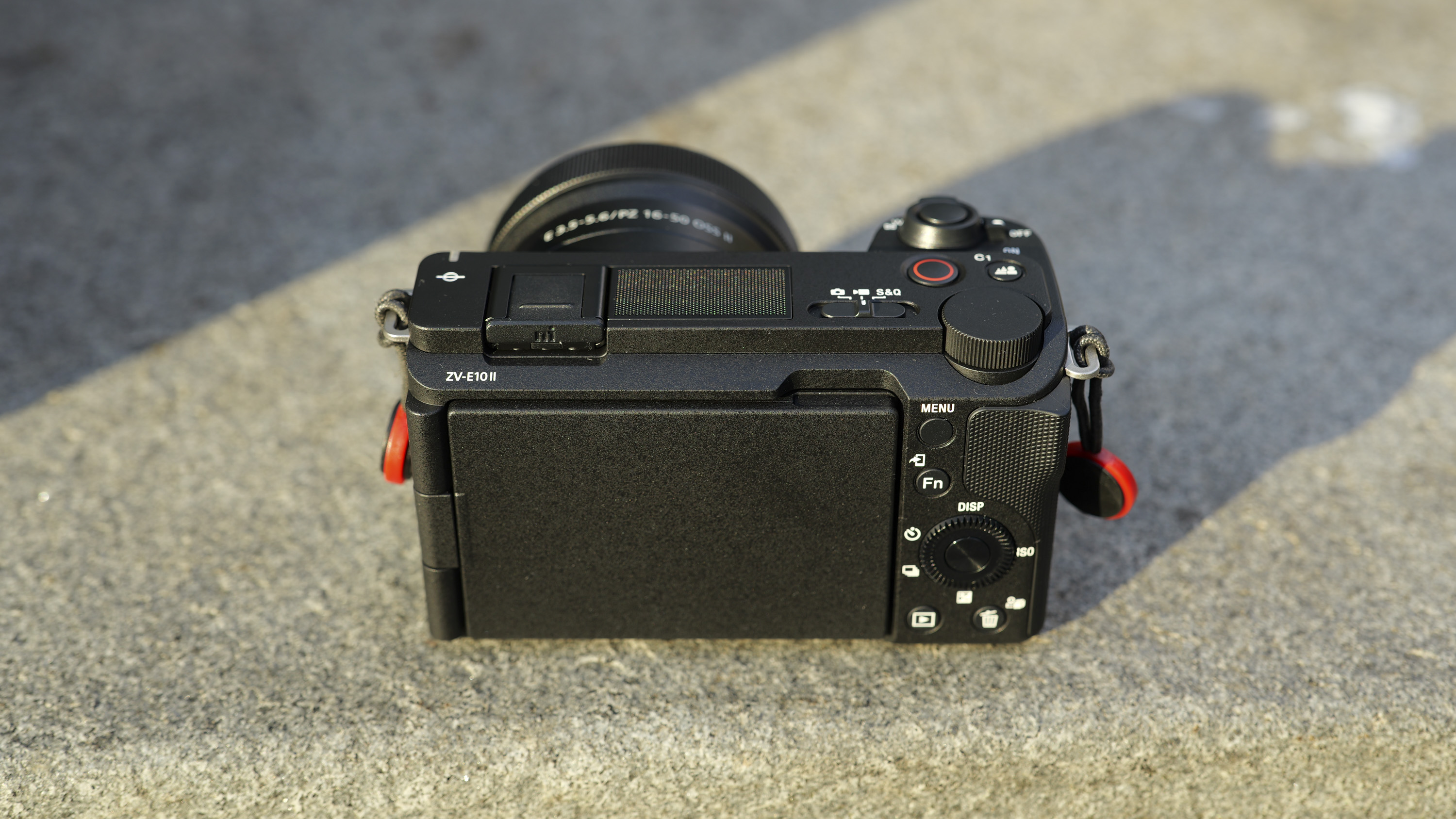
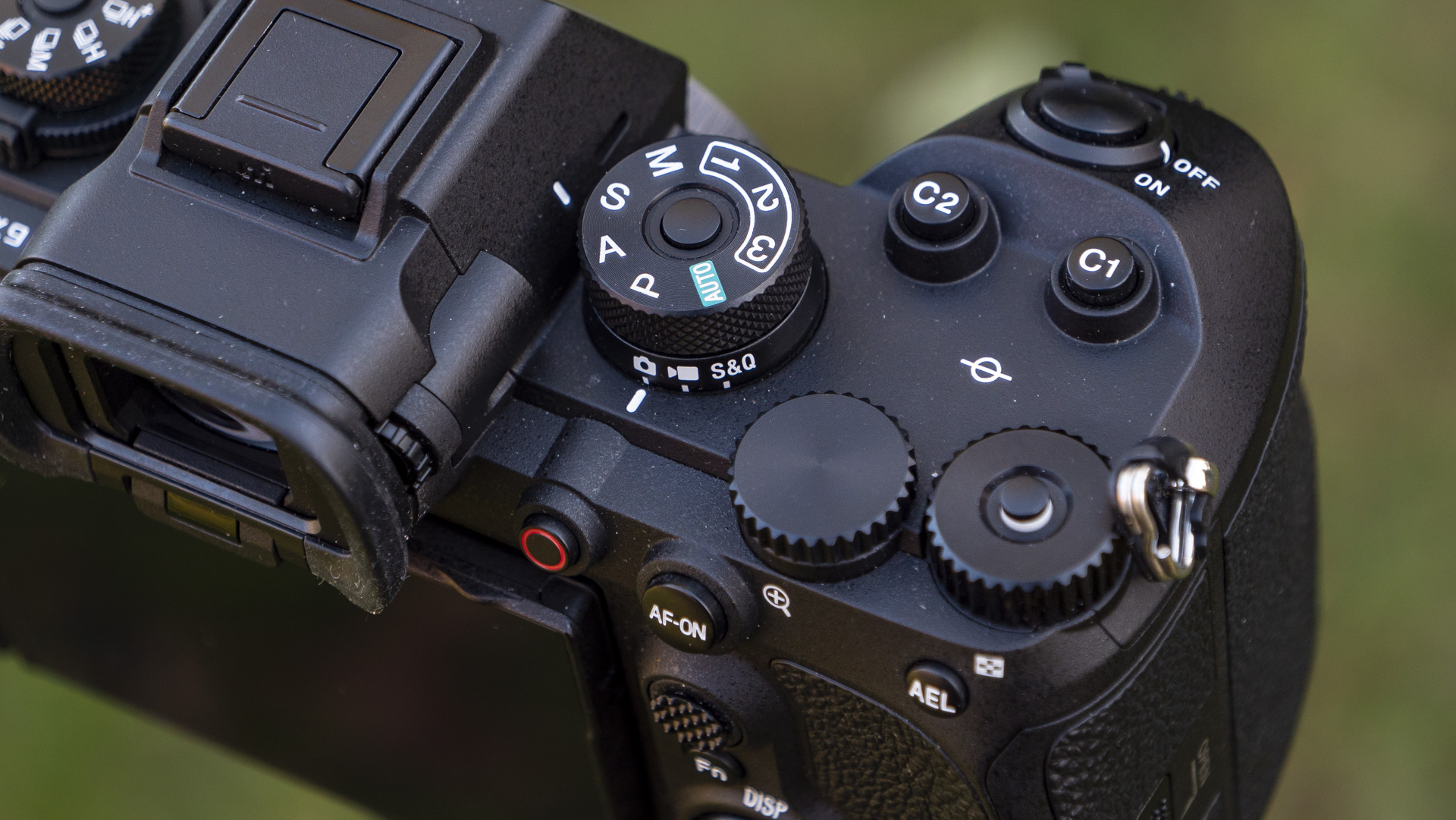
Overall, the Z6 III is a fairly intuitive camera to use with everything pretty much where you’d like it to be. A useful joystick can be employed to move the AF point around, an "i" button houses a host of quick settings, and the rear and front dials work in tandem to control shutter speed and aperture.
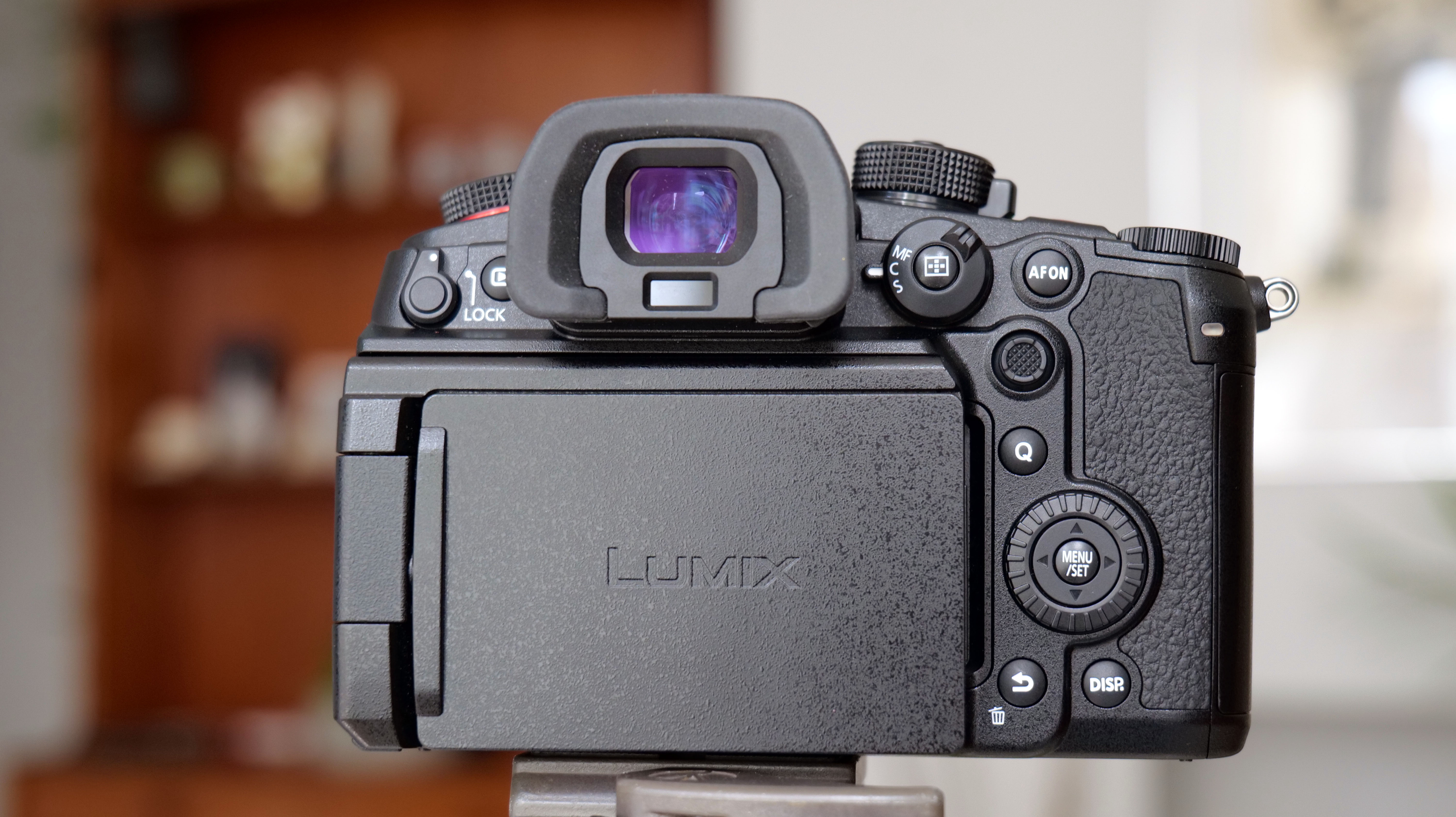
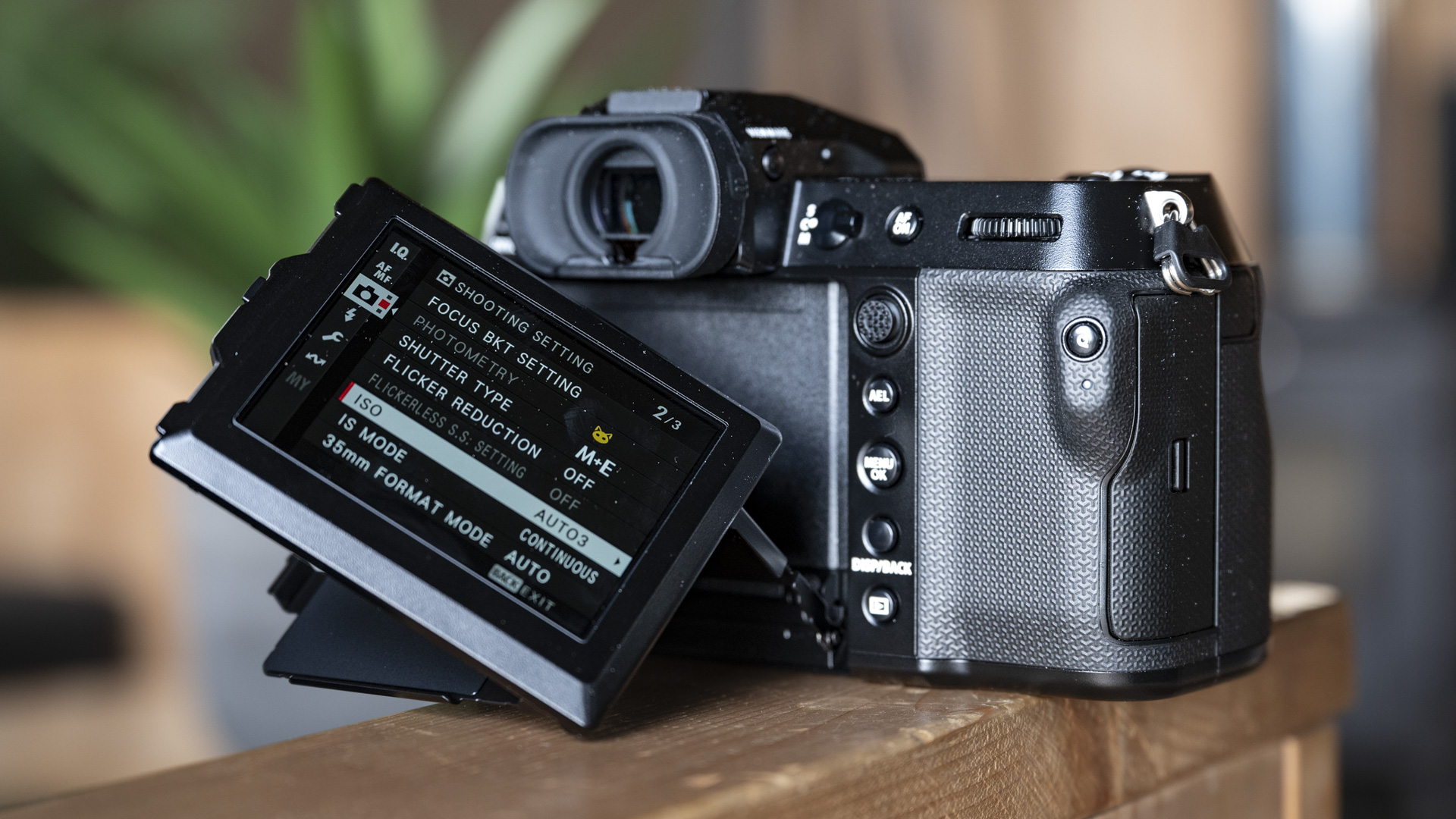
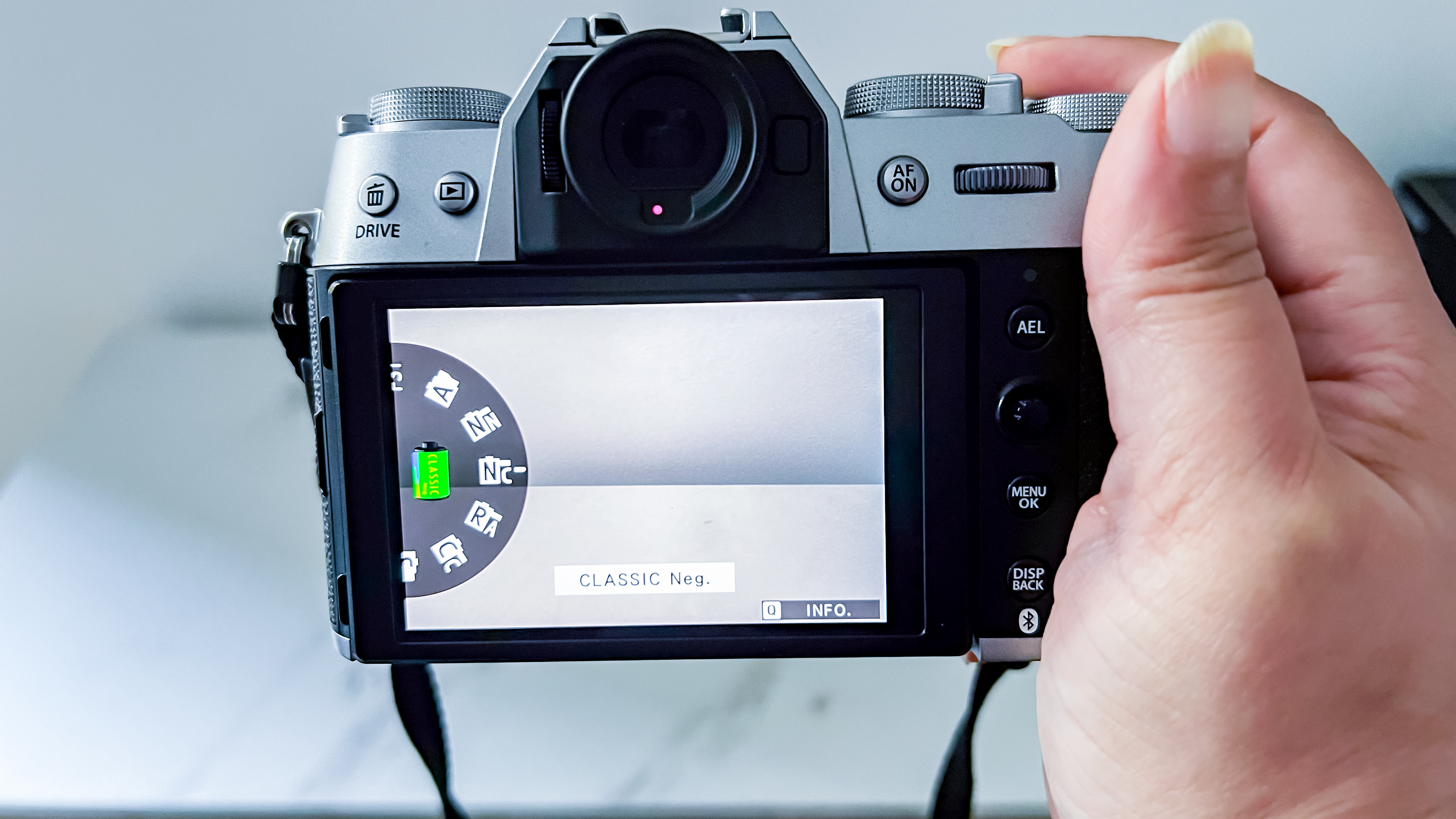
Elsewhere, a pretty big difference compared with the old Z6 II is the new screen, which is now a fully articulated device designed to appeal to the video crowd. It’s also useful for shooting things like selfies, or anything awkwardly positioned that you want to frame vertically. Previously, we had a tilting display, which personally I prefer for stills, but I can see why articulating made more sense in this all-rounder model. The size and resolution of the screen, at 3.2”/2100k-dots remains the same as in the Z6 II.
