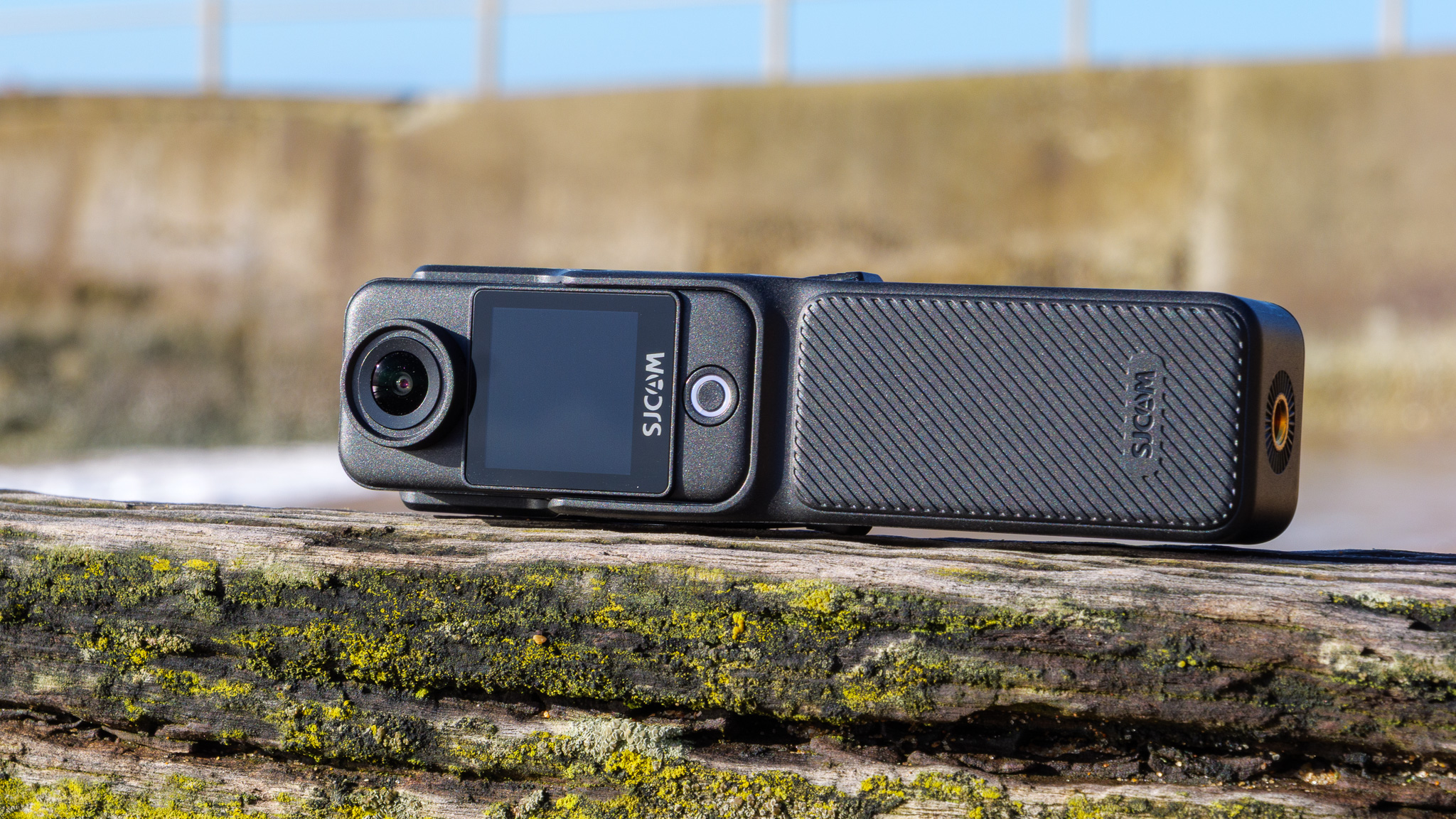
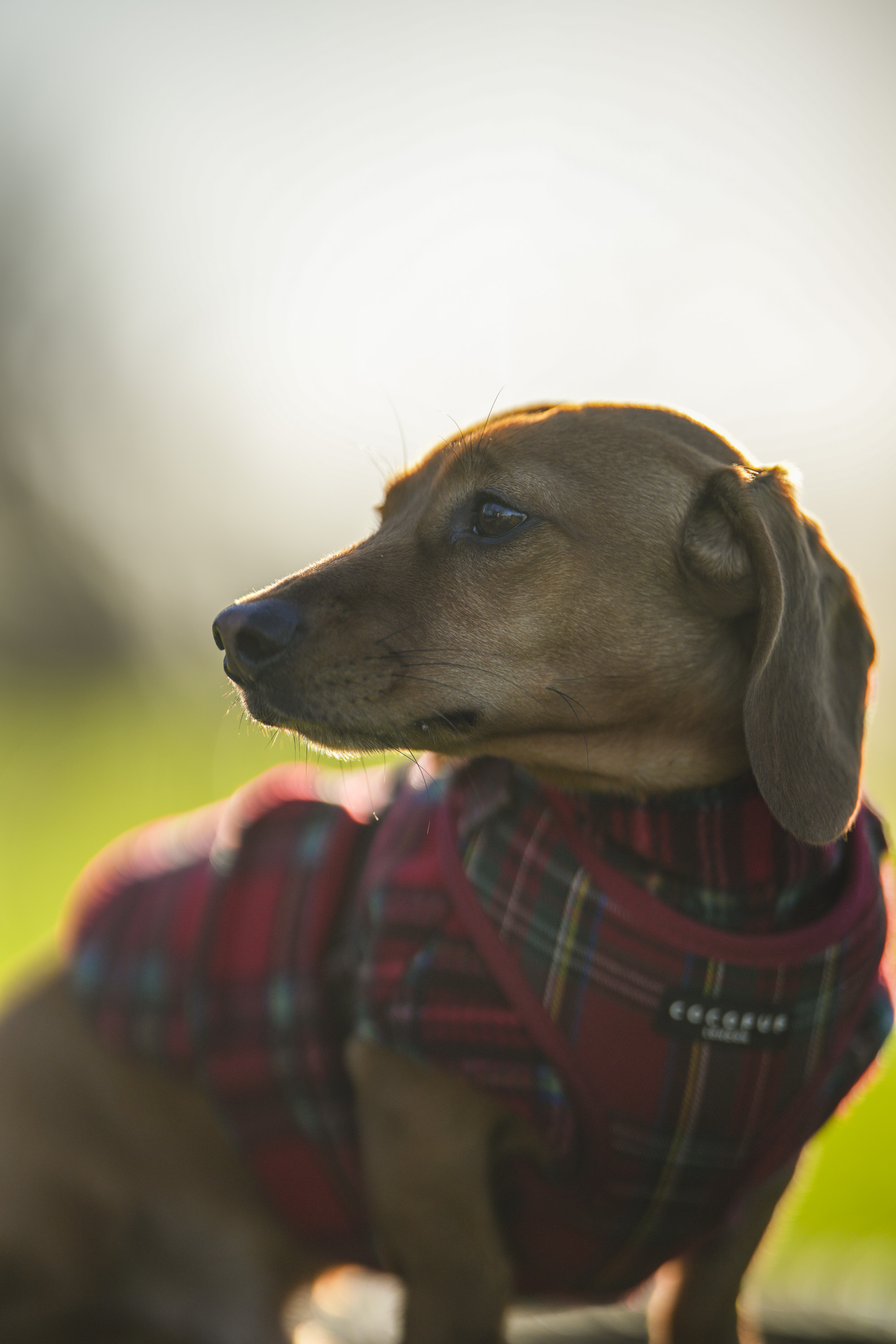
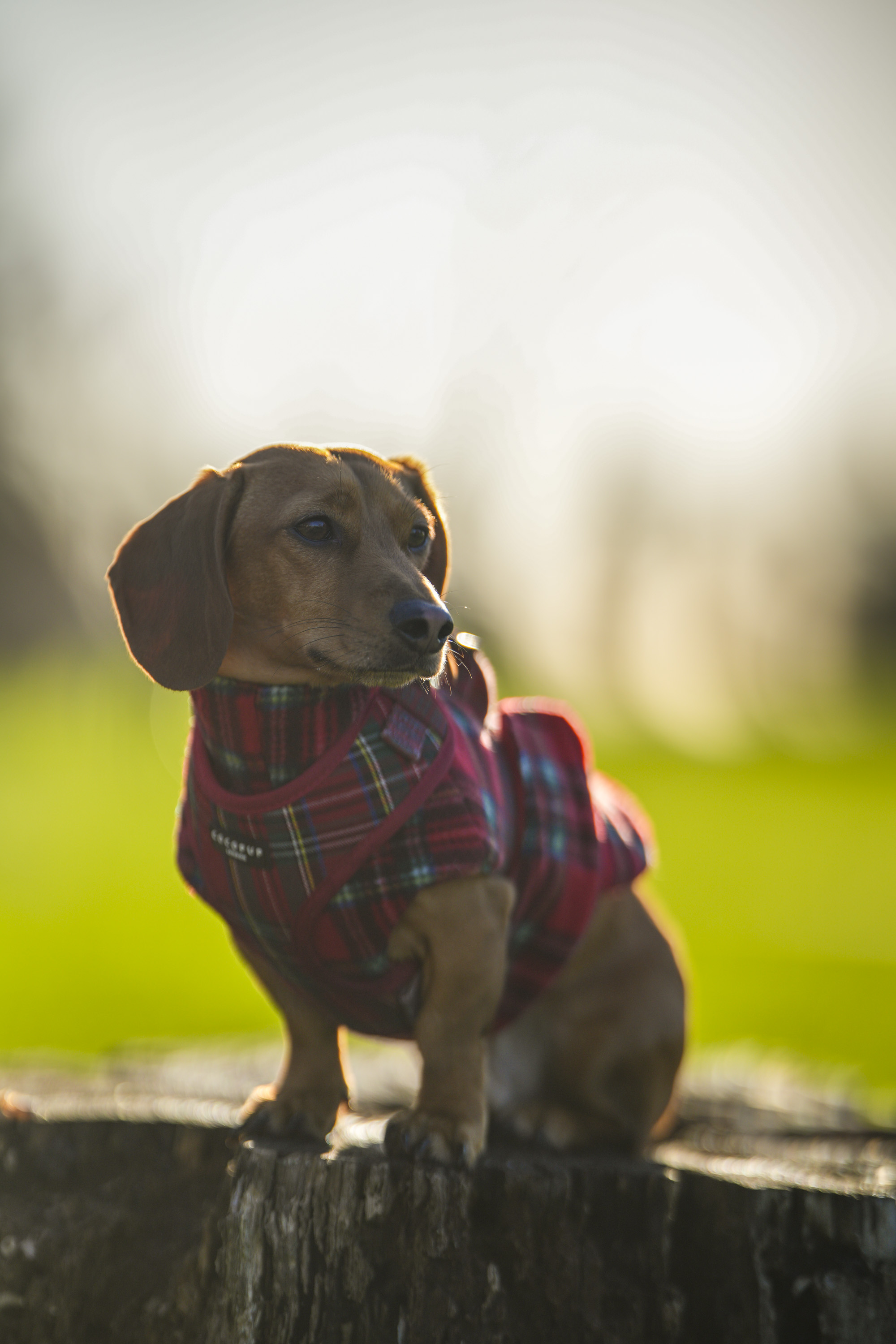
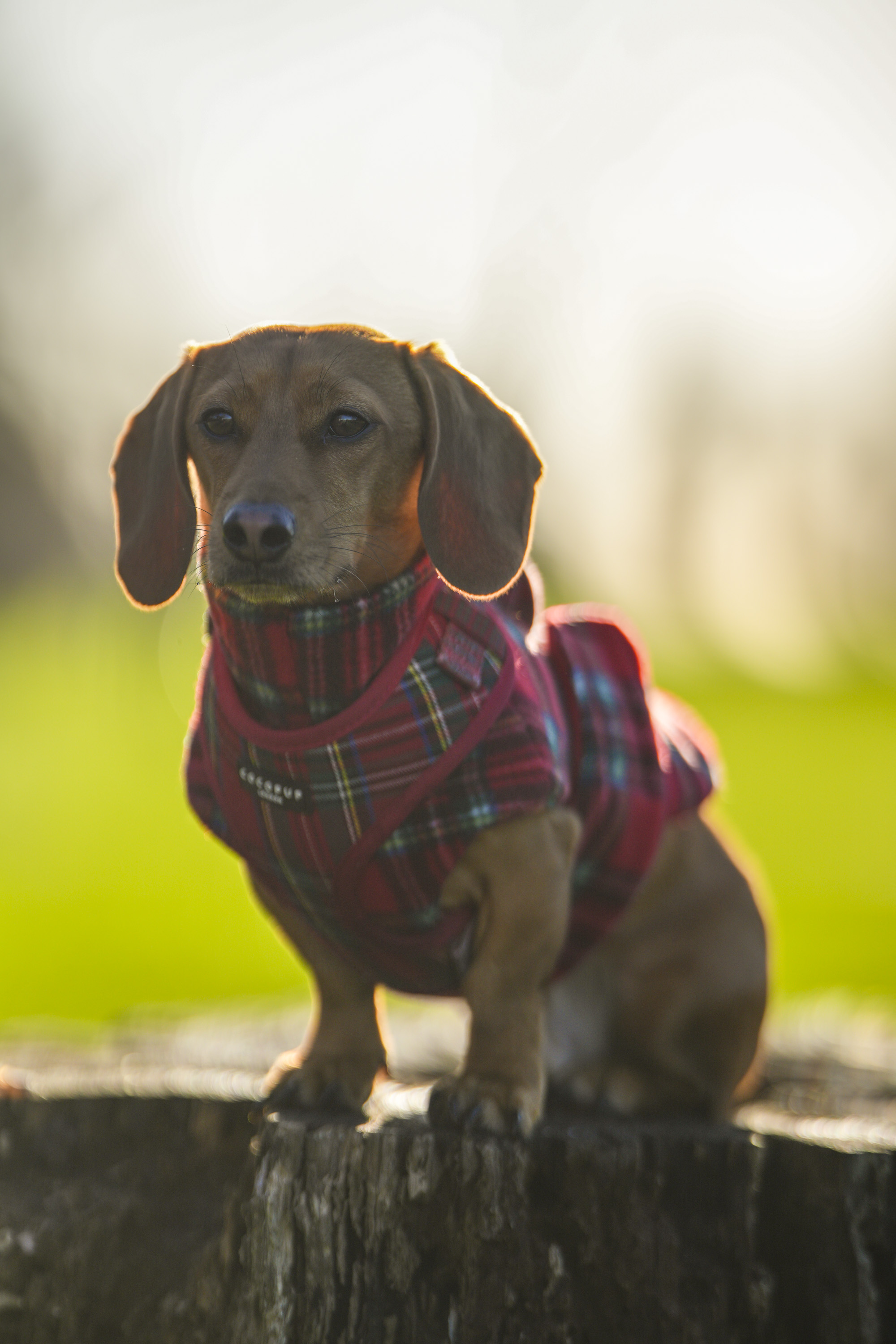
One minute review
The Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM is a beautiful mess of a lens. It's impossibly light, cheap, and wide, but nonetheless comes with a few optical niggles that will likely make the more discerning pixel peepers baulk.
At $599 / £479 / AU$699.95, the RF 45mm f/1.2 has the potential to be an essential component of any Canon shooter's kit bag. And, it has to be said, it's a lens that doesn't really have any rivals or alternatives at this price point. No other brand, third-party or otherwise, offers an autofocus full-frame lens with f/1.2 for $600. Canon is definitely worthy of praise for this - it's an innovative, forward-thinking lens from a brand that's often criticized for its closed mount.
As mentioned, however, optically, the RF 45mm f/1.2 leans more towards 'character' than perfection. The bokeh is busy and swirly, while the chromatic aberration is off the charts at the widest aperture. Even with in-camera corrections, this lens imparts its character on every image if you're shooting wide.
You also don't get weather sealing or a lens hood. While this lens is well built and a great pairing with any of the brand's high-end mirrorless bodies, it's very much a lens that's been shoehorned into a specific price point. I can forgive the lack of weather sealing, but paying extra for the hood feels slightly miserly to me.

If you can look past its flaws, however, the 45mm f/1.2 does offer a lot for the price. No other Canon lens right now offers as many creative options as this 45mm in the standard focal length. Emphasis on the 'creative' here, mind you, because the wide aperture opens possibilities for shots simply not possible on the usual kit lens.