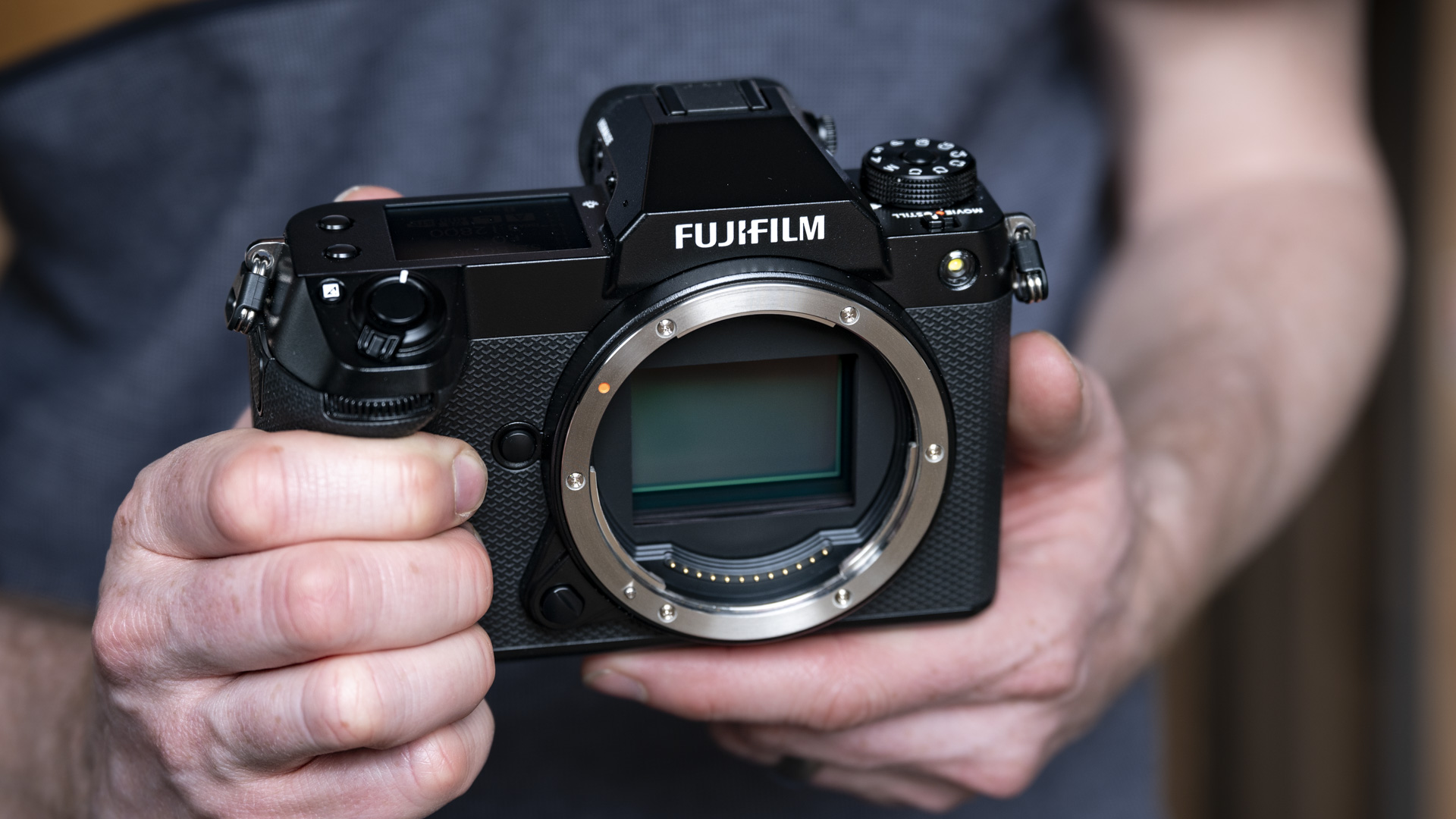
Sensor: 24.5MP
AF System: Hybrid phase-detection / contrast AF
EVF: 0.5in, 5760k-dot UXGA OLED electronic viewfinder, 0.8x magnification
ISO range: 100-64000 (50-204800 extended)
Video: 6K 60p / 4K 120p / Full HD 240p
LCD: Vari-angle TFT touch-sensitive, 2100k-dot
Max burst: 120fps (crop mode)
Connectivity: Wi-Fi 5GHz, Bluetooth 5.0
Weight: 670g (body only), 760g (with battery and memory card)
The EVF has also had a bit of a glow-up. While the previous 3,690k-dot resolution EVF of the Z6 II was by no means bad to use, once you look through the 5,670k-dot device found on the Z6 III, you might find the Z6 II's viewfinder has been well and truly ruined for you. Not only is the Z6 III's high in resolution, it has also got an ultra-wide color gamut (DCI-P3, the first time this has been used in a mirrorless camera), and a fast 60fps refresh rate for a smooth display even shooting at high frame rates.