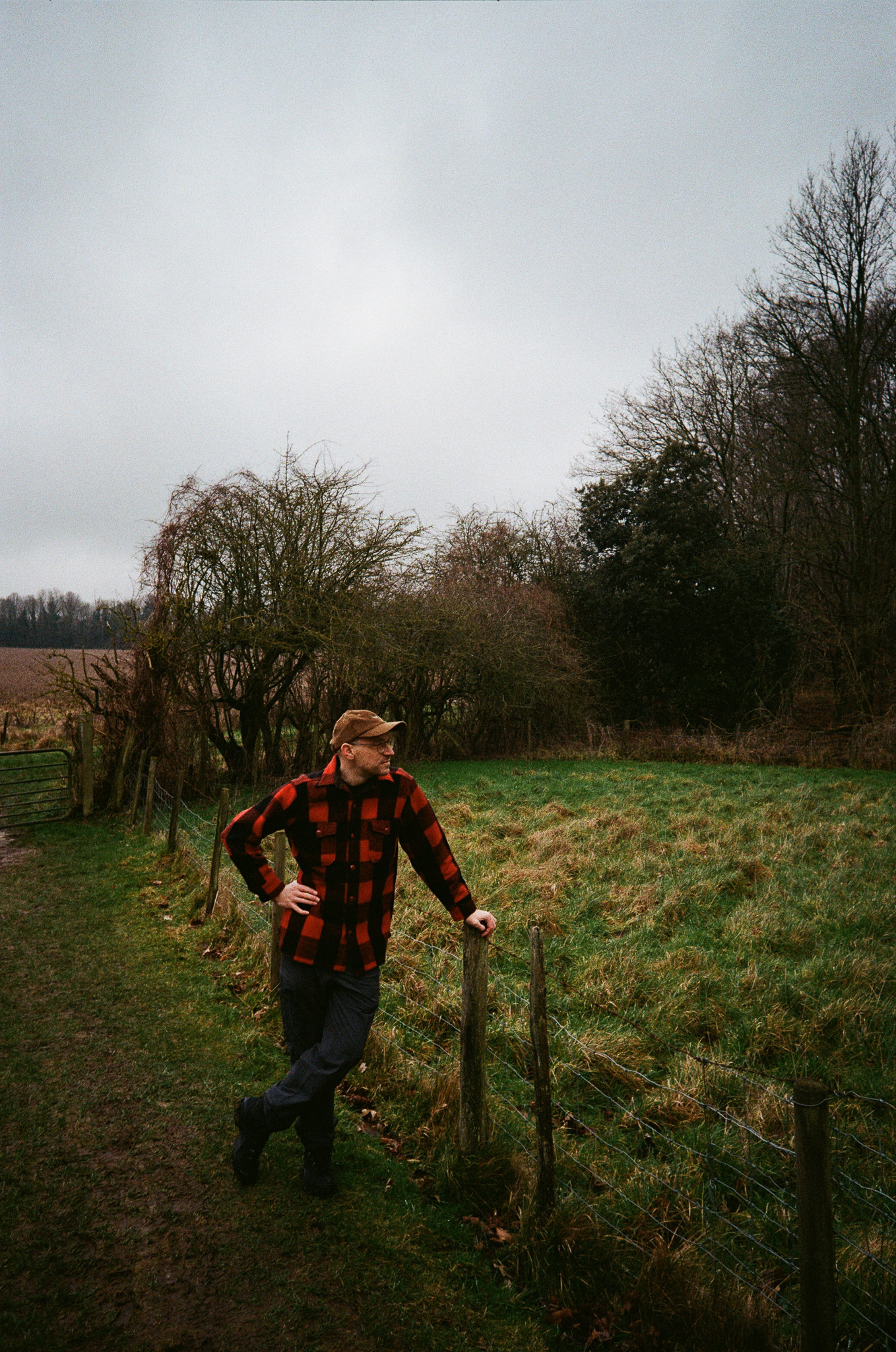
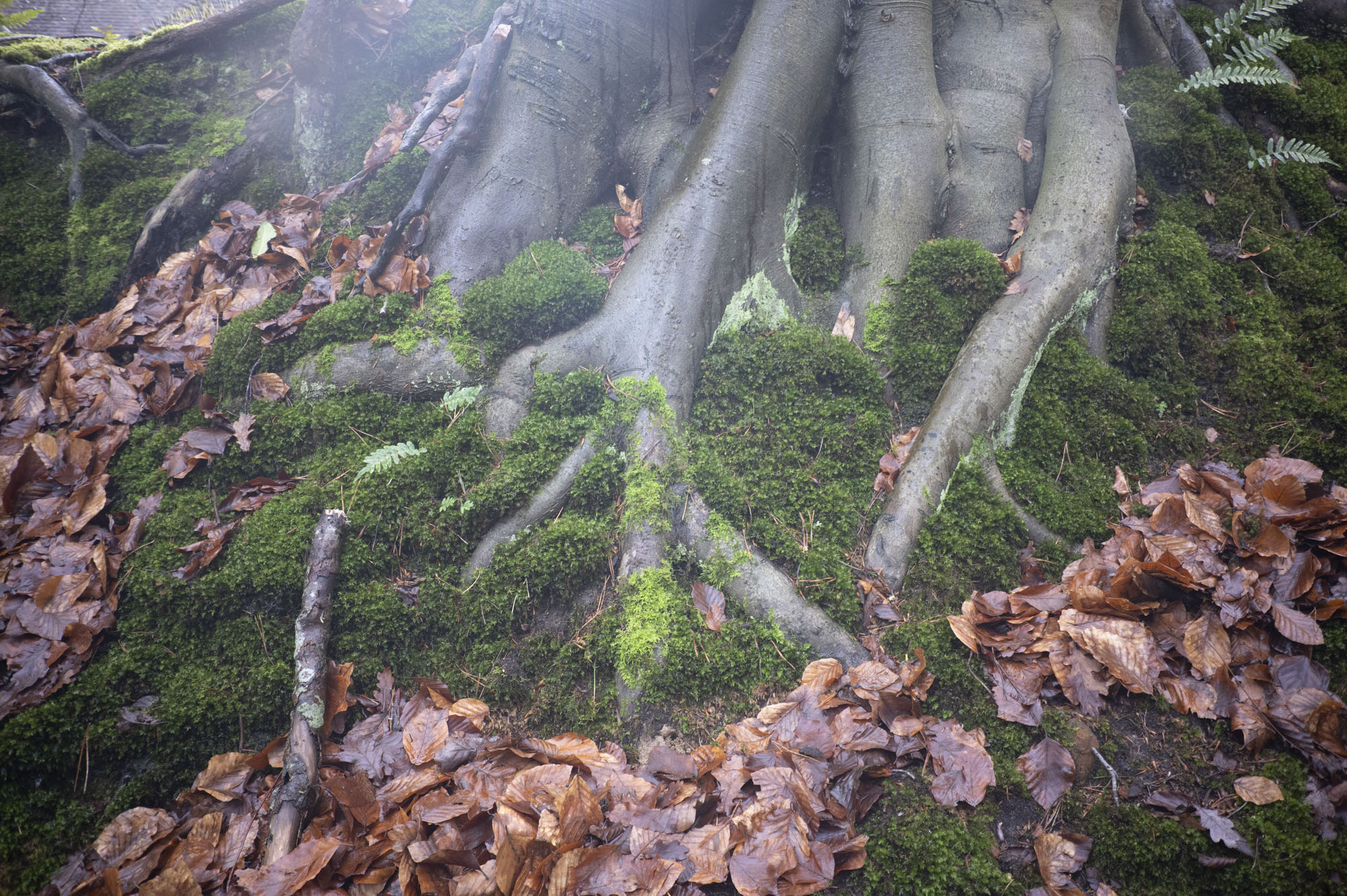
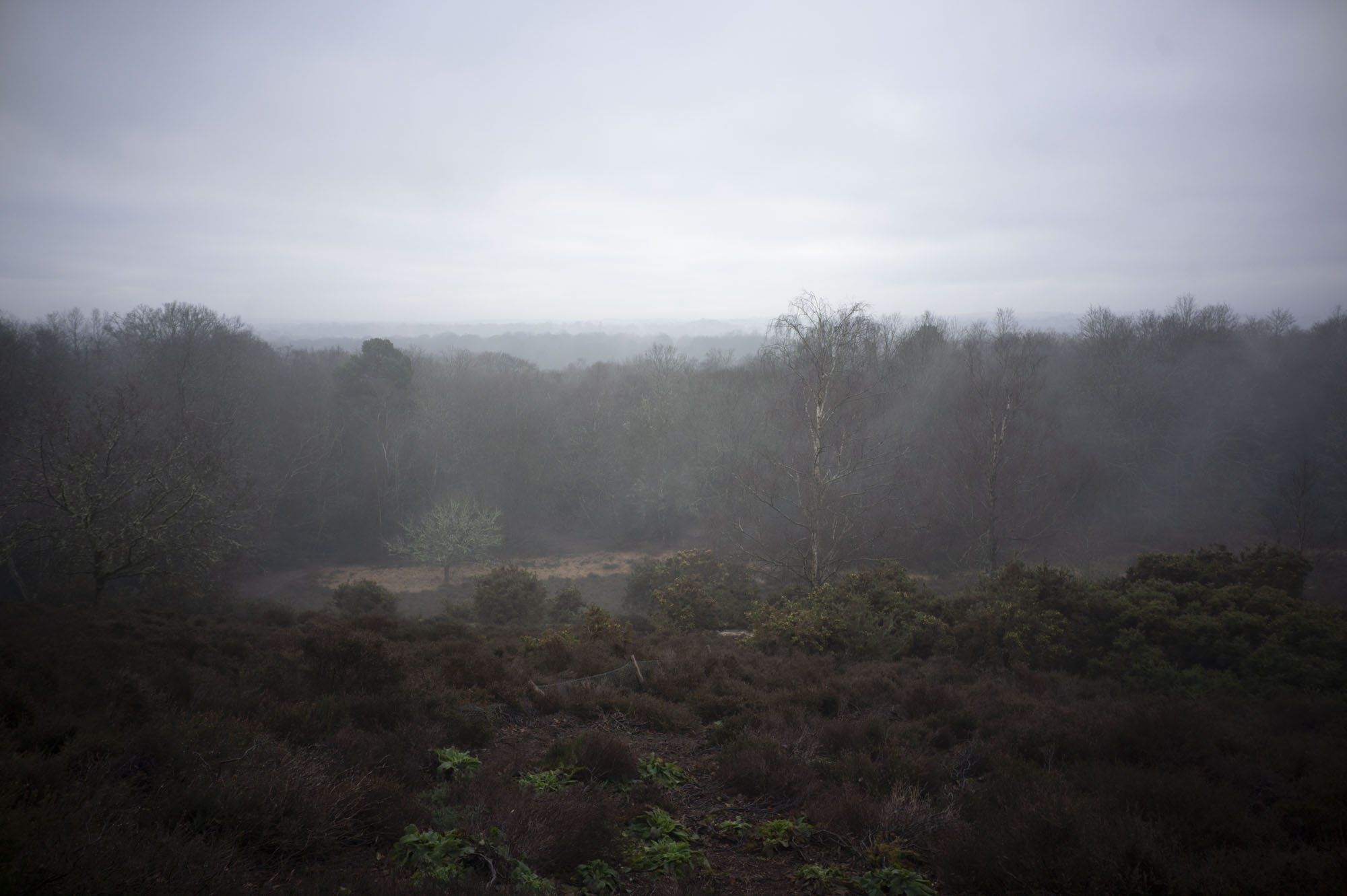
Aside from serious low-light chops, this lens is also fantastic for environmental portraits, where you can blow out the background on a relatively wide scene.
In summary, the 45mm is an often frustrating lens, but one I can't help but like. I don't think it's a 'killer' lens that will cause Nikon and Sony users to switch, but it certainly is unique and praiseworthy. Is it one of the best Canon lenses? Technically, absolutely not. But is it worth it? Absolutely... if you're looking for 'character' rather than 'perfection', that is!
Price and availability
- It costs $599 / £479 / AU$699.95
- Lens hood is a separate purchase
At $599 / £479 / AU$699.95, the RF 45mm f/1.2 is cheap for a Canon full-frame RF lens, let alone one with such a wide aperture. It's much closer in price to the entry-level Canon RF 50mm F1.8 STM (£239 / $219 / AU$299) than premium L-series glass - and offers a similar level of optical quality for the budget-conscious.
It's a good thing Canon has made this lens, too, as the brand currently doesn't support third-party glass on its full-frame mount. Unlike rival mounts from Nikon and Sony, Canon users have fewer low-cost alternatives outside of the usual starter primes and kit lenses.
Luckily, this lens is a great example of Canon doing something a little different. It's not quite a budget lens, but it's certainly unique, and definitely a sign that the brand is willing to try new things for its RF mount.
Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM: specs
Type: | Standard prime |
Mount: | Canon RF |
Sensor: | Full-frame |
Focal length: | 45mm |
Max aperture: | f/1.2 |
Minimum focus: | 0.45m, 0.13x max magnification |
Filter size: | 67mm |
Dimensions: | 78 x 75mm |
Weight: | 12.2oz / 346g (lens only) |
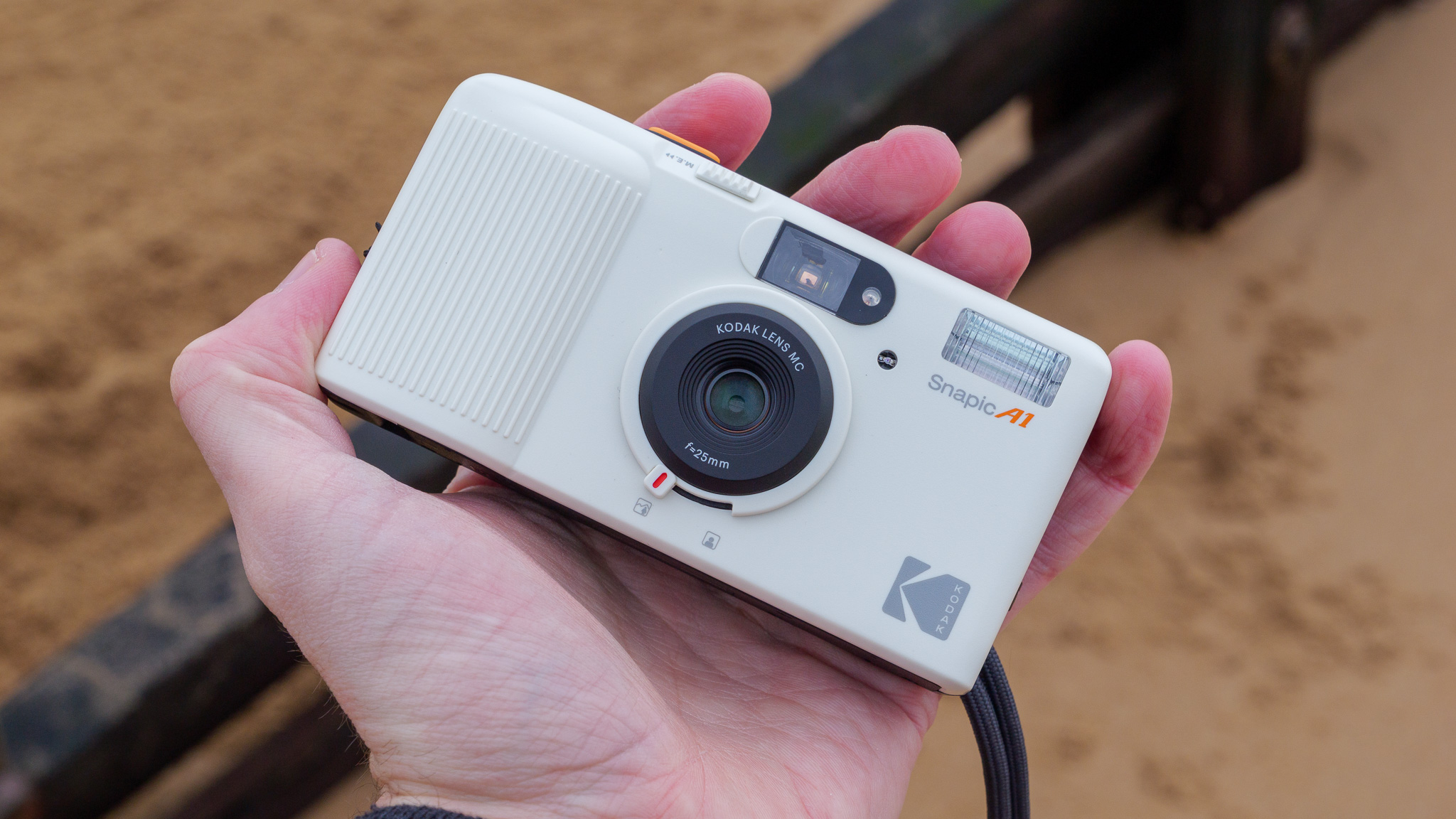
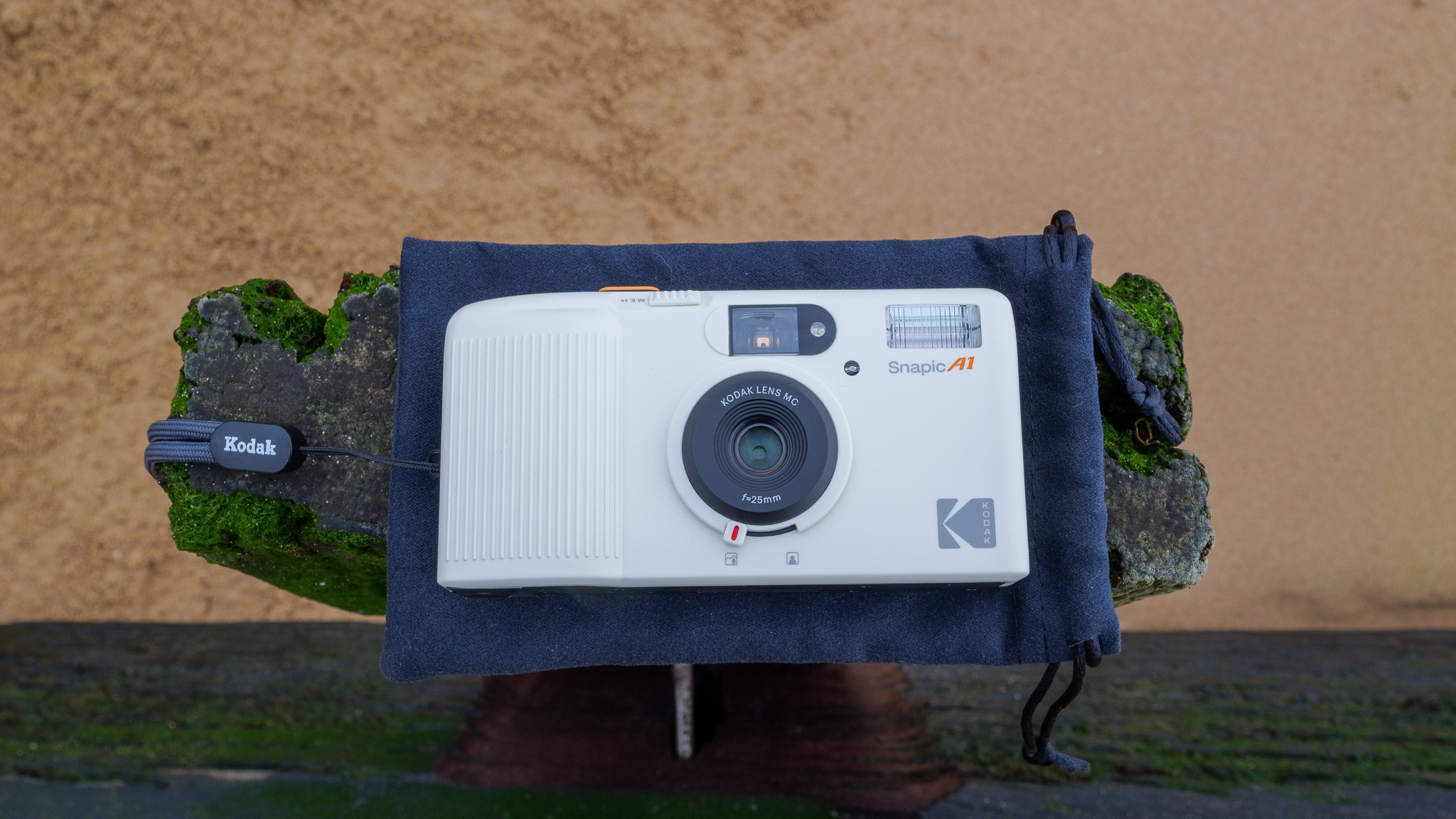
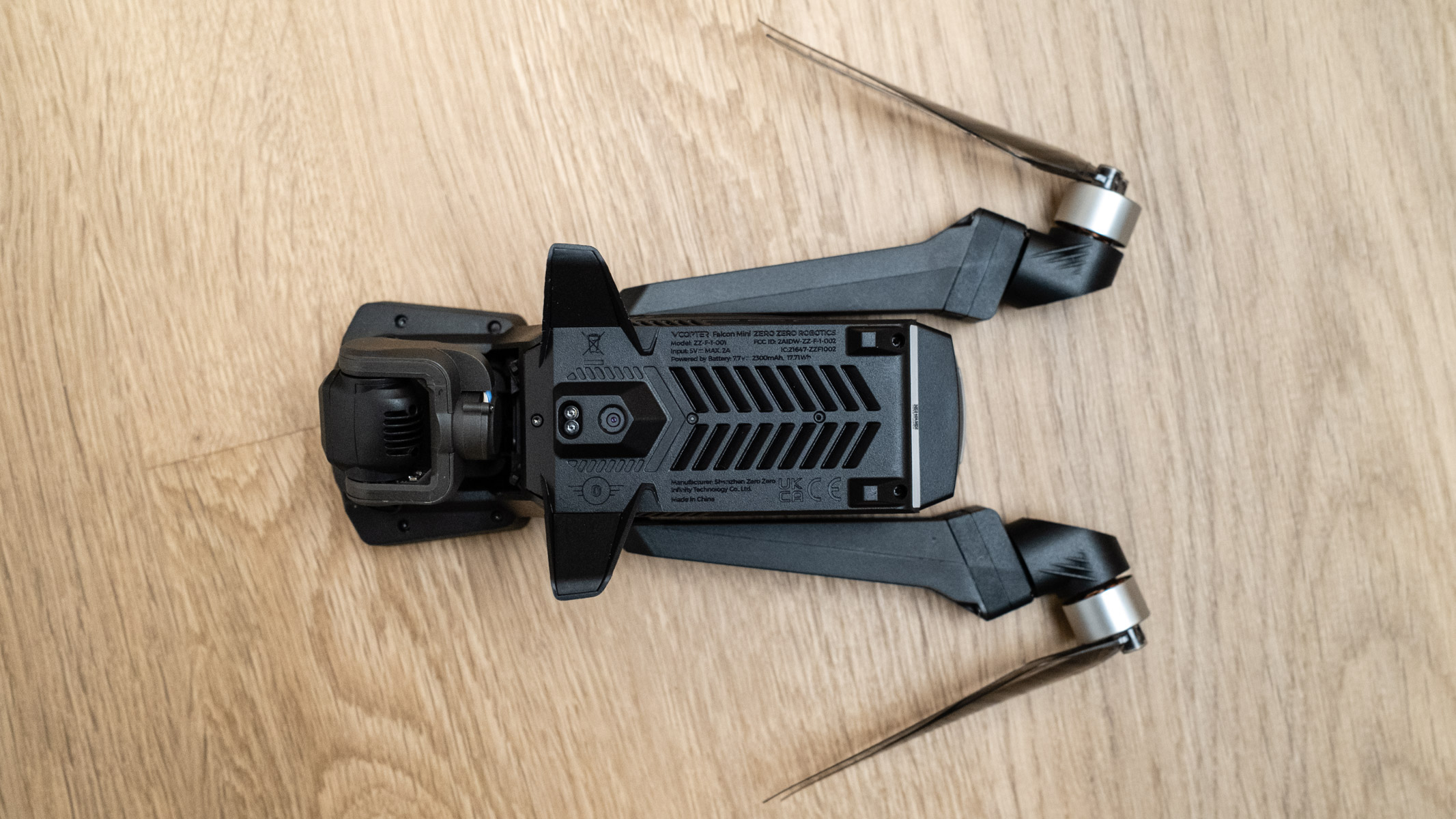
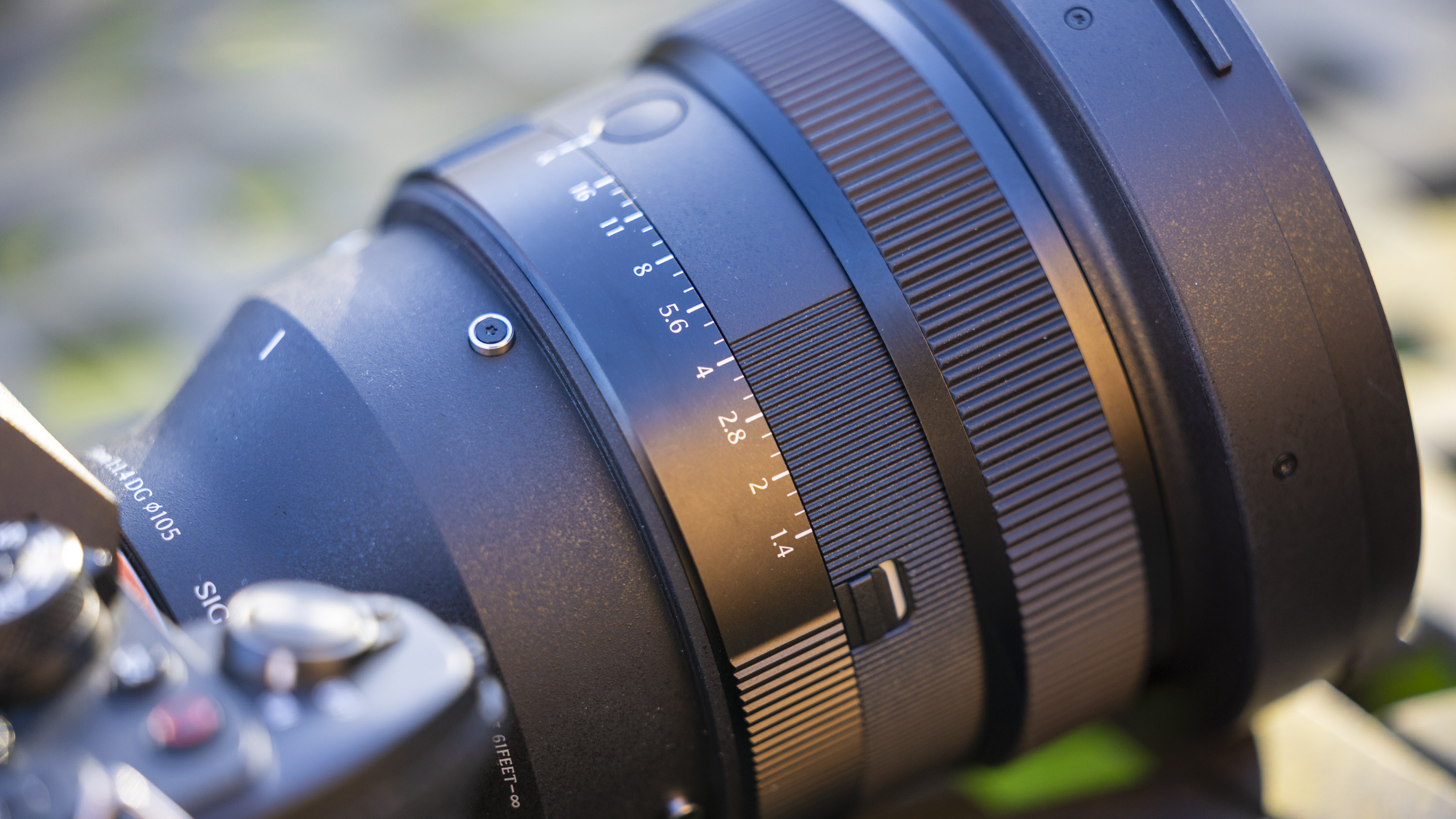
Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM: design
- Extremely lightweight for such a prime
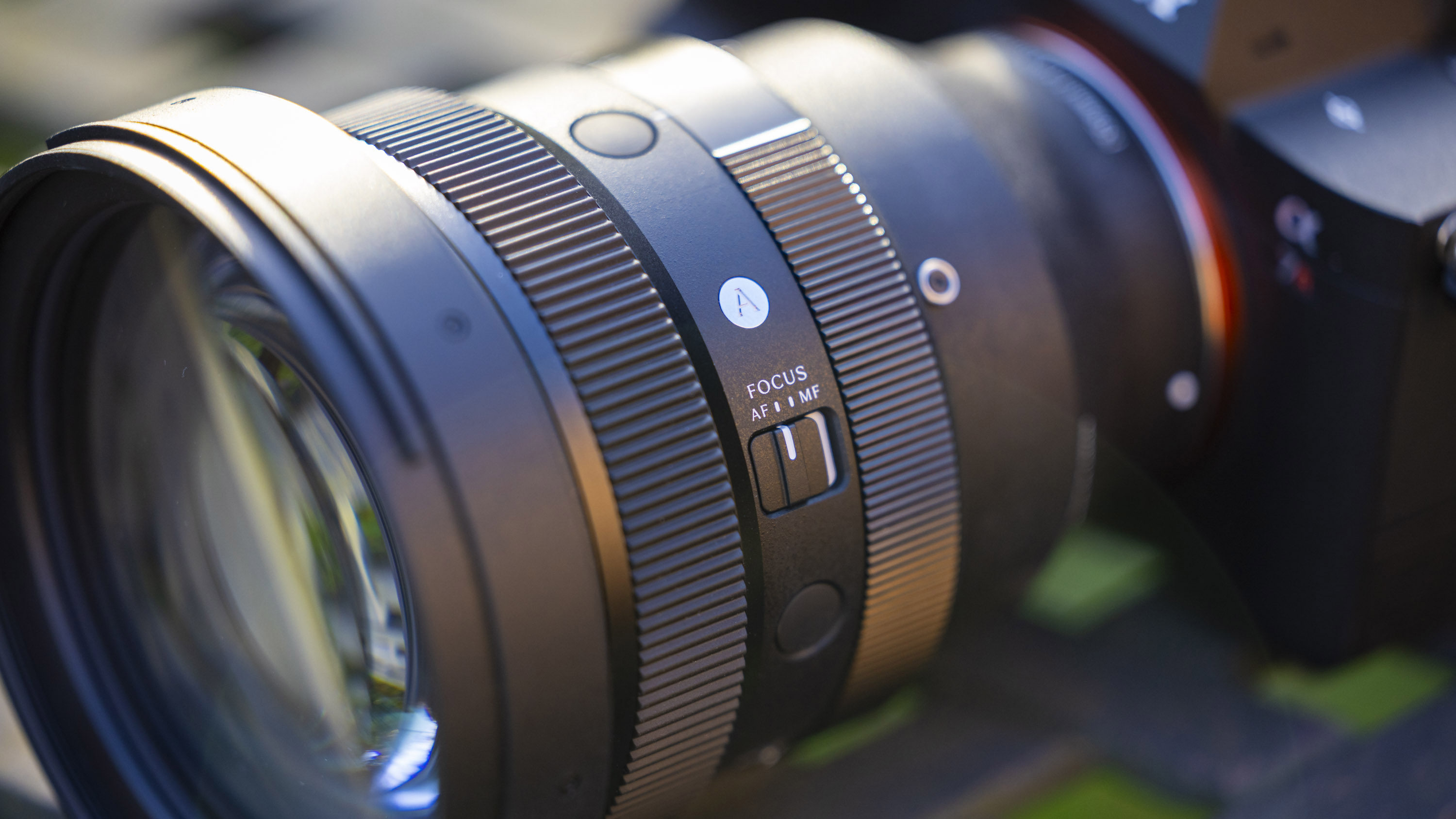
- AF/MF switch, but otherwise very basic
- Customizable control ring
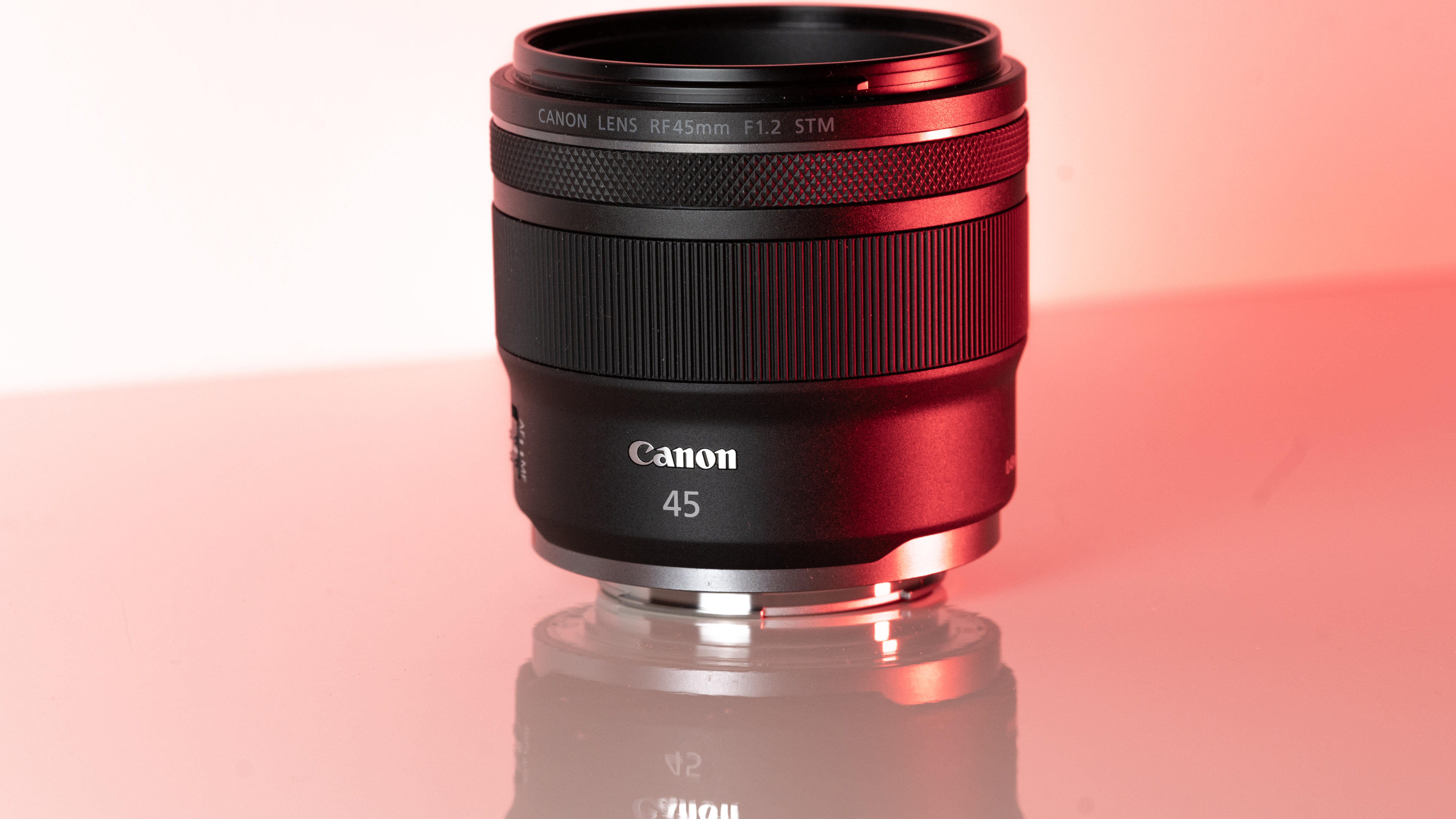

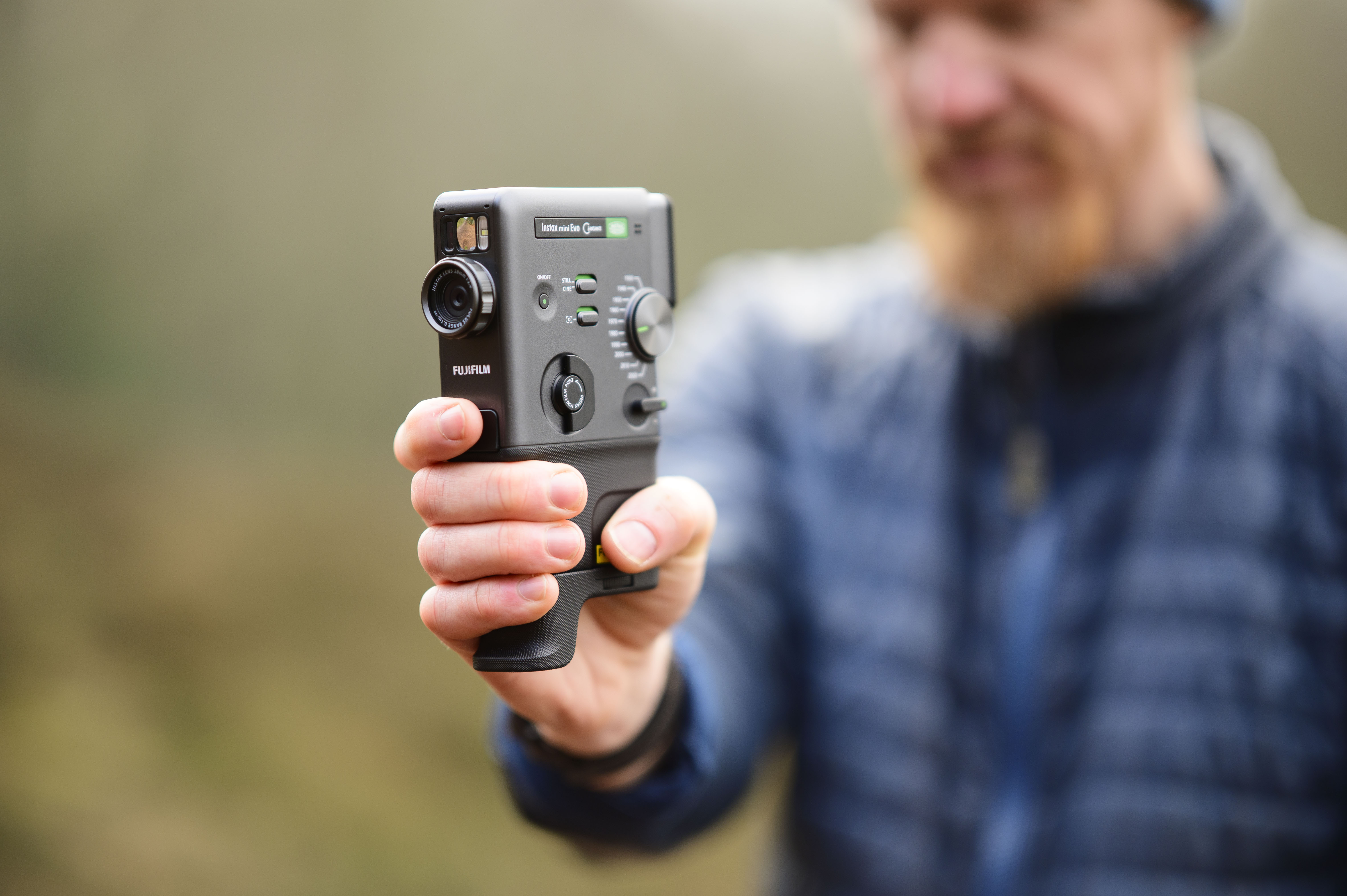
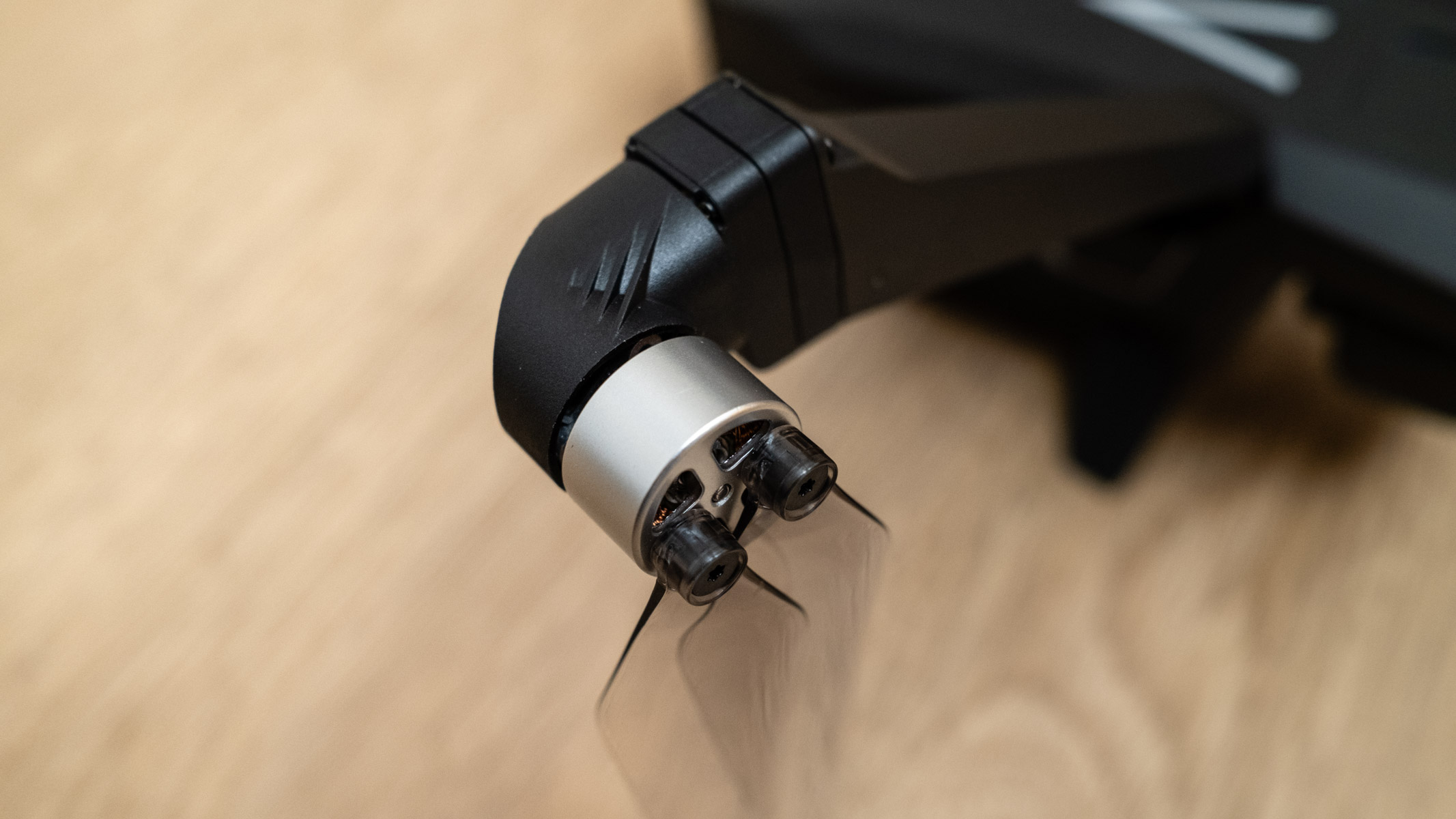
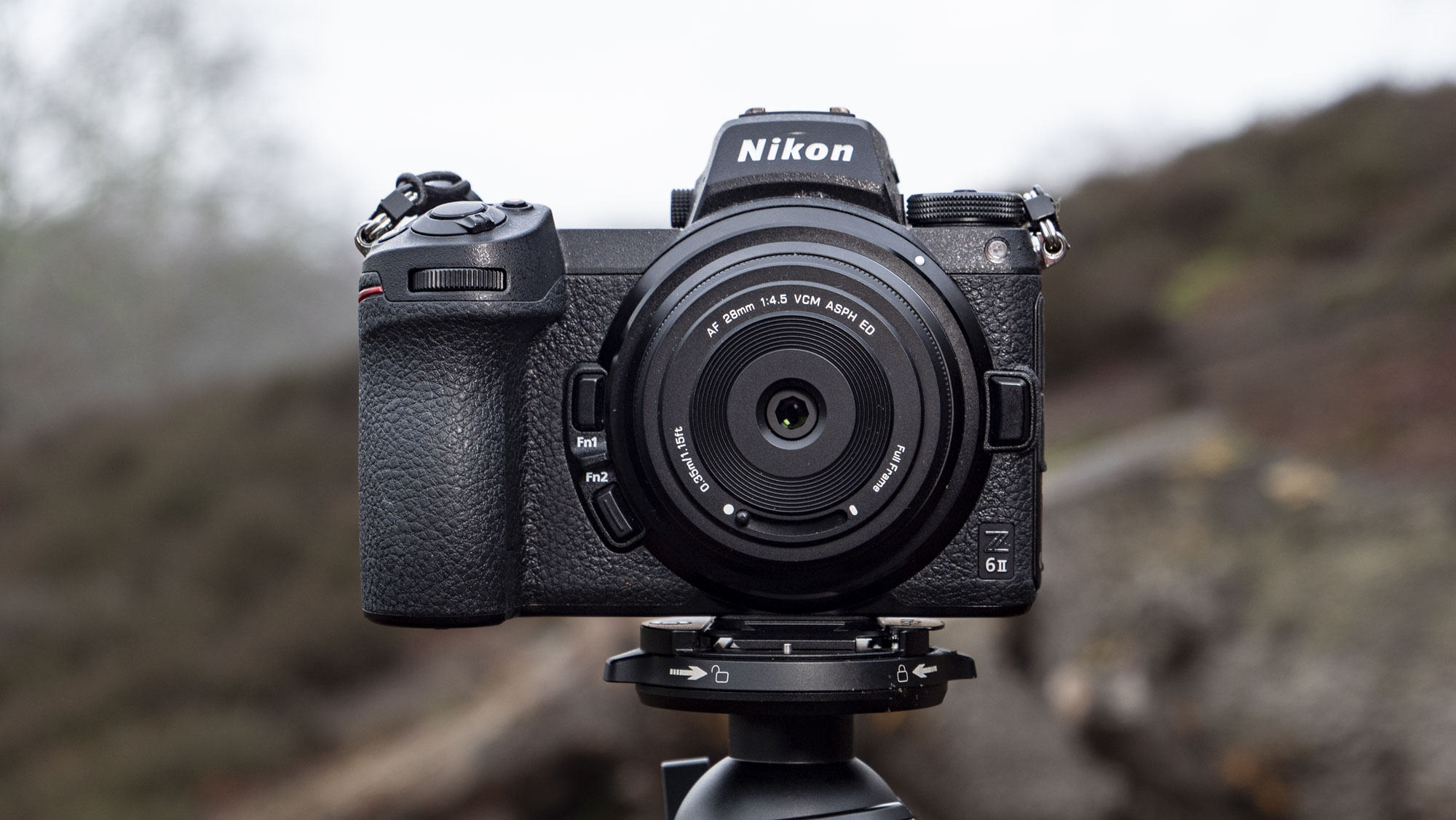
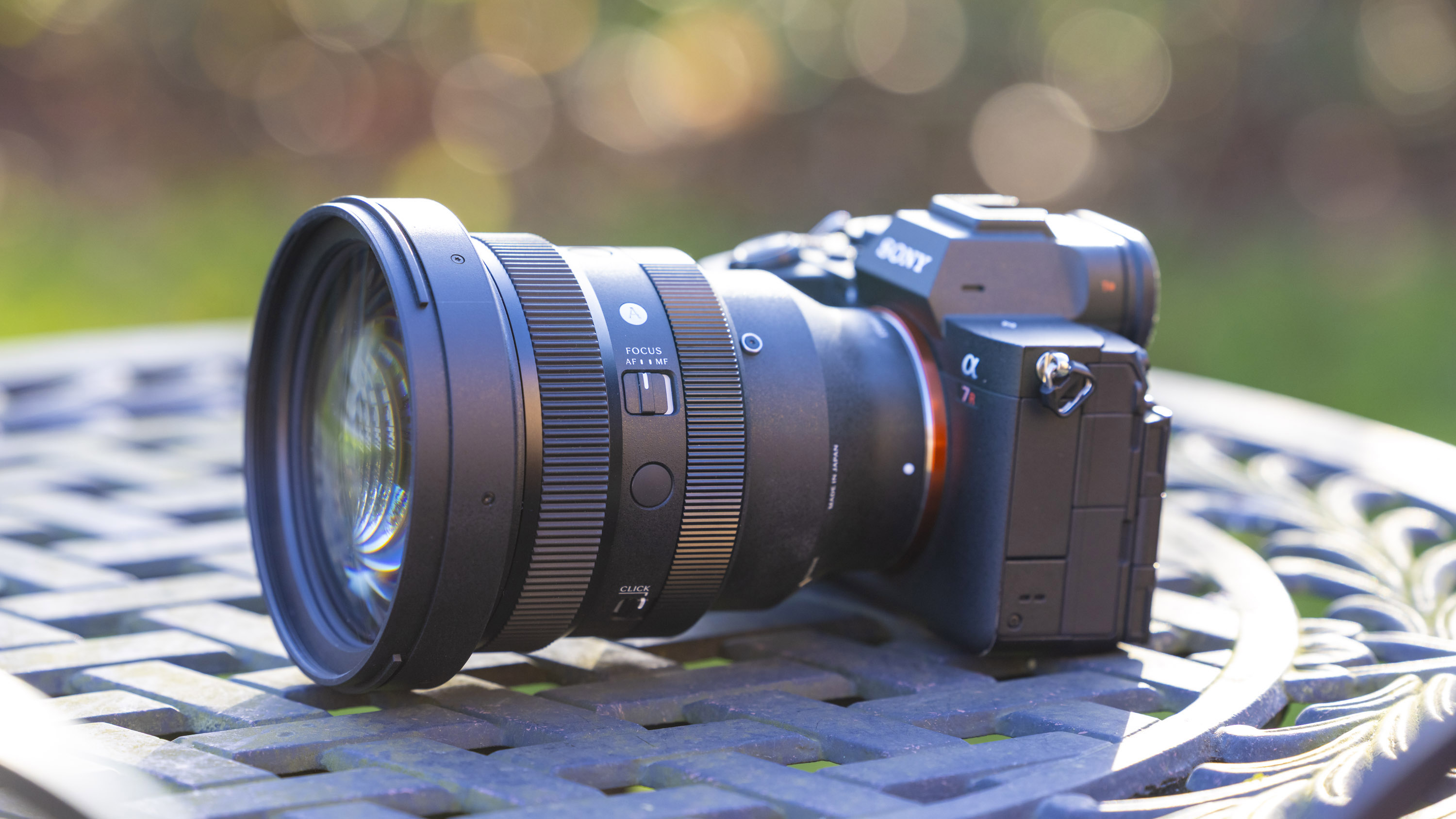
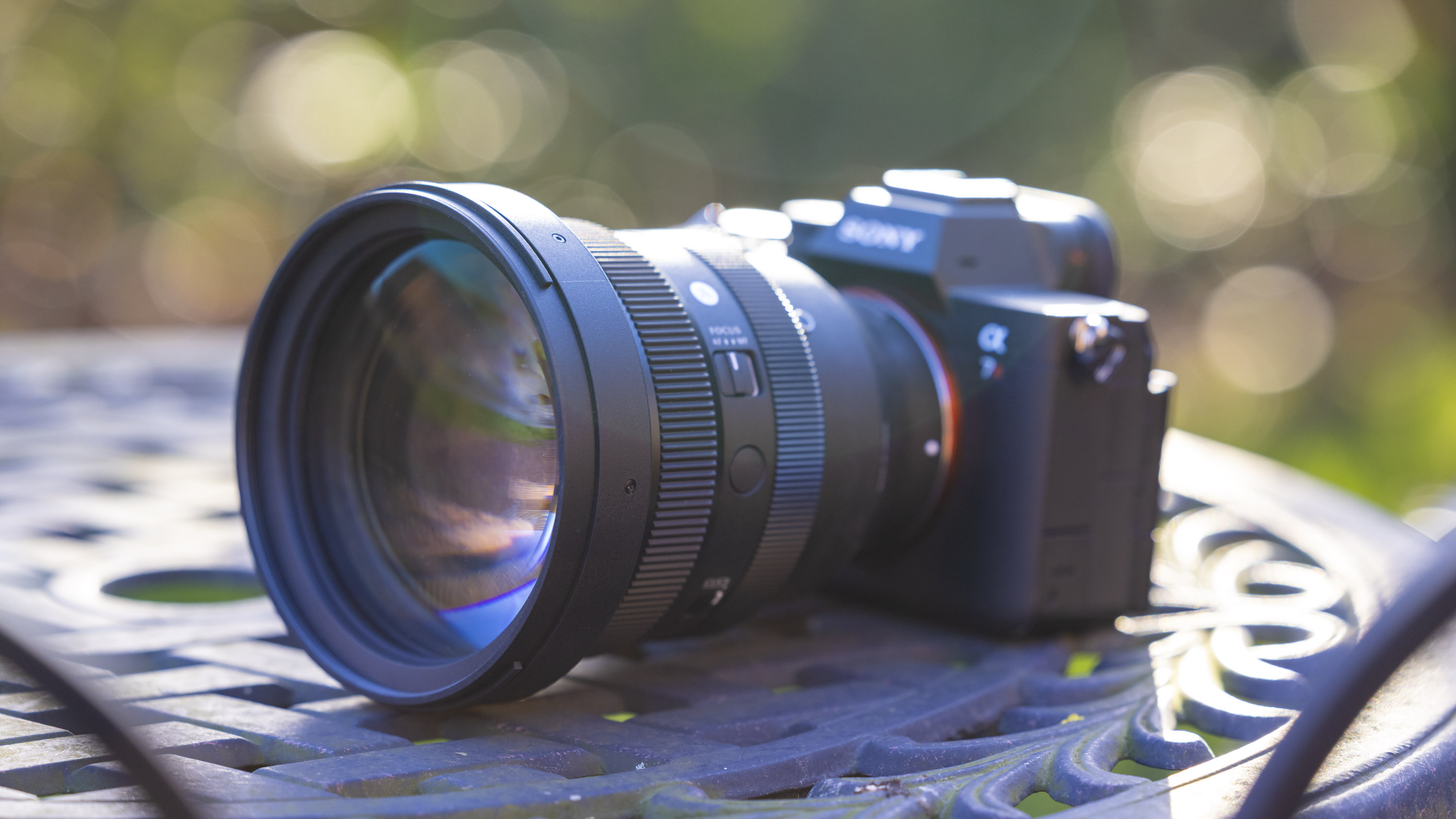
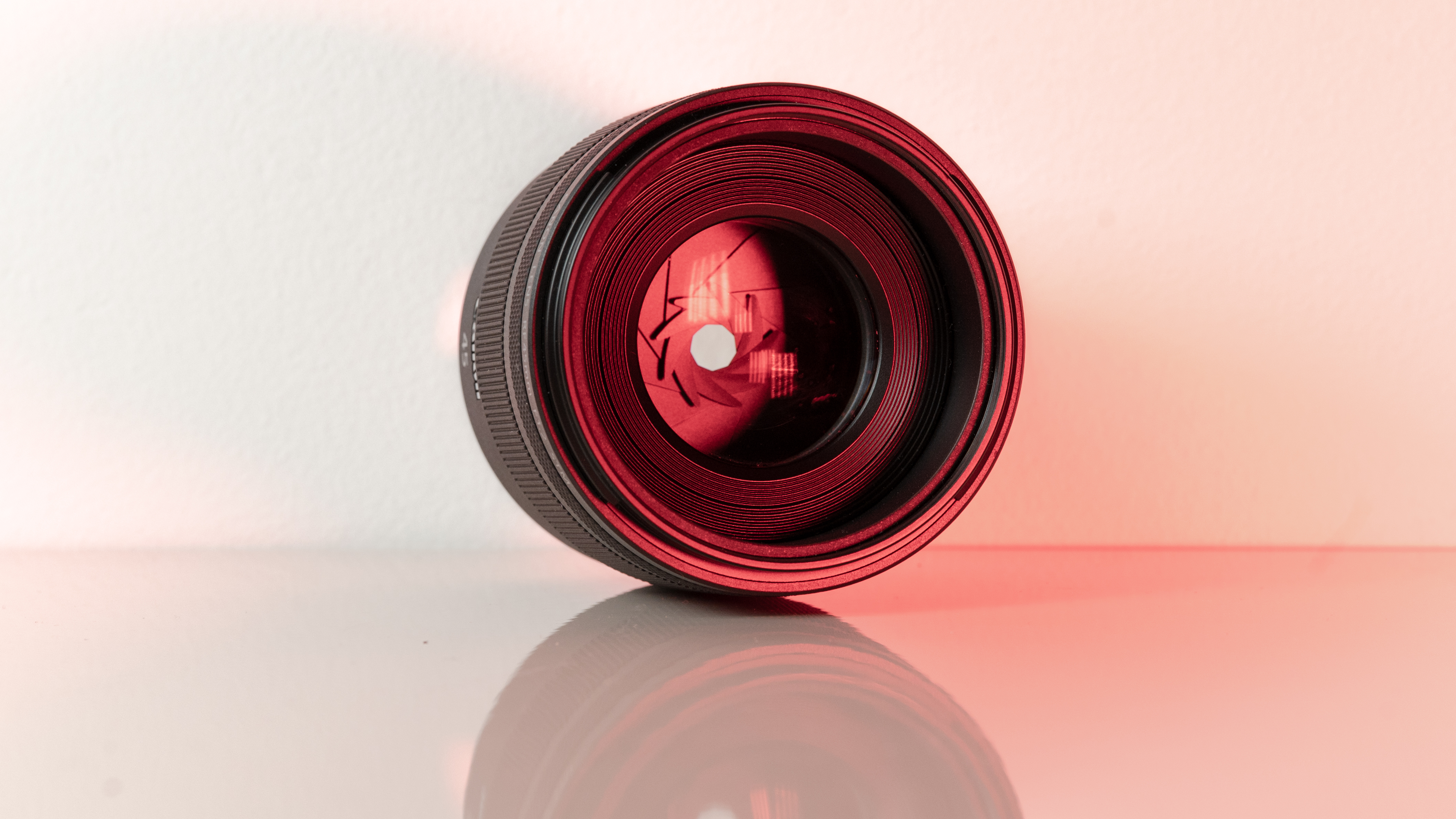
As you'd imagine from a relatively affordable lens, the RF 45mm f/1.2 has quite a minimalist design. You do get a few handy controls, however, such as the MF/AF switch and a fully customizable control ring right next to the lip of the lens' barrel.