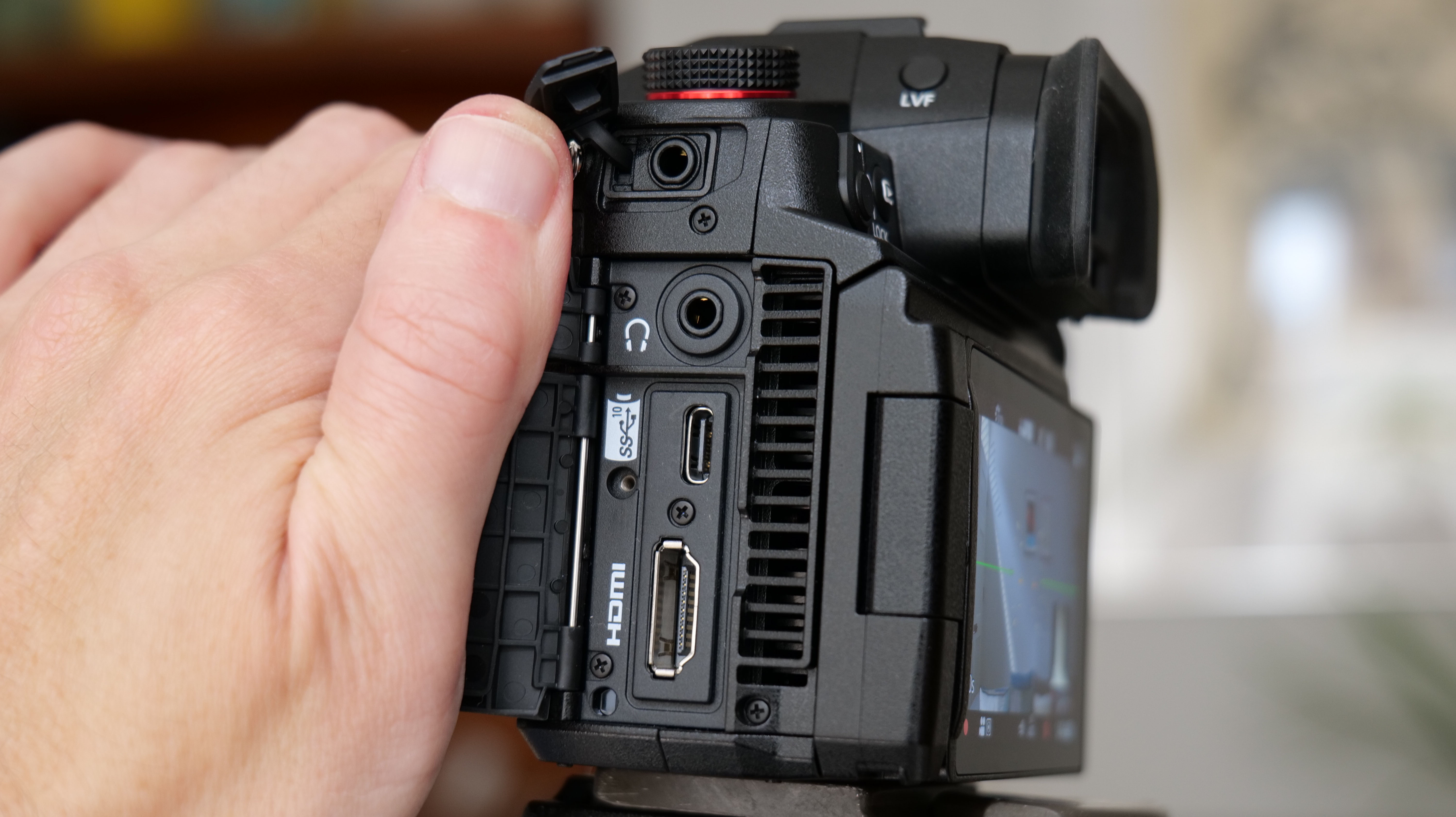
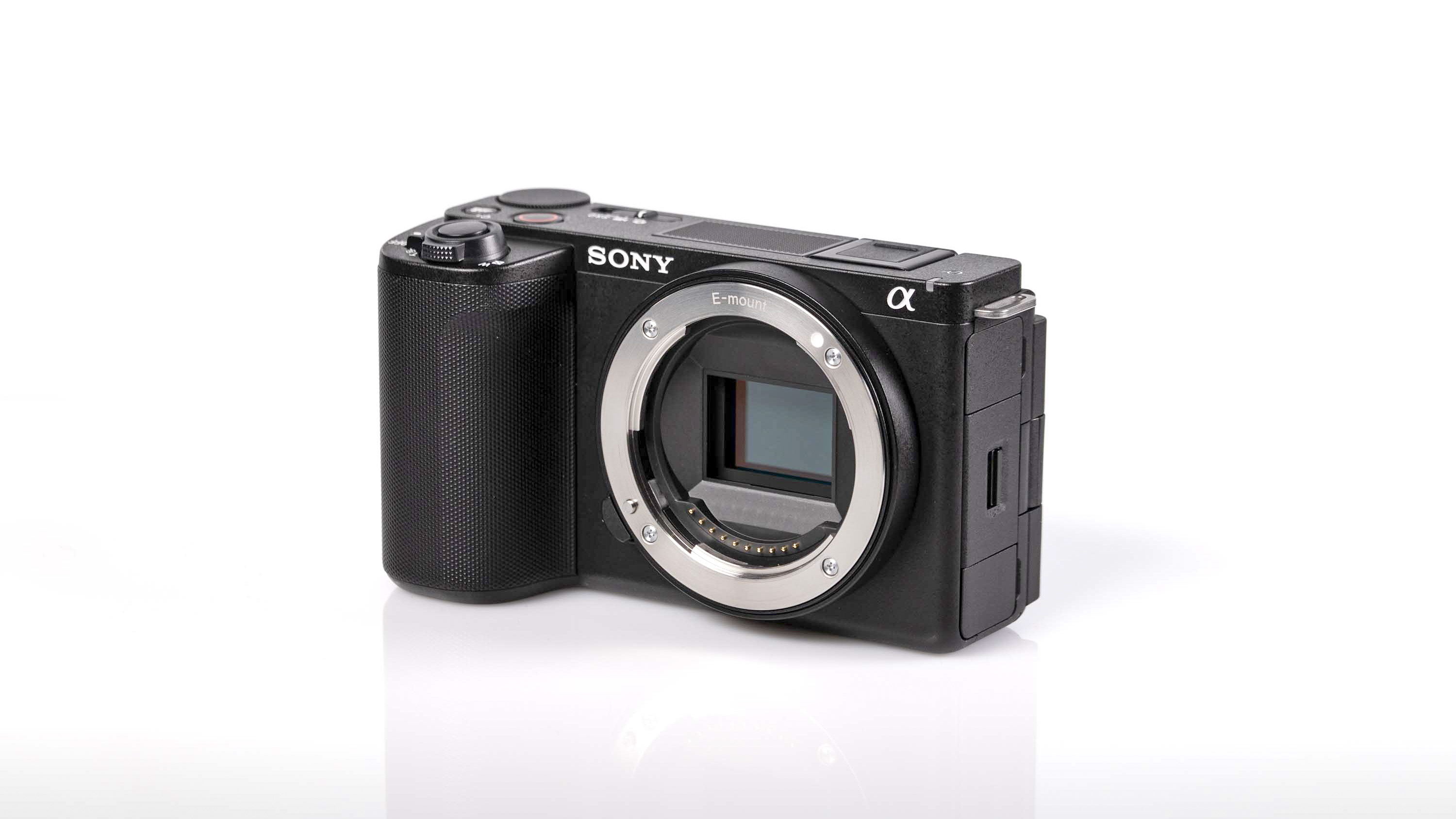
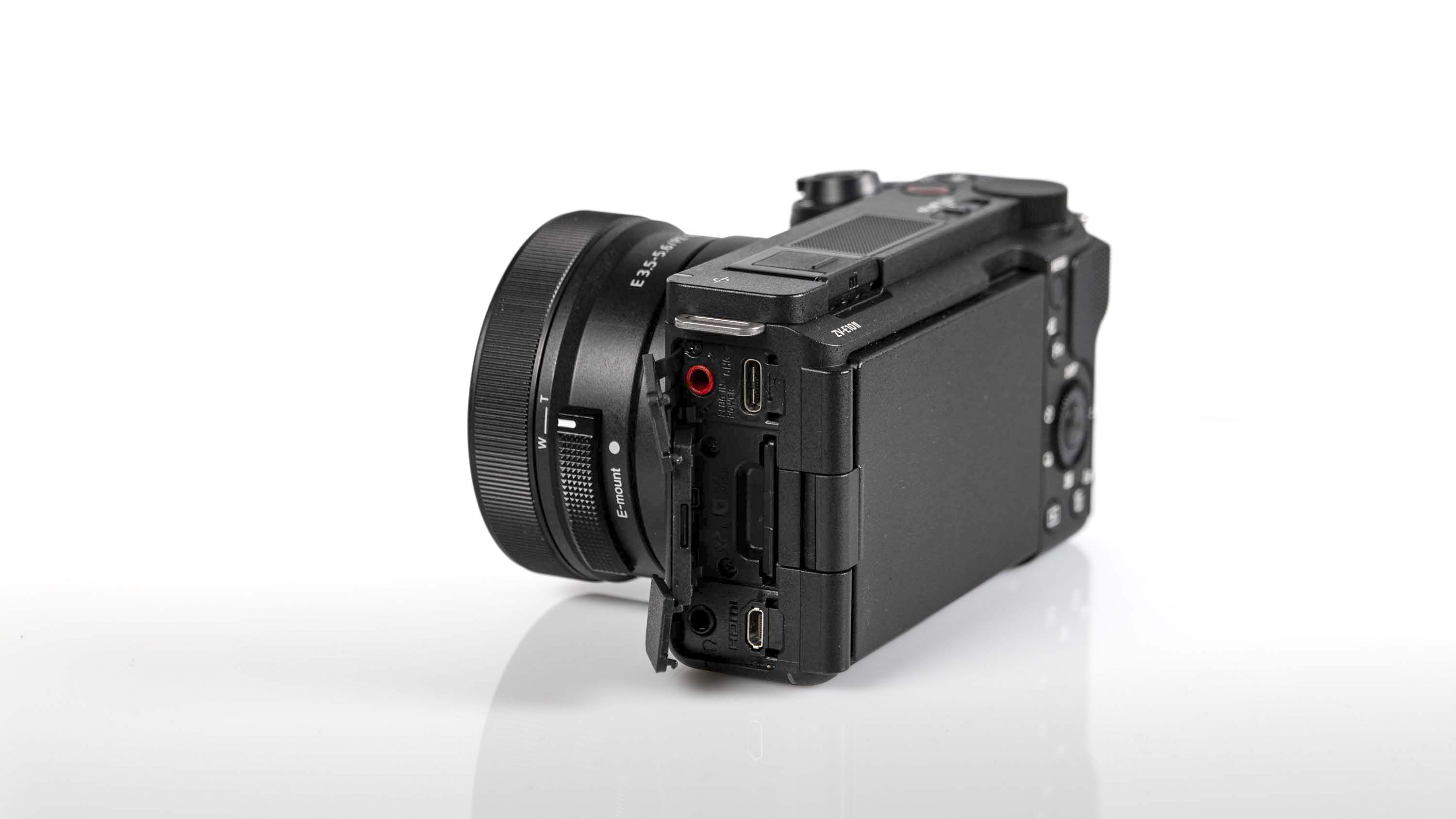
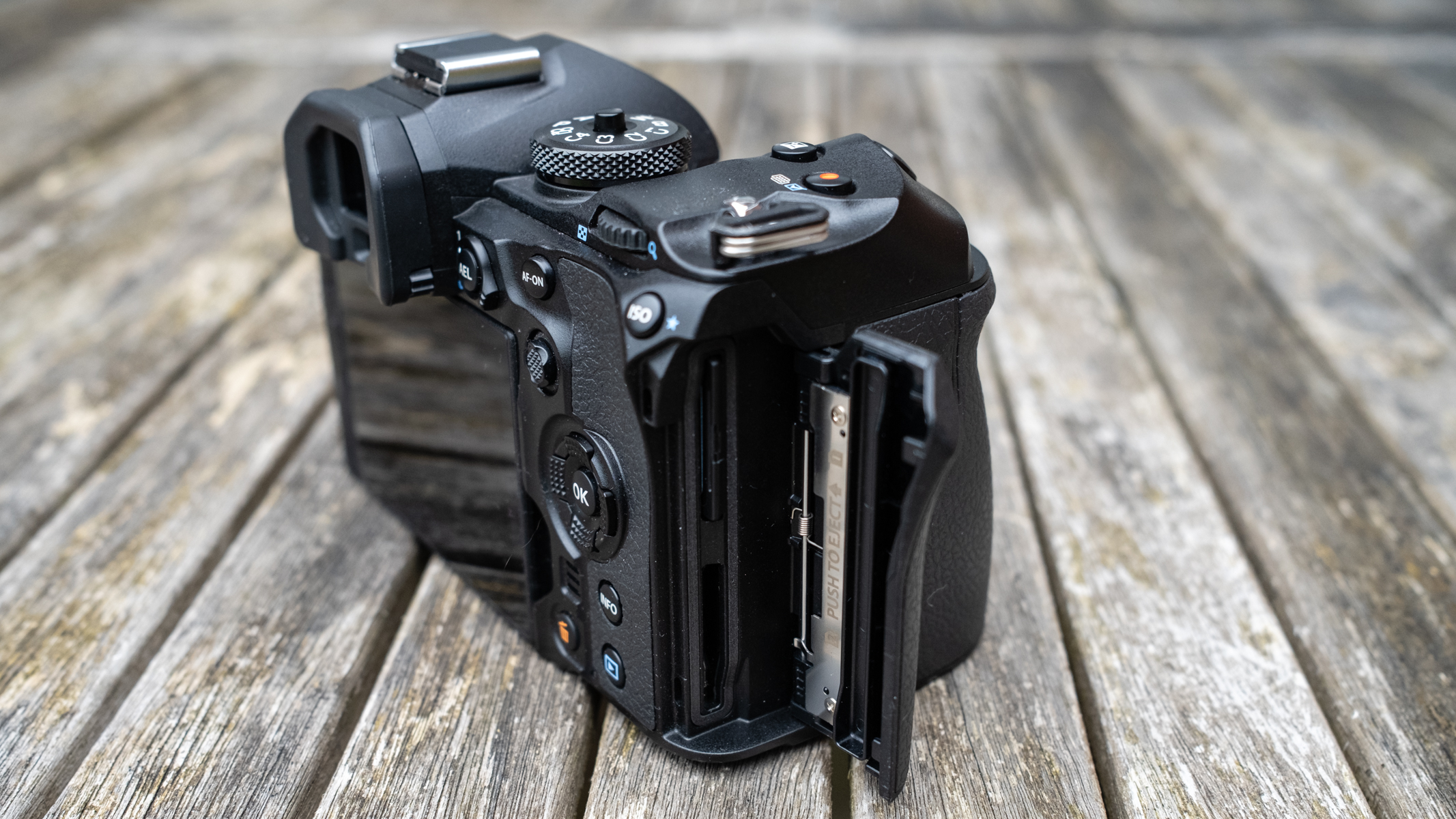
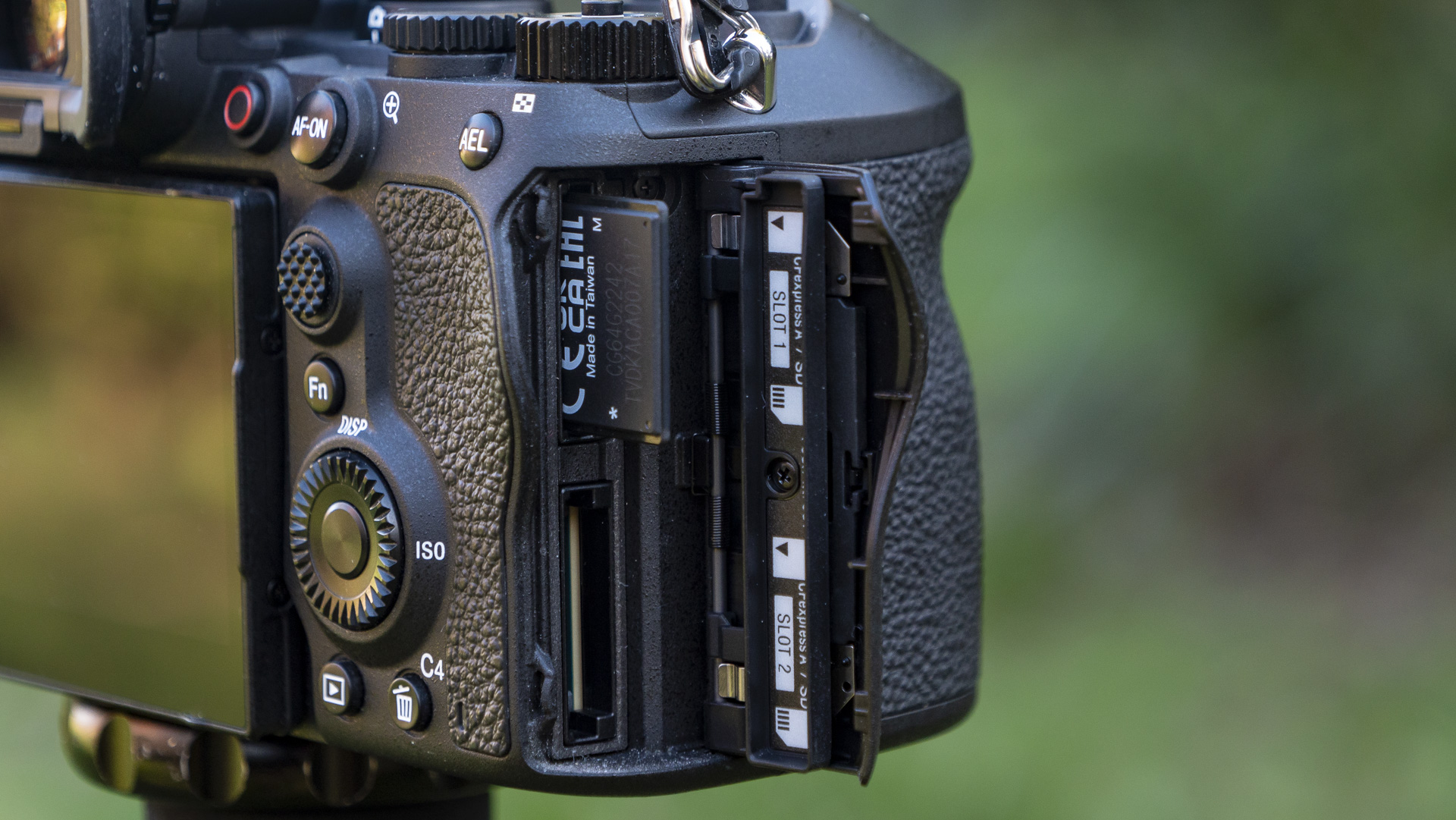
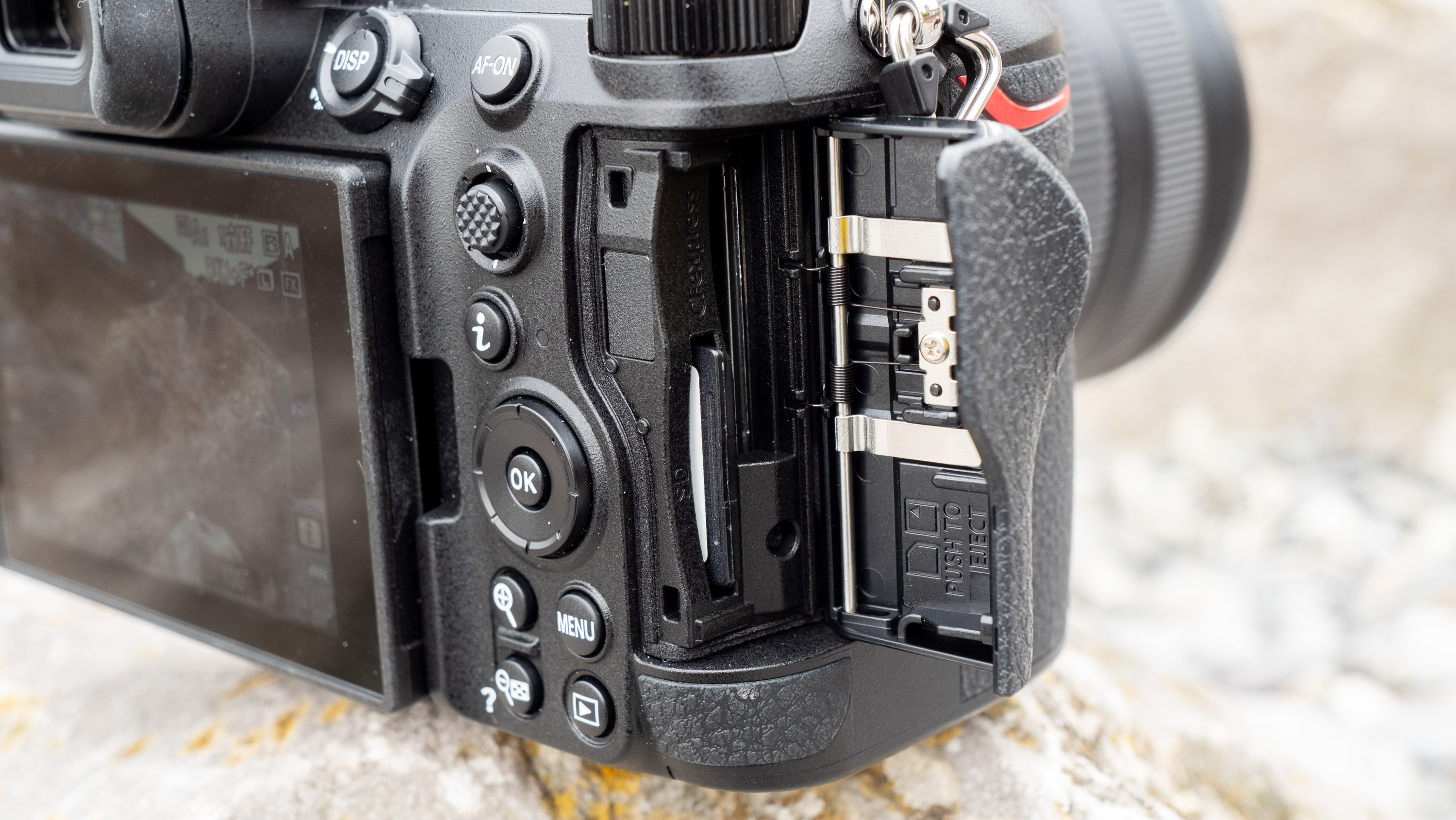
As with the Z6 II, we’ve got dual memory card slots. One is for CFExpress B, and is also compatible with the older XQD format. Another is the more widely used SD format with support for the faster UHS-II version, which is good news for anyone who doesn’t necessarily want to fork out on expensive memory cards to use this camera.

If you want extra battery power, or better handling when shooting vertically, there’s an optional MB-N14 battery grip you can also buy. If you’ve already got an older battery grip, it’s a bit annoying that the old MB-N11 or MB-N12 battery grips from previous Z series models aren’t compatible here, though. On the plus side, the MB-N14 is compatible with both the newer and older models, so if you’re toting a multi-device setup, you can at least swap between the two.



- Design score: 4.5/5
Nikon Z6 III: features and performance
- Up to 120fps shooting with Pre-Release Capture
- World’s first partially-stacked 24.5MP sensor
- 8-stops in-camera image stabilization
- 3D tracking and subject detection focus, plus focusing down to -10EV
- 6K video up to 60fps
- New Nikon Imaging Cloud service
The Z6 series has always been Nikon’s “all-rounder”, with a lower resolution sensor than the likes of the Z7 and the Z8/Z9, at a more attractive price and more-rounded feature set.
With the Z6 III, you really do get an incredibly versatile piece of kit that's markedly more powerful for landscapes to sports and action, as well as meeting video and content creators needs too.