The action on the focus ring is smooth and well-damped, but the control ring has a nice solid click to it that pairs nicely with its burled metal finish. Otherwise, the lens features a wholly plastic build apart from the mount — you can expect a metal mount in all modern Canon lenses, including the higher-end L series models.
Speaking of which, build quality for the RF 45mm f/1.2 doesn't feel that far off from the premium lenses. There's nothing here to suggest that this is a cheaper lens in the RF line-up, aside from the lack of the distinctive red barrel ring. In the hand, the RF 45mm f/1.2 feels solid and sturdy enough for a lens of this type.
With that said, Canon has cut a few corners to build this lens at a price. For one, you don't get a lens hood included - nor does the lens feature any weather sealing. Perhaps the lens will hold up to some light rain, but I certainly didn't want to risk it with my review unit.
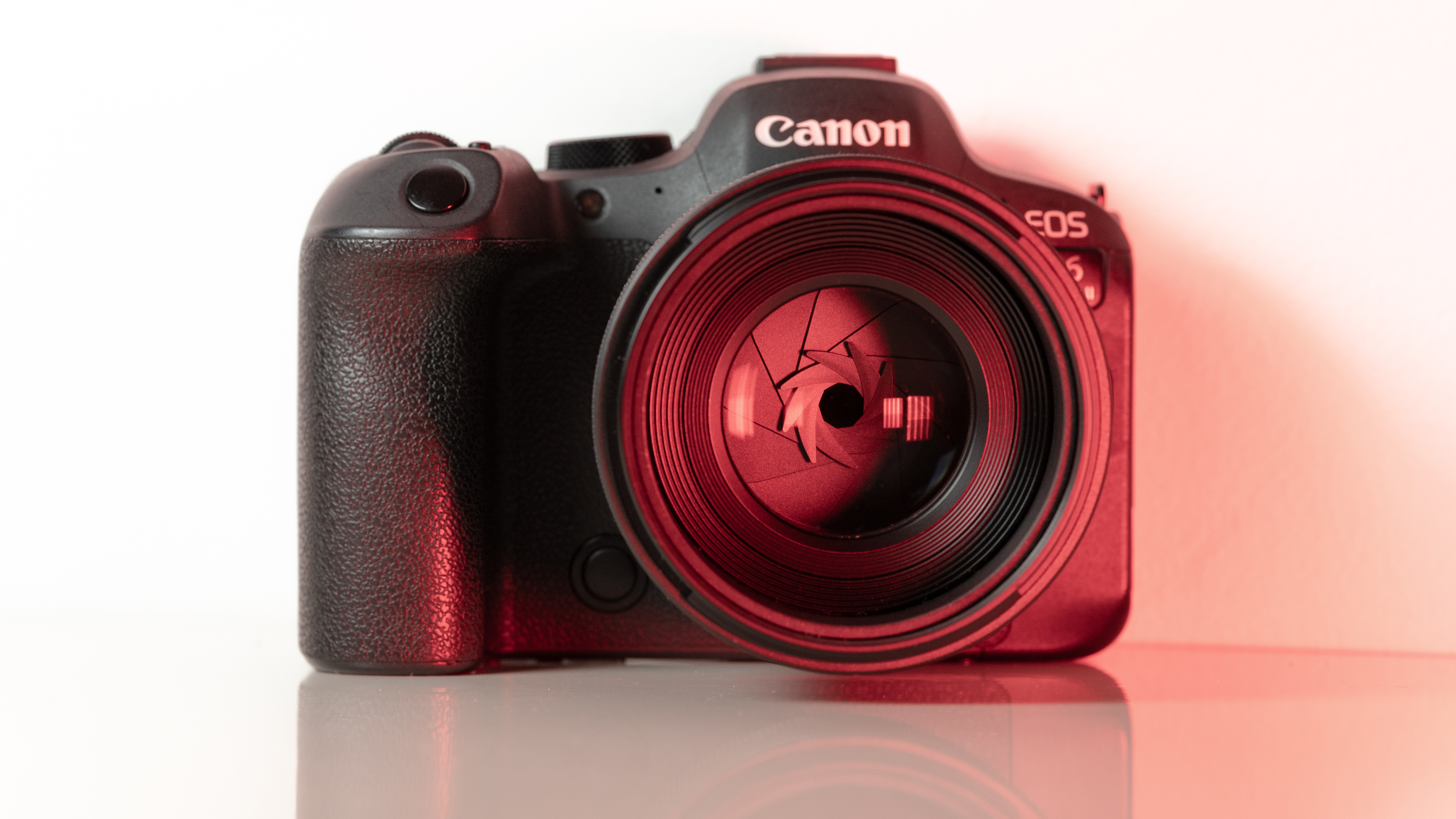

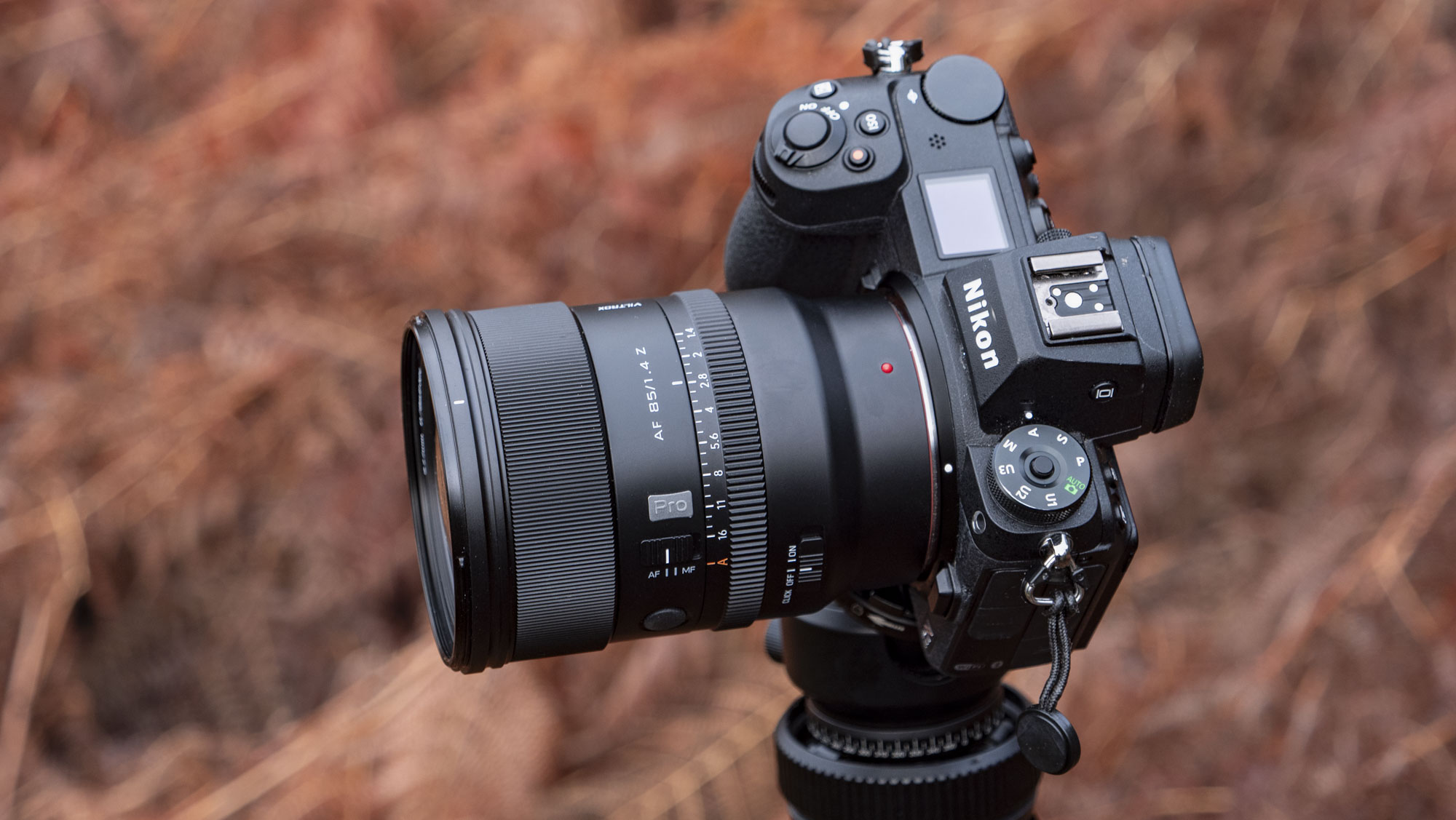
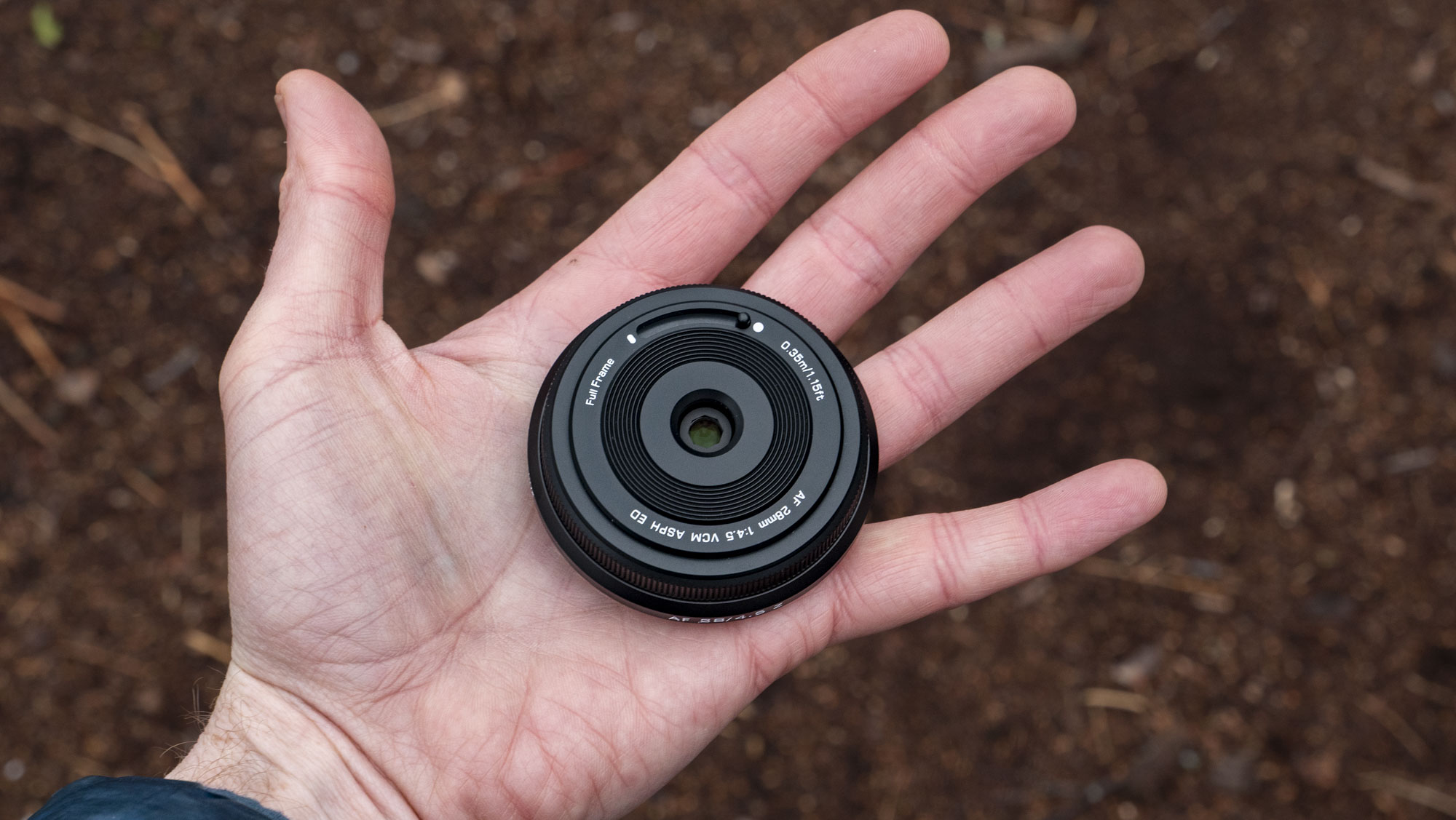
These points aside, the most impressive thing about the RF 45mm's design is that it weighs just 12.2oz / 346 grams - something that feels almost impossible for a lens with this kind of aperture. It really is the main selling point for this lens, in my opinion. The 45mm is so compact that you'd be mistaken into thinking this lens is an f/1.8 prime, given its size.
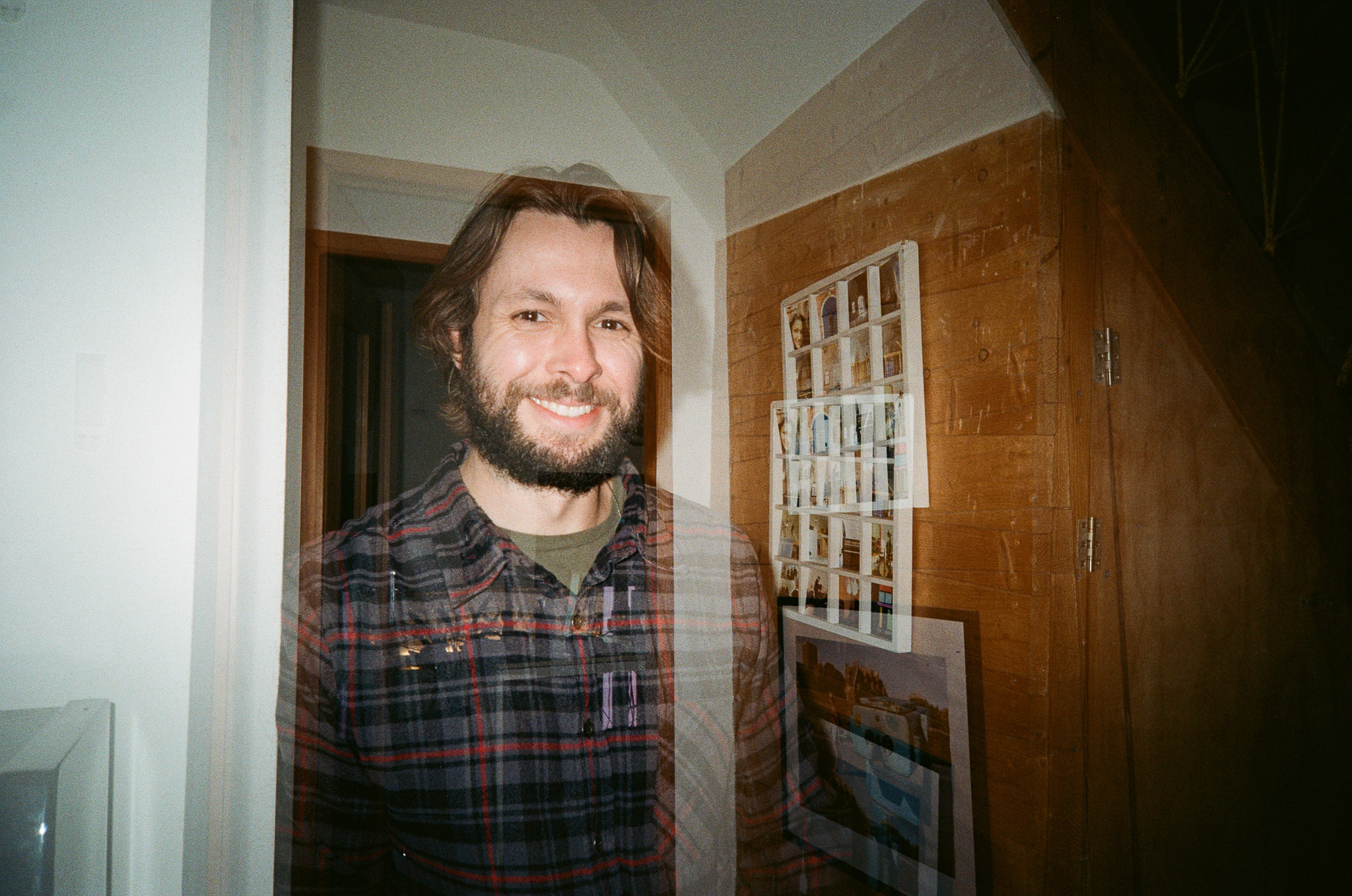
As you can see from the product pictures on this page, the 45mm pairs nicely with the EOS R6 Mark II, which is a full-frame body with a substantial hand grip. The lens is actually twice the weight of Canon's RF 50mm F1.8 STM prime (160g), but it's still light enough to hit that sweet spot where you don't feel like you're lugging around a huge piece of glass everywhere.
As stated, I tested this lens on the R6 Mark II. I think you'll also be fine if you pair this 45mm up with the Canon EOS R8, but the R8's comparatively small grip may result in a slight amount of front-heaviness. This is a light prime considering the aperture, but it's certainly no pancake lens.
Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM: Performance
- Significant chromatic aberration at f/1.2
- STM autofocus is reliable
- Good center sharpness at all apertures

You may be wondering - if the RF 45mm is cheap, small, and extremely wide, what's the catch? Well, unfortunately, there are a few quirks when it comes to outright image quality for the 45mm F1.2 STM. This is definitely a 'character lens', for better or worse.
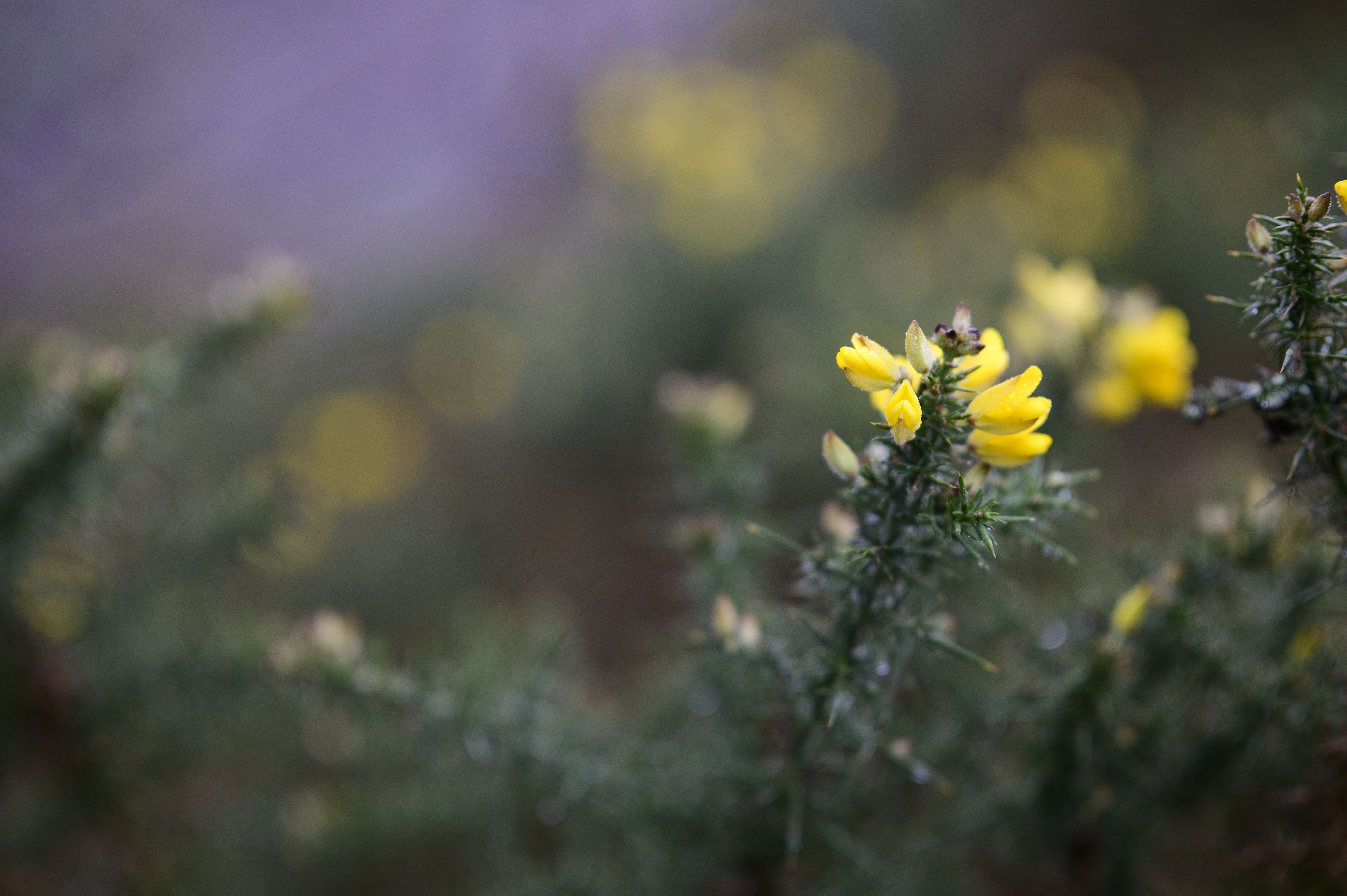
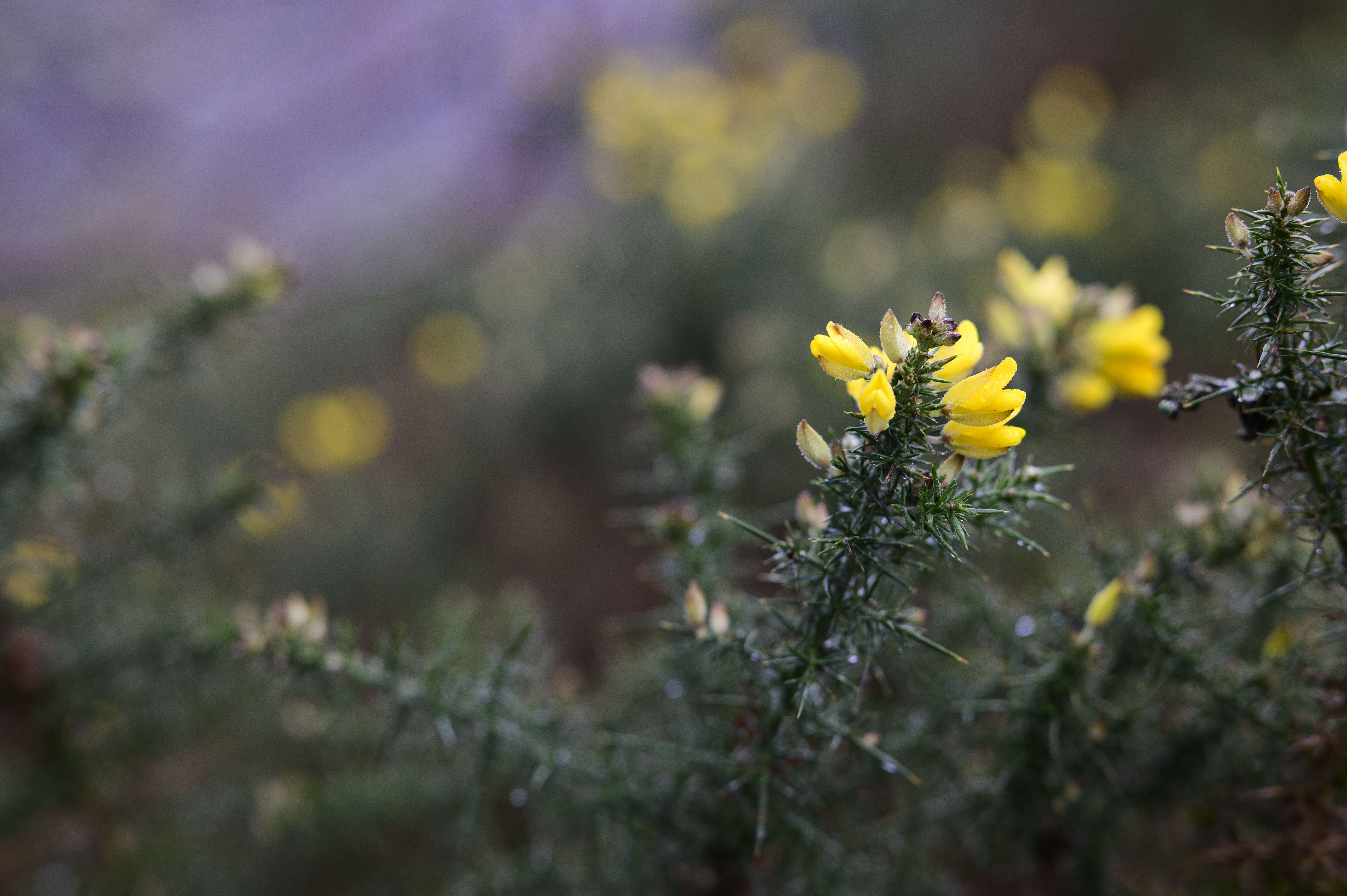
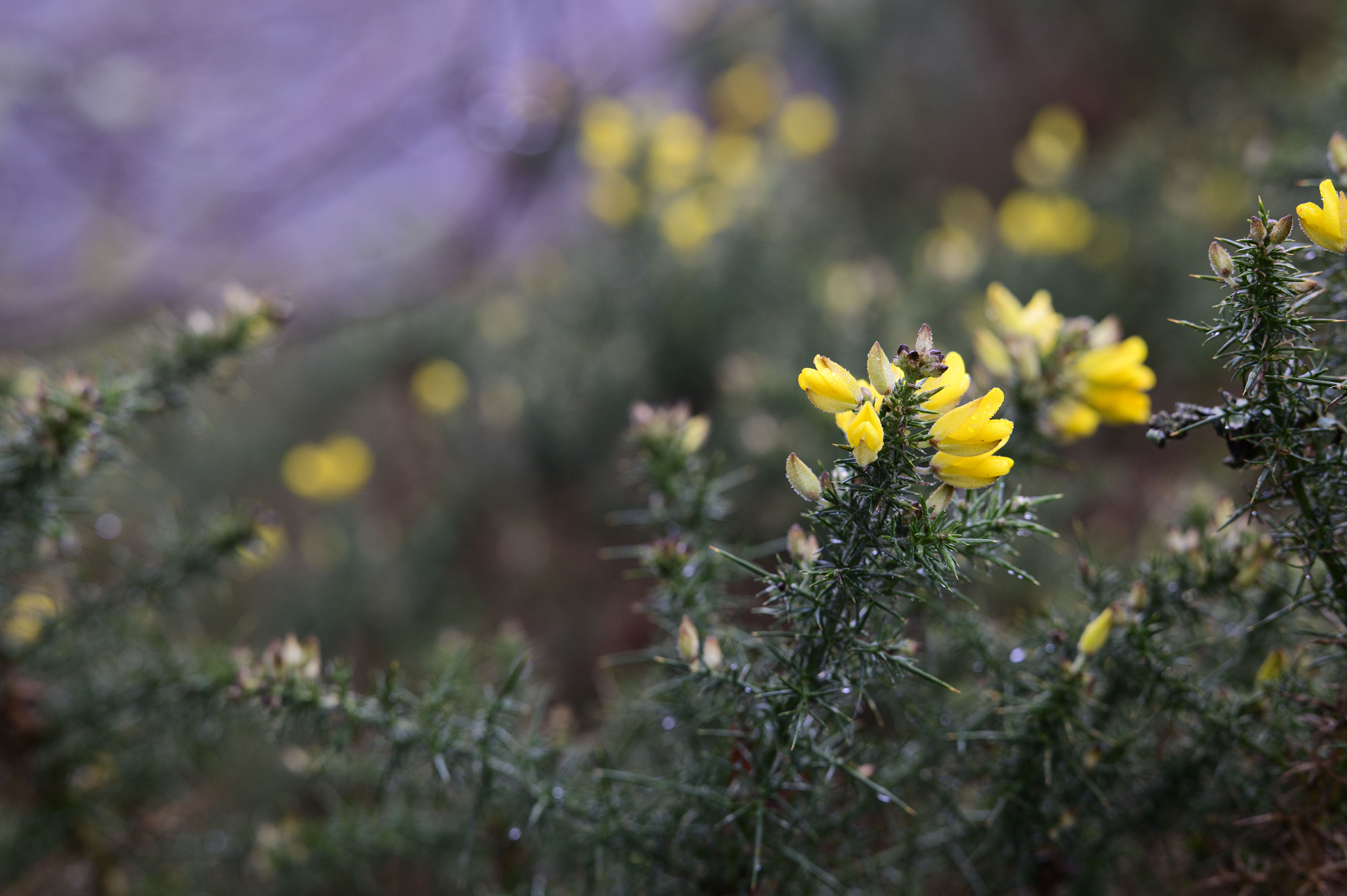
Firstly, the good stuff. If you're looking for those dreamy, blown-out backgrounds, then this lens definitely delivers. The aperture is so massive that you can get a good level of background separation here, even with relatively wide scenes. I could see this being a good option for environmental or full-body portraits on a budget.
The 45mm also offers a good level of sharpness. This is particularly the case in the centre of the frame, but stopping down the lens offers a great level of edge-to-edge sharpness. But of course, who's buying this lens to stop it down?
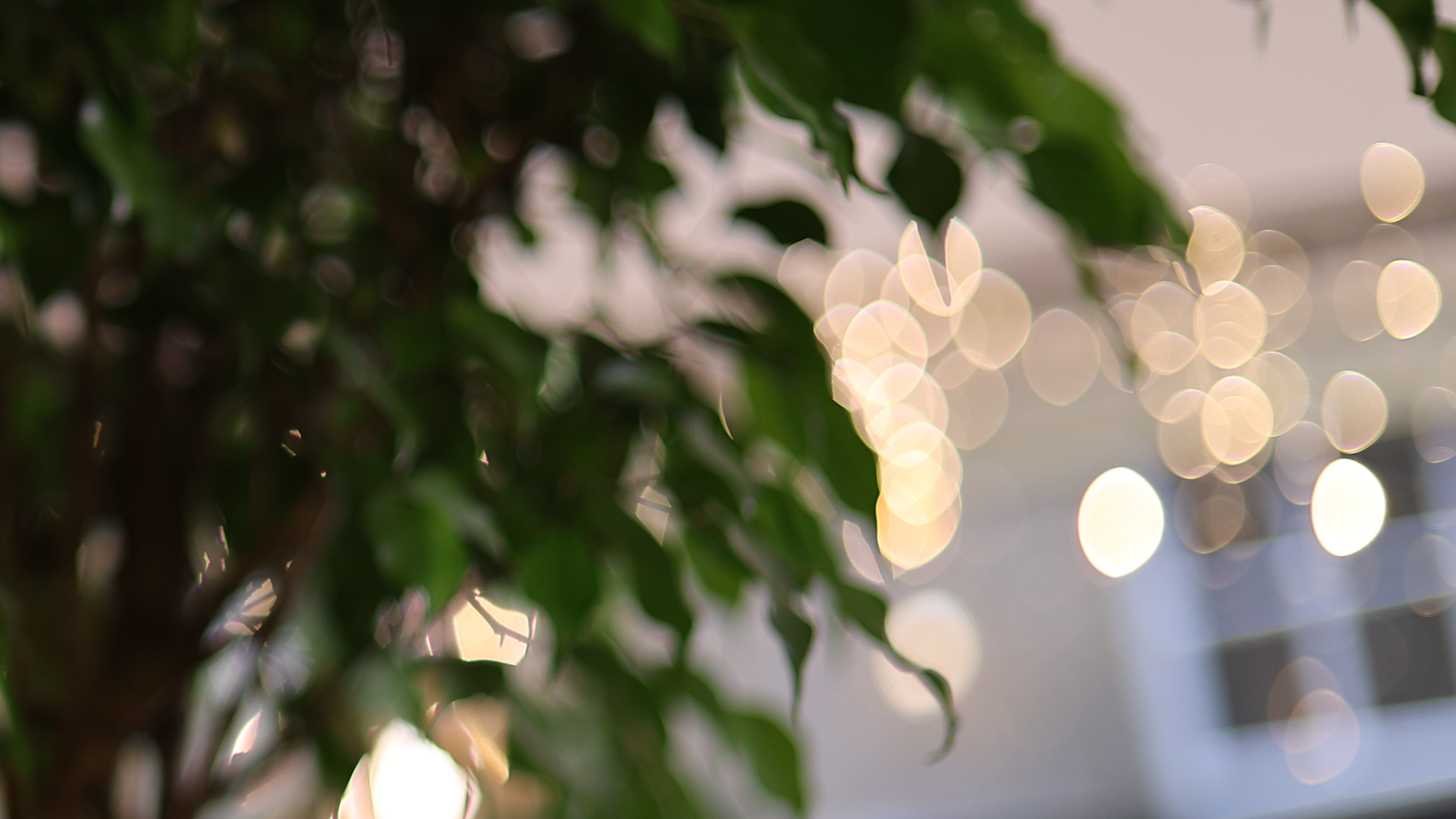




No, people are going to buy this lens because they want to make full use of that f/1.2 aperture at this exceptional price. Annoyingly, there are a few caveats when shooting wide open with this lens, however.