Although resolution has stayed on the “low” side at 24.5MP (only by comparison with the super high-resolutions we’ve become a little bit spoiled by), we now have what’s known as a “partially-stacked” sensor which has been designed to be fast, without quite such a high-cost as we’d expect from a fully-stacked sensor found in the Z8 or Z9 camera. It’s also got the same EXPEED 7 processor as found in the Z8 and Z9.
So, while the Z6 III's sensor is still not quite as speedy as the Z8/Z9, it’s still 3.5x quicker than that found in the Z6 II, and what’s more, it’s better equipped to deal with rolling shutter distortion that you might expect to see when recording moving subjects.
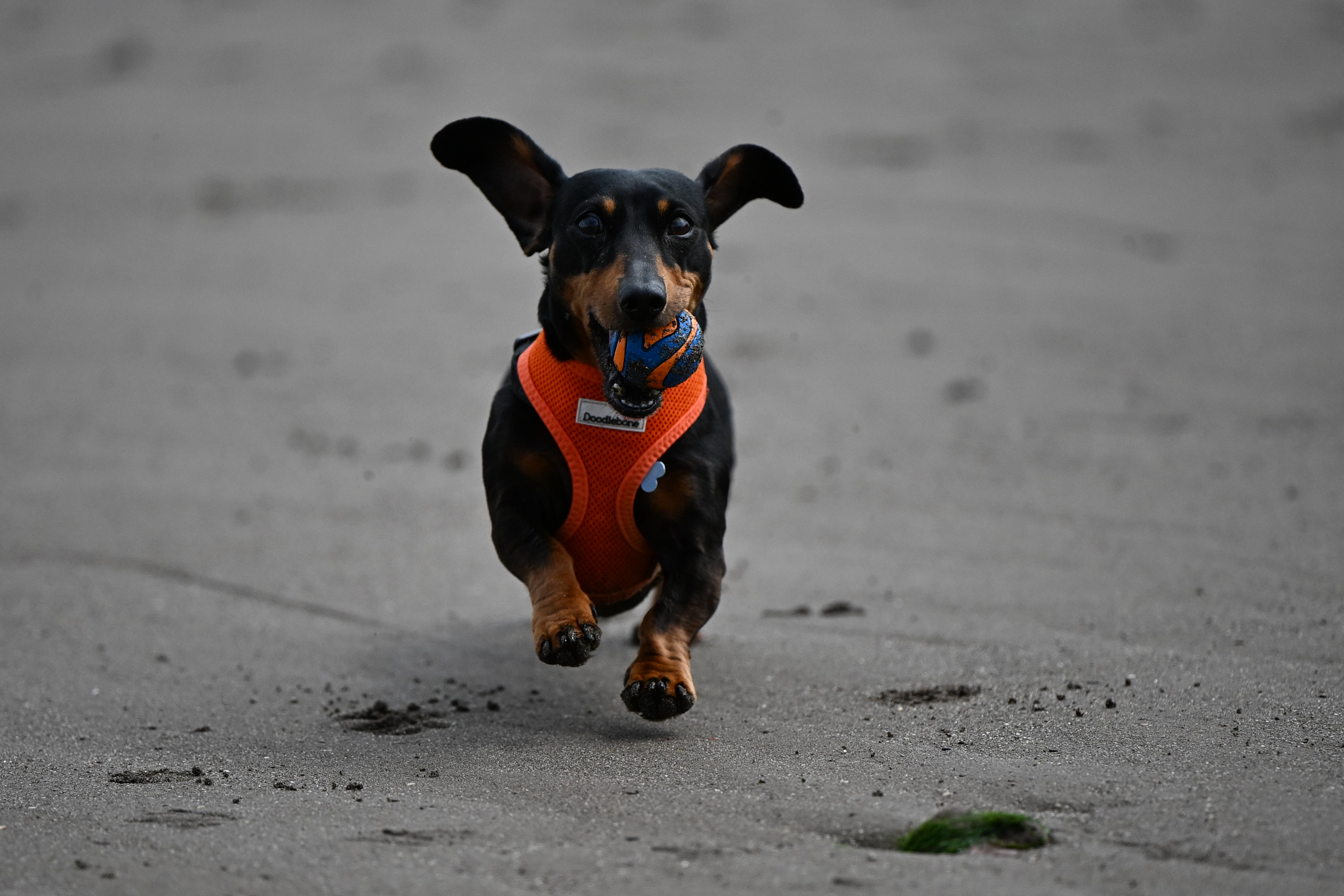


As a result, we get up to a ludicrously fast 120fps shooting available - though you will have to shoot DX (APS-C) format JPEGs which end up at only 10MP. You do get full AF/AE while recording though.
For full-frame shooting, up to 60fps is available (JPEG only), which should still be more than you really need for most types of moving subject. As if that wasn’t enough, there’s also pre-release capture which will start recording frames before you’ve even fully engaged the shutter button - super handy if you’re not sure exactly when a piece of action is about to begin. If you want RAWs to go along with JPEGs, you can shoot at 20fps with the electronic shutter.
Having super-fast frame rates is no good without a great AF system to go with it and there's good news there too. You get the latest autofocusing system available from Nikon, as seen in the Z8 and Z9, to give you 3D tracking and subject-detection options including humans, animals and a range of vehicles.
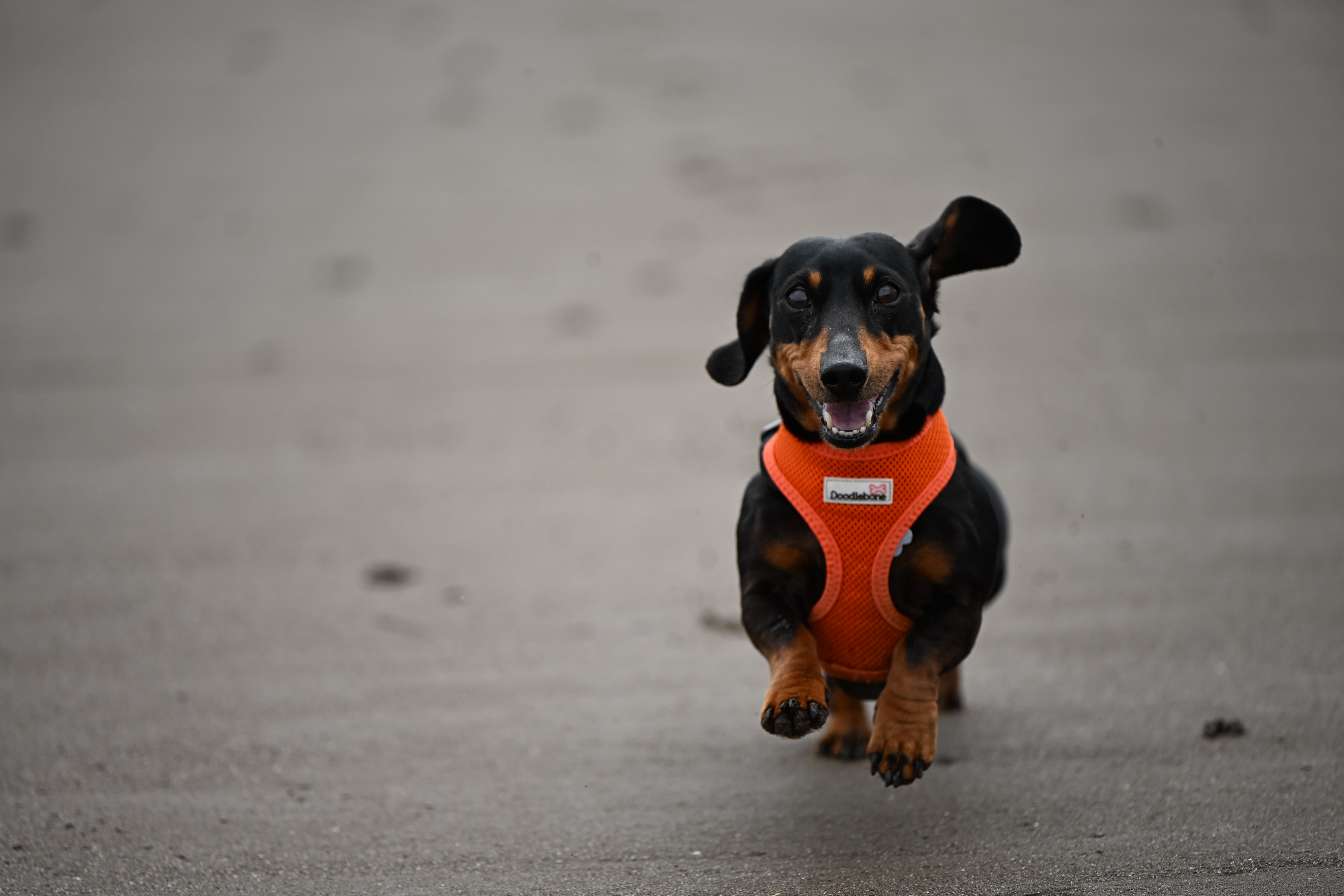
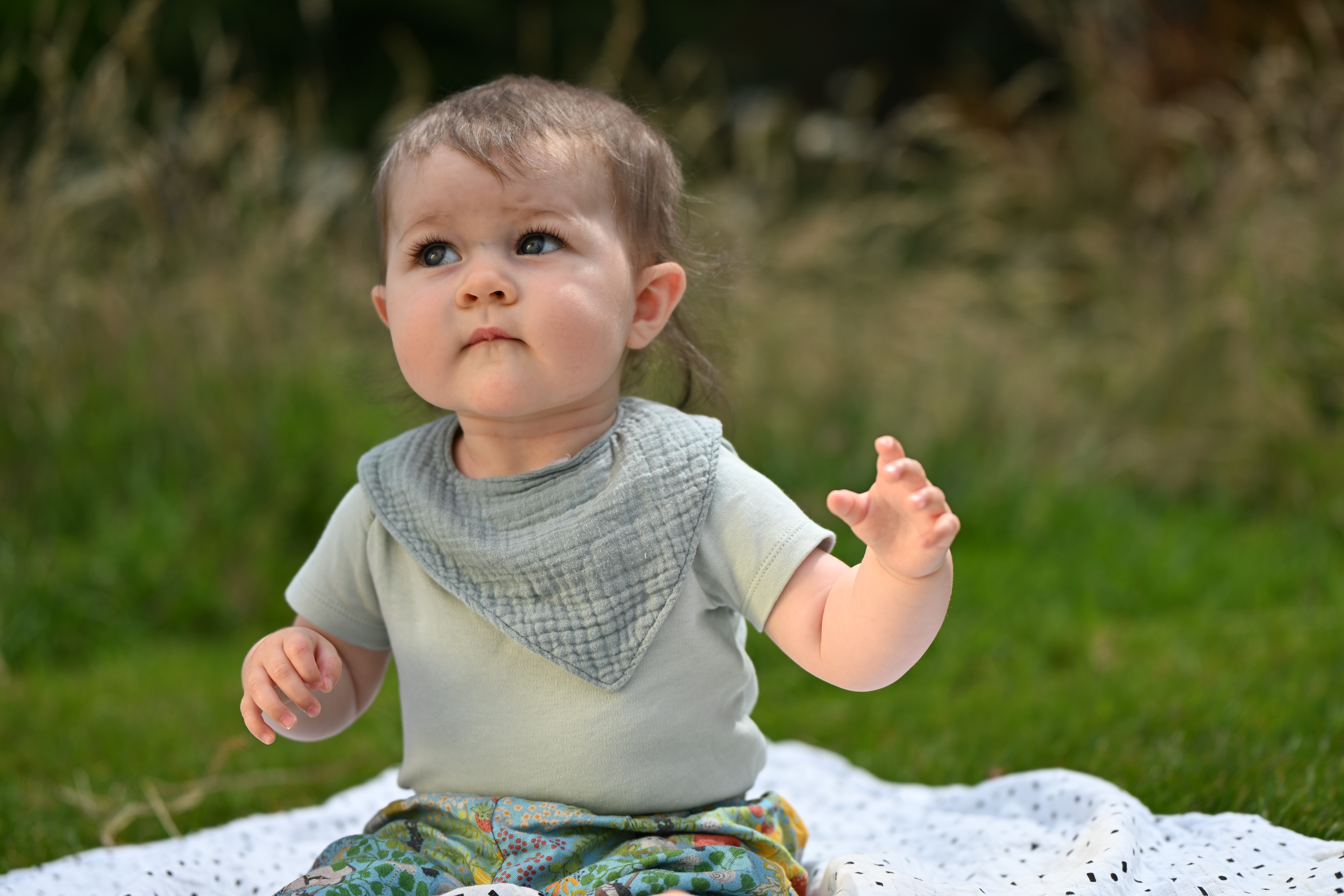
It’s got to the point now where I’ve stopped using single-point AF, and leave it on automatic subject recognition and let the camera decide for me at least half of the time. If I’m photographing anything that is likely to move around the frame, such as my baby or my dog, then it just makes sense to let the tracking do what it does best and keep up with them.