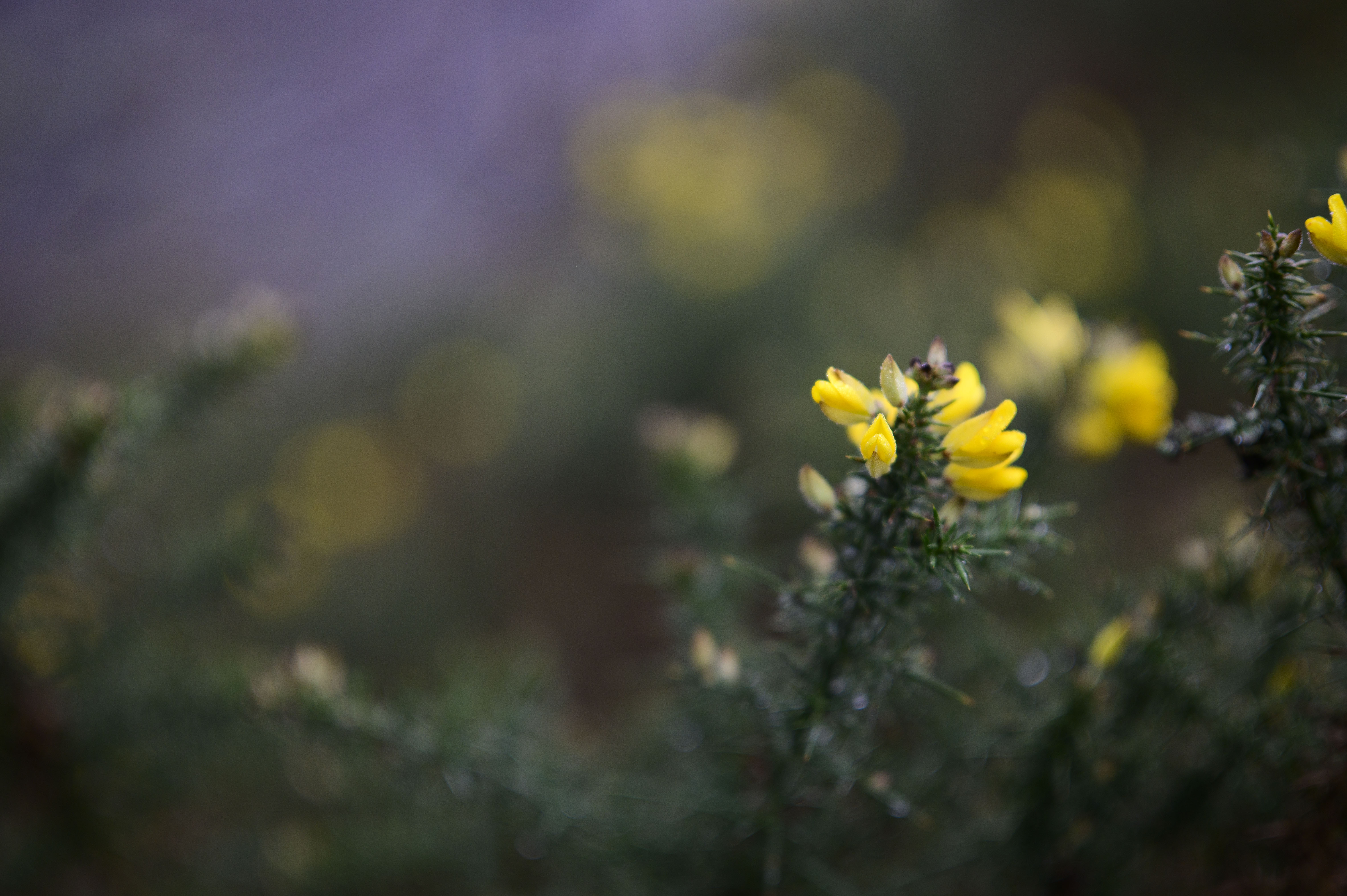
The first is the busy bokeh - something which I think will likely be the most contentious attribute for prospective buyers. There's no escaping that, at f/1.2, you get a significant cat's-eye effect on the bokeh with the 45mm. Once you see it, you can't really un-see it, and the swirling effect gets more extreme towards the edge of the frame. I think some people will love the distracting swirly effect of this lens, whereas others will find it too busy.
After using the lens in a range of scenarios, I'm somewhere in the middle of the two camps. As you can see from the samples, the bokeh balls not only have quite strong cat's-eye shapes, but also hard to remove fringing. They're technically very imperfect, but there's obviously something to be said for a lens with this much character if you're going for a certain 'vintage' look. It's definitely subjective.
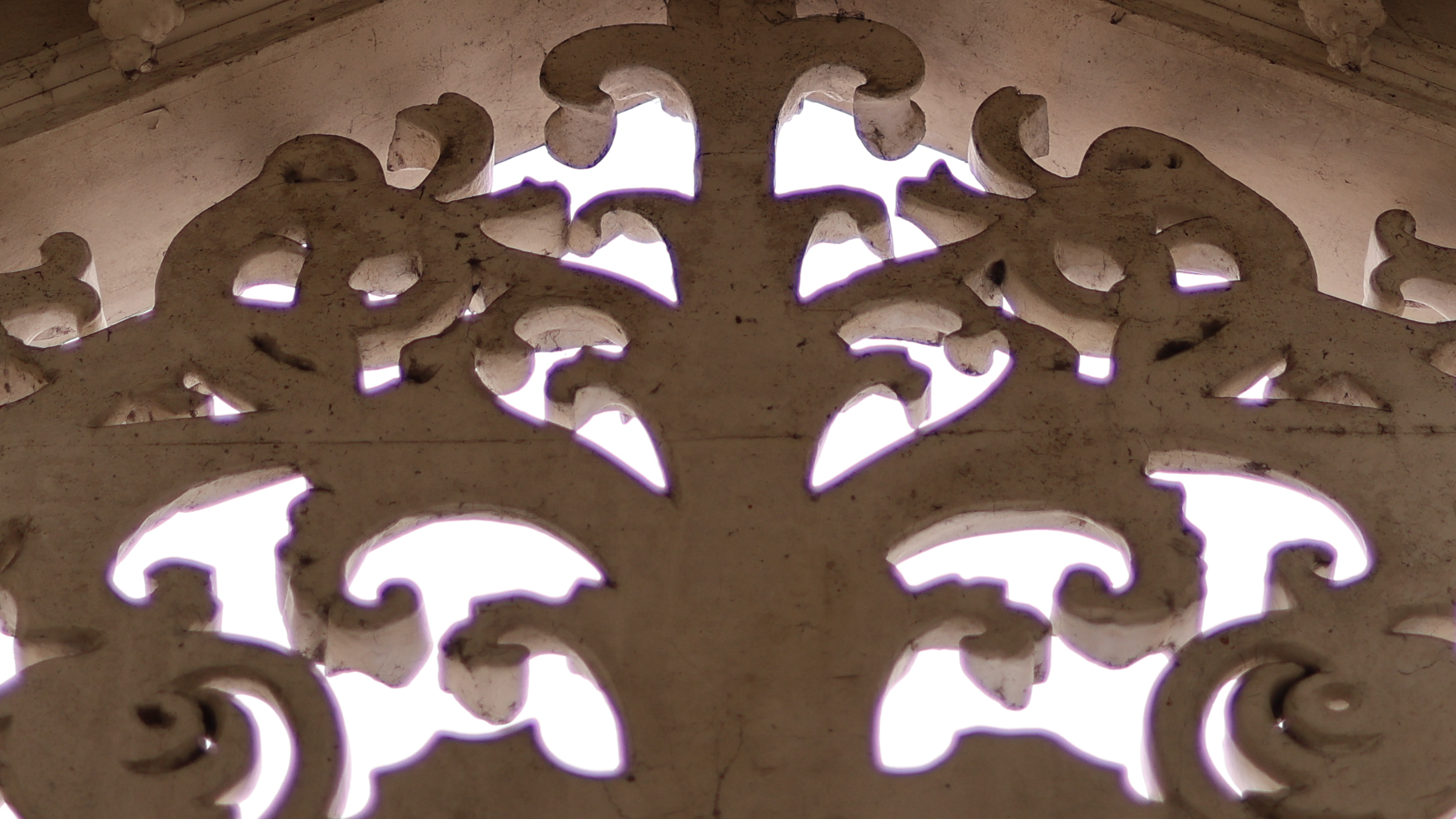


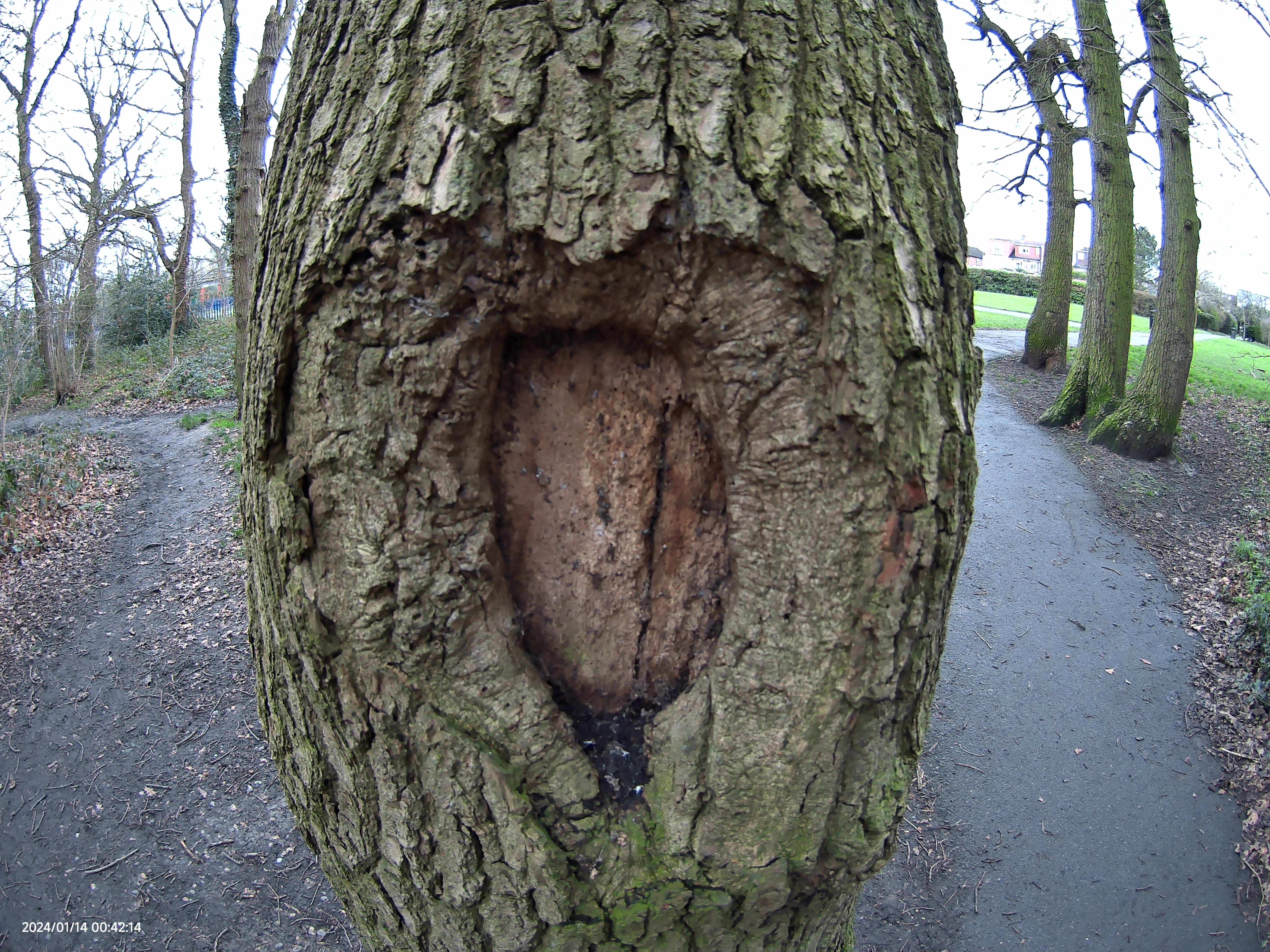
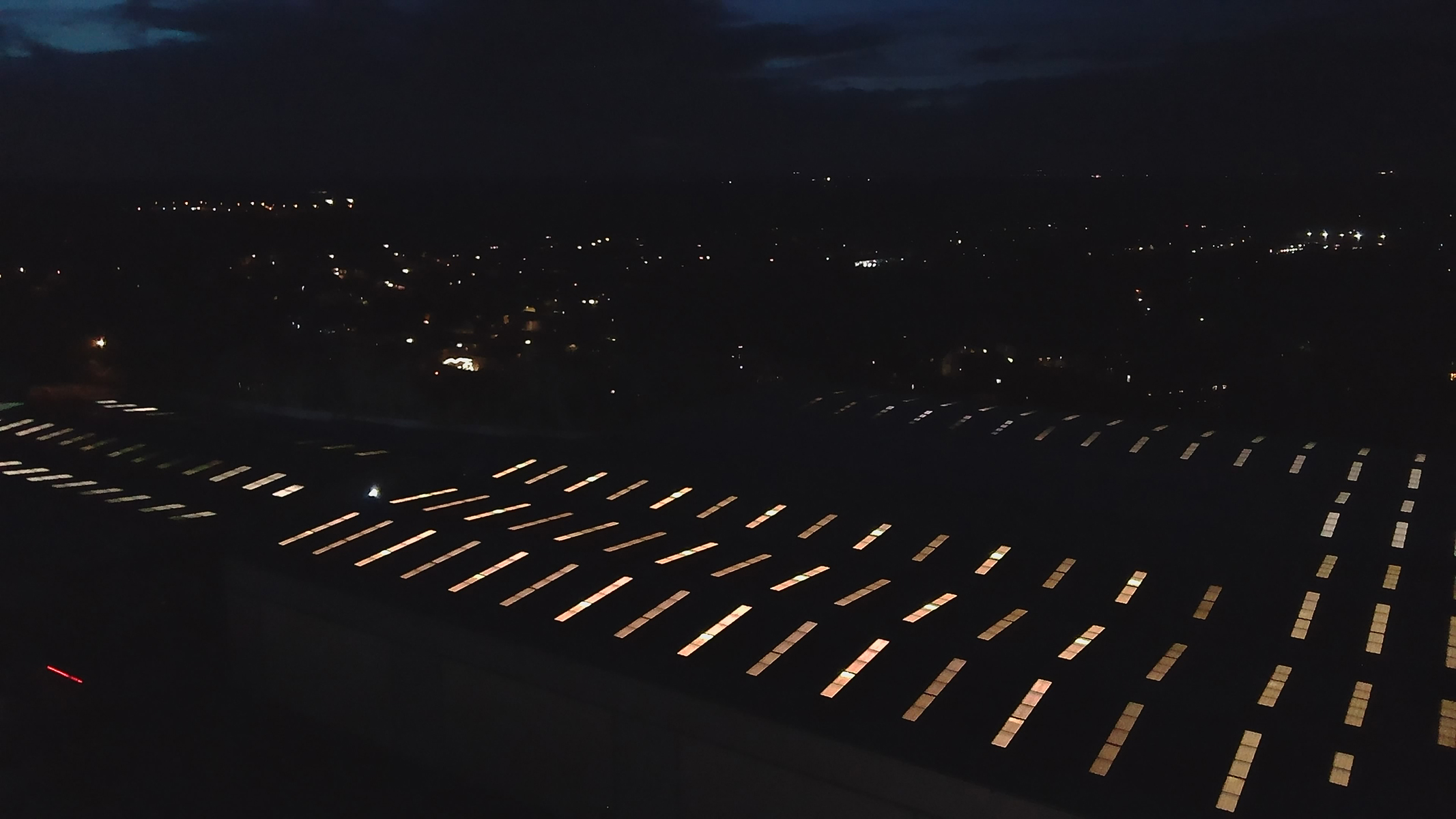
One thing I'm less on the fence about, however, is the extreme level of chromatic aberration this lens exhibits at its widest aperture. I don't think I've used a modern lens with this much CA in recent years.