Also new is the ability to focus down to -10EV, making it superb at locking onto the subject in low-light too. There’s no messing about here.
Image stabilization has also been given a boost, with the Z6 III benefiting from the same 8-stop system as seen in the Nikon Zf. This 8-stops is measured using the 24-120mm f/4S that I’ve been using myself during this review. I’ve found that I can happily shoot with the telephoto end of this lens, at a fairly narrow aperture, in less than perfect lighting conditions and still get sharp shots almost all of the time, and the same is true of using longer lenses too.
Content creators who crave decent video specs should find a lot to like about the Z6 III too, with this being a real hybrid shooter. There’s 6K recording and a variety of different frame rates, plus the ability to shoot at different bit rates and codecs including Nikon’s N-raw, Pro Res Raw HQ, ProRes 422HQ / H.265, H.264 codecs in 12-bit raw, and 10-bit log recording.
OK, so there’s no 8K available, but 6K gives you lots of flexibility to crop in and produce oversampled 4K video, which is the quality most people require right now. Other functions here include 240p slow-motion, up to 120 minutes of record time, and the ability to use an external mic as a line-level input for recording sound directly in camera as you go. Having the screen now articulating means that those who want to record pieces to camera can do so easily, too.
It’s worth mentioning Nikon’s new Imaging Cloud service here. This is an instant backup and transfer service that will store your images for free for up to 30 days after they’re first transferred. It’s a neat way to back up your images on the fly, and only requires setting up the service once. Then, so long as you can connect freely to a WiFi network you can use it easily - although it's worth noting that if you need to login via a web browser it won’t work, which could be a problem in public locations such as cafes and hotels.
As part of Nikon's new cloud service, you also get color-profile image recipes which can be transferred to the camera, as well as firmware updates that can be transmitted and either installed automatically or manually. For now, this is only available for the Z6 III, but it is due to come to other Nikon models at a later date.