The image above is a good example. You can see a significant amount of purple fringing around the backlit pattern on the wall. Towards the center of the frame, CA is relatively well controlled, but the fringing gets progressively worse toward the edges. It's notable because this particular shot is a JPEG straight from the Canon EOS R6 Mark II, with all in-camera lens correction applied.
If you do buy this lens, you're going to have to get well acquainted with the de-fringing tool in your photo editing app of choice. Luckily, this is one of the quickest and easiest fixes that anyone can make these days, so it's not a complete deal breaker for a relatively affordable lens like this.
In terms of focusing, the RF 45mm F1.2's proprietary STM stepping motor isn't as quick or silent as the ones featured in Canon's higher-end models, but it is more than sufficient, and able enough to provide quick and reliable autofocus at f/1.2 when paired with the brand's latest full-frame bodies.
One thing I did notice is a very small amount of focus breathing when close focusing at f/1.2. There is also a very slight whining noise when acquiring focus, which again, could be something worth considering if you're thinking about using this lens for video. With the example I've included above, you can see the lens slightly hunting for focus when it attempts to re-lock on the closer object.
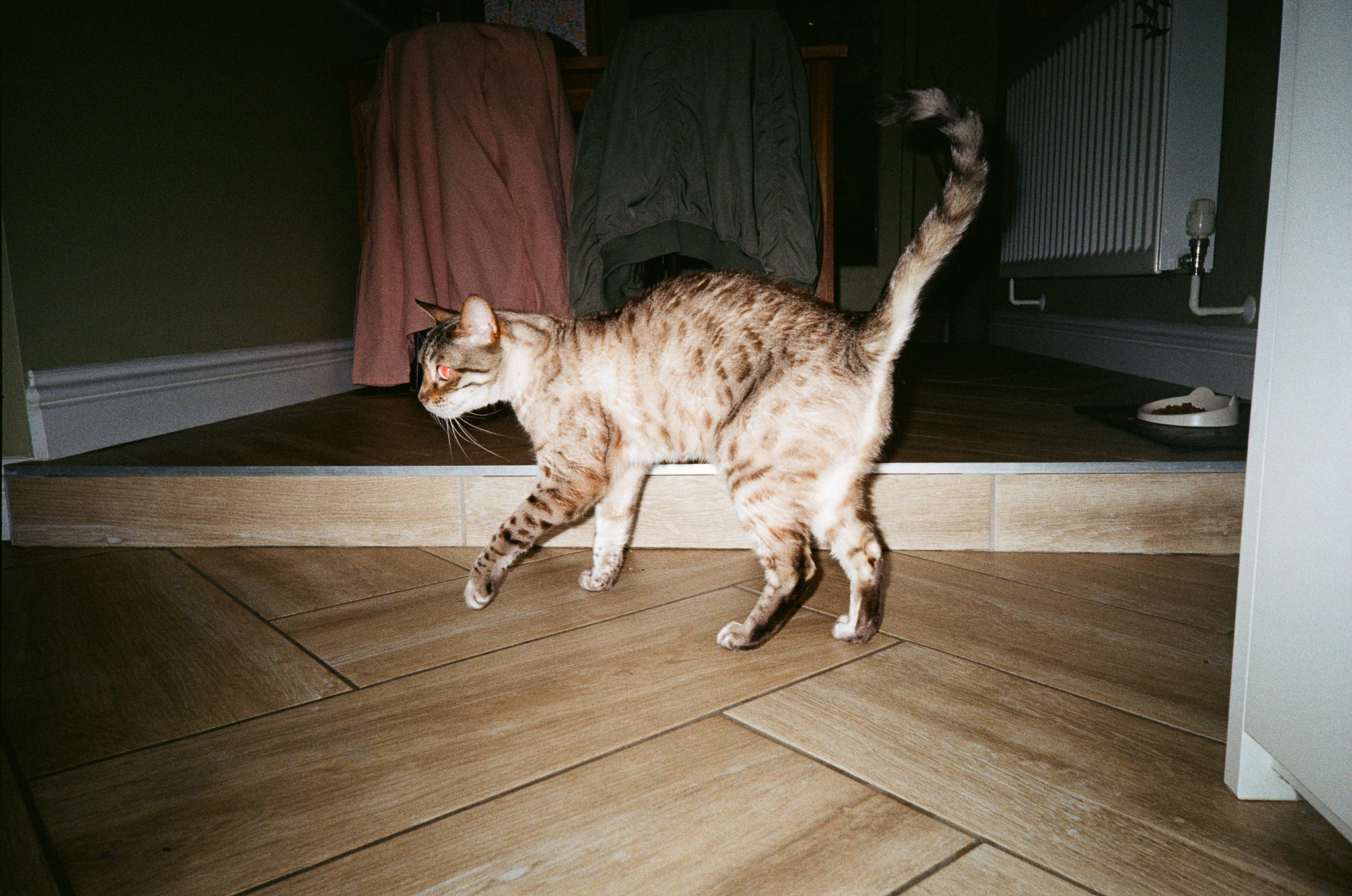
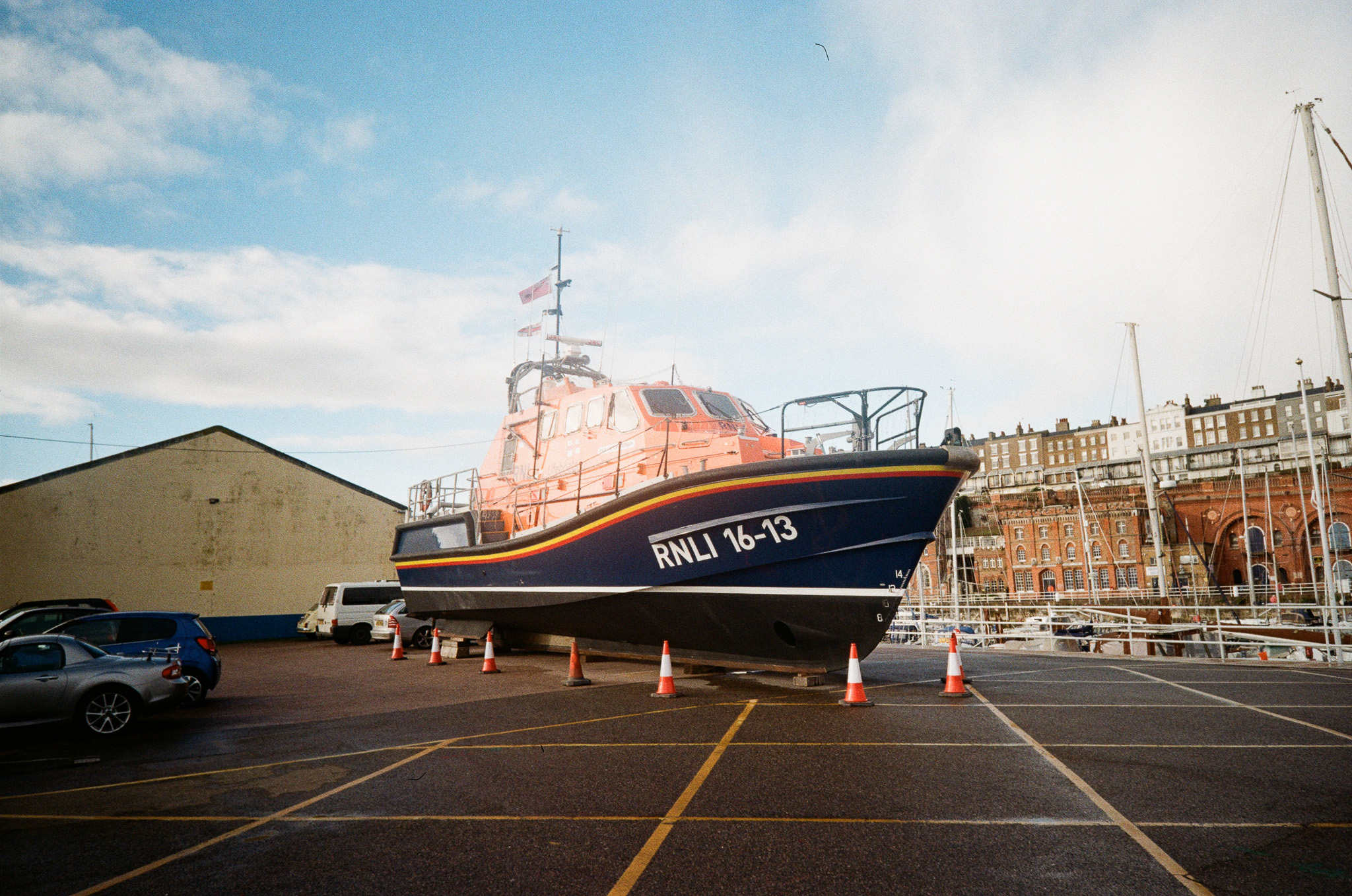
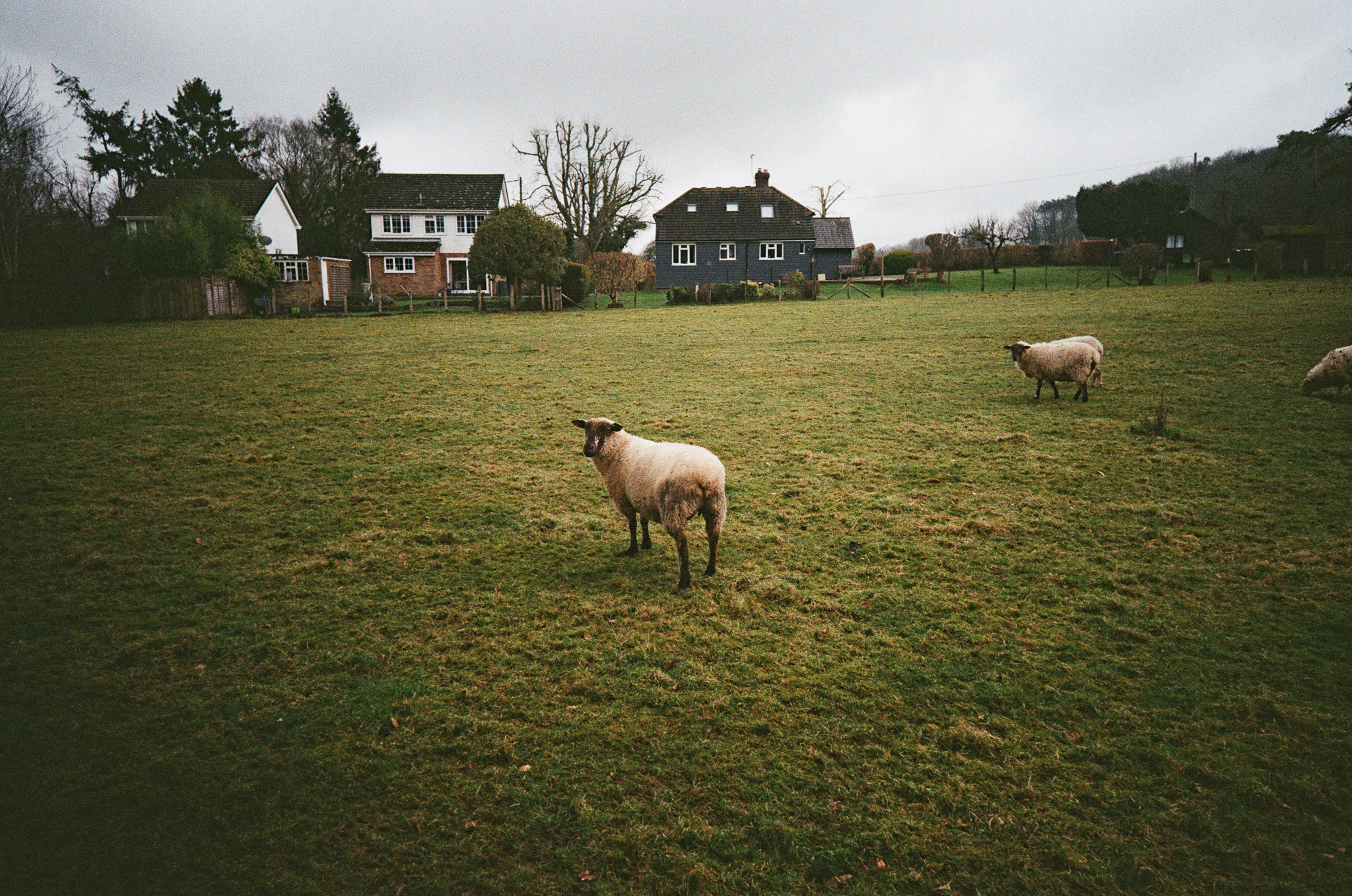
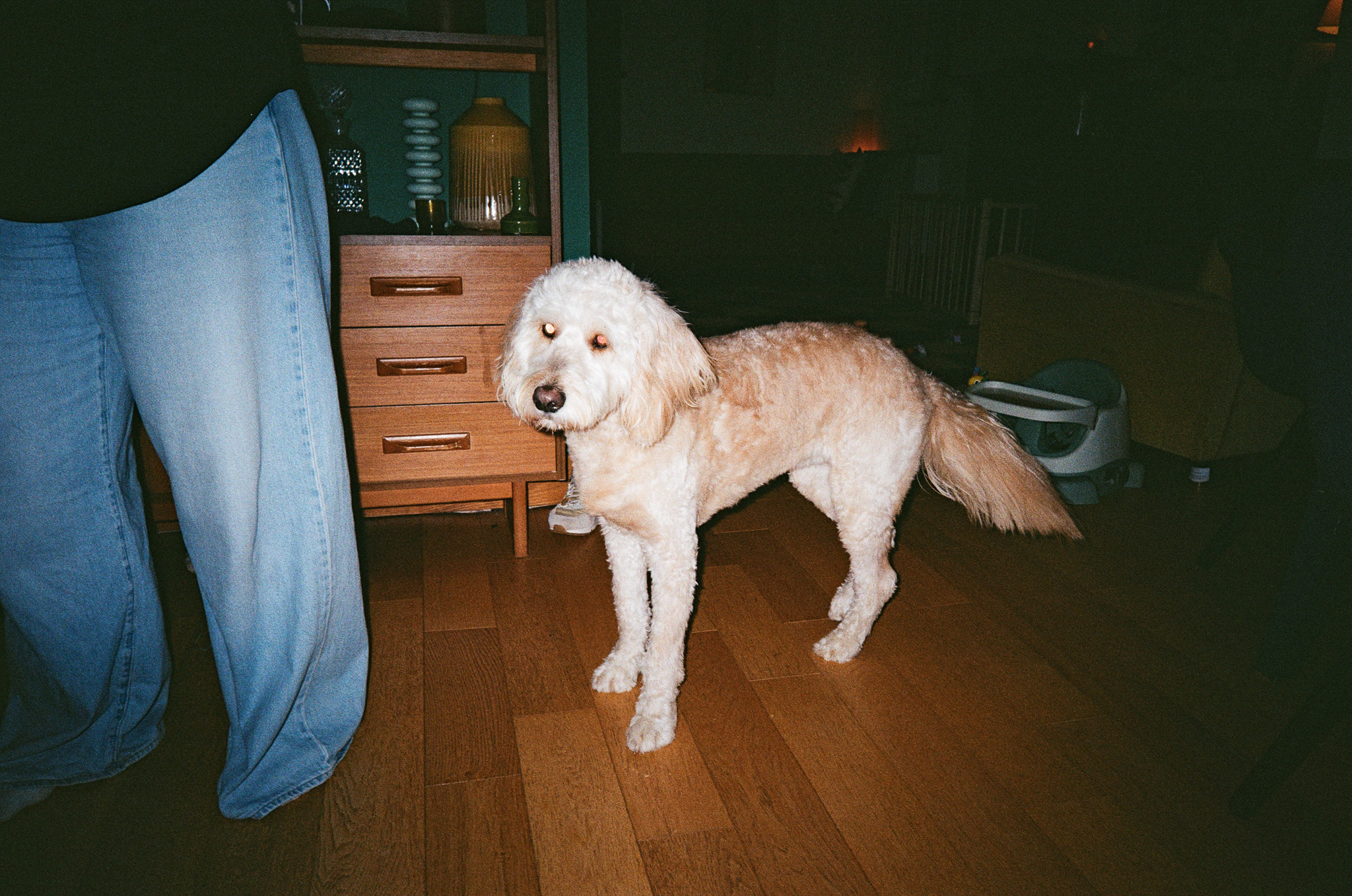
Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM sample images







Should you buy the Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM?
Buy it if...
You want to shoot environmental portaits
I think this lens is perfect for slightly wider scenes where you still want to separate the subject from the background.
You shoot a lot of low-light work
What's an f/1.2 aperture good for? Low light, of course! It shouldn't even need to be said that this lens's extremely wide aperture is fantastic for making sure as much light as possible hits your camera's sensor.
Don't buy it if...
You need something weather sealed
As a cheaper lens in the Canon line-up, the RF 45mm doesn't feature any environmental sealing. This one isn't for use in extreme inclement weather.
You need perfect image quality
While the RF 45mm offers an extremely wide aperture, this comes with some optical trade-offs. This lens has a lot of character, unlike the more 'perfect' L-Series models.
How I tested the Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM

- Canon provided me a sample unit for one week
- I paired the lens with the Canon EOS R6 Mark II
- I compared optical performance at various apertures
Canon provided TechRadar with the Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM for one week only, which is a relatively short window for a lens review. With that said, I was able to fully test the lens in both studio and real-world scenarios.
During my week with the Canon RF 45mm F1.2 STM, I tested the lens across a wide range of apertures for both video and photography. In that time, I made sure to try to get examples at f/1.2 to show prospective buyers what to expect with such a wide aperture - including the various flaws that this lens sometimes showcases.
First reviewed March 2026