- Features and performance score: 5/5
Nikon Z6 III: image and video quality
- Similar performance to Nikon Zf
- Great detail and and sharpness
- Good colors and dynamic range
- Excellent video results
Although there will always be those who are drawn to very high resolution cameras, models such as the Z6 III show that you don’t necessarily need all those megapixels to still get excellent shots - and there’s actually plenty of benefits to sticking on the low side too.
Pair the Z6 III with excellent Nikon Z glass and you'll find that you’ve got some incredibly sharp images, and while you don’t have the kind of fine-grain detail you’d expect from the likes of the Z7 II, the Z8 or the Z9, for most ordinary all-rounders, you’ve got plenty to be getting on with here.
That said, with the lower pixel count, shooting in DX (APS-C) crop mode leaves you with only 10MP, which is a bit less usable than you would get from the same setup with Nikon's 45MP cameras. If this is something you think you’ll find yourself doing frequently, you might want to consider whether it’s worth paying the extra cash for the Z8.
That said, it really does depend on what you intend to do with your images. I’ve taken some impressively sharp images of my dog using the 120fps DX-crop mode, which are - as you might imagine - more than fine to share on social media, or print at what you might call “normal” sizes (A3 or below).
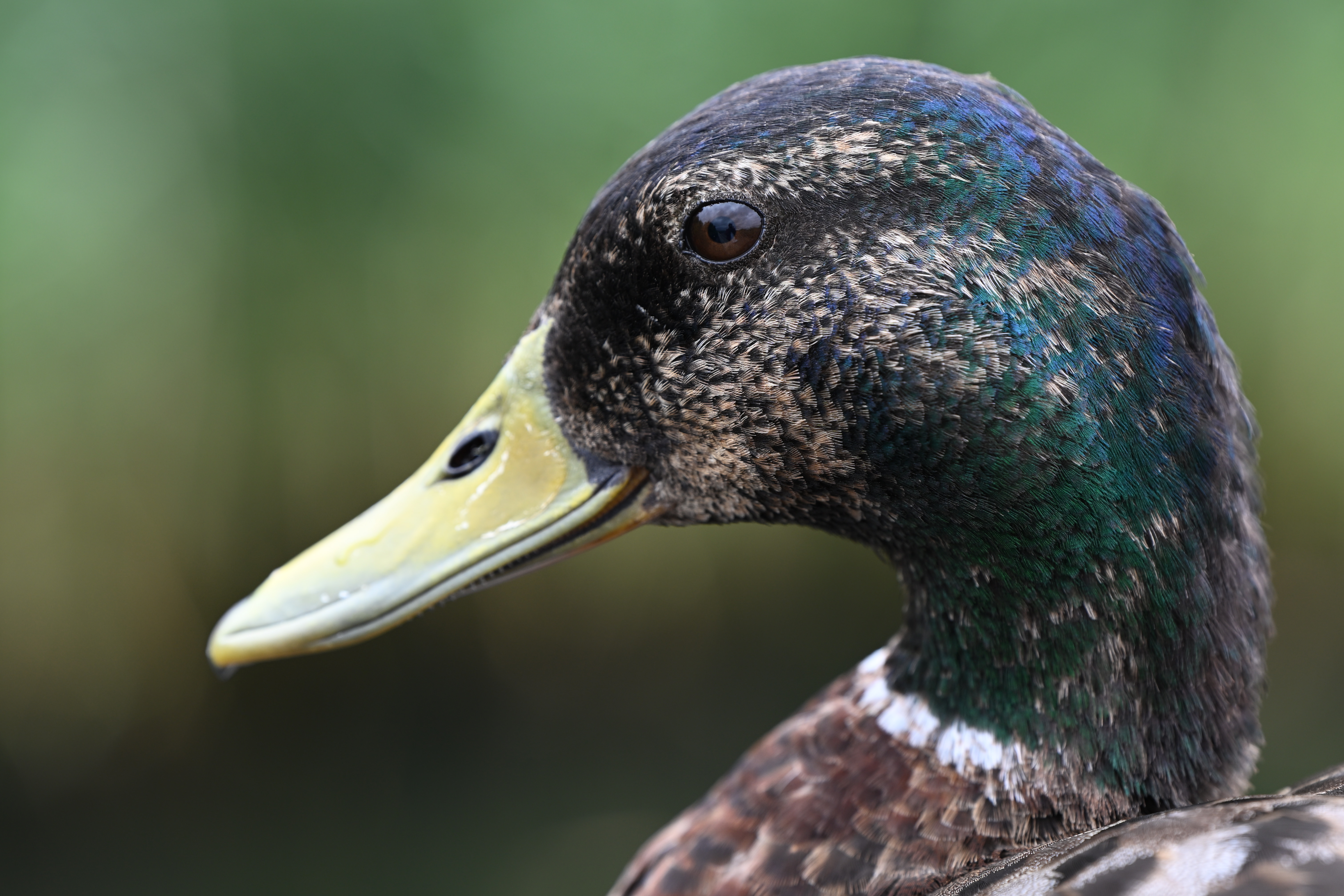
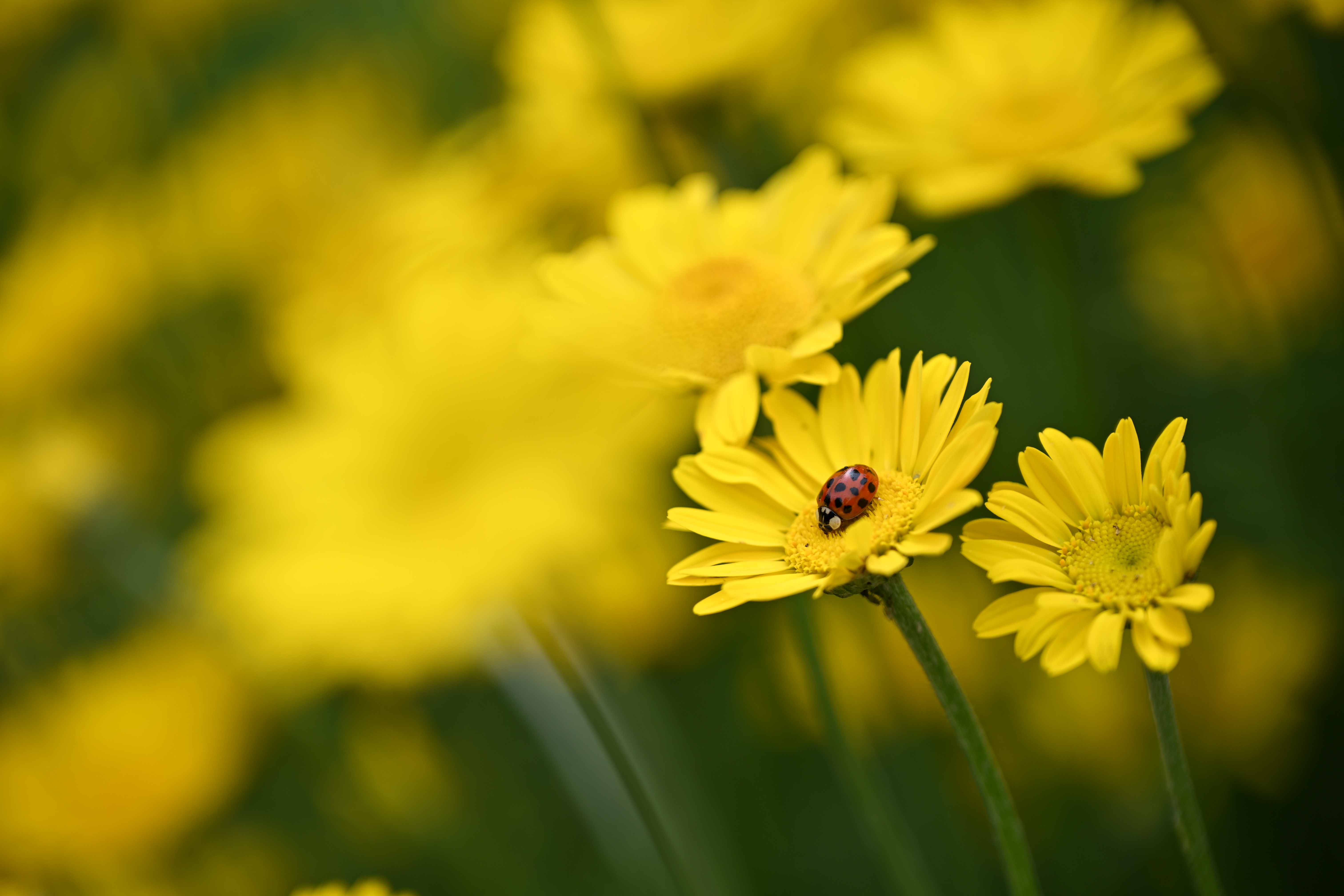
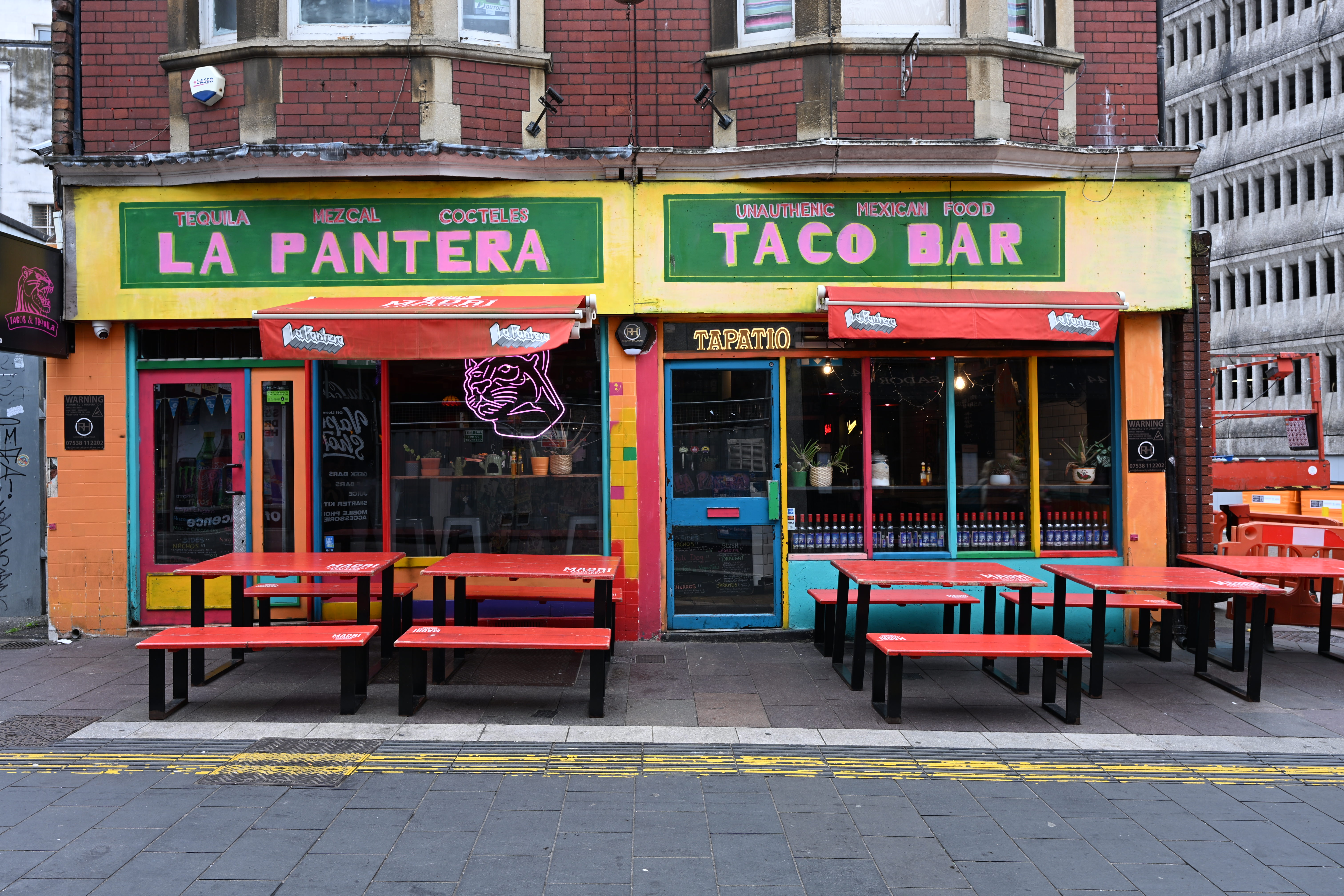
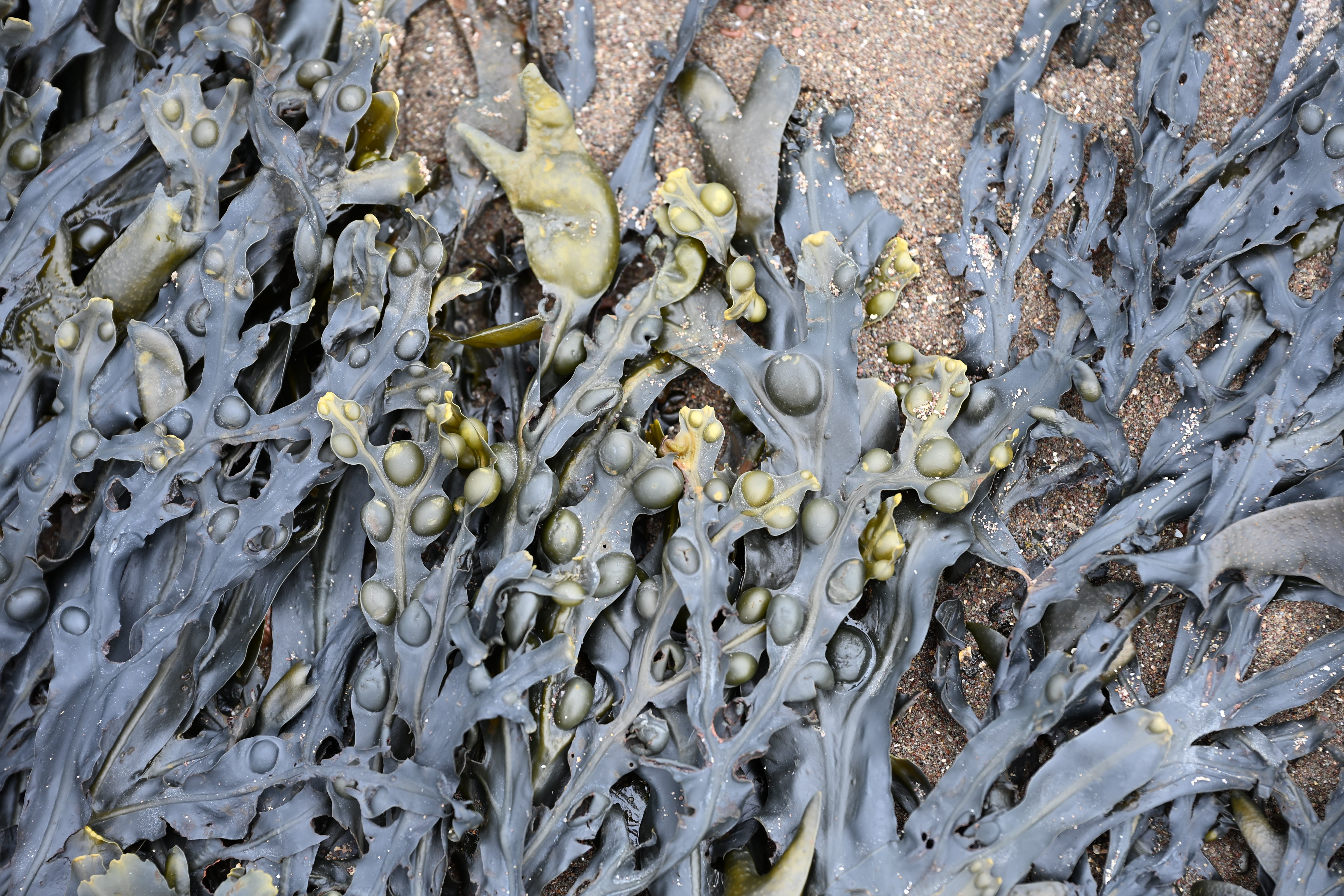
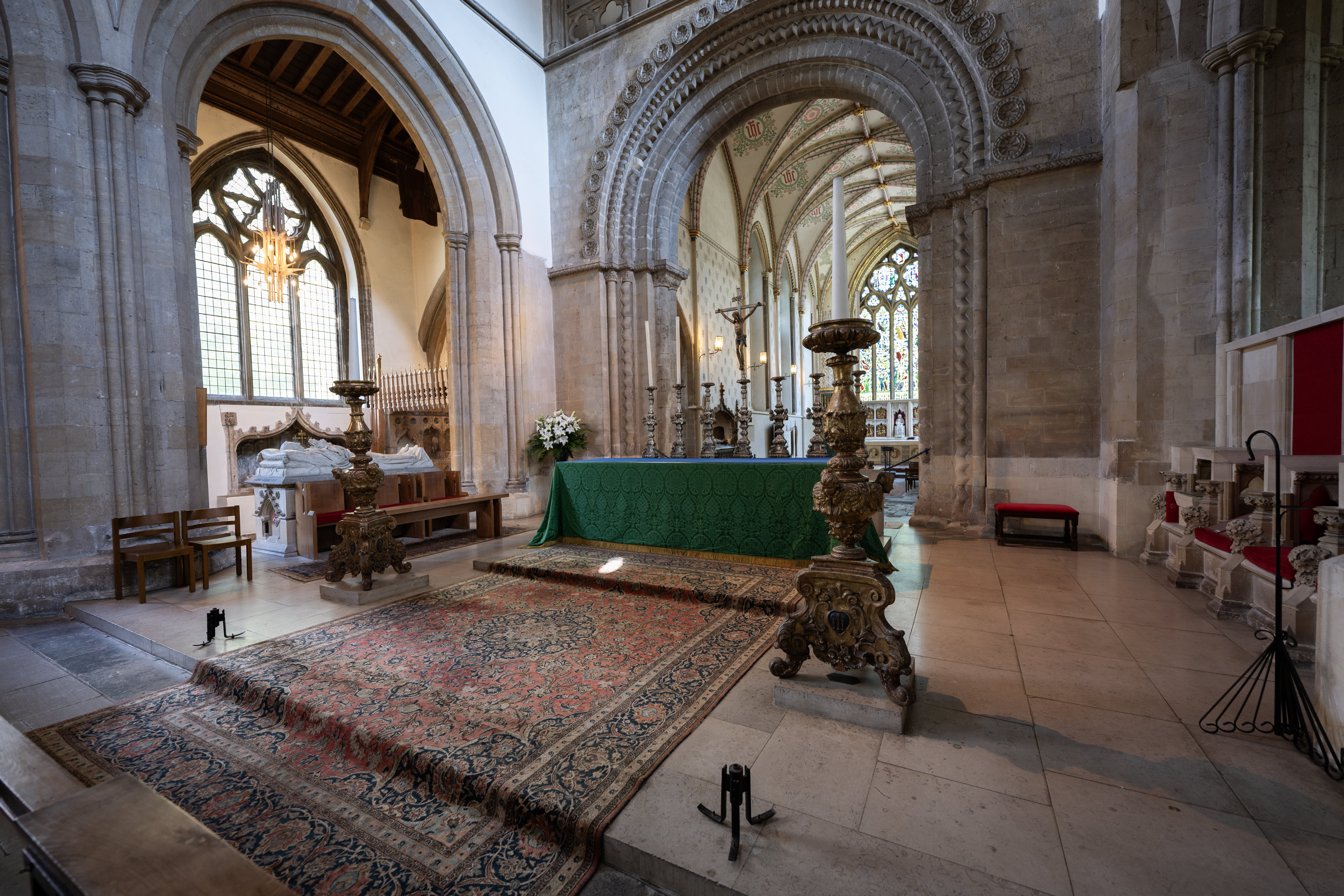
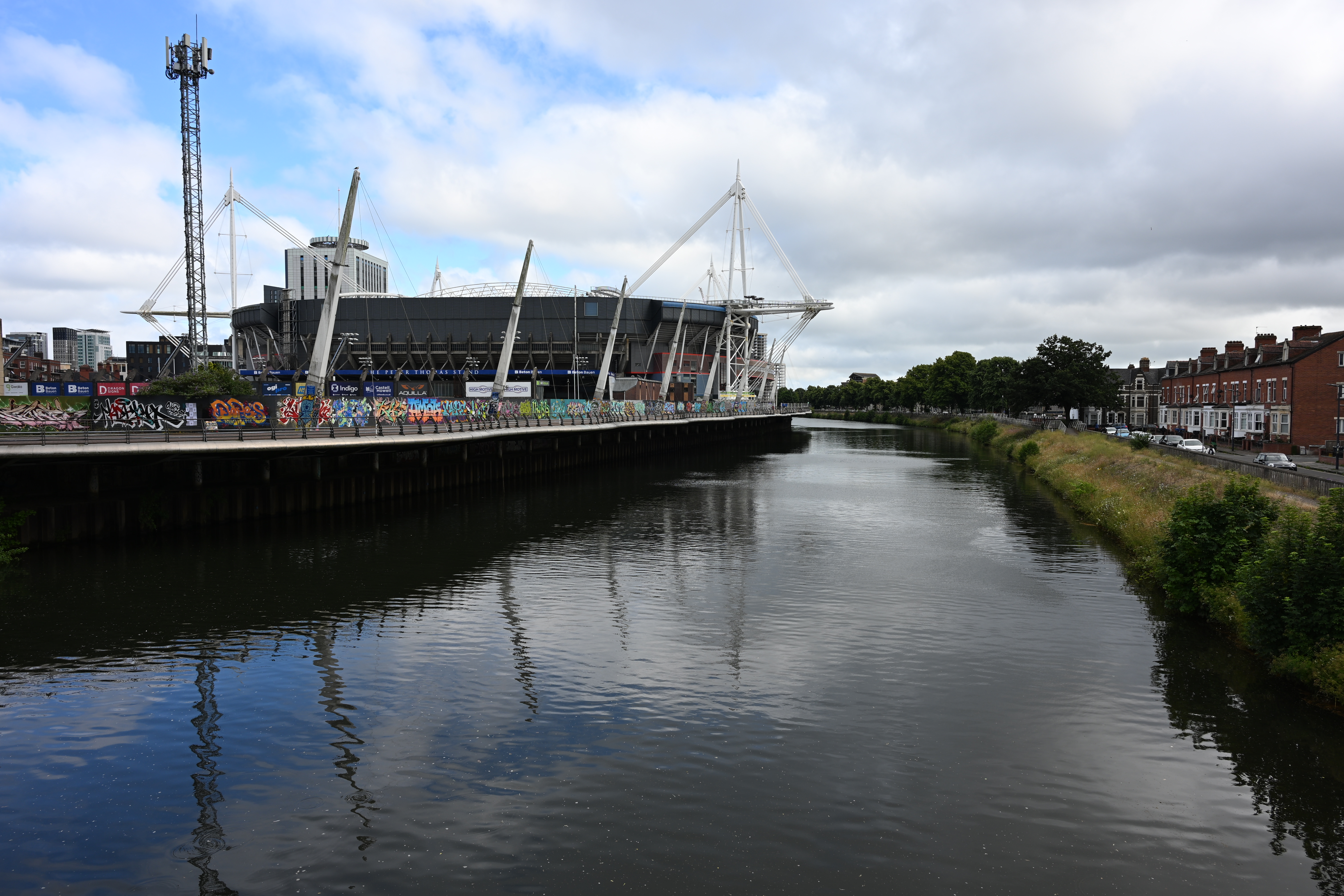










There have been some reports that the new partially stacked sensor found inside the Z6 III performs worse for dynamic range than the predecessor, the Z6 II, in lab tests. While that may be true, it’s not something I can say I’ve noticed in my real-world shots, and I’ve actually found the colors and dynamic range to be excellent.
Most of the time the “Auto” Picture Style results in colors which are a decent blend of vibrant and realistic - if you're shooting in raw you’ve got plenty of scope to adjust colors exactly how you want after the fact, too. Nikon’s Active D-Lighting does a great job of producing well-balanced exposures that require minimal post-production tweaking too, with good detail in the shadows and keeping blown-out highlights under control. Similarly, automatic white balance generally produces accurate results in a variety of situations.
It’s often the case that lower resolution sensors perform better in low light situations, so if that’s something you do quite a bit of, the Z6 III could be a good choice. I’ve found it to produce very clean images in low light situations, with even very high ISO shots (such as ISO 64000) resulting in a high-detail, low noise JPEG. There’s more noise in the corresponding raw file, which gives you the option to tweak noise-reduction settings as you see fit.
Overall, image quality here is pretty similar to the Nikon Zf, which also has a 24.5MP sensor, as well as the Z6 II. There was never really an issue with the quality of the final image from the Z6 II, but it was undeniably more difficult to get what you desired if you were shooting fast-moving subjects - in short the new sensor and focusing system makes the journey to a great picture far more achievable.
4K video sample
6K video sample
Video quality is just as great as picture quality, with plenty of detail and very little in the way of rolling shutter effect, thanks to the new sensor. You don’t have 8K video here, but the 6K option is excellent, as is the oversampled 4K. The internal mic is fine for clips on the fly, coping relatively well with some background noise. Of course, serious content creators will likely invest in external audio kit. Either way, there’s really a lot for hybrid content creators to get their teeth into here.
- Image quality score: 5/5
Nikon Z6 III: testing scorecard
Should I buy the Nikon Z6 III?
Buy it if...
Don't buy it if...
Nikon Z6 III: also consider
How I tested the Nikon Z6 III
- Three week-review period
- Paired with 24-120mm f/4, 50mm f/1.8, 14-28mm f/2.8 and 70-180mm f/2.8 lenses
I’ve had three weeks with the Nikon Z6 III, having previously used all of Nikon’s Z series since the format was first introduced in 2018.
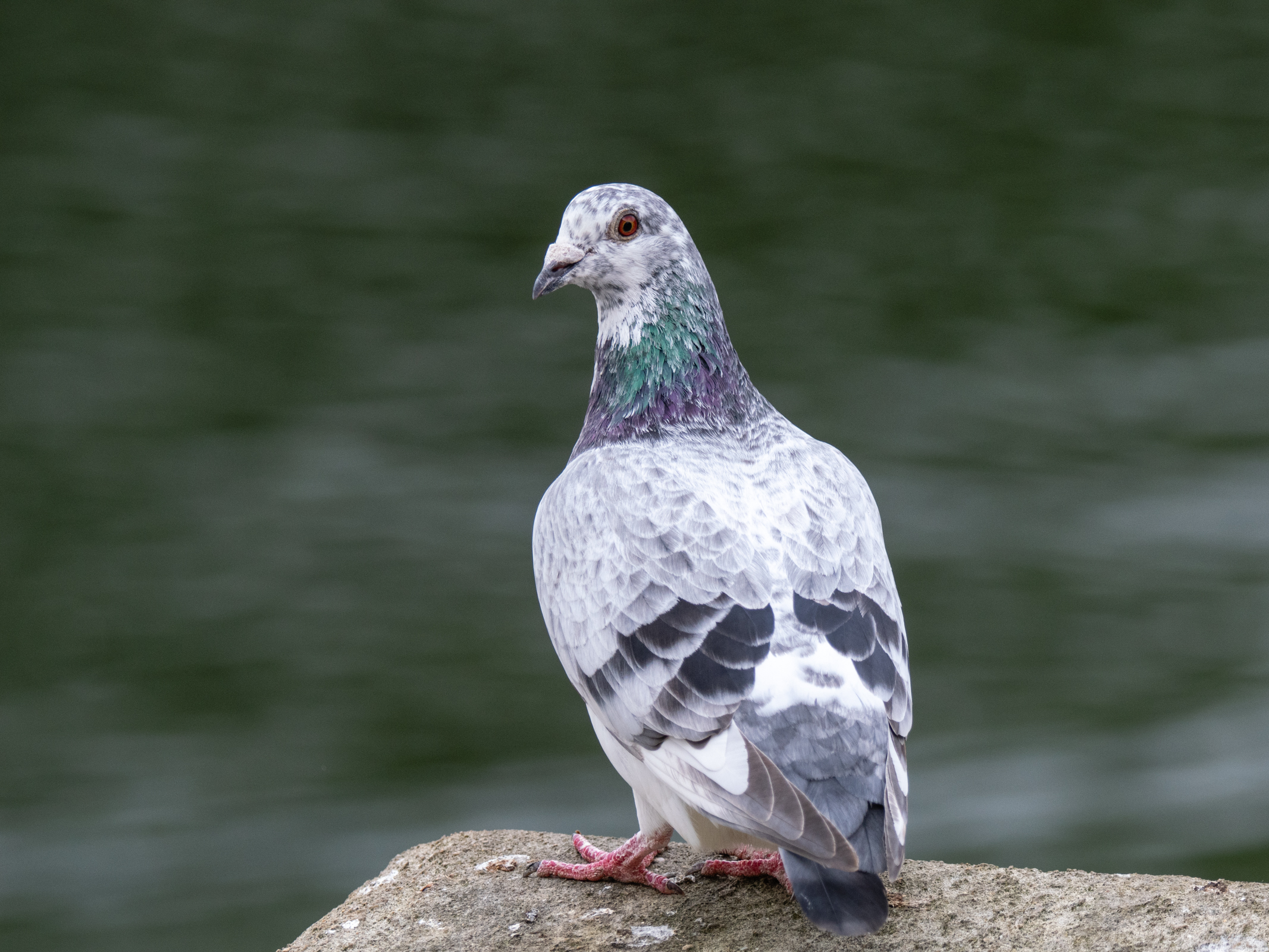
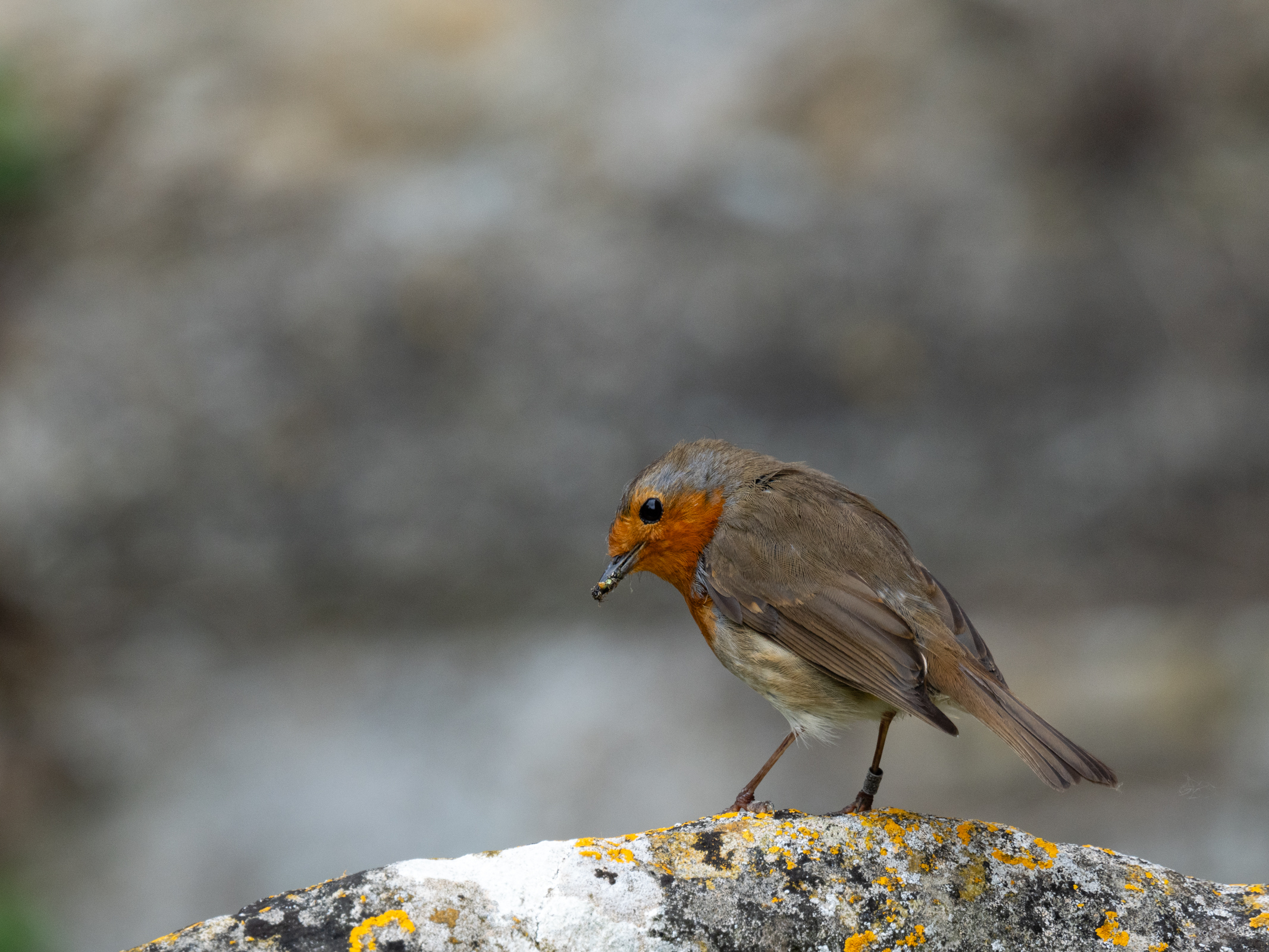
During my two weeks with the Z6 III, I have tried it in a number of different shooting situations. I’ve photographed landscapes and interiors to get a feel for general image quality. I photographed my dog in action to give fast shooting and AF capability a good test run, as well as photographing birds to check that the Eye AF works across different species. I also photographed my daughter in a number of different situations to get a feel for how portraiture feels with the Z6 III.
I have been using the Z6 III with four different lenses. The 24-120mm f/4 lens was chosen for its versatility and used most frequently. It was joined by the 70-180mm f/2.8 lens for action and (fairly close) wildlife, as well as portraits, the 14-28mm f/2.8 for interiors and landscapes and the 50mm f/1.8 for portraits, street and candid shots.
First reviewed July 2024